Neurones
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Structure of a neurone
- Cell body
- Dendron
- Axons
Cell body
- Nucleus
- Large amounts of endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria which are involved in the production of neurotransmitters
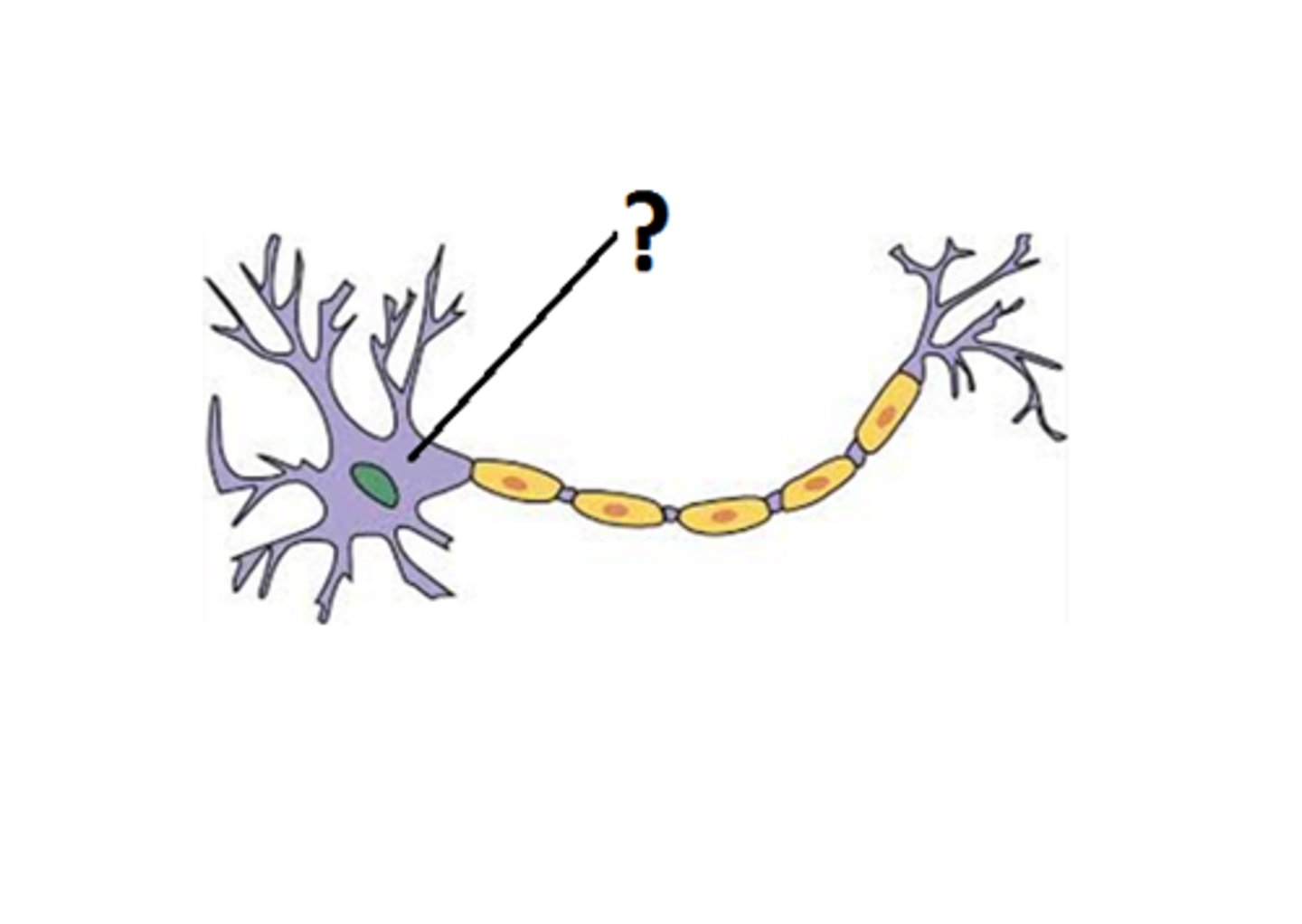
Dendrons
Short extensions which come from the cell body.
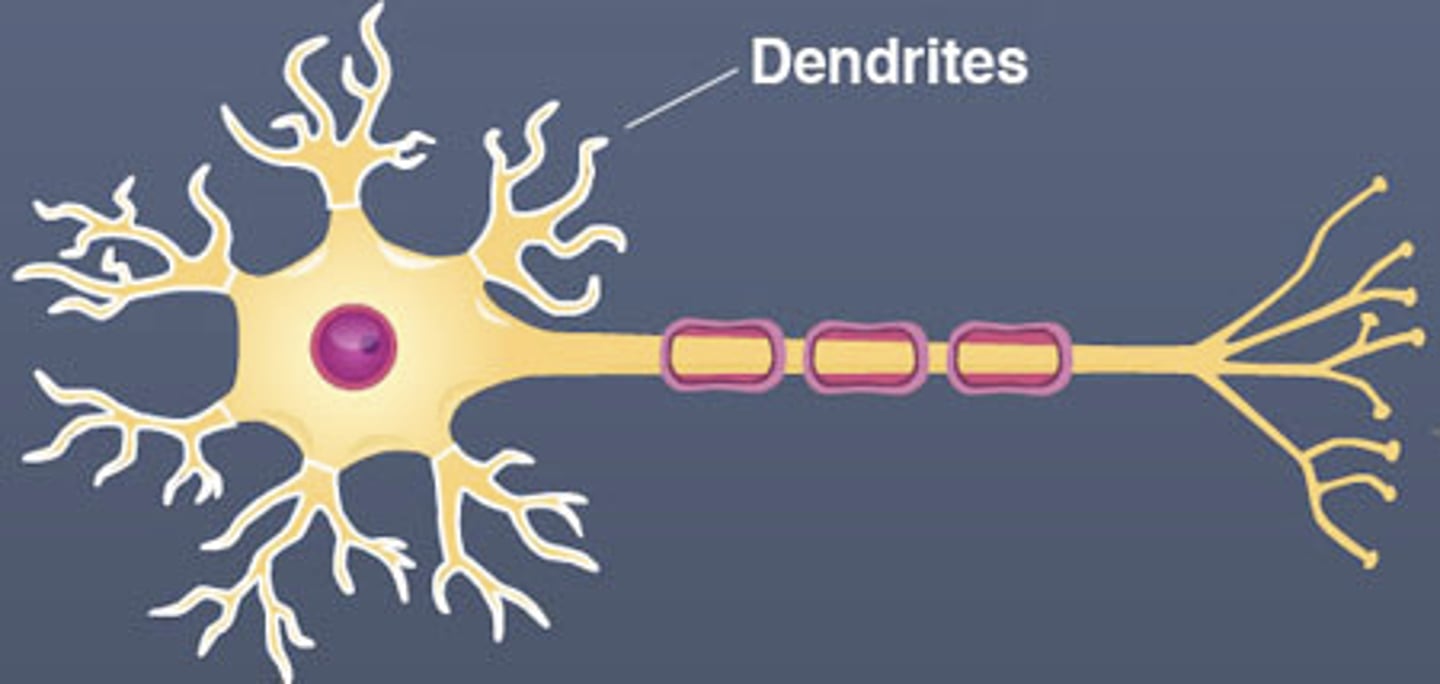
Dendrites
Dendrons divide into smaller branches, known as dendrites.
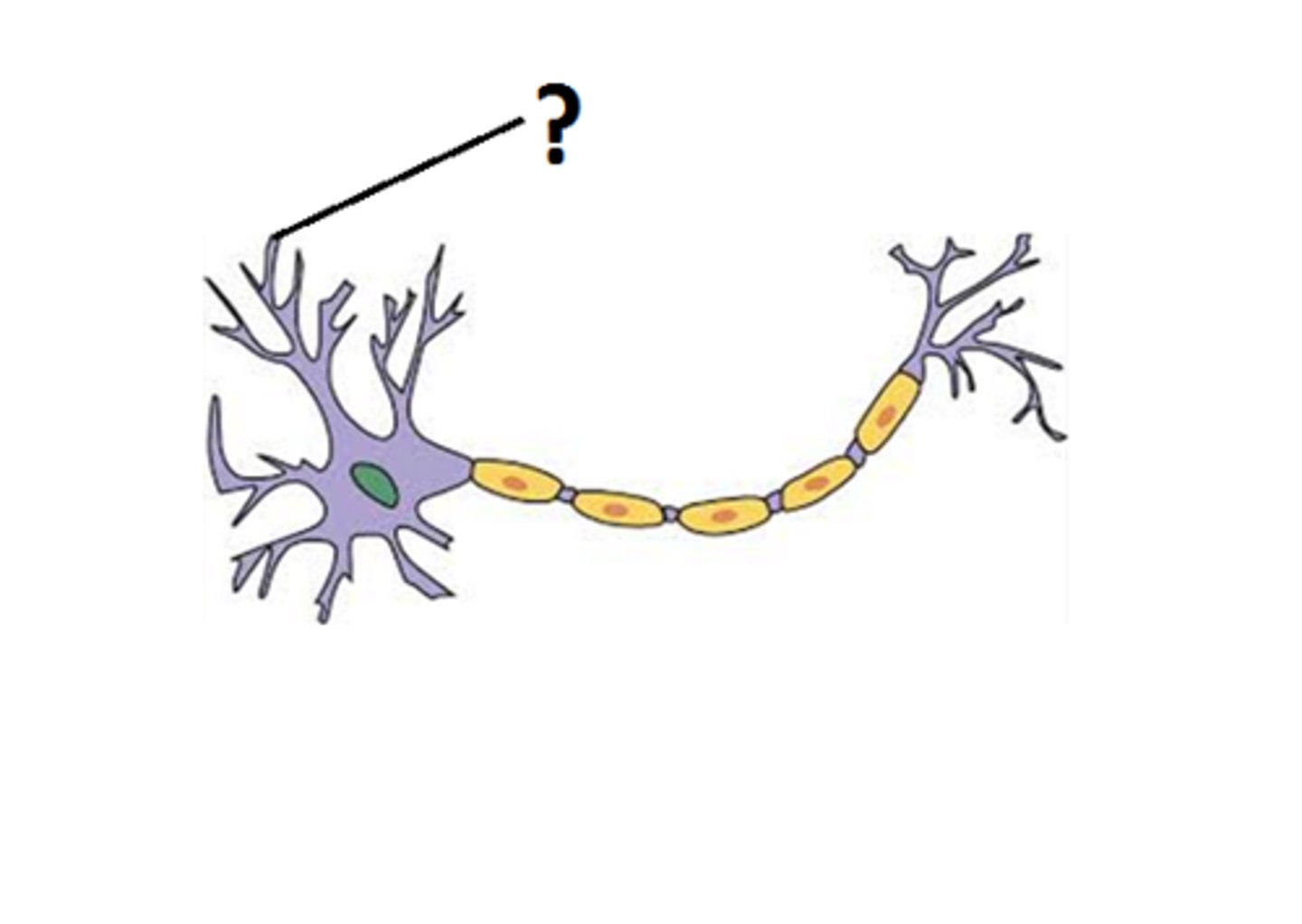
What are dendrites responsible for?
Transmitting electrical impulses towards the cell body.
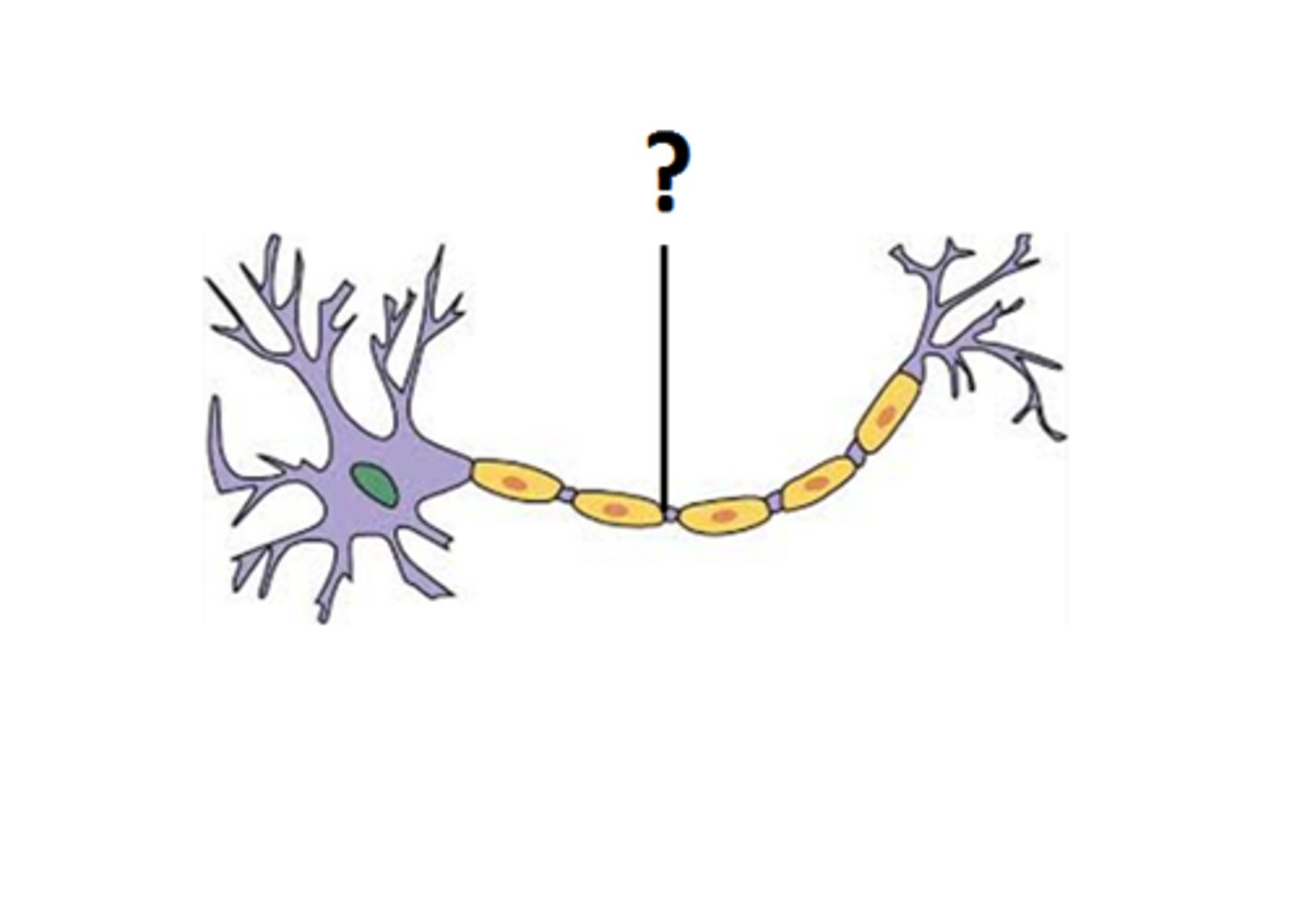
Axons
Singular, elongated nerve fibres that transmit impulses away from the cell body.
Name the different types of neurones
- Sensory neurones
- Relay neurones
- Motor neurones
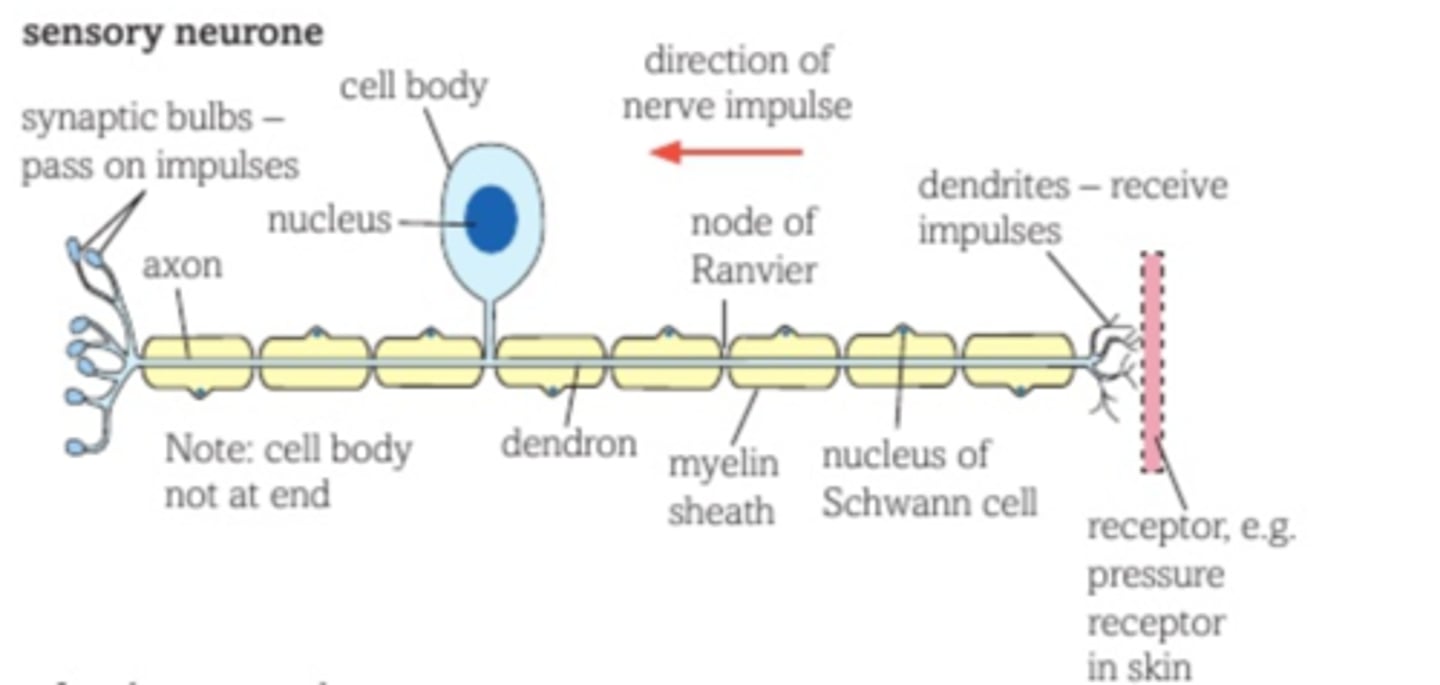
Sensory neurone
Transmits impulses from a sensory receptor cell to a relay neurone, motor neurone, or the brain.
- Dendron present and links to the body cell
- Cell body in the middle of the neurone
- It is not in the CNS
- Dendrites don't connect to the cell body
- Axon is shorter than the motor neurone
- Neurone connects to the sensory receptor
Relay neurone
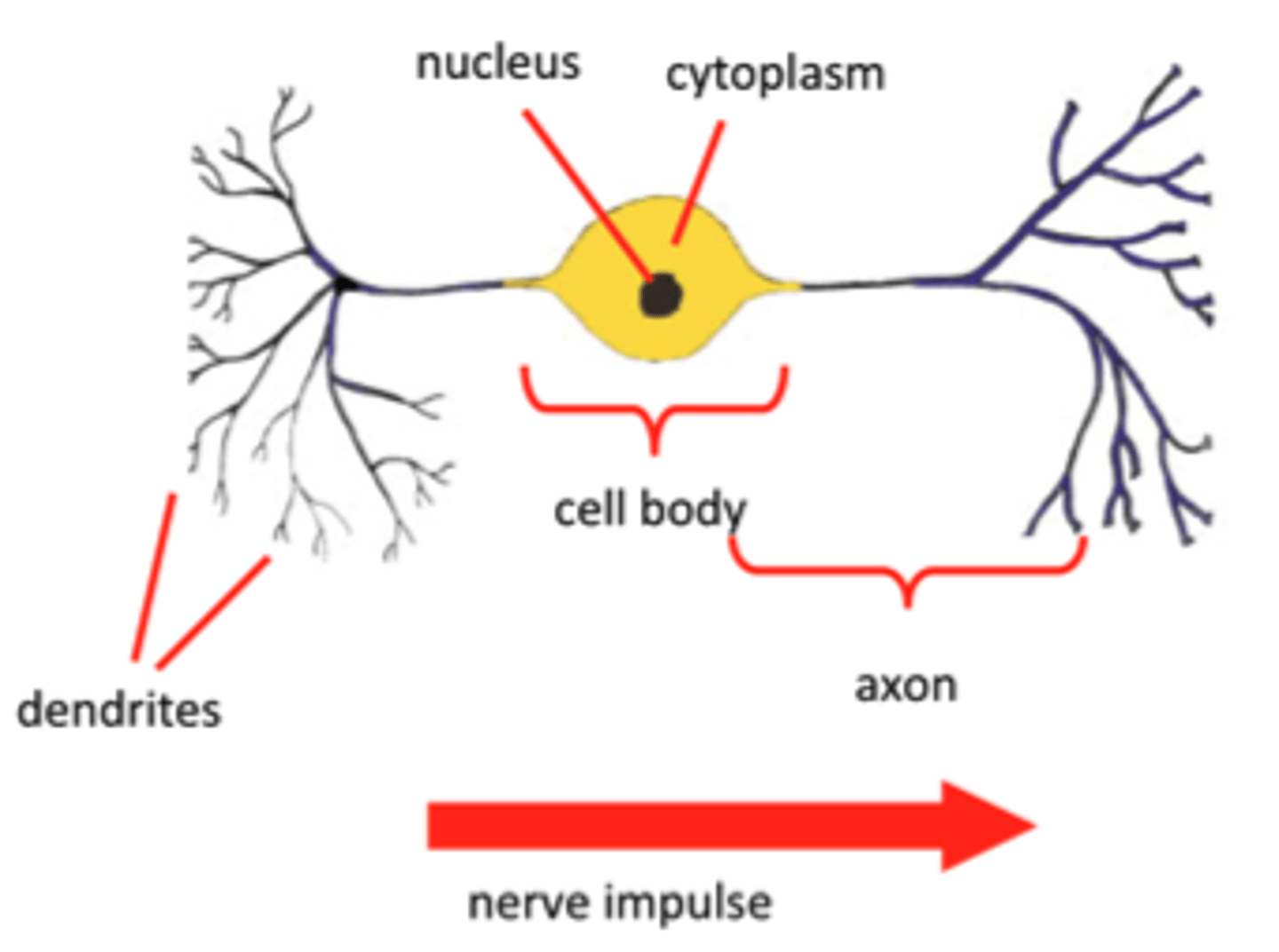
Transmits impulses between neurones.
- Short axon
- Dendrites present
- Found in CNS
Motor neurone
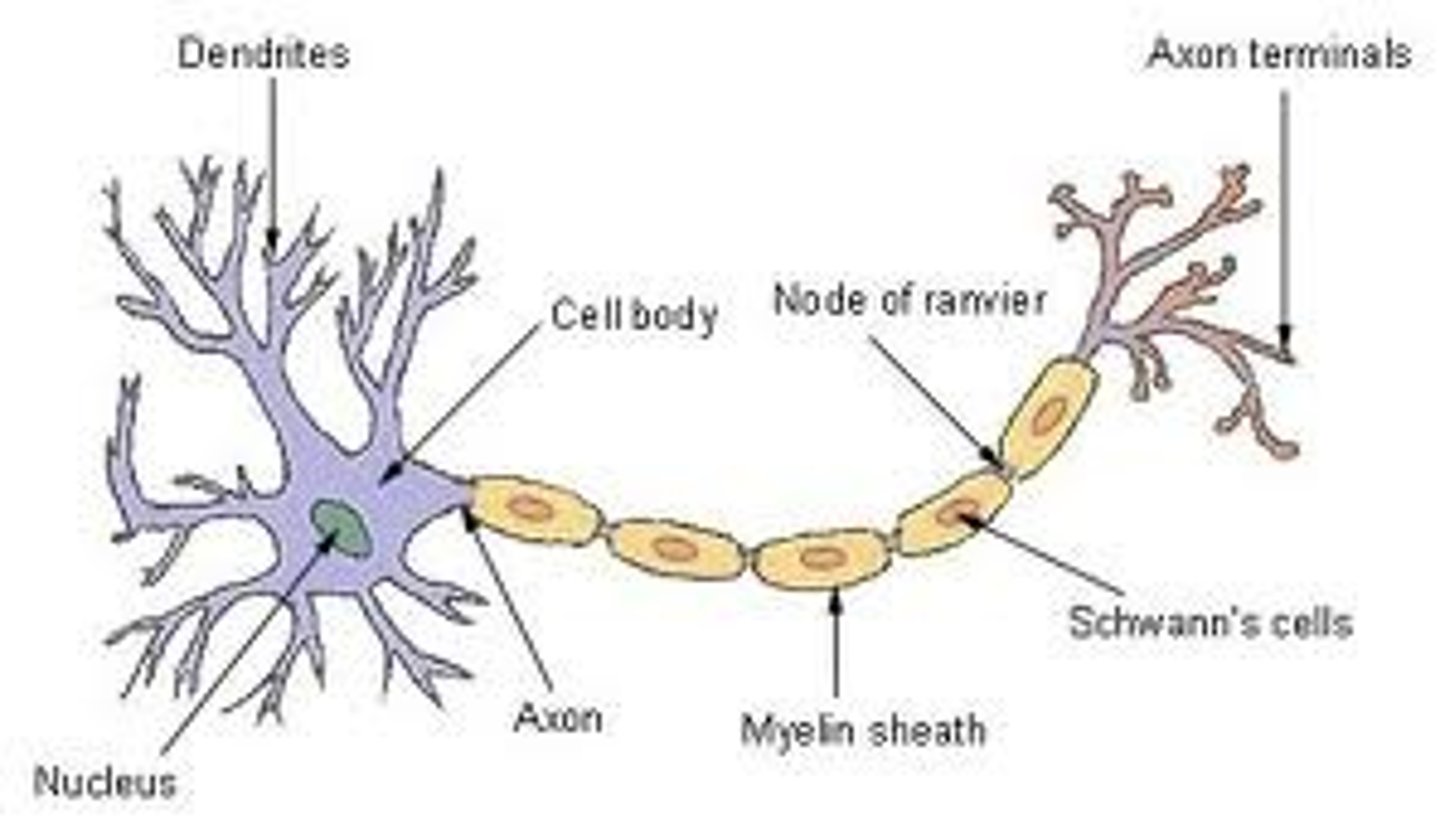
- No dendrons
- Cell body is at the end of the neurone
- In the CNS
- Dendrites are directly connected to the cell body
- Axon is longer than the sensory neurone
- Neurone ends at the motor end plate
Electrical impulse follows what pathway?
Receptor → sensory neurone → relay neurone → motor neurone → effector cell