MITRAL REGURGITATION
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
The _________has two leaflets arranged to form a ring and a complex supporting structures consisting of muscles and tendons that support the leaflet like the string on a parachute
Mitral Valve
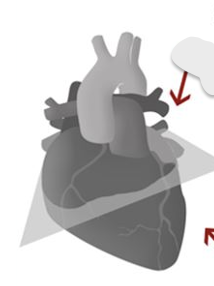
The surgeons view is looking _____?
DOWN
The Sonographer view is looking _____?
UP
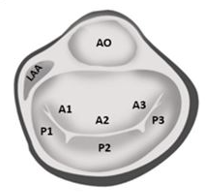
Surgeons View
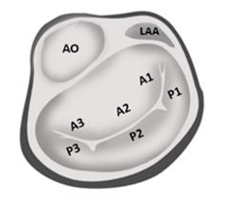
Sonographer view
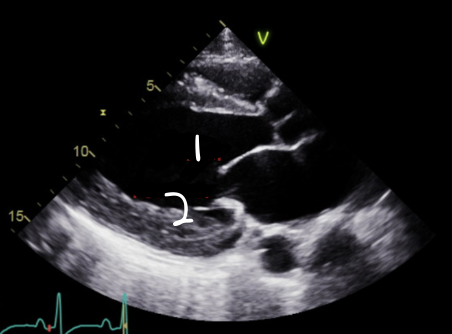
This is PLAX,What is 1?
Anterior
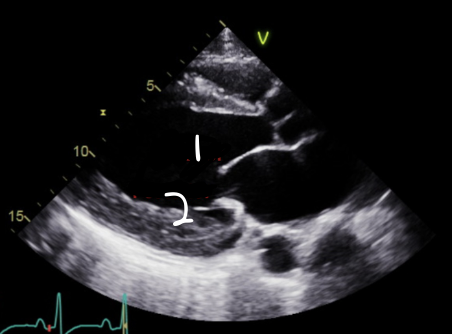
This is PSLAX, What is 2?
Posterior
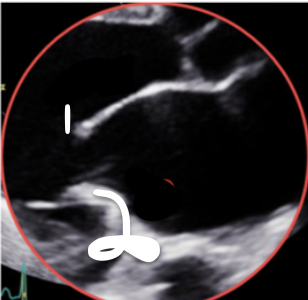
This is PSLAX, What is 1?
A2
This is PSLAX, What is 2?
P2
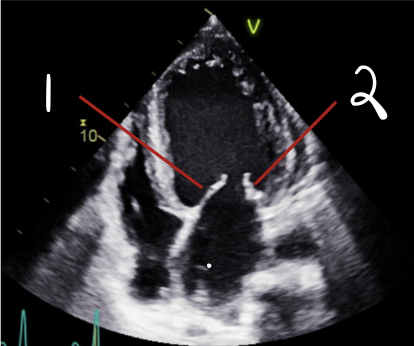
This is 4CH, What is 1?
Anterior
This is 4CH, What is 2?
Posterior
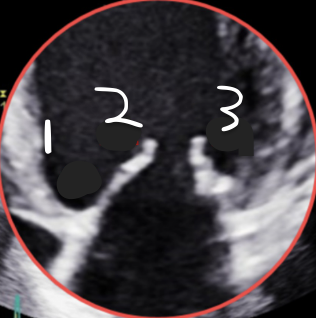
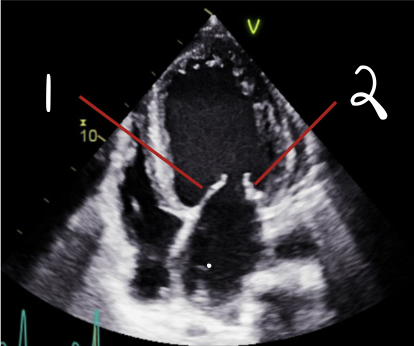
This is 4CH, What is 1?
A3
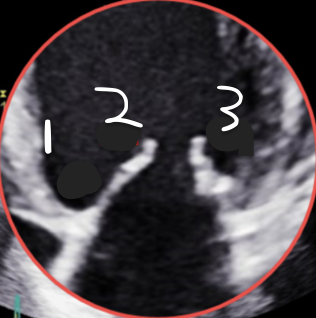
This is 4CH, What is 2?
A2
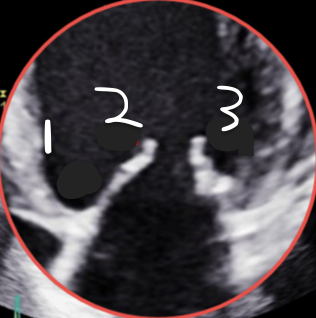
This is 4CH, What is 3?
P1
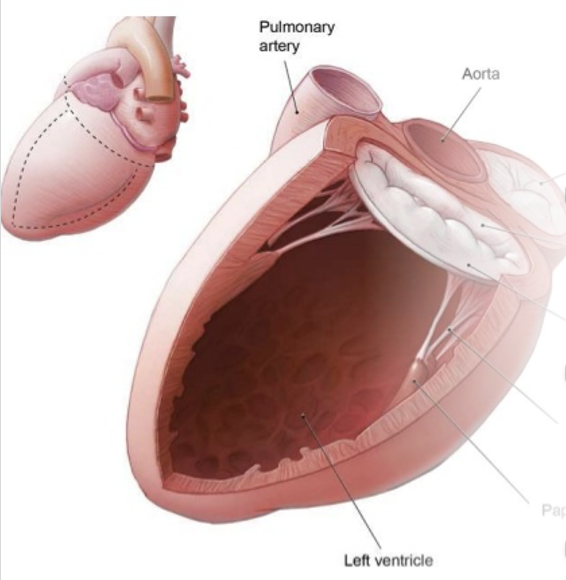
•The mitral valve acts as a gate between the left atrium and the left ventricle; the leaflets open and close as the heart beats and act as a 1-way valve.
•Any abnormalities with the _____________can lead to mitral regurgitation.
Mitral Valve Apparatus
Mitral Regutitation (Mr) is also called _______or ______________.
mitral insufficiency or mitral incompetence
__________happens when the mitral valve allows a backflow of blood into the left atrium.
Mitral Regurgitation
Mitral regurgitation may take years to reveal itself. But, if it goes on long enough, it can cause a _________________.
buildup of pressure in the lungs or cause the heart to enlarge
What is the MR Murmur?
Holosystolic murmur that radiates to axilla & may be blowing/high-pitched
What are the complication of MR?
LA volume overload
LA thrombus formation & embolization
increased preload → LV Volume Overload Pattern
long standing MR → Pulmonary HTN & Heart Failure
Pulmonary edema
With______, LA does not have time to compensate for additional flow à increased LAP
Acute MR
With _______, LA compensates for additional flow by dilating
Chronic MR
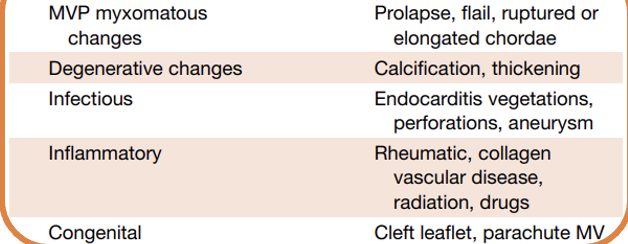
This is ?
Primary MR (Leaflet abnormality)
In Primary MR, ____________________________?
an intrinsic abnormality of the leaflet causes MR

This is?
Seconday MR (Ventricular Remodeling)
Secondary MR,
result from distortion of the MV apparatus due to LV and/or LA remodeling
Most secondary MR is _____________?
disease of the LV
It is important to distinguish primary from secondary MR as _____________?
therapeutic approaches and outcome differs
Primary MR (_____________) is caused by a problem with the mitral valve itself.
Degenerative
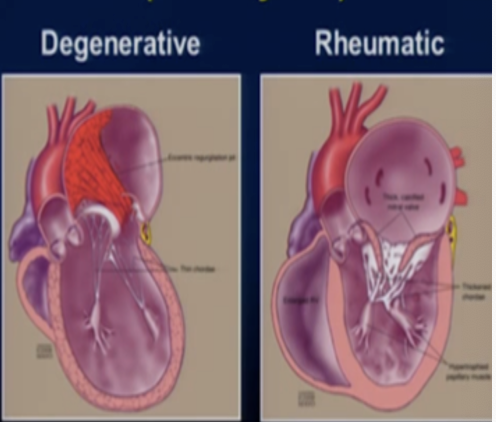
If there is excess tissue or a loose or ruptured chordae that is cause of the MR. This is called___________________.
Primary Mitral Regurgitation
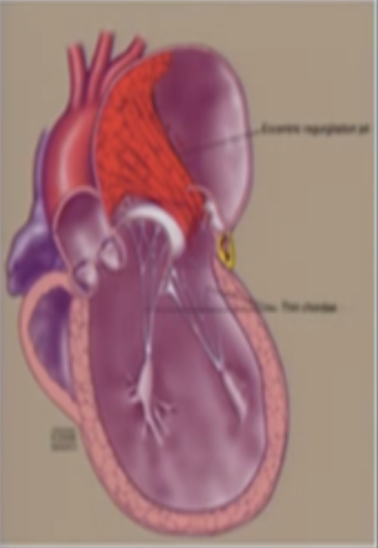
This is?
Degenerative of the Primary MR
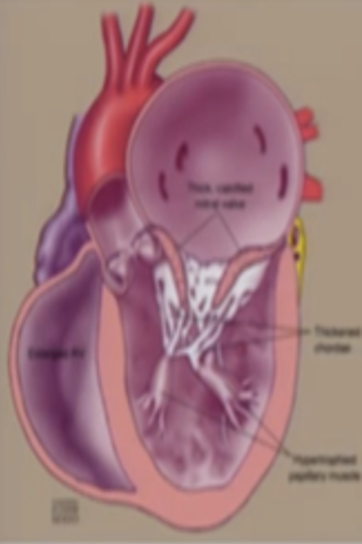
This is?
Pheumatic
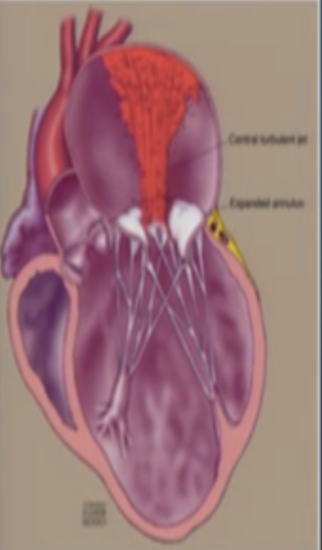
This is?
Primary MR
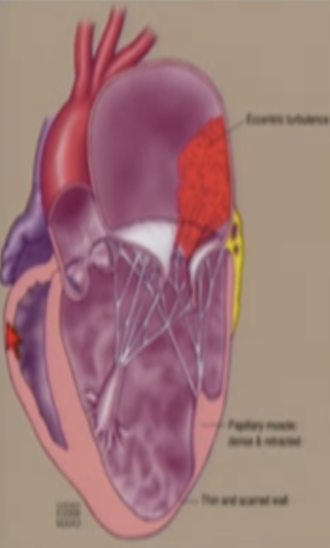
This is?
Flail P2 - P3
Secondary Mr (_____________) is caused by a problem with the LV.
Functional
__________________(SMR) occurs when coronary disease with myocardial infarction or primary dilated cardiomyopathy cause a combination of left ventricular (LV) wall motion abnormalities, mitral annular dilatation and papillary muscle displacement
Secondary Mitral Regurgitation
This is?
Dilated of the Secondary MR
This is?
Ischemic of the Secondary MR
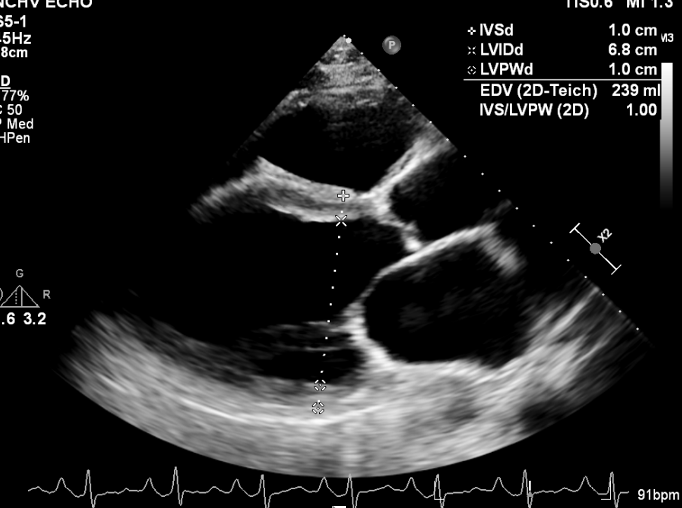
This is?
Secondary MR
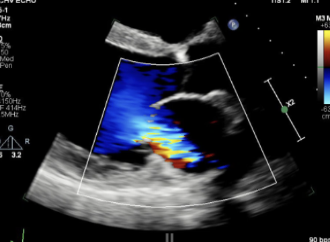
What are the signs and symptoms of MR
Dyspenea, Fatigue, Irregular Rhythms, Orthopnea, Palpitation
What are the treatment options for MR?
Monitor, Medical Therapy (Treat secondary cause), Valve repair- open heart surger, cath procedure (mitral clip procedure), minimally invasive surgery, MV replacement
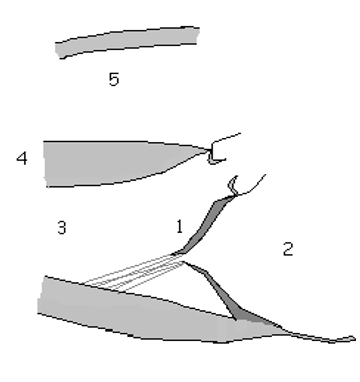
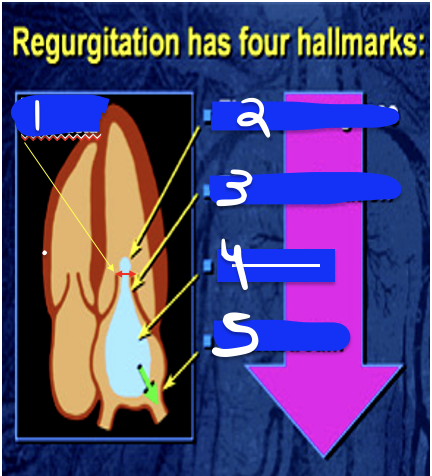
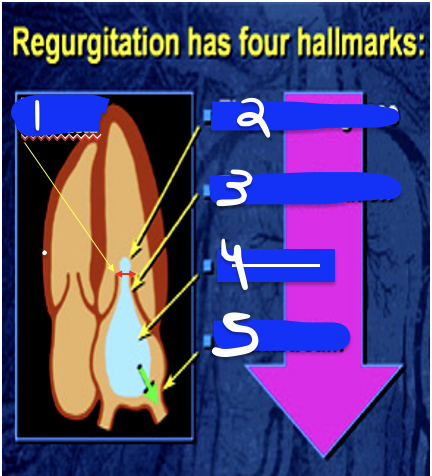
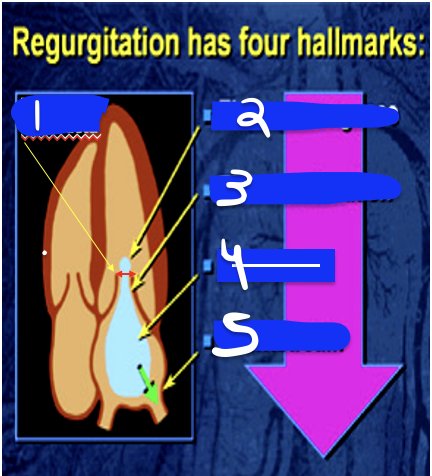
1
anatomic basis for defect
2
Lt Atrial Enlargment (LEA)
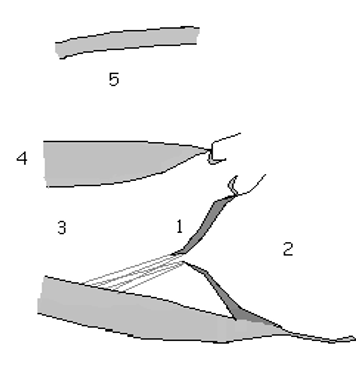
3
LV Overload pattern (LVVO)
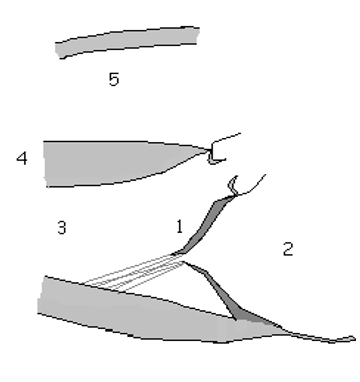
4
LV Hyperthrophy (LVH)
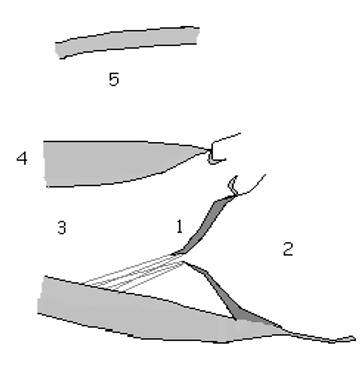
5
RT Ventricular Dilations (RVD)
What are the 2D assessment for MR
Structure & coapatation of Valve leaflet
annulus size
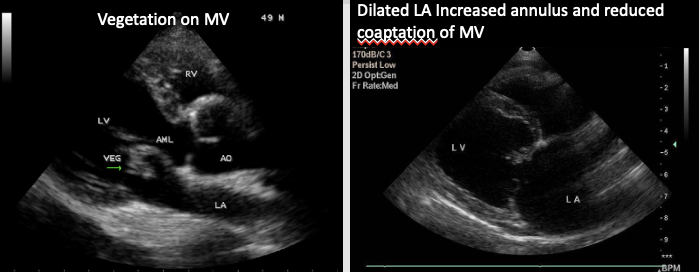
Vegetations, masses or thrombus
Size and functioning atria & ventricles
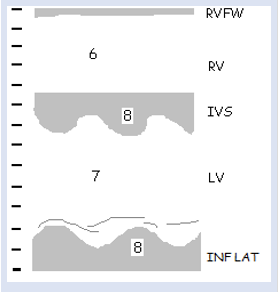
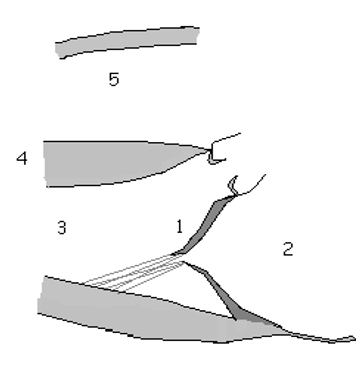
6
RVD
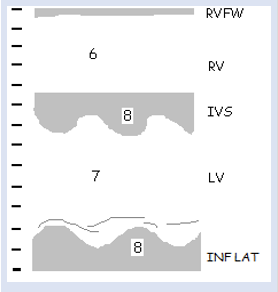
7
LVD
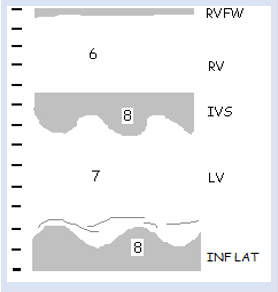
8
LVVO
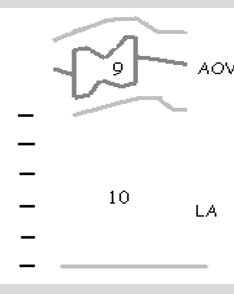
9
AOV notching due to sudden decrease in the amount of volume leaving the LV
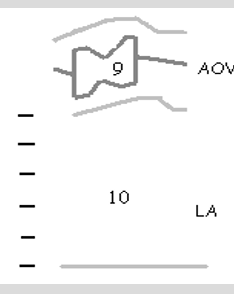
10
LAE
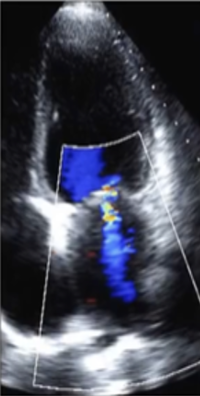
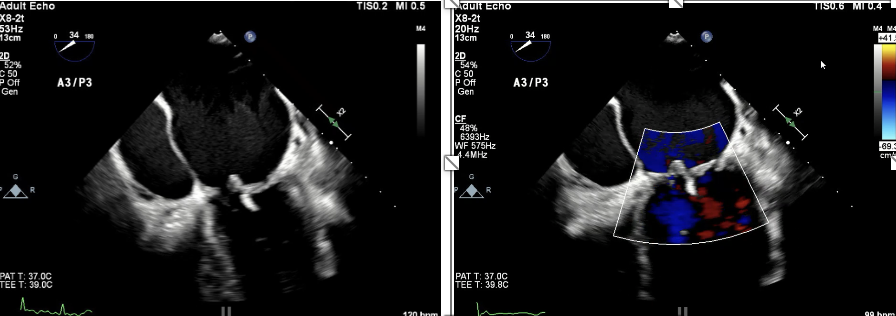
This is ?
Mild Central
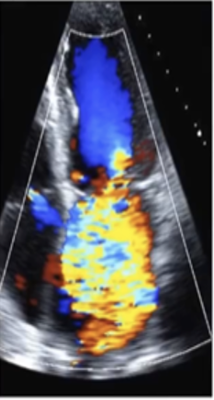
This is?
Severe Central
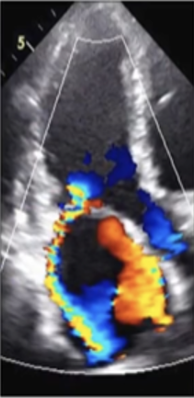
This is?
Severe Eccentric
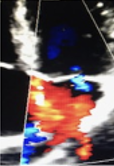
This is?
Grade I, Mild MR, Jet just beyond MV Leaflet
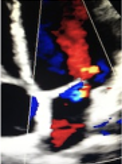
This is?
Mild-to-mod MR, Jet between mild & moderate
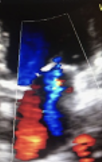
This is?
Grade II, Moderate MR, Jet 1/3 way into LA
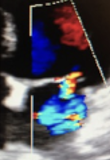
This is?
Grade III, Mod-to-severe MR, Jet ½ way into LA
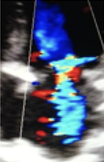
This is?
Grade IV, Severe MR, Jet Mid-to-back wall LA
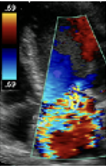
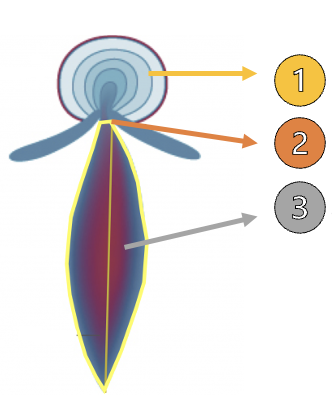
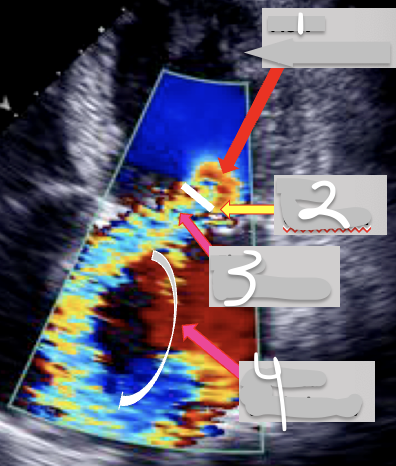
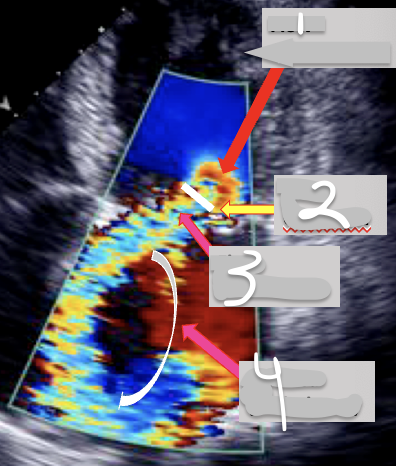
What is 1?
FlOW cONVERGENCE (PISA)
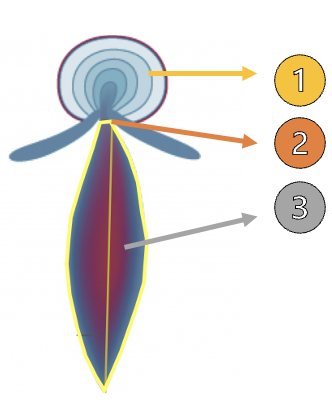
What is 2?
Vena Contracta
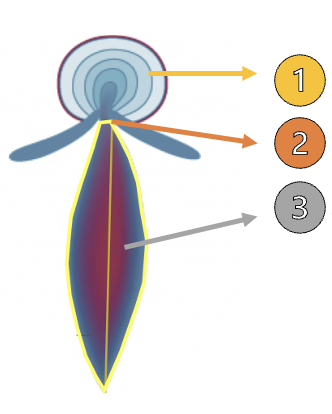
What is 3?
Jet Area
1
Vena Contracta
2
Flow Convergence
3
Flow Acceleration
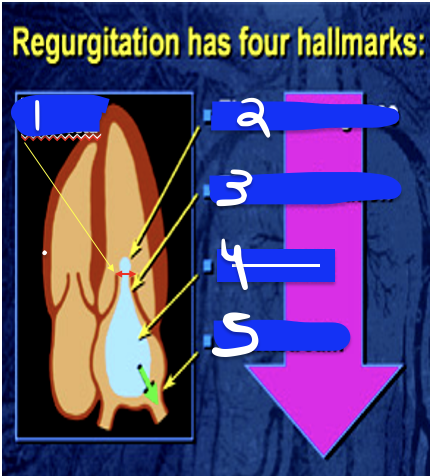
4
Turbulence
5
Downstream
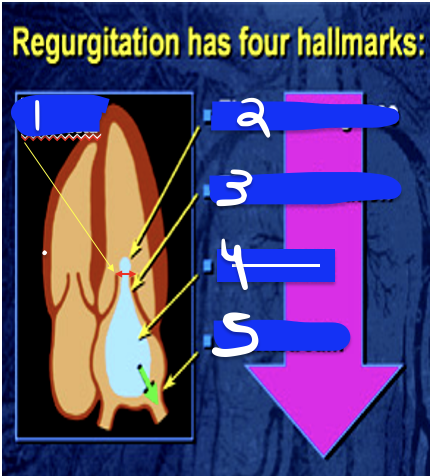
1
Flow Convergence
2
Vena Contracta
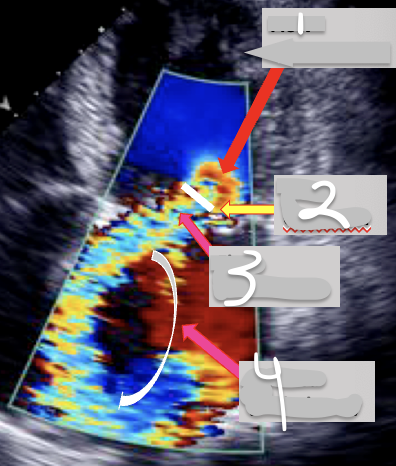
3
Flow acceleration
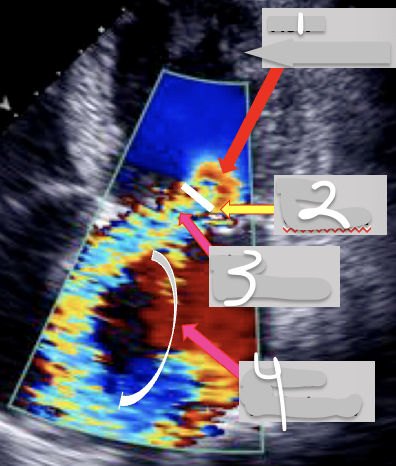
4
Jet Area (Turbulence)
•The __________ is the area of increased flow velocity before the regurgitant orifice.
•The size of this region corresponds to the magnitude of blood flow and the size of the regurgitant orifice.
Flow convergence
•The ____________ corresponds to the region in which blood passes through the valve (velocity is highest here).
•The width of the ………↑……. is a good marker of the severity of MR because it corresponds to the diameter of the regurgitant orifice area.
A diameter exceeding 7 mm indicates severe regurgitation
Vena contracta
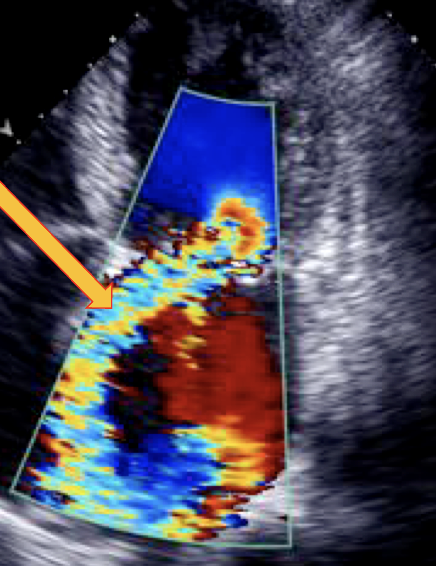
•The portion of the jet that is seen in the "receiving camber" (the left atrium) is the "________".
•Its size also corresponds to the severity of mitral regurgitation.
Jet Body
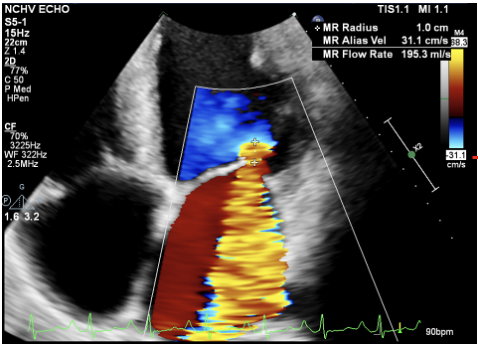
How to measure MR radius?
Simplified estimate of EROA = R² /2
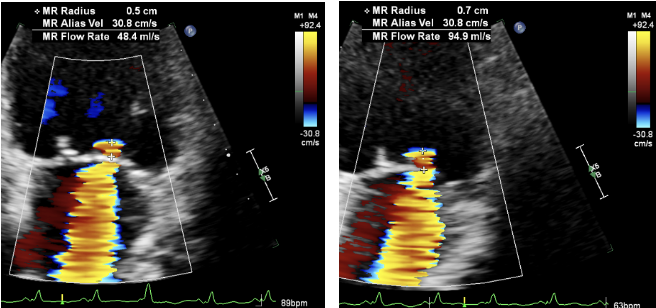
Use the best “Frame”……
Scroll to largest shell
Increase sweep speed for….?
bigger waveform
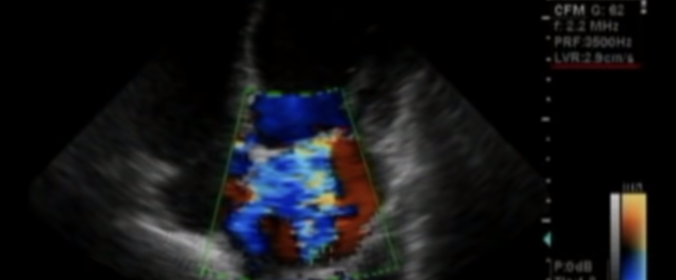
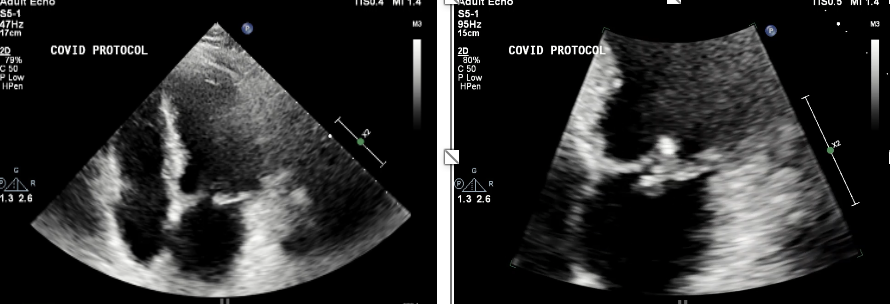
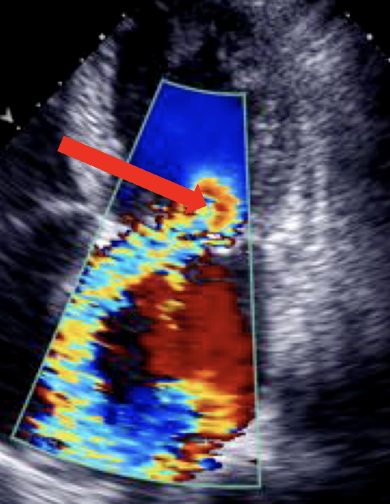
this is?
Multiple mitral regurgitation jets in 4CH
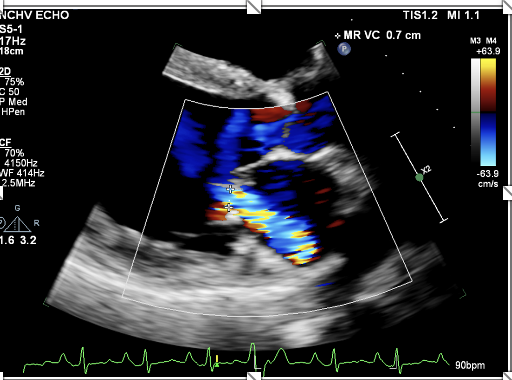
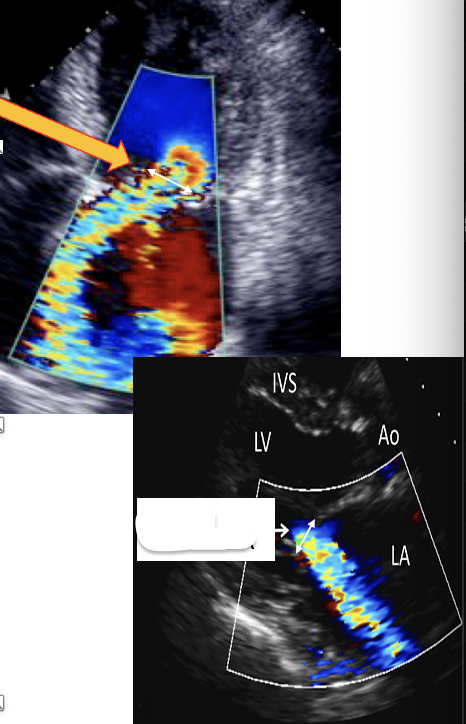
This is to measure ?
VCW
________/ focus within the MR jets optimise doppler angle compare view,aquire spectral strength, hspae, peak velocity, aquire MR VTI & Calculate MR Volume.
CWD
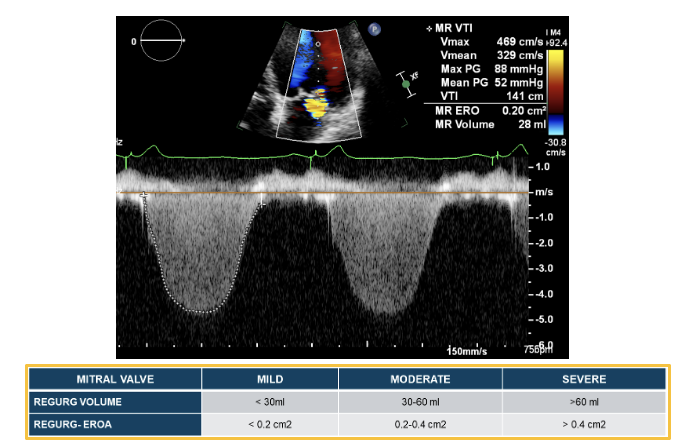
MR VOLUME = ?
EROA x MR VTI
___________ Out of date useful if CFD suboptimal systematically reposition …. gate througout LA to determine MR Length & width expect aliasing
PWD Mapping
This is ?
Dopple Angle
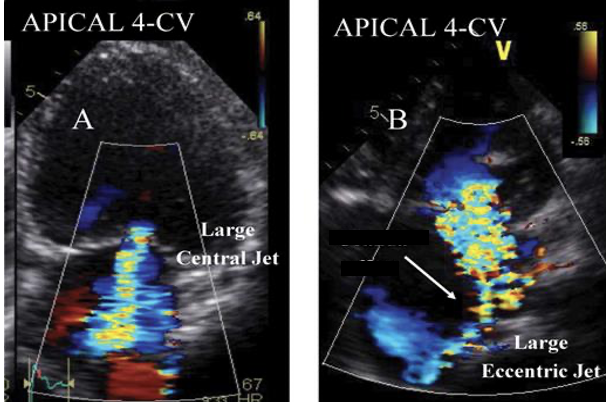
The ___________is when a regurgitation jet “wraps around” (or hug) the Lt atrial wall.
Coanda effect
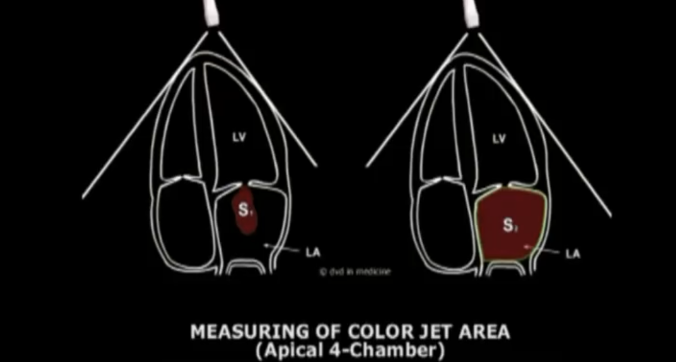
S1 / S2 × 100% = % of total LA area
What is the grading of (Color jet area) for a MILD MR?
<20% of total area (or a maximal jet area < 4.0 cm²)
What is the grading of (color jet area) for MODERATE MR?
20-40% of total area (or maximal jet area 4-10 cm ² )
What is the grading of (color jet area) of SEVERE MR?
> 40% of total LA area ( or maximal jet area > 10cm²)