CT1 W5 Mod 16, 17, Supragingival calculus removal, Sickle Scalers + Ch 28 - Specialized Perio Instruments
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
The correct angulation for calculus removal is…
45-90 degrees face-to-tooth surface angulation
incorrect angulation results in tissue injury or incomplete calculus removal
What happens when you angulate more than 90 deg?
one cutting edge will contact the lining pocket causing tissue damage
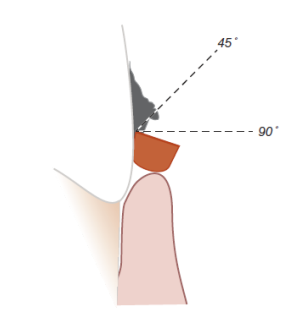
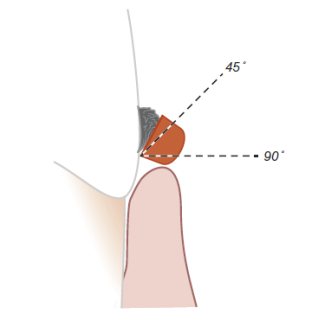
What happens when you angulate less than 45 deg?
cutting edge will slide over surface of deposit
What are the 3 types of forces used for Calculus Removal? Define each.
Pinch pressure → exerted by fingers in modified pen grasp holding instru. handle
Stabilization → fulcrum
Lateral Pressure → created by applying pressure with index finger and thumb INWARD against instrument handle
Which uses the most amount of lateral presure? Assessment, Calculus Removal, Root debridement.
Calculus removal > Root Debridement > Assessment
Effective calculus removal depends on … (3)
Firm lateral pressure
Correct angulation
correct adaption of the tip-third of cutting edge
When should you relax your finger muscles during Calculus removal?
Between strokes
when returning working-end to base of pocket
**Constant pressure on fulcrum is stressful to the muscles as well!
What are the 3 forces that must be balanced for effective instrumentation stroke.
Fulcrum finger is straight to support the hand
Fulcrum finger presses down against occlusal/incisal surface
Index and thumb press INWARD against instrument handle
What is burnishing? Why is it bad?
removing only outer layers of deposits (instrument angulation less than 45 deg)
smooth, burnished deposits are more difficult to remove and the plaque biofilm continues to live on and cause damage at burnished deposits.
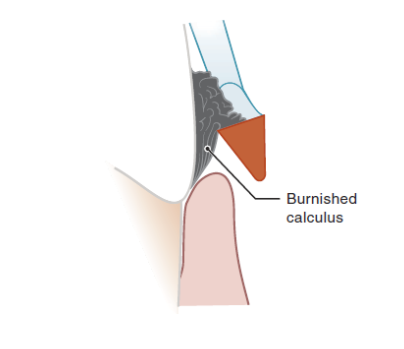
What are some strategies for avoiding injury during calculus removal/instrumentation?
Relax → only apply pressure when actively removing calculus
Slow down → debridement strokes should NOT be made in rapid, non-stop manner; should be controlled and slow
Pause → relax muscles at the end of each calculus stroke
20 minutes → return instrument to tray, stretch fingers and curl fingers
10-minute/hour → take a break for 10 mins each hour
Rest eyes periodically
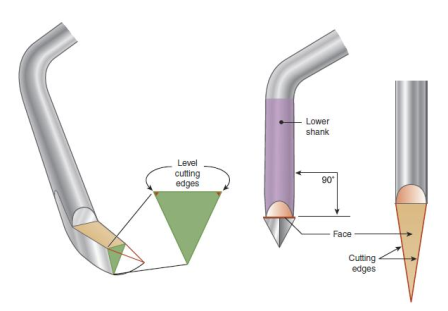
The face of a sickle scaler is ___ to the lower shank
perpendicular (90deg)
Describe Anterior sickles
often single ended, may have 2 ends with 2 different sickles on each end
simple shank
only used supragingival
Describe Posterior sickles
usually 2 sickles paired on double-ended instrument
working ends are mirror images
complex shank
only used supragingival
What is the correct angulation for Sickle scalers ?
70-80 degrees (may be 60-80, depending on who you ask) tilted TOWARDS tooth surface
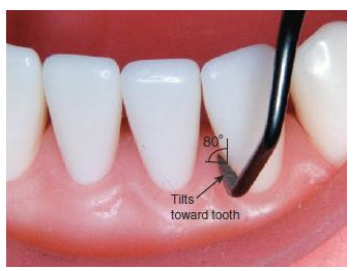
What is the correct position for the cutting edge when instrumenting on proximal surfaces next to papillary gingiva?
Position cutting edge AGAINST proximal tooth surface → tilt and angle instrument deeper towards tooth surface
The inner and outer cutting edge of a posterior sickle is used on….
Inner edge → distal surfaces only
Outer edge → facial, lingual, and mesial
What are 2 challenges that primary teeth present to sickle scalers?
Smaller size of primary teeth present challenge for sickle scalers
primary crowns have roughter enamel surfaces and CEJ
What is a periodontal instrument?
An instrument used to prepare calculus deposits before removal with another instrument
ex. periodontal file is used to crush or roughen heavy deposits so taht it can be removed with a sickle or curet.
Where can a periodontal file be used?
limited to enamel surfaces or on OUTER surfaces of calculus deposits
Periodontal files come in sets. What does this mean?
Each perio file SET is only used on specific tooth surfaces. A set of files is needed to instrument entire mouth.
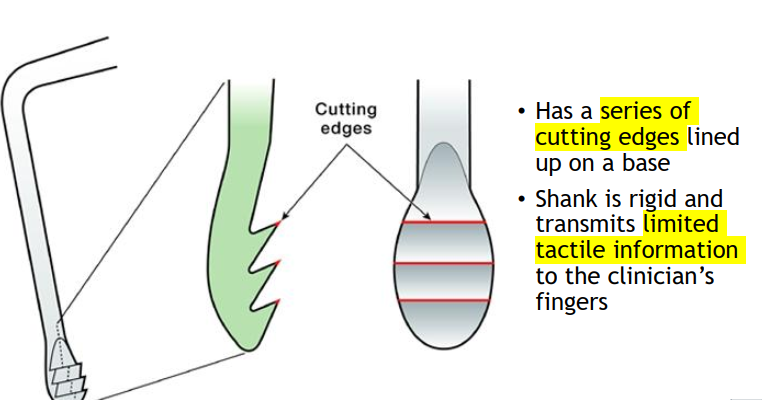
What is the two-point contact technique of the periodontal file?
Adaptation of the working end to a calculus deposit
Resting lower shank AGAINST tooth.
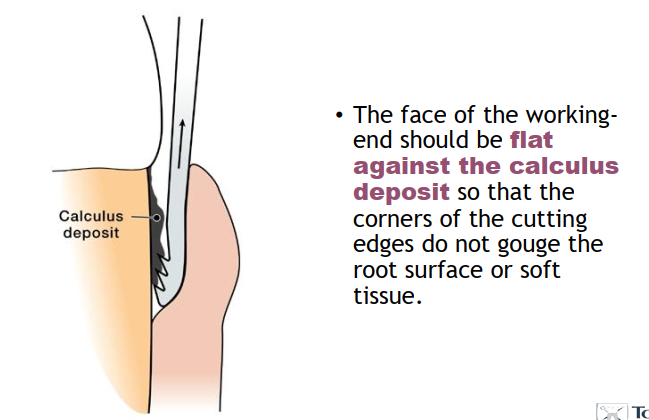
How many files are required to instrument posterior teeth, anterior teeth?
Posterior teeth → 2 double ended files
Anterior teeth → 1 double ended file
Periodontal file has been replaced by which instrument in current practices?
Ultrasonic instruments