Nature of Religion
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
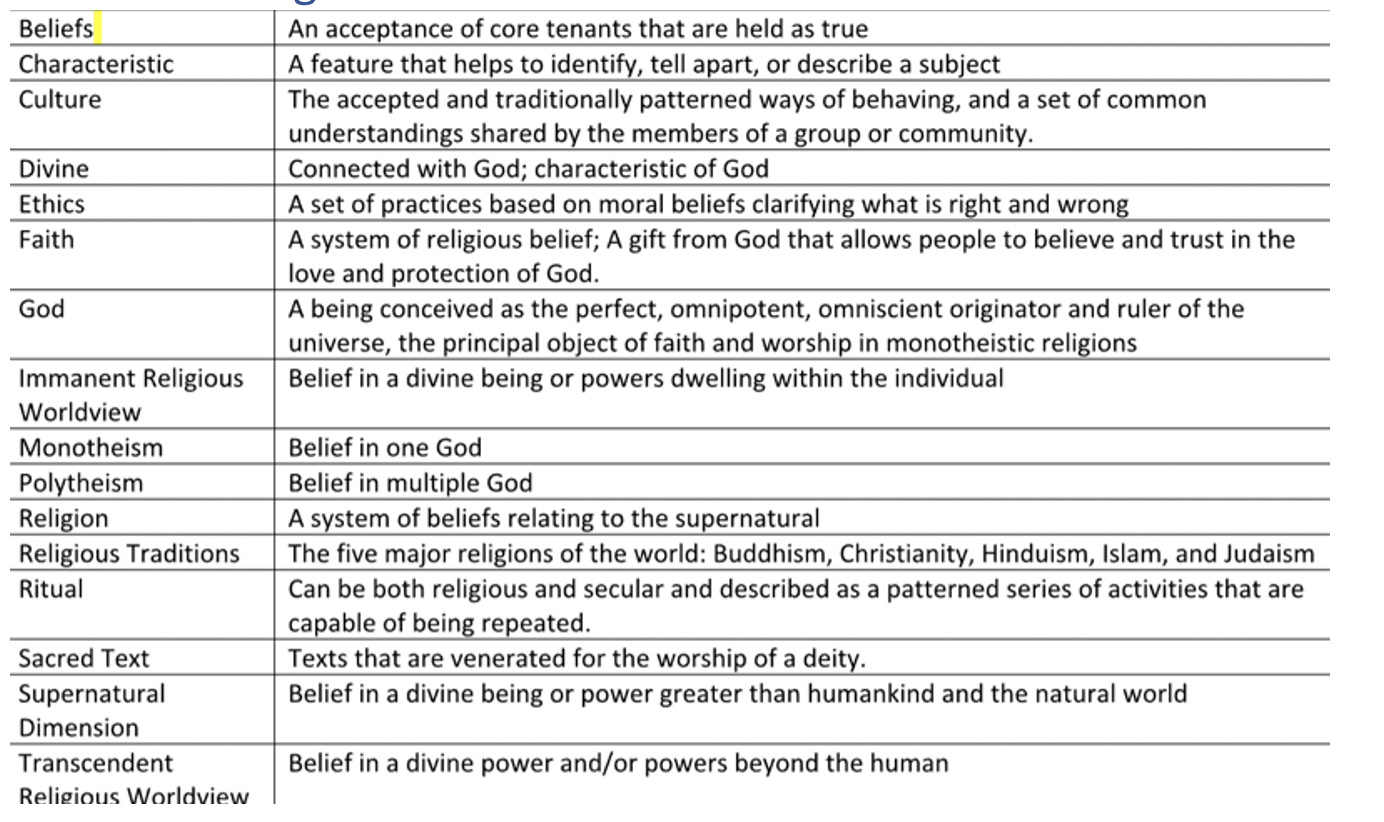
Define the supernatural dimension + supernatural
Belief in the existence of a divine being(s) beyond human limitations and the natural world.
• Believed to be responsible for creation of earth and being the ultimate destiny
• Supernatural: a force beyond scientific understanding or the laws of nature
define worldview, religion, mono/poly theism, secular
Worldview: the way someone sees the world
· A system of beliefs, ethics and practices, that provide purpose for an individual or group
o E.g. Abrahamic faiths = time is linear, Indian religions = time is a cycle
· Dependent on culture, morals, and upbringing
Religion: Source of meaning where people try to make sense of supernatural dimension.
Monotheism: belief in one God (Abrahamic faiths)
Polytheism: belief in many gods (Indian religious traditions)
Secular: Non-religious
define transcendent worldview + identify components
A belief in a divine power and/or powers beyond the human.
· Point believers to divine world beyond earthly concerns
Abrahamic faiths (Christianity, Islam, Judaism)
· Monotheistic - One God exists beyond humans and guides them
· Task is to transform world to a perfect state
· One life
· Salvation + life after death
· One God is eternal, all knowing and good
· Knowledge of God is sent to humans from beyond human spirit (holy books) - Angels, prophets, holy spirit
define immanent worldview + identify components
A belief in a divine being or powers dwelling within the individual.
· Emphasis place on Gods in human existence in day to day life
Indian religious traditions: (Hinduism + Buddhism)
· Task is to be released from cycle of rebirth
· Ultimate goal is to reach nirvana/enlightenment within oneself
o Find truth within human spirit
After each death spiritual knowledge is experienced
What are characteristics of a religion
Belief and believers |
Sacred Texts and Writings |
Ethics |
Rituals and Ceremonies |
what are beliefs and believers
Values and how they shape how adherents follow a religion. 1. Beliefs about supernatural dimension 2. Beliefs about the creation of the world 3. Beliefs about life and purpose 4. Beliefs about afterlife |
what are sacred texts + what do they do
Contains most important beliefs of a religion. Instil law, character, and spirituality.
· Visual, written and oral
1. Creeds - Set of beliefs 2. Doctrines - Teaching
3. Dogmas - More than a teaching. 4. Catechisms – Questions and answers
GAIN INSIGHT INTO RELIGION + HOW TO LIVE
ALWAYS STAY THE SAME (just different interpretations)
what are ethics
Religious reflection on moral beliefs (conscience)
· Determine right and wrong.
Regulate moral decision making which justify accepted norms
what are rituals
Reflect dynamic religion
· Adherents live out and celebrate beliefs
· gestures, words, and objects
PRACTICE BELIEFS AND ENGAGE WITH SCRIPTURE/TEXT
what is a living, dynamic religion
describes religions that update their interpretations of sacred texts, central beliefs and traditions based on social and cultural contexts in which adherents live
· A practical religion that is expressed in society + everyday life of adherents
· IMPACT ON INDIVIDUALS + COMMUNITY
· How characteristics interact (sacred texts stay the same but new interpretations)
· Through rituals/ceremonies (traditions) + ethics
Apply beliefs through texts
give example of a living dynamic relgion
Example: Catholicism, Second Vatican Council
· Adapting and changing to suit the times
· Modernise the church (Liturgical reforms)
o Idea of Christian unity was furthered as Catholics could now collaborate with protestants
o Priests faced assembly
o Official translation of mass (vernacular language allowed, not just Latin)
characteristics of buddhism
Ethical Teaching | Beliefs and Believers | Sacred Text | Rituals |
Karma Good karma gained through the Five Precepts to reach Nirvana 1. Refrain killing 2. Refrain stealing 3. Refrain from misuses of the sense or sexual misconduct 4. Refrain from wrong speech (lying, gossip) 5. Refrain from intoxications (alcohol) | - Nirvana o Escape samsara+ suffering o Stop accumulating karma - Samsara (rebirth) - The path of enlightenment is through the practice and development of morality, meditation and wisdom - The life is suffering - The four noble truths | - Tripitaka (Pali Canon) - Mahayana Sutras - The Tibetan Book of the Dead | - Meditation - Mantras - Mudras: Symbolic hand gestures - Prayer Wheels: Reciting mantras with the turn of a wheel - Monasticism - Pilgrimage Veneration of Buddha’s and Deities |
characteristics of hinduism
Ethical Teaching | Beliefs and Believers | Sacred Text | Rituals |
Dharma ‘right way of living’ to achieve good karma and then enlightenment - Brahmacharya (chastity unless for procreation) - Grihastha (marry and have kids) - Vanaprastha (prepare for the next life) - Sannyasa (person denounces material desires) | - Enlightenment = release from suffering o reuniting with Brahman (ultimate reality) o release from suffering and rebirth o soul merges with Atman (true, perfect self) - Strive to achieve dharma - Brahman is the creator spirit and binds each soul (atman) - The Vedas are the ultimate authority - Individual souls are immortal | The Vedas | 1. Marriage 2. Prayer for children 3. Prayer for the fetes 4. Baby shower 5. Celebrating Birth 6. Giving name 7. Piercing earlobes Beginning of education |
characteristic christianity
Ethical Teaching | Beliefs and Believers | Sacred Text | Rituals |
- 10 commandments - Beatitudes - Golden rule “Do unto others as you would have them do unto you” (Love thy neighbour) | - In Nicene Creed o Belief in God the Father, Jesus Christ as the son of God and the Holy Spirit (trinity) o The death, descent into hell, resurrection, and ascension of Christ o The holiness of the Church and the Communion of Saints o Humans made in likeness of God o God the creator - Humans made in God’s image | The Bible | Sacraments: 1. Baptism 2. Eucharist 3. Confirmation 4. Reconciliation 5. Anointing of the sick 6. Marriage 7. Holy Orders
Place of worship: church |
characteristics of islam
Ethical Teaching | Beliefs and Believers | Sacred Text | Rituals |
The Five Pillars of Islam
|
Muhammad ≠ God but a prophet | The Quran and the Hadith
| - The Five Pillars of Faith (prayer = uniting mind to and submitting to Allah) - Ritual purity in Islam - Khitan (circumcision)
Place of worship: Mecca |
characteristics of judaism
Ethical Teaching | Beliefs and Believers | Sacred Text | Rituals |
- Jews see themselves as a reflection of God - 613 mitzvot o Most famous are the Ten Commandments - Duty to seek holiness within themselves.
| - Monotheistic - Forbidden to worship of any other God - God is the creator of everything - God is eternal - God will help the Jewish people if they remain obedient to his - law and loyal to him - The Messiah will come and transform the world - Moses was the greatest Prophet - The whole of the Torah was revealed to Moses Jesus ≠ God but a prophet | The Torah, the Prophets and the Writings | - Life events o Bar/t mitsvah - Prayer in morning, afternoon + evening - Jewish festivals - Kosher foods o Nothing from pigs
Place of worship: Synagogue |
what does relgion do/contribute to
Attempts to answer the fundamental questions of human existence.
· Why am I here? Is there a supreme being? Why we suffer? Is there life after death?
Religion provides humans with an understanding to these questions, and helps to construct meaning, provides ethical guidance, and provides a sense of belonging.
religion Contribution to individuals
· Give guidance in life through ethics and sacred texts which people can draw on for wisdom.
· Contribute to an individual’s sense of self and understanding and belonging.
Example 1: Martin Luther King Junior – A man whose religion guided him ethically to make changes.
religion contribution to society
Culture - Customs + behaviours of a society
Positives | Negatives |
Different religions = diverse society
Legal and judicial systems are based off religions
Social justice initiatives driven by religion, and address societal issues · E.g. Australian Culture and Society paper on Homelessness in 2014: “Australian churches… play an important role… in reducing the prevalence of homelessness.” Inspiration of art (e.g. music + literature)
Believers from the same belief can create social cohesion · Doing the same thing at the same time (e.g. prayer) · Enforce beliefs | Led to violence when adherents believed their world view was being challenged · E.g. Christian Crusades (West sent armies over to help East but differences started fighting) |
Example 1: Prayer in Islam
The magnitude of people praying in Egypt during Ramadan, whilst buses and trains frequently go past, show how religion is integrated into society and everyday life in Egypt.