Key concepts in chemistry
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
How is an atom structured?
Has and equal amount of protons and electrons but can have a different number of neutrons
The electrons orbit the nucleus of an atom
The protons and neutrons are in the nucleus
What Are the charges and masses of a proton, neutron and electron?
Particle | Relative charge | Relative mass |
|---|---|---|
Proton | +1 | 1 |
Neutron | 0 | 1 |
Electron | -1 | 1/1836 (or 0) |
What does the mass number and atomic/proton number tell us about an element?
The atomic number tells us how many protons and electrons are in an element
The mass number tells us the relative mass of an atom which is made up of its protons and electrons in its nucleus
We can find the amount of neutrons in an atom by doing mass number - atomic number
What are isotopes?
Atoms with the same number of protons and electrons but a different number of neutrons
How do we calculate the relative atomic mass of an isotope?
(% abundance x mass + % abundance x mass)
sum of abundance
How did Mendeleev develop the periodic table?
He put the elements in order of their relative atomic mass
He checked the properties of the elements and their compounds
He swapped the places of some elements so that elements of similar properties lined up
He left gaps where he thought there were other elements and predicted their properties
When these elements were discovered, Mendeleev’s predictions fitted the properties very well
Why did Mendeleev switch around Iodine and Tellurium in the periodic table?
He arranged them in terms of their properties but not according to their relative atomic mass, iodine should be first
What are the rows on the periodic table called and what do they tell us?
The rows are called periods and they tell us how many electron shells there are
What are the columns on the periodic table called and what do they tell us?
The columns are called groups and they tell us how many electrons are on the outer shell
How do electrons fill the shells of an atom?
The first shell holds 2 electrons, the rest can hold up to 8
What are cations?
Positive ions formed when an atoms loses one or more electrons
What are anions?
Negatively charged ions which are formed when an atom gains one or more electrons
Why do atoms want to fill their outer shell?
In order to become stable
What kind of ions do metals form?
Cations
What kind of ions do non-metals form?
Anions
What will an ion do if it has less than four electrons to fill it’s outer shell?
It will lose those electrons and become a cation
What will an ion do if it has more than four electrons to fill it’s outer shell?
It will gain electrons to fill it’s shell and become an anion
How are ionic compounds made?
When a metal ion loses electrons it becomes positively charged and is then attracted to the non-metal which is now negatively charged because it has gained electrons
How are ions in ionic compounds bonded to each other?
There are strong electrostatic forces of attraction between the two ions
What is the structure of an ionic lattice?
A regular arrangement between ions (cation, anion, cation, anion…)
There are electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely charged ions
What do ionic compounds usually have relating to melting and boiling points?
They have high melting and boiling points
Why are ionic compounds at a solid state in room temperature?
There are many strong ionic bonds
Large amounts of energy must be transferred to break these bonds
What is a giant ionic lattice?
A lattice containing many ions
What is covalent bonding?
When a pair of electrons is shared between two non-metals
Are covalent bonds strong or weak?
Strong
What does covalent bonding often produce?
Molecules which can be made up of elements or compounds
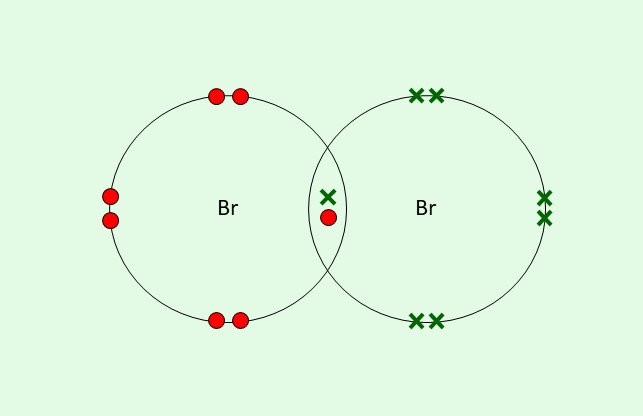
What is a dot and cross diagram?
A diagram showing how non-metals share electrons (see image)
Both of these bromine atoms have shared an electron so they both have a full outer shell
There are dots and crosses so we can tell which electrons came from which atom
We can see the shared electrons in the overlapping section
An atom will share as many electrons as it wants to gain
What are simple molecules and what are their properties?
A simple molecule consists of just a few atoms joined together by strong covalent bonds. Their properties are:
Low melting points
Low boiling points
What state of matter are simple molecules in at room temperature and why?
They are a gas or liquid because their intermolecular forces are weak and it does not take much energy to overcome them. It is important to note that covalent bonds do not break when this happens.
What are intermolecular forces?
Forces between molecules
Why can’t most simple molecular substances conduct electricity?
They are not electrically charged
The electrons are not free to move
Why can metals conduct electricity?
Because they have a sea of delocalised electrons meaning the electrons can move, conducting electricity
What do SOME simple molecular substances do when dissolved?
They break down, forming ions
These ions can move around, so the solution conducts electricity
What are giant molecular substances?
Giant molecules contain very many atoms
What are the atoms like in giant molecules?
The atoms have strong covalent bonds
They are arranged in a regular lattice structure
What are the properties of giant molecular substances and why?
High melting points
High boiling points
They are solids at room temperature and a lot of energy must be transferred to break the many strong covalent bonds during melting and boiling.
These substances are insoluble in water.
What are allotropes of carbon?
Different physical forms of carbon
What are the properties of diamond?
Is an allotrope of carbon
Each carbon atom is bonded to 4 others
This means it cannot conduct electricity as each carbon atom shares electrons to get a full outer shell meaning the electrons can’t move
Strong covalent bonds between atoms
Very high melting and boiling points
Very hard
What are the properties of graphite?
Is an allotrope of carbon
Soft
Each carbon atom is bonded to 3 others
Graphite has many layers joined by weak intermolecular forces
Strong covalent bonds between atoms in a layer
Slippery because the layers can slide off each other
High melting and boiling points
Can conduct electricity as carbon atoms only make 3 bonds which means there is one extra electron which is delocalised (free to move)
What are the properties of graphene?
Is an allotrope of carbon
Very similar to graphite but only one layer (See image)
Graphene is almost transparent because it’s layers are just one atom thick

What are the properties of buckminsterfullerene (buckyballs)?
Is an allotrope of carbon
Hollow balls
Can conduct electricity as there are delocalised electrons
Are soft in a solid state because they have weak intermolecular forces
What are the properties of nanotubes?
Is an allotrope of carbon
Can be several mm long
Can conduct electricity because they have delocalised electrons
Are very strong because of the many strong covalent bonds
What are the properties of metals vs non-metals
Property | Metals | Non-metals |
|---|---|---|
Appearance | Shiny | Dull |
Electrical conduction | Good | Poor |
Density | High | Low |
Melting point | High | Low |
What are metals like as a solid compared to non-metals in terms of how malleable they are?
Metals are malleable- they can be pressed into shape without shattering
Non-metals are brittle in the solid state- they shatter when bent or hit
What are metallic bonds like?
Consists of a giant lattice of positively charged metal-ions
Has a sea of delocalised electrons
There is a strong force of attraction between the positive metal ions and the delocalised electrons
When happens if a force is applied to a metal?
The layers of positive metal ions slide over each other but the sea of delocalised electrons hold the lattice together
The metal changes shape without shattering
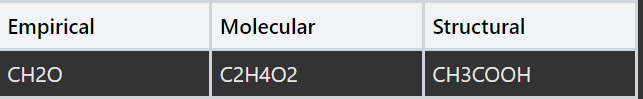
What are the positives and limitations of written formulae? (see image)
Empirical | Molecular | Structural |
|---|---|---|
CH2O | C2H4O2 | CH3COOH |
The simplest whole number ratio of atoms in an element. Doesn’t show how atoms are arranged and (usually) the actual number of atoms | Shows the number of atoms in each element . Does not show how the atoms are arranged | Shows the number of each element. Does not show how they are arranged |
What are the positives and limitations of drawn molecular structures?
Shows atoms covalently bonded
Shows double bonds if there are any
Does not show three-dimensional shapes
Does not show the shared electrons
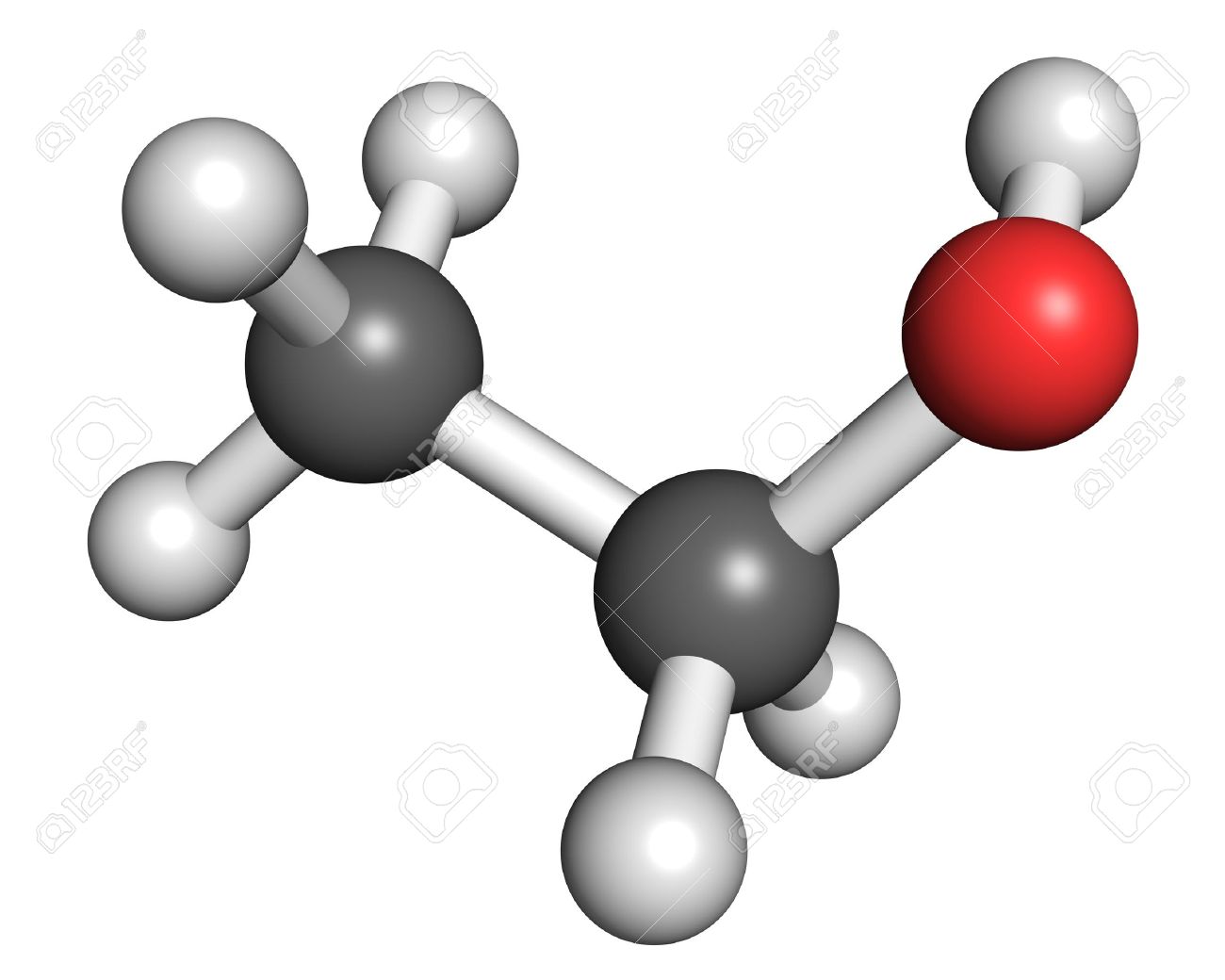
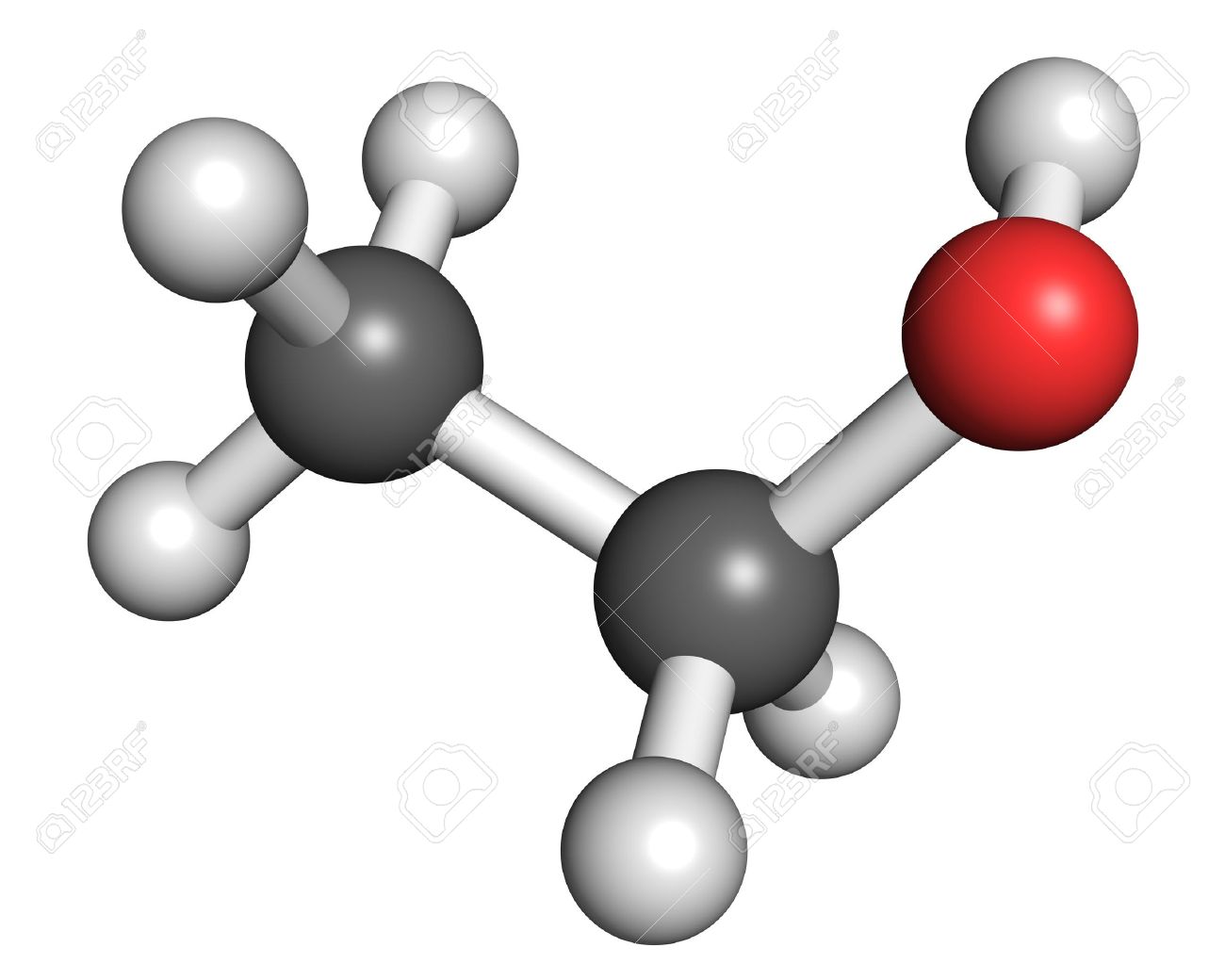
What are the positives and limitations of the ball and stick model? (see image)
Shows how each atoms is bonded to other atoms
Shows the molecules three dimensional shape
Does not show the shared electrons
Does not show each atom’s chemical symbol
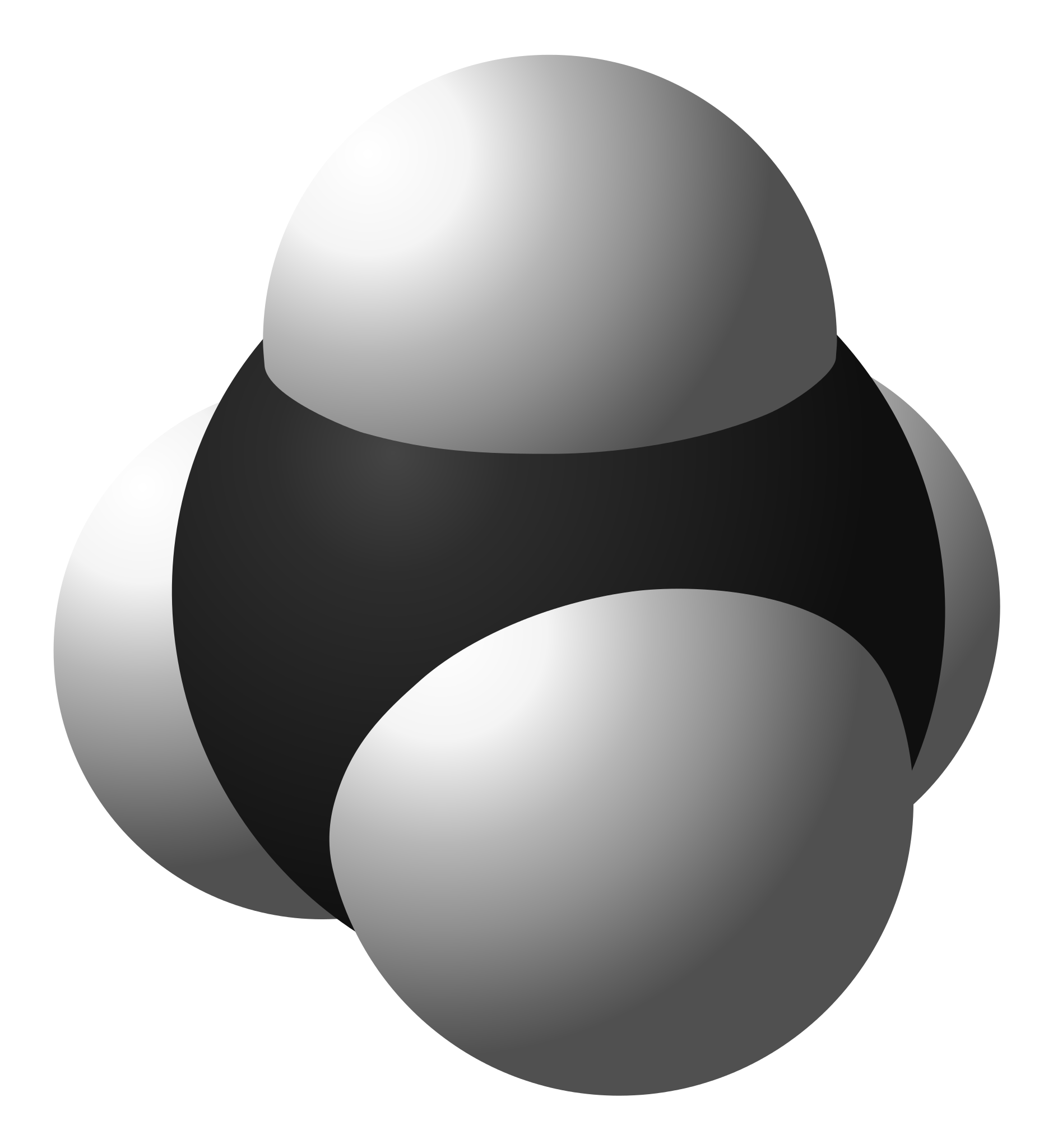
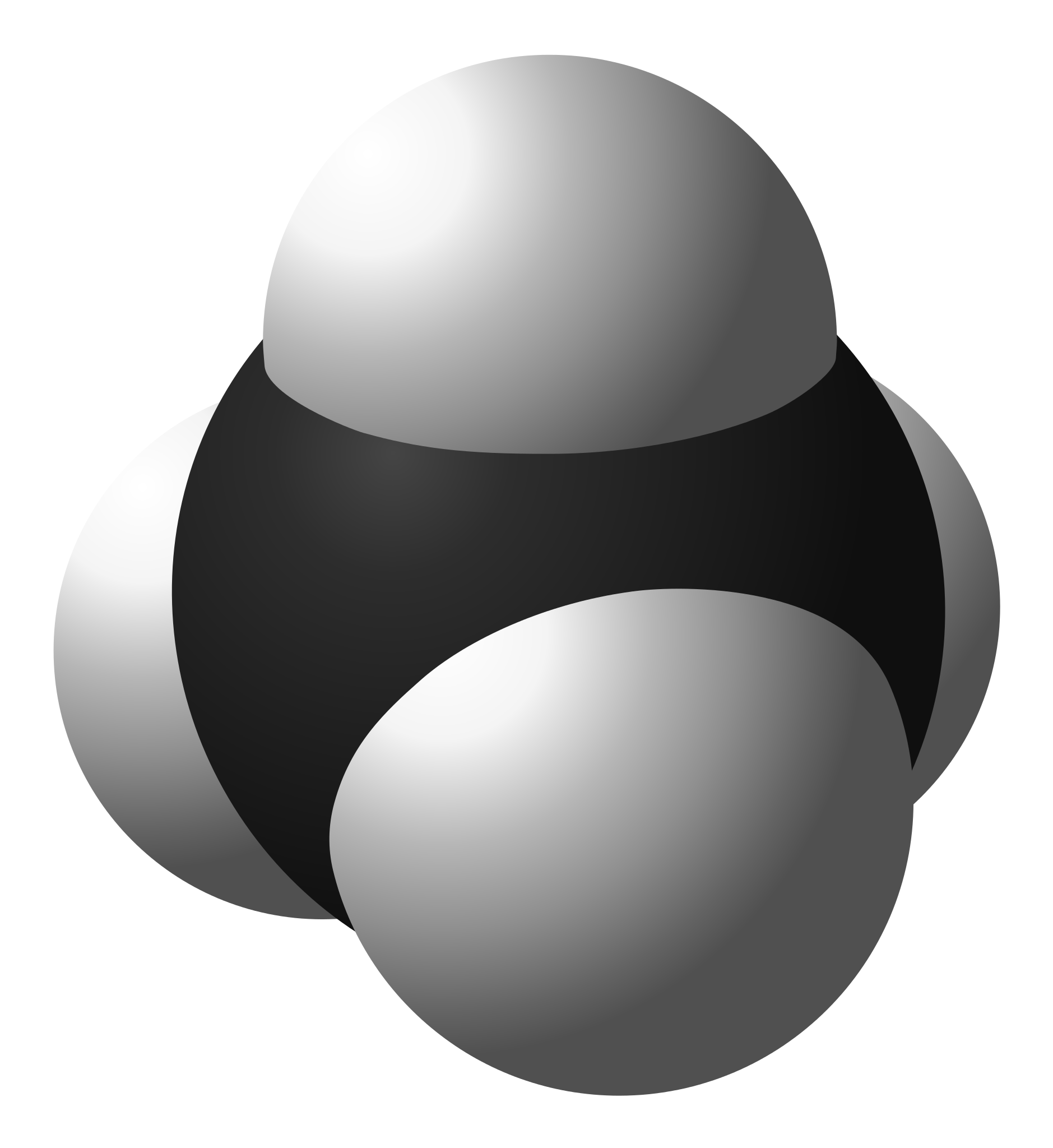
What are the positives and limitations of the space-filling models? (see image)
Shows how each atoms is bonded to other atoms
Shows the molecules three dimensional shape
Does not show the shared electrons
Does not show each atom’s chemical symbol
Shows the sizes of the atoms relative to their bonds
You may not be able to see all of the atoms
Doesn’t show single or double bonds
How do we calculate relative formula mass?
Add together the masses of all atoms shown in the formula
For example: H2O= 16+(1×2)=18
What is the empirical formula?
The simplest whole number ratio of atoms of each element in a compound
How do we calculate empirical formula?
Write down the mass of each element in g
Write down the relative atomic mass of each element
For each element calculate mass/relative atomic mass
Divide each answer by the smallest number
You may then need to multiply the numbers to remove fraction
(See image), note that if the element is something like Pb5O10 you can just divide it by 5 to find the empirical formula
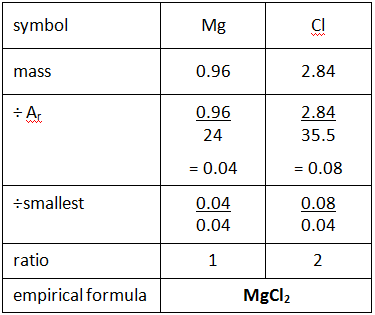
What is the law of conservation of mass?
The total mass of reactants at the start of a reaction is the same as the products at the end of a reaction
What is a closed system?
A situation where no substance an enter or leave during a reaction
What is an example of a closed system?
Reactions in a sealed container such as a flask fitted with a bung
What is a non-enclosed system?
A situation in which substances can enter or leave during a reaction
What is an example of a non-enclosed system?
Reactions in an open flask where a gas can leave
What will we observe in an open system?
The mass of a reactive metal increase because it will bond with oxygen to make a metal oxide
The mass of a reactive non-metal decreases if it is heated in air because the products in the gas state escape to the air
The mass of a metal carbonate decreases if it is heated because carbon dioxide is produced and escapes from the container
What are limiting and excess reactants?
Limiting- The reactant that limits the amount of product formed because it is used up
Excess- A reactant that is left over because there was too much of it
How does the limiting reactant affect the mass of product?
The mass of product formed is controlled by the mass of the reactant that is not in excess. This means the reaction will continue until the limiting reactant is used up
What is a solution?
A mixture of a solute and a solvent
What is a solute?
The substance that dissolves
What is a solvent?
The substance that the solute dissolves in
How do we convert cm³ to dm³?
Divide by 1000
What is the equation for concentration involving mass and volume?
Concentration (g/dm³)= mass of solute (g)/volume of solution (dm³)
What is the unit for the amount of a substance?
A mole (mol)
What number is Avogadro’s constant?
6.02 × 10²³
What is the equation for the number of particles in a substance?
Number of particles = Avogadro constant × amount (mol)
What is the equation for the mass of a substance including formula/atomic mass and moles?
mass (g) = relative atomic (for atoms) OR formula (for molecules) mass x moles
What are the uses of fullerenes?
Bucky balls can be formed around a drug to make a cage around it which can then be used to deliver the drug to other parts of the body
Fullerenes have a high surface area : volume ratio so they can be used as industrial catalysts
Nanotubes can be used in electric circuits because it can conduct electricity
Nanotubes used in nano technology
Nanotubes can be used to strengthen other materials like on tennis rackets because then have a very high length : diameter ratio meaning you can add strength without adding much weight