CHINESE ARCHITECTURE
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
chinese architecture
It is characterized by bilateral symmetry, use of enclosed open spaces, feng shui, a horizontal emphasis, and an allusion to various cosmological, mythological or in general symbolic elements. Palaces and temples are the chief building type. Diverse architecture caused by differences in geographic and climatic conditions.System of wood frame construction
Arrangement of buildings
Buildings and structures around a courtyard
Entire grouping is organized around a central pathway or axis.
Largest and most important building at the northernmost.
Surrounding structures and courtyards increase in size as they get closer to the main building.

Yin-yang
It is the interaction of two opposing and complementary principles. Classical Chinese courtyard houses with solid buildings (Yang) surrounding the void (Yin) courtyard spaces is a vivid illustration of the theory in practice.
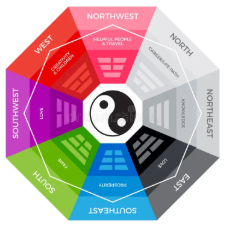
Feng shui
The fundamentals of _________ bring the ideals of function, flow, and harmony into the visions of architectural ideation. __________ literally means ‘wind-water" in English and is the Chinese art or practice of positioning objects or structures so as to harmonize with spiritual forces.

Jian
The basic measurement used in construction Standard unit of space marked by adjacent frame supports.
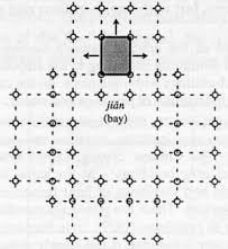
Dougong
An Interlocking bracket system used in traditional Chinese construction to support roof beams.Has both structural and decorative purpose.The interlocking brackets transfer weight to vertical columns, lessening the strain on the horizontal beams.
Green
wood element and represents east.
Yellow
earth; spaces reserved for emperors and represents the center.
Blue and black
water and represents north.
White and gray
metal and represents west.
Red
fire; hope and satisfaction and represents south

Pailou
Also called paifang. A monumental gateway to a palace, tomb, or sacred place.

Zhonglou
A bell tower or pavilion at the right side of a city gate, palace entrance, or forecourt of a temple.
Ex Bell Tower Xian China

Golou
It is the left side counterpart (belltower) of a zhonglou.

Ta
The Chinese Pagoda made its first appearance in China about 68 A.D. when Buddhism arrived from India. Square or polygonal in plan, with roofs projecting from each storey; erected as a memorial or to hold relics
Ex. Mu Ta Pagoda, Yingxian China.

Fogong Pagoda
A 200-foot-high tower built entire layout of wood.

Temple of Heaven
It is a complex of imperial religious buildings situated in the southeastern part of central Beijing. The complex was visited by the Emperors of the Ming and Qing dynasties for annual ceremonies of prayer to Heaven for a good harvest. Circular Mound Altar, ritual platform and considered as the Imperial Vault of Heaven.

Forbidden City
A palace complex including temples,reception halls, residences, and service buildings. Palace of Heavenly Purity, the residence of the son of heaven and the conceptual center of the empire. Hall of Supreme Harmony, emperor's throne room; also where he met daily with his officials.

Palace of Heavenly Purity
It is a palace in the Forbidden City in Beijing, China.
Itis the largest of the three halls of the Inner Court (the other two being the Hall of Union and the Palace of Earthly Tranquility),located at the northern end of the Forbidden City.

Summer Palace
Itis a vast ensemble of lakes, gardens and palaces in Beijing. It was an imperial garden in the Qing dynasty. It is the royal retreat for emperors fleeing the suffocating summer torpor of the old imperial city.

Great Wall of China
A series of fortifications that were built across the historical northern borders of ancient Chinese states and Imperial China as protection against various nomadic groups from the Eurasian Steppe.