Everything
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
what is the process of cell division in prokaryotes called
binary fission
The phases of Interphase are?
G1
S
G2
how many chromosomes are in the Interphases
G1 - 10
S - 0
G2 - 20
when does these things happen:\
intact nucleus
duplication of chromosomes
centrioles are copied
Interphase
DNA is copied where
the S part of Interphase
when does these things happen:
nuclear membrane pops
chromosomes coil up
spindle forms
Prophase
when does these things happen:
chromosomes line up at the equator
attach to the spindle fibers
Metaphase
when does these things happen:
spindle fibers pulls the chromosomes away from each other
Anaphase
when does these things happen:
2 nuceli are re-formed
spindle fibers breaks down
chromosomes uncoils
cytokensis begins
Telophase
the difference of mitosis in plant and animals cells?
plants - forms a cell plate
animals - cell membrane pinches inwards
where is the centromere located
where the chromosomes copies are joined
what is the kinetochore and what is it connected to?
a bean shaped protein; connected to the centromere
what is the kinetochore fibers and what can it attached to?
are thin protein fibers; attach to spindle (like a handle)
Explain how ATP is created?
H+ is pumped into the IM space from the matrix then pumps back into the matrix by ATP synthase
Energy from NADH & FADH2 is shifted into what?
ATP
what is the final acceptor
O2
what is produced in the ET?
H2O (water)
Why do we breathe
so ET can happen, and if you dont then the ET can get trapped leading to us dying
without O2 in fermentation, what happens?
aerobic respiration stops
what does pyruvic acid converts into for fermentation?
latic acid - in mammals
ethanol or CO2 - in bacteria & yeast
Fermentation is the only option for what?
bacteria
What is the purpose of cellaur respiration
to make energy (ATP)
1 NADH equivalent too:
3 ATP
1 FADH2 equivalent too:
2 ATP
what are the low energy levels of
ATP
NADH
FADH2
ADP
NAD+
FAD+
Glycolysis located in the
cytoplasm
how many ATP does Glycolysis needs to start and how many does it release?
needs 2 ATP; releases 4
Glycolysis turns ? into ?
glucose into 2 pyruvic acids
Intermediate step turns ? into ?
2 pyruvic acid into 2 acetyl- CoA
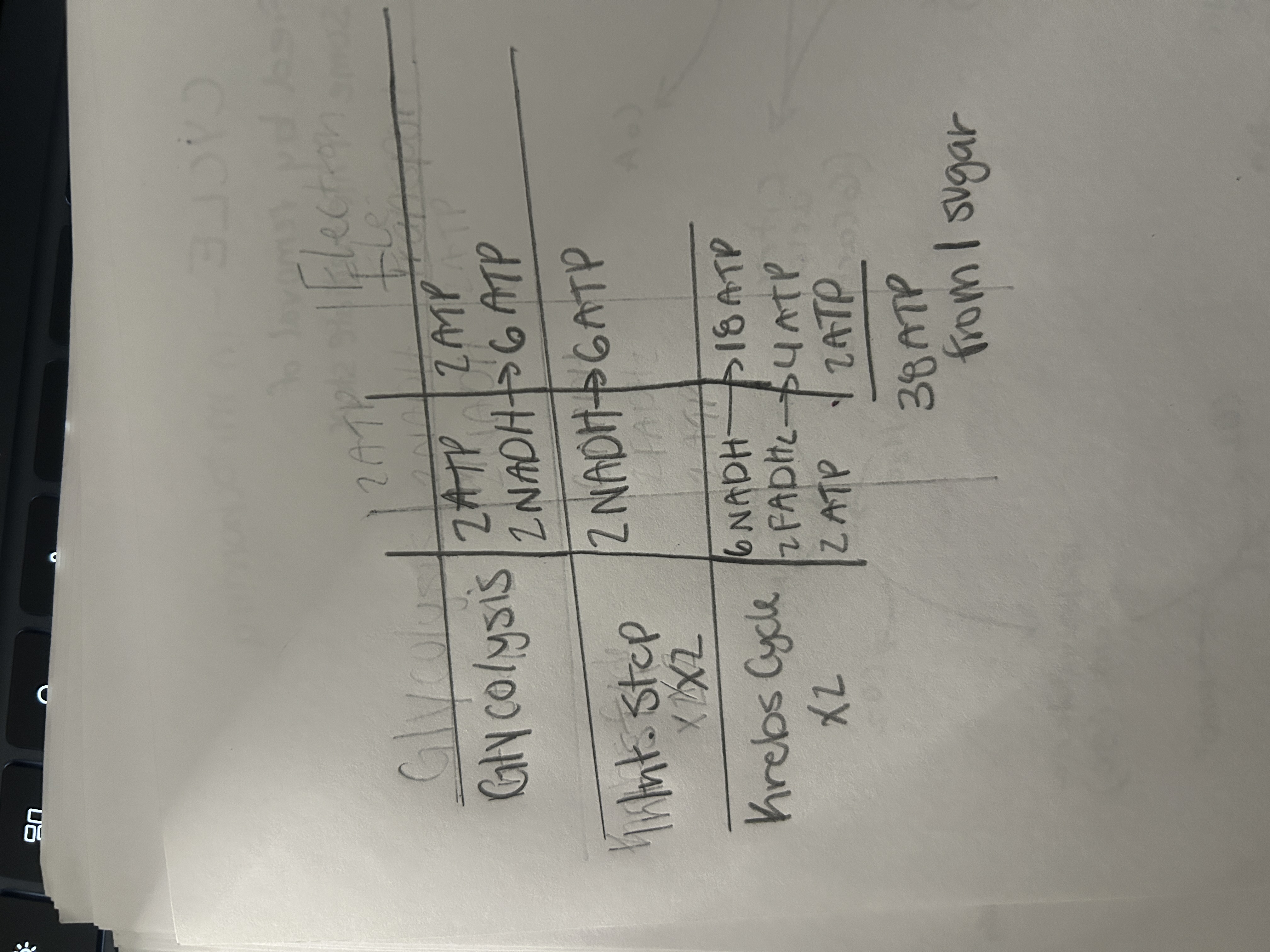
1 Krebs Cycle prodcues
3 NADH
2 CO2
1 FADH2
1 ATP
how is energy released in the Krebs Cycle
breakage of C-C bonds
molecule is rearranged to a more stable form
how many ATP’s are created
38
Memorize