IB Biology, ecology
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:54 PM on 10/1/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
1
New cards
Ecology
The science of the relationships between organisms and their environments.

2
New cards
Organism
an individual living thing that uses energy, reproduces, responds, grows, and develops

3
New cards
Species
a group of similar organisms that can breed and produce fertile offspring

4
New cards
Population
group of individuals of the same species that live in the same area at same time

5
New cards
Community
a number of different populations living and interacting in the same area (all the living things in an area)

6
New cards
Ecosystem
a community and its abiotic environment (all the living things in an area interacting with the non-living things)

7
New cards
Autotroph
- also known as a producer
- an organism capable of making its own food from inorganic substances using light or chemical energy.
- eg. Green plants, algae, and certain bacteria
- an organism capable of making its own food from inorganic substances using light or chemical energy.
- eg. Green plants, algae, and certain bacteria

8
New cards
Heterotroph
An organism that obtains organic food molecules by consuming other organisms or substances derived from them.

9
New cards
Carbon cycle
the continuous process by which carbon is exchanged between organisms and the environment
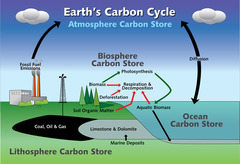
10
New cards
Energy flow
energy from the sun is captured by producers and passed along food chains by consumption and decomposition. Energy is lost at each stage.
11
New cards
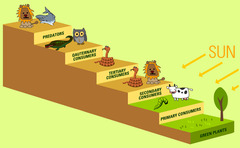
Trophic level
each step in a food chain or food web. producers are at level 1.
12
New cards
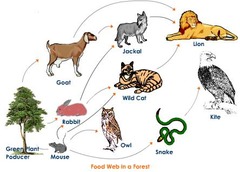
Food web
network of complex interactions formed by the feeding relationships among the various organisms in an ecosystem (all interconnected food chains)
13
New cards
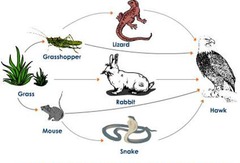
Food chain
shows the transfer of energy along a feeding relationship from producers along the different trophic levels
producer --> primary consumer --> secondary consumer --> tertiary consumer
eg. grass --> cricket --> mouse --> snake
producer --> primary consumer --> secondary consumer --> tertiary consumer
eg. grass --> cricket --> mouse --> snake
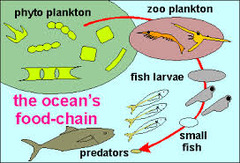
14
New cards
Pyramid of energy
a diagram to show the energy contained in a food chain, web or community
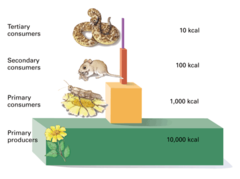
15
New cards
10% Rule
the idea that only 10% of the energy in one trophic level gets passed onto the next trophic level due to losses of heat (respiration), feces, decomposition, etc

16
New cards
Producer
organism that can capture energy from sunlight or chemicals and use it to produce food from inorganic compounds; also called an autotroph

17
New cards
Consumer
organism that relies on other organisms for its energy and food supply; also called a heterotroph

18
New cards
Primary Consumer
Consumer that feeds directly on producers; (animals that feed on plants, algae or phytoplankton)
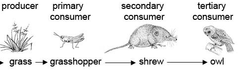
19
New cards
Secondary Consumer
An organism that eats primary consumers; (animals that generally feed on herbivores)

20
New cards
Tertiary Consumer
An organism that eats secondary consumers;
The third trophic level of consumer in a food chain;
A carnivore that eats other carnivores.
The third trophic level of consumer in a food chain;
A carnivore that eats other carnivores.
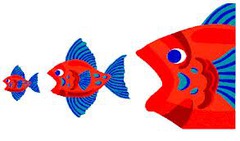
21
New cards
Detritivore
A specific type of heterotroph that eats plant and animal remains and other dead matter (ex. vultures, earthworms, crabs, etc.)

22
New cards
Saprotroph
A specific type of heterotroph that lives on or in non-living organic matter, secreting digestive enzymes into it and absorbing the products of digestion (e.g. mushrooms, bacteria);
= a type of decomposer
= a type of decomposer

23
New cards
Precautionary Principle
The principle that states that when an activity raises threats of harm to human health or to the environment, safety should prevail and control measures should be initiated even if cause-and-effect relationships are not fully established

24
New cards
Detritus
nonliving organic matter; typically includes decaying dead organisms as well as fecal matter

25
New cards
Habitat
the area where an organism lives, including the biotic and abiotic factors that affect it

26
New cards
Limiting factor
factor that is needed for continued population growth - if in short supply it will stop the population growing or cause decline

27
New cards
External factor
any living or nonliving factor that impacts the survival of an organism, population, or community (can be a limiting factor or a non-limiting factor)

28
New cards
Abiotic
non-living
29
New cards
Biotic
living
30
New cards
Greenhouse effect
Natural phenomenon which maintains temperatures required for life to live on Earth where short wave (visible light) radiation from sun is absorbed by the surface of the planet and re-radiated at longer wavelengths which get trapped by gases in the atmosphere

31
New cards
Potential problems associated with climate change
1) ice habitats are melting (destruction of habitats)
2) flooding (destruction of habitats)
3) desertification
4) more extreme weather events
5) species extinction
6) movement of species further north
7) destruction of food webs
2) flooding (destruction of habitats)
3) desertification
4) more extreme weather events
5) species extinction
6) movement of species further north
7) destruction of food webs
32
New cards
Chemoautotrophs
organisms that obtain energy from chemicals to make their own food;
Autotrophic bacteria that derive energy from inorganic sulfur compounds; often live in deep-ocean vents
Autotrophic bacteria that derive energy from inorganic sulfur compounds; often live in deep-ocean vents

33
New cards
Quadrat Sampling
Using a known small area at random to count organisms within that area. The number of organisms within that area can give an approximate estimate of the population of that particular species in a larger area.

34
New cards
(Line) Transect
use string across a place where you collect data, collect the data of whatever passes the string

35
New cards
Plant/animal distribution
The number of a particular organism in an given area (measured using quadrats and represented either as percentage coverage or organisms per squared area)
36
New cards
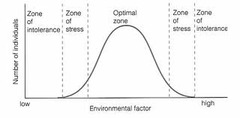
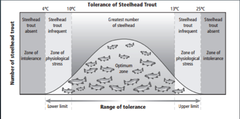
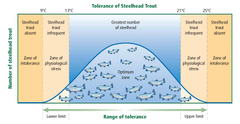
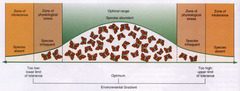
limits of tolerance
The range of a particular environmental factor (e.g. temperature, soil pH, elevation, etc) that an organism can survive within
37
New cards
optimal zone
The optimal range of an environmental factor that an organism survives best in
38
New cards
zone of stress
Within the limits of tolerance but the range where the envirnmental factor means an organism is struggling to survive
39
New cards
zone of intolerance
The range of an environmental factor where an organism is unable to survive (e.g. too hot/cold, too salty, not enough oxygen, etc)
40
New cards
Niche concept
The environmental role that and organism plays within its environment
41
New cards
Fundamental Niche
all of the places a species can live if no competition;
The entire range of resource opportunities an organism is potentially able to occupy within an ecosystem
The entire range of resource opportunities an organism is potentially able to occupy within an ecosystem
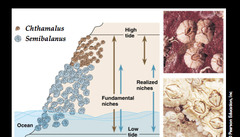
42
New cards
Realised/Applied Niche
the actual areas a species tends to occupy due to competition with other organisms in the same area
43
New cards
Competitive exclusion principle
The idea that two organisms can't occupy the exact same niche due to competition
44
New cards
Keystone species
A species that plays an important role in its environment and helps to maintain the biodiversity of the ecosystem
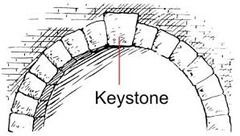
45
New cards
Natality
Birth rate;
increases population size as offspring are added to the population
increases population size as offspring are added to the population
46
New cards
Immigration
Movement of individuals into a population
47
New cards
Emigration
Movement of individuals out of an area.
48
New cards
Mortality
Death rate
49
New cards
Competition
A common demand by two or more organisms upon a limited supply of a resource; for example, food, water, light, space, mates, nesting sites.
50
New cards
Predation
An interaction in which one organism captures and feeds on another organism

51
New cards
Parasitism
A relationship in which one organism lives on or in a host and harms it (+/-)

52
New cards
Mutualism
A relationship between two species in which both species benefit (+/+)

53
New cards
Biomass
-the mass of living biological organisms in a given area or ecosystem at a given time.
-A measure of the total dry mass of organisms within a particular region.
-A measure of the total dry mass of organisms within a particular region.
54
New cards
Biosphere
The area on and around Earth where life exists.

55
New cards
Biome
A group of ecosystems that share similar climates and typical organisms.
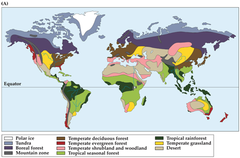
56
New cards
Invasive Species
species that enter new ecosystems and multiply, harming native species and their habitats
57
New cards
Biomagnification
accumulation of pollutants at successive levels of the food chain;
due to inability to excrete pollutants and bioaccumulation
due to inability to excrete pollutants and bioaccumulation
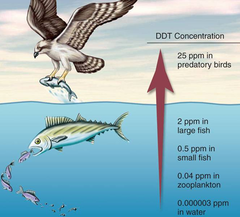
58
New cards
Bioaccumulation
The build up of pollutants in a particular trophic level of a food chain as the pollutants can't be excreted
59
New cards
Primary succession
The series of stages of growth in plant life on newly exposed rock (= bryophata, grasses and small plants, small trees and shrubs, larger trees)
60
New cards
Secondary succession
The series of stages of growth in plant life in an area where the previous ecosystem has been destroyed (e.g. after a fire or clearance for agriculture)
61
New cards
Nutrient cycling
The cyclic systems in which certain elements are exchanged between the biotic and abiotic realms. e.g Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus cycles.
62
New cards
Microplastics
Tiny pieces of plastic that can cause damage to zooplankton and other small aquatic creatures
63
New cards
Macroplastics
Larger pieces of plastic debris that causes problems for large fish and seabirds through ingestion and even strangulation.
64
New cards
Closed systems
Systems where energy can be exchanged but matter can not - e.g. mesocosms
65
New cards
DDT
A pesticide used to kill mosquitoes to control malaria - a good example of the problems caused by biomagnification
66
New cards
Biotic index
A measure of the relative abundance of indicator species to compare pollution or damage to an environment
67
New cards
Biodiversity
The richness, variety and abundance of species in a given ecosystem or habitat
68
New cards
Simpson's diversity index
A way to estimate biodiversity by looking at the relative abundance of species in a given area
69
New cards
Nature reserves
Protected areas of land where building, poaching and and farming are restricted. Usually run by government agencies.
70
New cards
In situ conservation
Protection of species through efforts within the natural habitat of that species
71
New cards
Ex situ conservation
Protecting species away from their natural habitat (e.g. introduction to new areas or zoo breeding programs)
72
New cards
The corridor effect
Pockets of forest or nature reserves will not support biodiversity well unless there are corridors (areas of natural land) connecting them.
73
New cards
The edge effect
Biodiversity is likely to be poorer on the outskirts of nature reserves as the organisms are more prone to influences from outside, e.g. poachers, pollution, etc
74
New cards
transpiration
the emission of water vapor from the leaves of plants