Kurt Von Seekamm Macroeconomics ECO 201 FINAL EXAM review (terms & equations)
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Potential GDP
The maximum output an economy can produce without triggering inflation, assuming full employment of resources.
Lump Sum Tax
A fixed amount of tax that is paid regardless of income or economic activity, often used in economic models to simplify analysis.
Deficit
The amount by which a government's expenditures exceed its revenues in a given period, leading to an increase in public debt.
Monetary Policy
The process by which a central bank manages the money supply and interest rates to influence economic activity, inflation, and employment.
Contractionary Fiscal Policy
A form of fiscal policy that reduces government spending or increases taxes to slow down economic growth, often used to combat inflation.
Tax Multiplier
A factor that quantifies the effect of a change in taxes on overall economic output, indicating how much GDP increases or decreases in response to tax changes.
MPS
Marginal Propensity to Save, which measures the proportion of additional income that is saved rather than spent.
Aggregate Saving
The total amount of savings in an economy, calculated as the difference between total income and total consumption over a specific period.
Aggregate Demand
The total demand for goods and services within an economy at a given overall price level and in a given time period. It represents the sum of consumption, investment, government spending, and net exports.
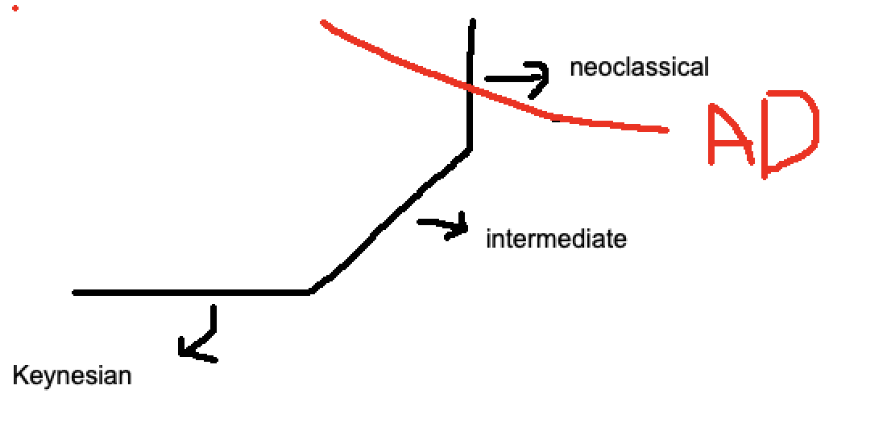
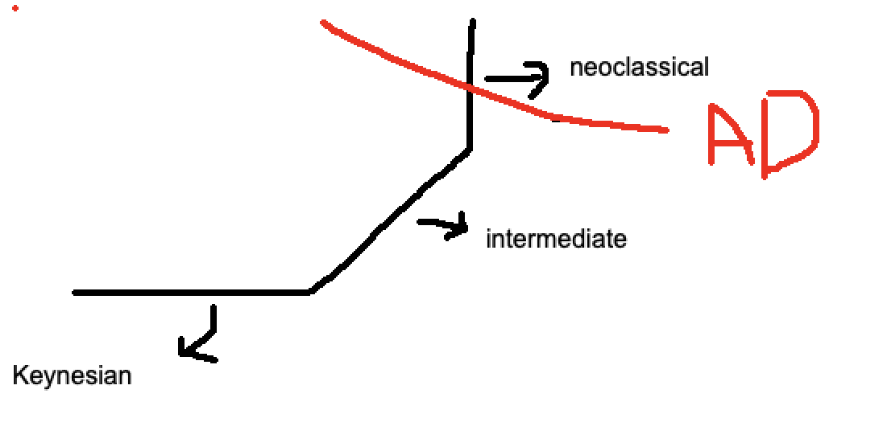
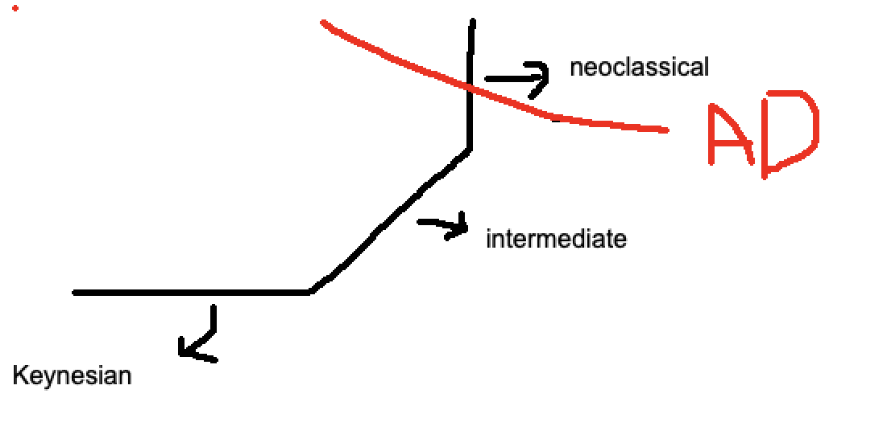
Intermediate Region
Middle, upward sloping part
Disposable Income
The income available to individuals after taxes, which can be spent or saved.
Government Spending
Expenditures made by the government on goods and services, which can influence economic activity and overall demand.
Surplus
A situation in which the quantity supplied of a good exceeds the quantity demanded at a given price, leading to excess supply.
Discretionary Fiscal Policy
a change in taxes or government spending (it is at the discretion of the present govt, not stuff like unemployment benefits which are in the law by previous legislators)
Keynesian Multiplier
A concept in economics that describes how an initial change in spending (usually government spending) can lead to a larger overall increase in economic output. It emphasizes the impact of fiscal policy on aggregate demand.
MPC
measures the proportion of additional income that a household consumes rather than saves.
Private Saving
The portion of income that households save rather than spend on consumption, typically calculated as disposable income minus consumption.
Consumption
The total amount of goods and services consumed by households in an economy over a specific period. It is a key component of aggregate demand and reflects consumer spending behavior.
Aggregate Demand Curve
A graphical representation of the total quantity of goods and services demanded across all levels of the economy at various price levels, typically downward sloping.
Neoclassical Region
vertical far right part of the economy graph
Shifts in AD
Changes in aggregate demand due to factors like consumer confidence, government spending, and monetary policy. An increase shifts the curve to the right, while a decrease shifts it to the left.
Fiscal Policy
The use of government spending and taxation to influence the economy. It aims to manage economic cycles and promote economic stability.
Public Saving
the budget surplus, is the term (T − G − TR), which is government revenue through taxes, minus government expenditures on goods and services, minus transfers. Thus we have that private plus public saving equals investment.
Transfer Payment
A payment made for which no current or future goods or services are required in return. Government transfer payments include Social Security benefits, unemployment insurance benefits, and welfare payments. Taxes are considered transfer payments.
Expansionary Fiscal Policy
an increase in government spending, a decrease in tax revenue, or a combination of the two—is expected to temporarily spur economic activity.
Autonomous Expenditure
Expenditures that occur regardless of the level of income or output, typically including investments, government spending, and net exports.
Exogenous Variable
A variable that is determined by factors outside the model being studied, often influencing the behavior of endogenous variables.
Aggregate Expenditure
The total amount of spending in an economy at a given level of income, including consumption, investment, government spending, and net exports.
Investment
the value of goods and services that businesses use to produce other goods and services. It's a key component of gross domestic product (GDP), and is calculated by subtracting consumption, government spending, and net exports from total expenditure.
Price Level
the average price of all goods and services produced in an economy at a specific time, essentially acting as a measure of the overall cost of living within that economy; a higher price level indicates generally more expensive goods and services, while a lower price level indicates cheaper goods and services.
Keynesian Region
Shifts in AS
Changes in the aggregate supply curve due to factors such as input prices, technology, and government policies, leading to variations in total output at different price levels.A right shift in the curve is caused by an increase in factors that allow producers to provide more goods at every price level, such as increased productivity, lower input costs, or technological advancements; essentially, a positive supply shock. A left shift in the curve is caused by an increase in the cost of production inputs, like wages or raw materials
Aggregate Expenditure =
Consumption (C) + Investment (I) + Government Spending (G) + Net Exports (NX)
Private Saving =
Y - C - T; where Y represents total income, C represents consumption, and T represents taxes.
Public Saving =
Tax Revenue (T) - Government Spending (G)
Spending Multiplier =
1/(1-Marginal Propensity to Consume)
Tax Multiplier Equation
-(NEGATIVE)Marginal Propensity to Consume/(1-Marginal Propensity to Consume).
Changes in GDP due to changes in economic policy
the impact that government decisions, such as fiscal and monetary policy, can have on the overall economic output of a country, influencing growth rates and economic stability.