OB Exam 1: Statistics, Fam, Culture, Genes
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What impacts fertility rates? (5)
age: declines w/ age (especially > 32y/o)
bad egg quality
elevated or low BMI disrupts hormones
diet
smoking
exercise

What factors contribute to high mortality rates in US? (7)
limited access to pre natal care
high prevalence for obesity/HTN
food desert
transportation
racial disparities
income
lack of familiar support
Maternal mortality vs morbidity:
mortality: deaths of pt during pregnancy
morbidity: acute/chronic health complications d/t pregnancy or childbirth
What are some leading causes of maternal morbidity and mortality? (5)
excess blood loss and postpartum hemorrhage (PPH)
infections
sepsis
cardiovascular events (embolisms, strokes, HTN)
mental health disorders (suicide, drug use)
How can beneficence and autonomy conflict in care?
When a pt refuses tx that the nurse believes is safest
ex: recommending c-section for moms safety but she wants a natural birth
What injury prevention strategies do maternal newborn nurses teach? (4)
safe sleep
car seat safety
fall prevention
infx prevention

What are postpartum blues?
when does it resolve?
mild, short term mood changes affecting many new moms
- resolves w/in 1-2 weeks
Whats postpartum depression?
when does it happen
persistent sadness, hopelessness w/in 12 months of birth that interferes w/ daily functioning and bonding with baby

Whats postpartum psychosis?
when does it start?
develops w/in 2-3 weeks of postpartum period
rare severe mental health emergency w hallucinations and delusions
may harm themselves or newborn!!!
How have recent legal issues affected reproductive healthcare in US? (2)
restrictions on abortions
decreased availability in some states for family planning
What interventions help reduce maternal morbidity rates? (5)
better access to prenatal/postpartum care in poor areas
have standard protocols for managing high-risk pregnancies (HTN, preeclampsia)
early screenings
lifestyle counseling
chronic disease management (DM, HTN etc)
How does midwifery integrate w/ traditional maternal healhcare?
midwives work alongside physicians to give care for LOW risk pregnancies
provide prenatal, labor, and postpartum care
Whats the benefits and challenges of @ home births?
benefit:
more personalized care and comfort
fewer interventions for low risk pregnancies
challenges:
limited access to emergency care if complication arises
Whats the benefits and challenges of hospital births?
benefit:
immediate access to interventions and emergency care
cons:
less individualized care
higher infx risk
higher rate of medical intervention
How do SDOH affect maternal newborn outcomes? (7)
income
education
housing
transportation
access to healthcare
nutrition
stress
What is cultural awareness in maternal healthcare?
recognizing that different cultures exist and understanding ones own biases
What is cultural competence in maternal healthcare?
Actively applying cultural knowledge to provide respectful, individualized care
Whats primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary prevention in maternal newborn care?
primary: preventing problem b4 they occur
ex: prenatal vitamins, vax, healthy lifestyle
secondary: early detection
ex: pap smear, colonoscopies, mammograms
tertiary: manage existing conditions to reduce complications
ex: chemo, pain management, cardiac rehab
quaternary: avoiding unnecessary medical interventions that could be harmful
How should nurses screen for interpersonal violence or substance use disorder?
private, calm setting
use HITS questionaire
active listening, silence, empathy, clarify, etc…
non-judgmental care
What are assessment questions used to assess cultural factors related to childbirth? (6)
who should be present?
are there foods that are appropriate/ inappropriate during pregnancy, birth and postpartum?
are there any beliefs/customs that prohibit physical activity during pregnancy?
how would u like to express pain during childbirth?
are there any precautions youd like to take w infant care?
how many visitors do u expect while ur in hospital?
Whats Trisomy 21?
Down Syndrome
xtra 21 chromosome → disability and physical features
flat nose
wide eyes
short neck
smaller ears
protruding tongue

Whats Turner Syndrome?
features: (5)
Females: only one functioning X chromosome (XO)
short stature
infertile
low hair line
wide chest/neck
amenorrhea

Whats Klinefelter Syndrome?
signs: (8)
Males: has extra X chromosome (XXY)
infertile
low testosterone
long limbs
increased height
small balls
delayed puberty
increased risk for breast cancer
female hair distribution
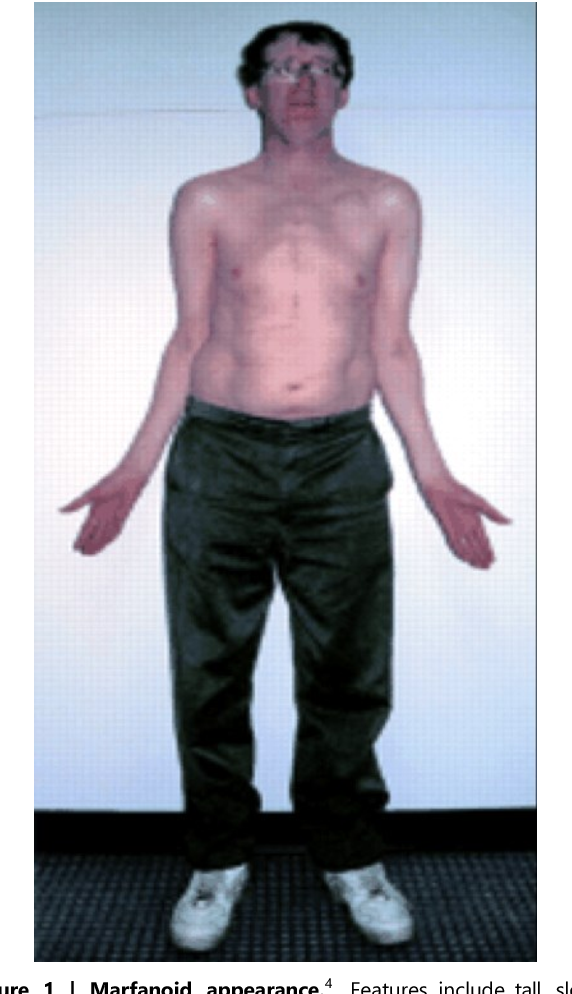
How does Trisomy 21 differ from sex chromosome anomalies?
trisomy 21 affects overall development
while sex chromosome disorder mainly affect sexual development
What are 3 1st trimester screenings taken?
Cell Free DNA
Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS)
Nuchal Translucency Testing
Whats Cell Free DNA?
BLOOD test after 10 weeks that screens for chromosomal abnormalities
Whats CVS and whos it mainly for?
whens it done?
Chorionic Villus Sampling
INVASIVE diagnostic test done @ 10-13 weeks to detect genetic disorders
cells from placenta gotten through cervix
for high risk pregnancies (> 35 y/o)
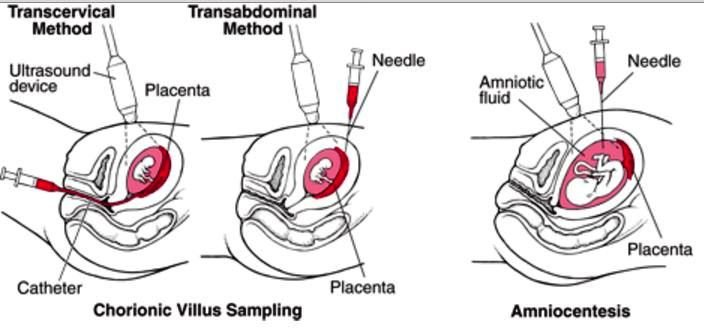
Whats some risks of CVS? (4)
increases risk of fetal hemolytic disease
fetus Rh+ and mom is Rh-
spontaneous abortions
rupture of membranes
infx
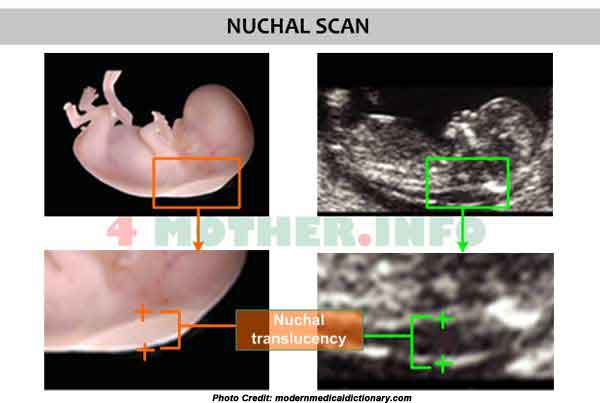
Whats Nuchal Translucency Testing?
USN measuring fluid behind the fetal neck to asses for risk for chromosomal abnormalities @ 11-13 weeks
Detect trisomy 21
Whats targeted carrier screening?
examples?
pros and cons?
tests for specific genetic conditions based on ethnicity or fam hx
ex: AA pts have higher risk of Sickle Cell Anemia
Jews, French, Canadians have higher risk for Tay-Sachs
Pros:
lower cost
focused and well-studied
cons:
many missed conditions outside selected test

What expanded carrier screening?
ex? (3)
pros and cons?
screens for 100+ genetic disorders regardless of background
carriers have the gene
ex: cystic fibrosis, sickle cell, Huntington’s
Pros:
more inclusive
IDs unexpected risks
Cons:
higher cost
increases anxiety
What are universal screenings for babies? (3)
Blood chemistry (not targeted)
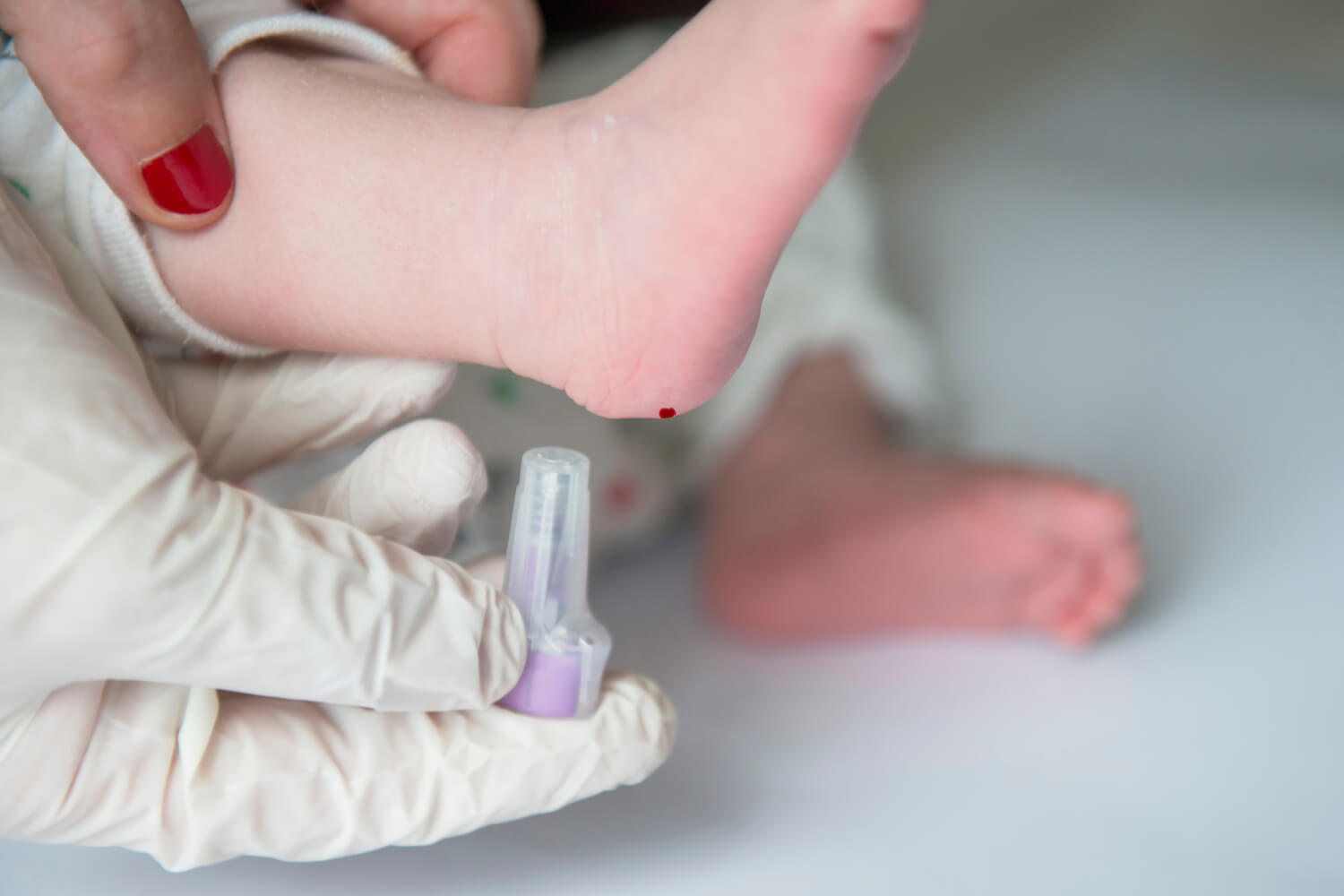
PKU: Heel Stick
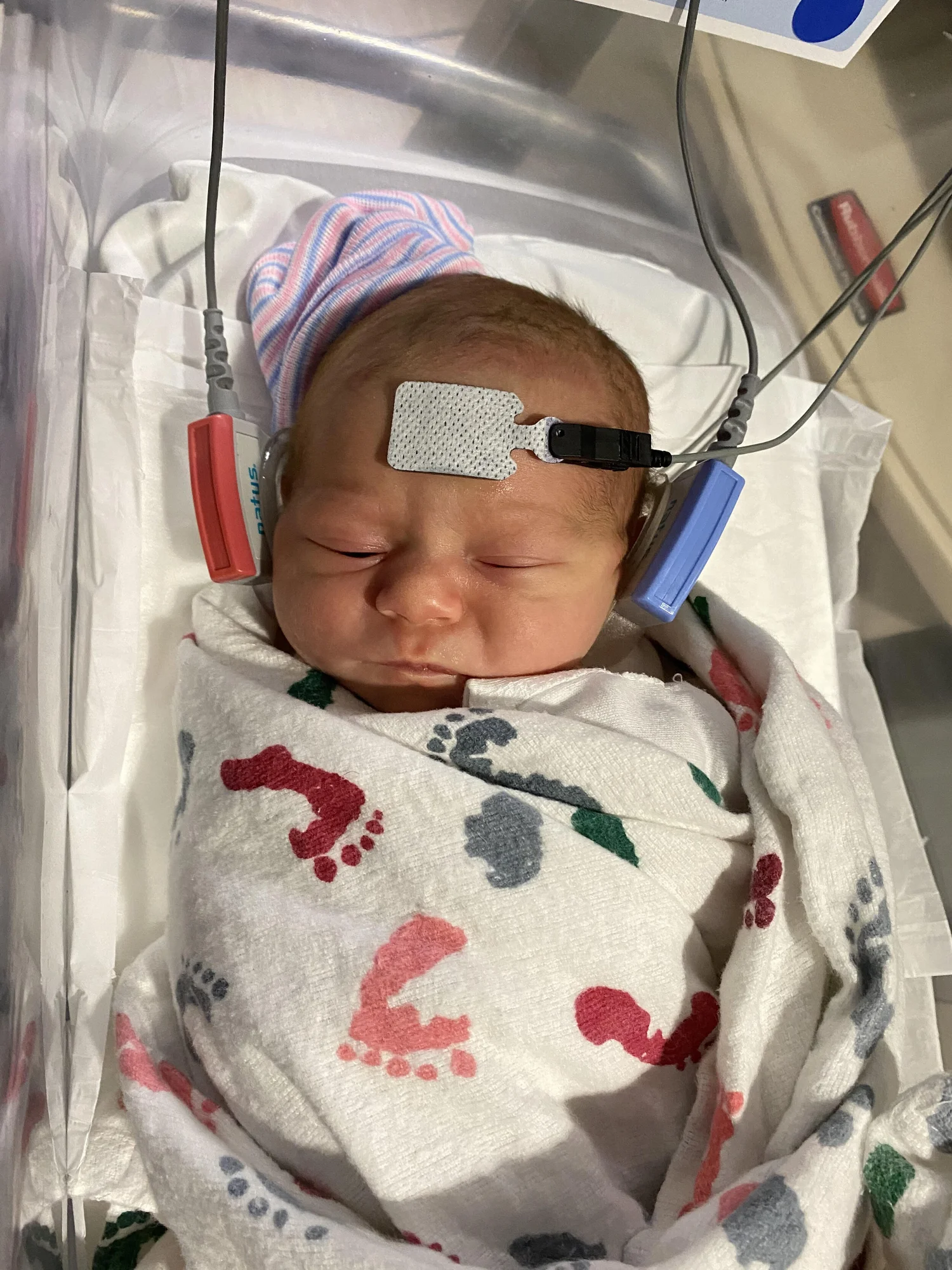
Hearing": ID’s congenital hearing loss
Cardiac
What does the Blood Chemistry test for?
metabolic disorder (PKU/Hypothyroidism)
done @ 24-48 hrs of life
How is Newborn Cardiac Screenings done?
Pulse Ox to detect critical congenital heart defects