Sense of Vision
4.8(8)
Card Sorting
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:38 AM on 11/26/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
1
New cards
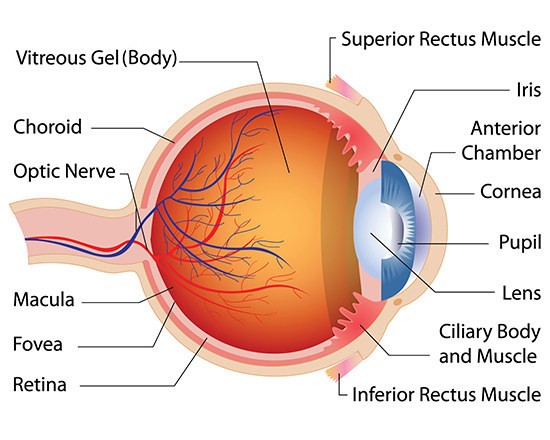
Eye is surrounded by a protective cushion of ____
fat
2
New cards
How much fraction of eye is visible to us
1/6. (Diameter of eye is 1 inch and we can only see 1/6 of it)
3
New cards
_____ is the dominant sense in humans
Vision
4
New cards
____% of sensory receptors are in human eyes
70%
5
New cards
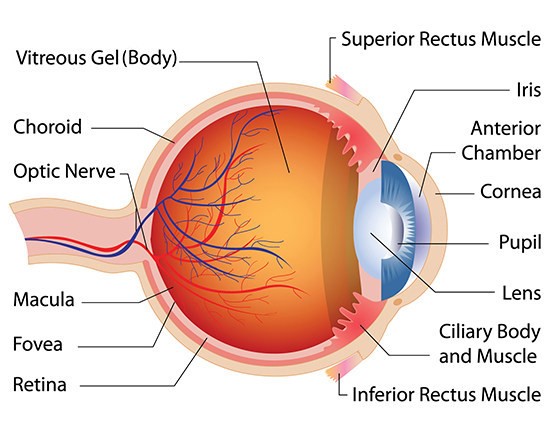
What is a Cornea?
Clear protective layer of eye
6
New cards
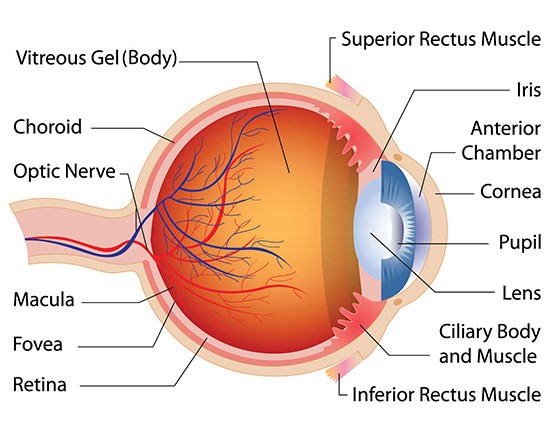
What is Iris?
Colored muscle that changes that amount of light that enters the pupil
7
New cards
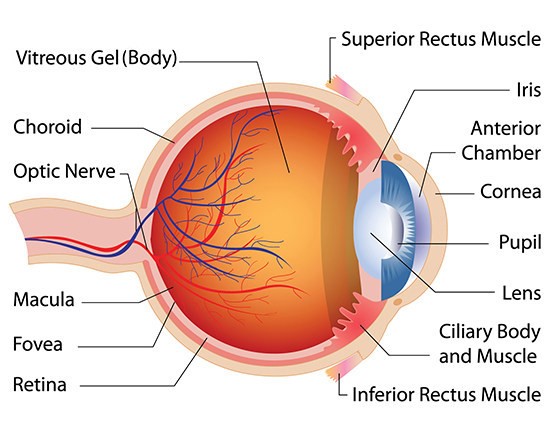
What is lens?
Focuses light onto the retina
8
New cards
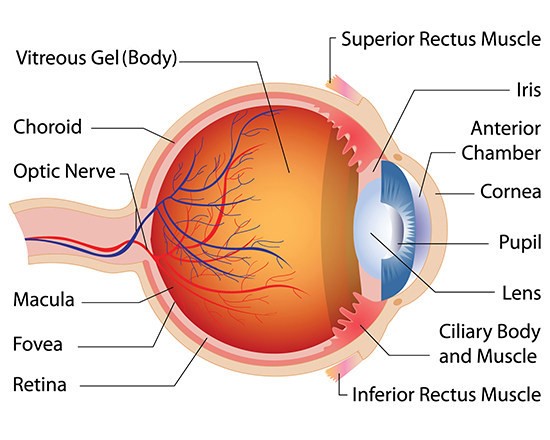
What is Retina?
Layer that contains photoreceptors
9
New cards
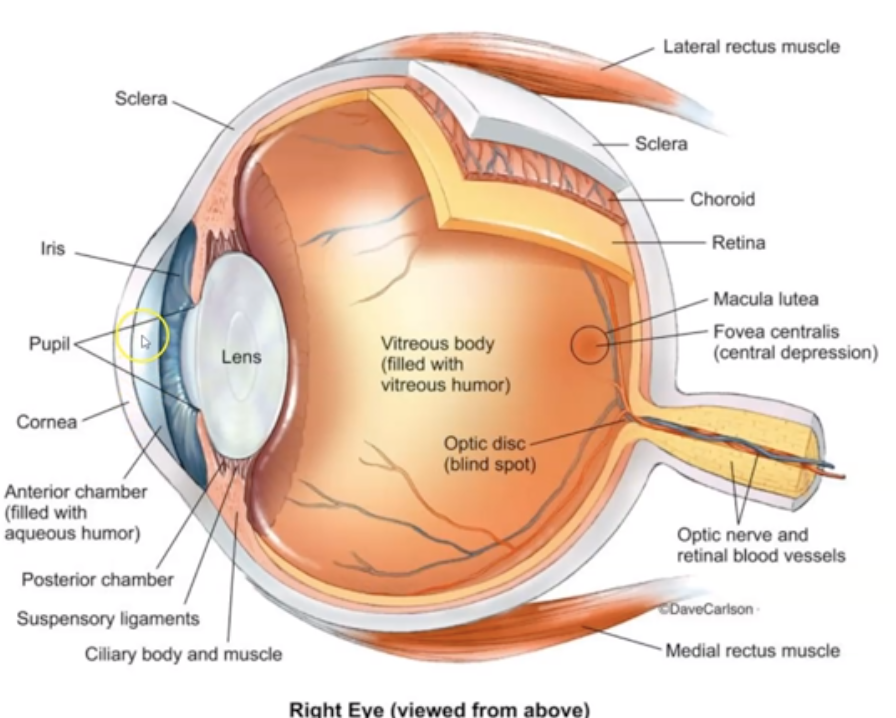
What is Optic Disc?
It's a point where retina enters the optic nerve
10
New cards
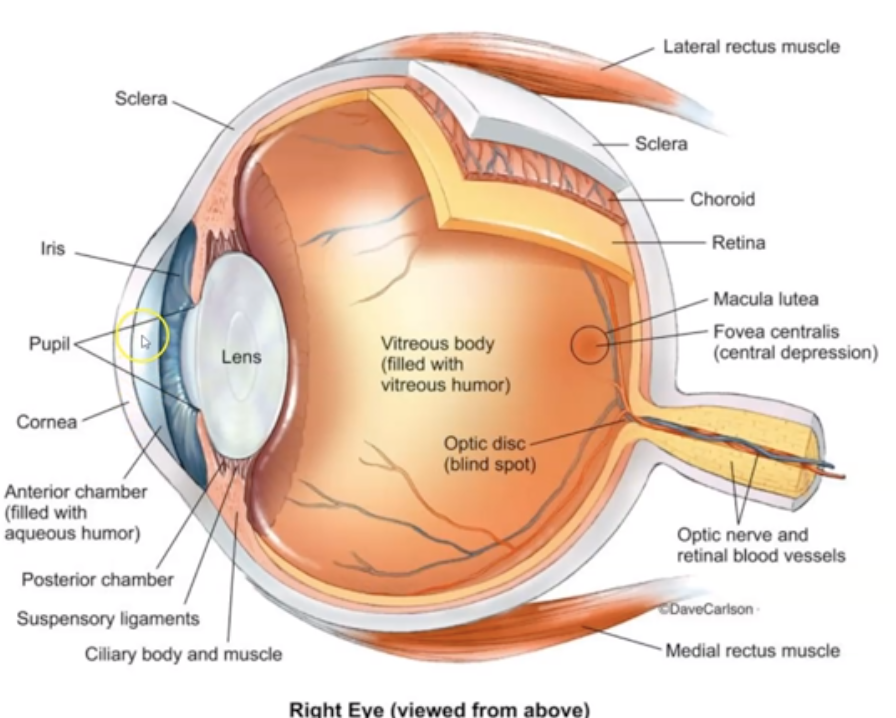
What is a choroid?
Vascular layer that assisting in protecting the eye
11
New cards
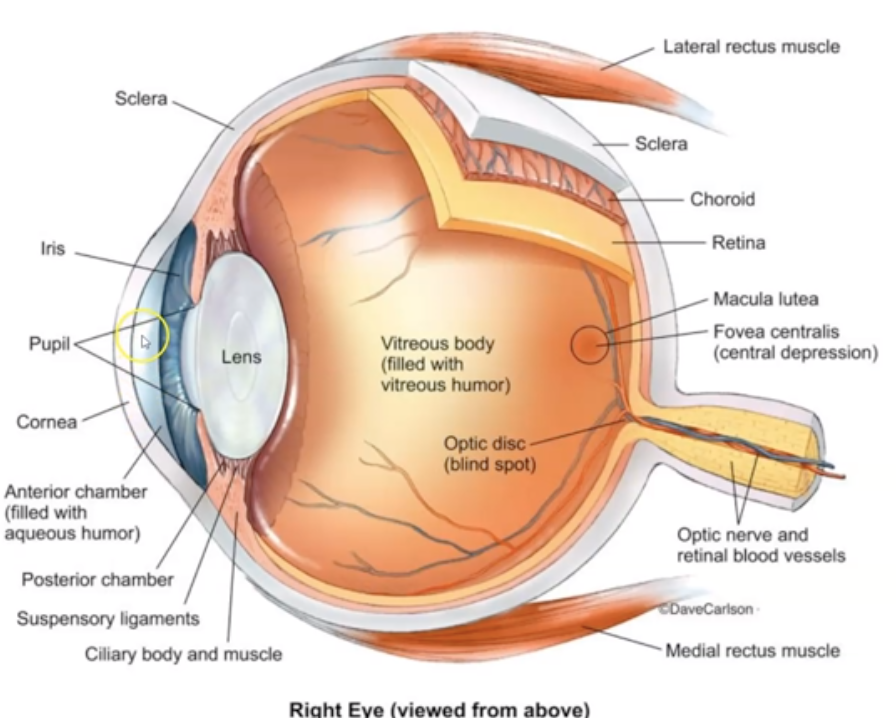
What is Sclera?
Opaque, protective layer
12
New cards
What does lenses do?
It changes shape to focus light onto the retina
13
New cards
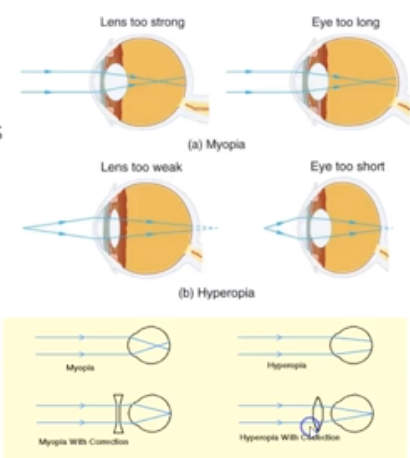
What is Myopia?
Light is focused in front of the retina (Nearsightedness). Eyeball is too long.
14
New cards
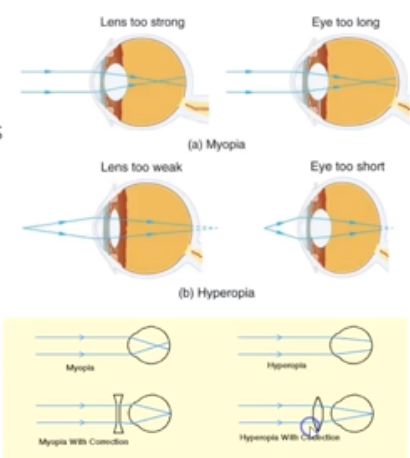
What is Hyperopia?
Light is focused behind the lens.
Eyeball is too short.
Eyeball is too short.
15
New cards
What color does rods distinguish?
Only black and white
16
New cards
What color does Cones distinguish
Colors. (ROYGBIV)
17
New cards
Where are Rods mostly found in the eye?
Thought the retina
18
New cards
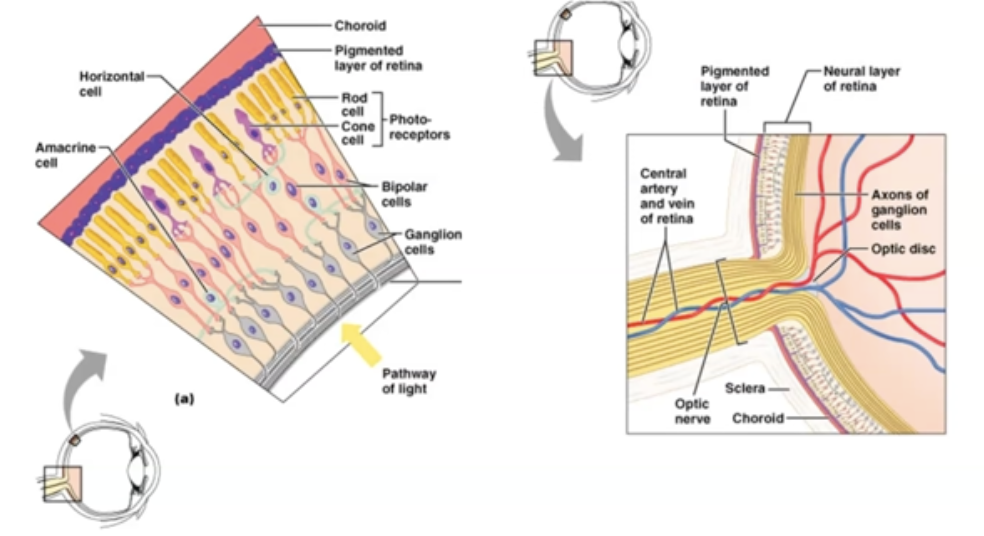
Where are Cones found in the eye?
Highly concentrated at fovea.
They are NOT present at periphery vision thus objects appear black and white when you see using periphery vision.
They are NOT present at periphery vision thus objects appear black and white when you see using periphery vision.
19
New cards
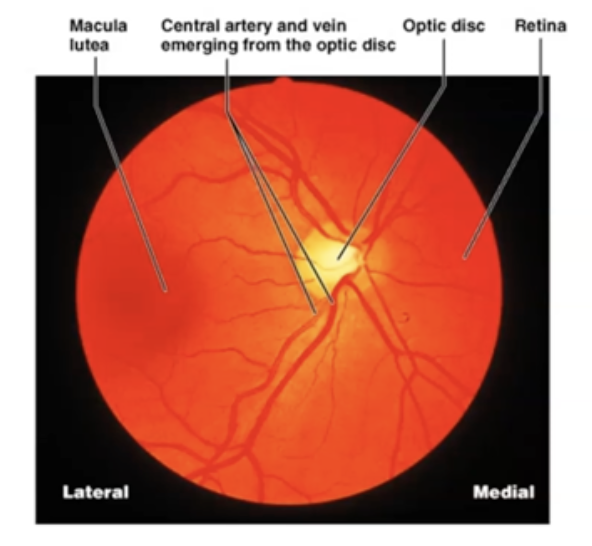
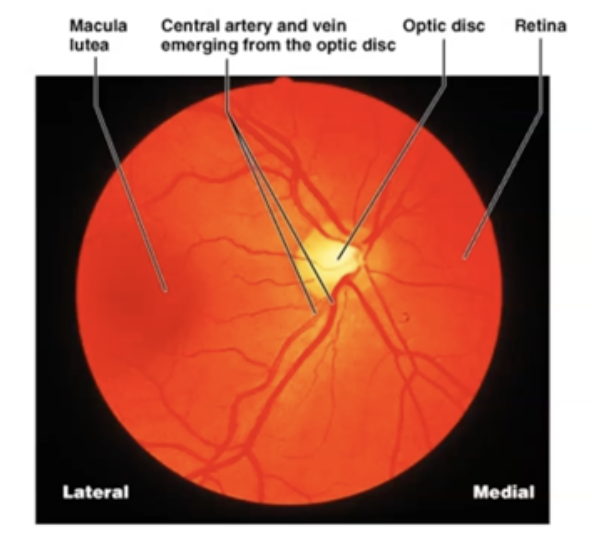
What are the four main parts of Retina?
Macula, Fovea, Optic Disc and Vessels
20
New cards
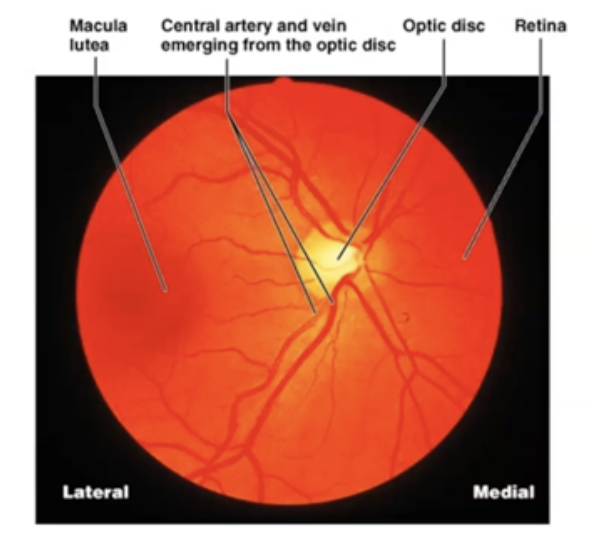
What is Macula
darker spot located at the posterior pole
21
New cards
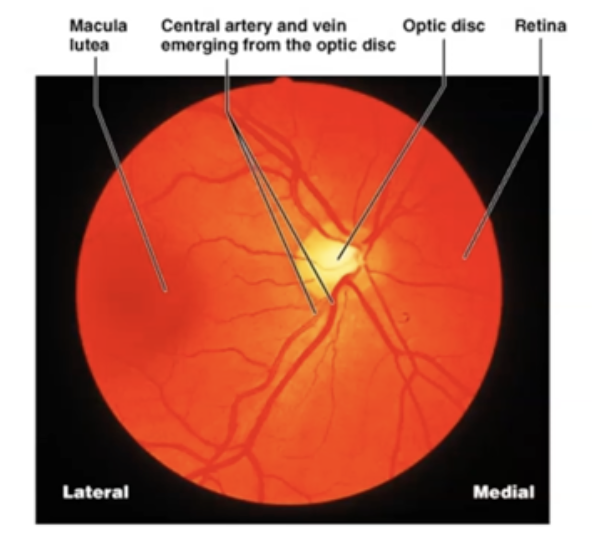
What is Fovea?
Maximal visual acuity (most concentrated cones)
22
New cards
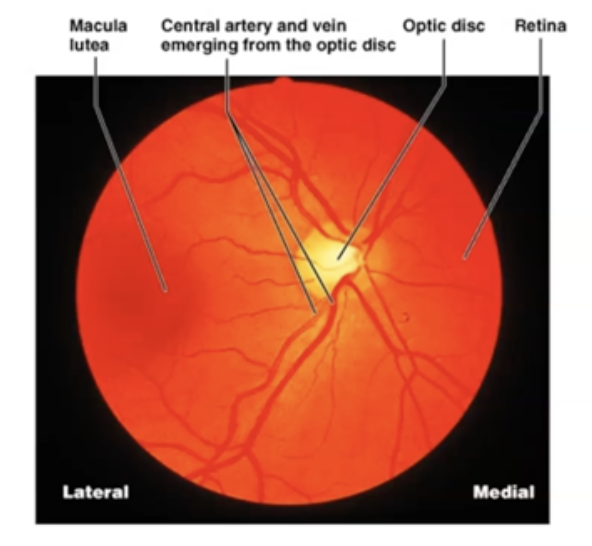
What is Optic Disc?
"Blind Spot" because there are no photoreceptor cells
23
New cards
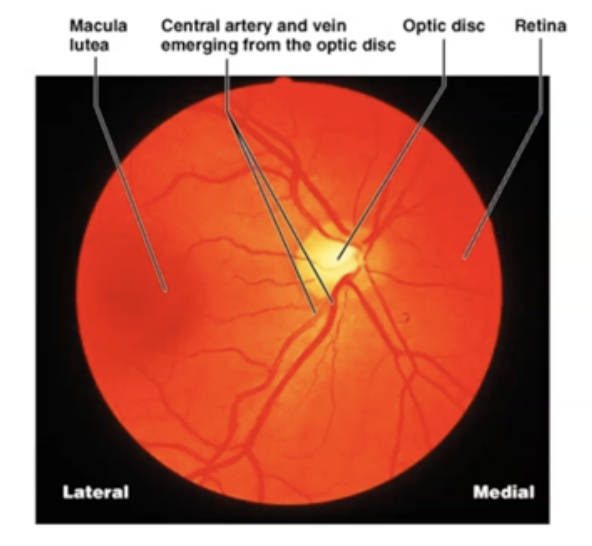
What is the function of vessels in the eye?
Transfer blood
24
New cards
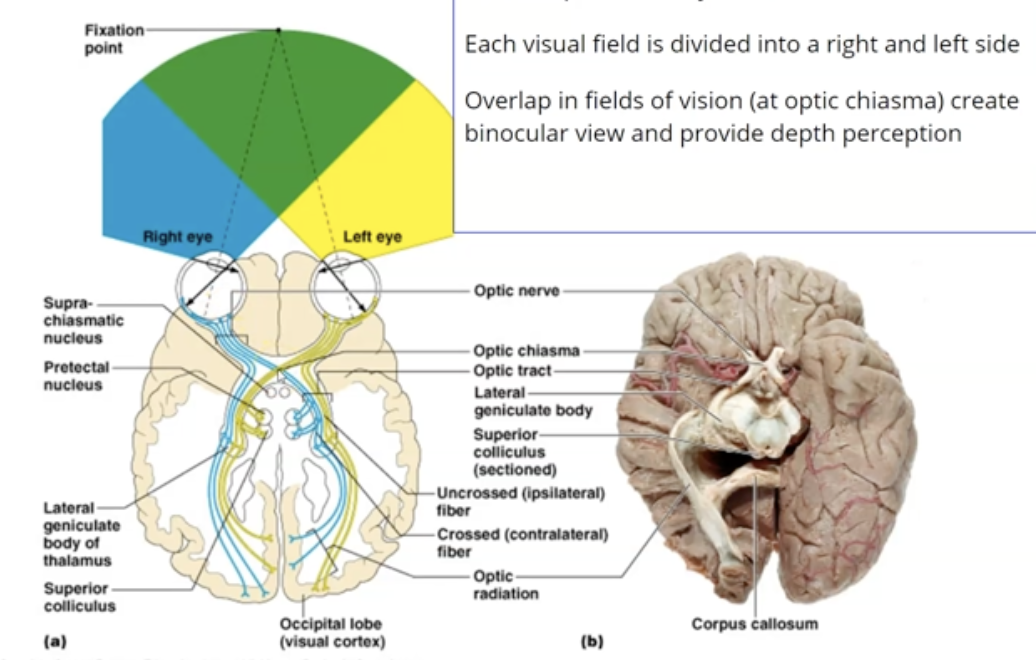
What is Contralateral processing?
Visual information is processed by the opposite side of the brain from which it enters, ex. right field of vision processed by left side of brain
25
New cards
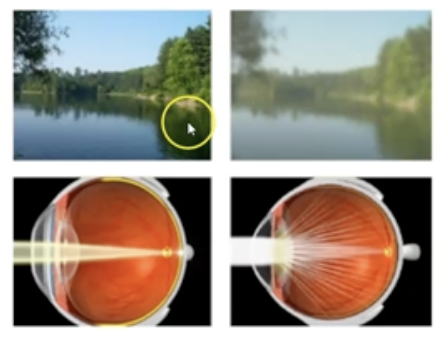
What is cataract?
Clouding of lens due to build-up of proteins.
26
New cards
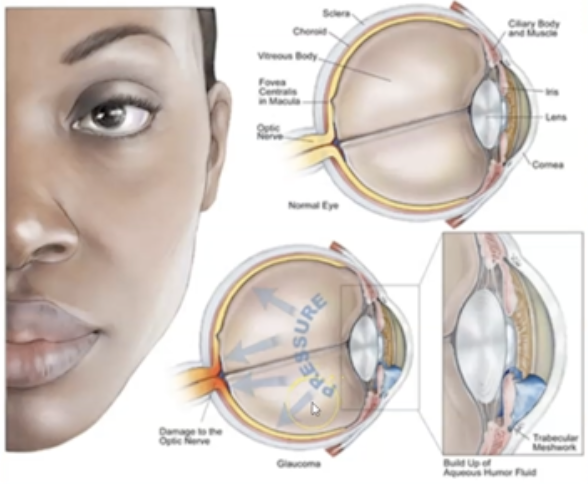
What is Glaucoma?
Occurs when there is a problem with drainage and intracellular pressure increases
27
New cards
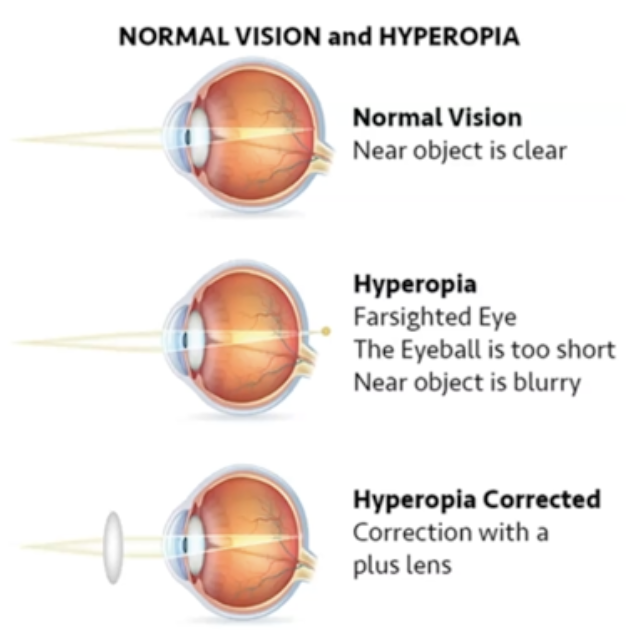
What happens to eyeball when hyperopia occurs?
The eyeball gets short
28
New cards
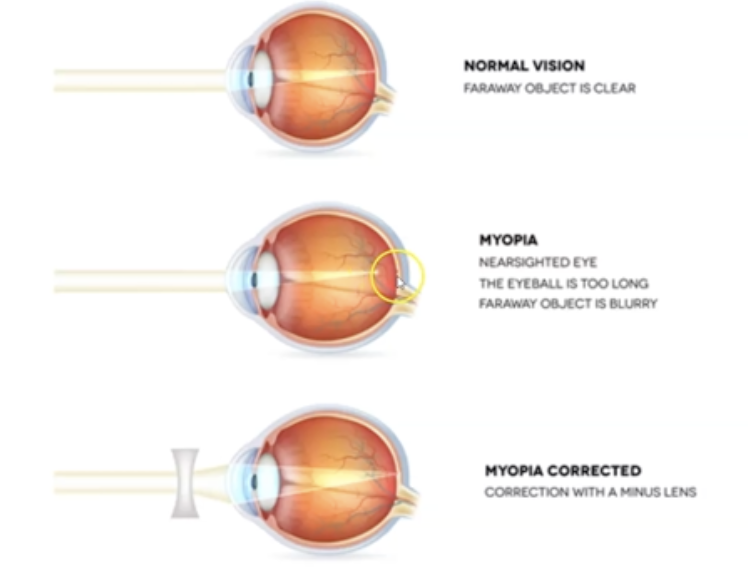
What happens when eyeball when myopia occurs?
The eyeball gets long
29
New cards
What is Viterous?
Gel like material that fills the inside of your eye.
30
New cards
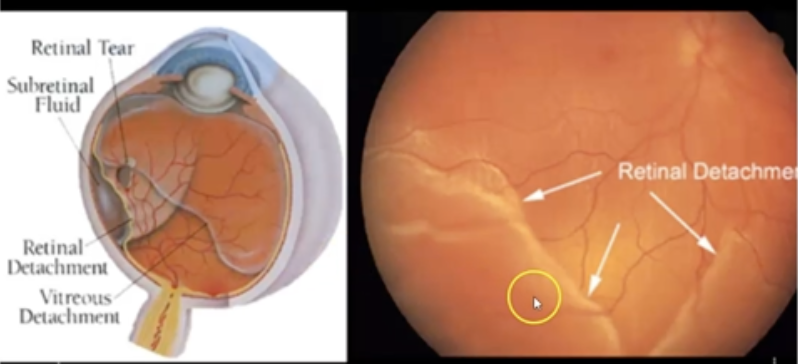
What is Retinal Detachment?
Shrinkage or contraction of the vitreous. Can also be caused by a blow the head or due to diabetes.
This shrinkage can create tugging on the retina and a retinal tear, causing retinal detachment.
This shrinkage can create tugging on the retina and a retinal tear, causing retinal detachment.