AP HUG U7 review
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Almost there!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Cottage industry
A small scale business usually operated out of a persons home. A modern day example would be etsy stores
Primary sector
Involves extracting natural resources from the Earth (Ex. farming, coal mining, logging)
Secondary sector
Takes raw resources to produce or manufacture products of greater value. (Ex. textile industry)
Tertiary sector
Provides a service for others (Ex. laywers, doctors, etc.)
Quaternary sector
Revolves around acquiring, processing and sharing information (ex. teachers, journalists)
Quinary sector
Revolve around decision making (ex. CEOs of businesses, gov officials)
Break-of-bulk point
A location where goods are transferred from one mode of transportation to another (ex. airports/ports)
Bulk-gaining product
Becomes heavier after they are produced, making them more expensive to transport and locate themselves closer to the market
Bulk-reducing product
Become lighter and easier to transport, allowing industries to locate themselves near heavier raw resources and farther away from the market
GDP
Gross domestic product: the total value of all goods and services produced within a country over a specific period of time
GNP
Gross national product: the total economic output produced by a country’s residents and businesses, regardless of their location
GNI
Gross national income: the total amount of income generated both domestically and abroad
GNI per capita
Gross national income per capita: measures the standard of living of a population by giving an estimate of the average income earned
GII
Gender inequality index: measures health, education and economic participation
Closer to 0 shows less inequalities
HDI
Human development index: measures social and economically, analyzing life expectancy, years of schooling and GNI
Closer to 1 shows a more developed country
Microfinancing
Financial services for people who lack access to traditional banking services
Traditional society (RMD)
Relies on subsistence agriculture, mostly in the primary sector
Preconditions for takeoff (RMD)
Society sees a demand from outside states for raw materials, changing the economic climate. New opportunities and a shift from the primary to secondary sector
Takeoff (RMD)
Urbanization as the secondary sector begins to take off. New technology as well as selling resources to the world market
Drive to maturity (RMD)
More specialization, global trade and a diverse economy. More jobs in the tertiary sector.
Age of mass consumption (RMD)
Beyond serving basic needs. Most jobs are in the tertiary sector and outside states have less influence
Dependency theory
A theory that suggests economically developing countries are dependent on developed countries for their economic growth
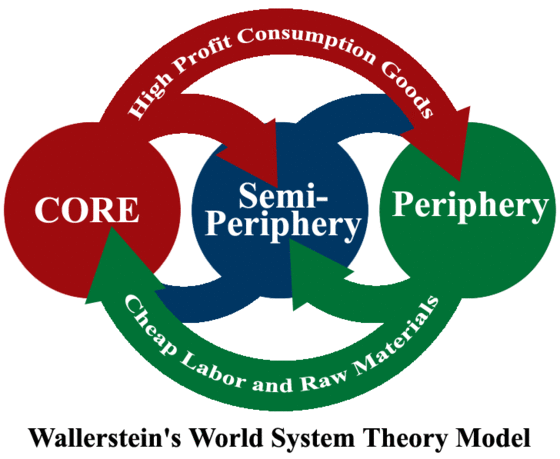
Wallerstein’s world systems theory
Core countries purchase consumption goods from the semi/periphery countries. Periphery countries provide cheap labor and raw materials for the core/semi periphery countries
Complementarity index
A measure used to assess the compatibility between the products and services that two countries produce and trade with each other.
A higher number indicates they should trade with each other
Neoliberalism
Emphasizes individual freedom, free markets and free trade over control
Special economic zone
Regions within a country that provide different economic incentives with the objective of attracting foreign investment and economic growth
Free-trade zone
A region within a country where imported goods can be stored and processed without being subject to tariffs/barriers
Export processing zone
Offers special economic regulations/incentives to promote the production of goods/services for export
Multiplier effect
An original investment in something leads to a chain reaction of spending and increased economic activity
Offshoring
Relocating a business process or service to a foreign country
Outsourcing
When a business contracts a service or job to an external provider
Agglomeration
Clustering of different economic activities/industries in an area
Growth poles
Specific regions, cities or economic sectors that are considered centers of economic growth and development
Ecotourism
Tourism focused on responsible travel to natural areas that conserve the environment and improve the well being of the local people
Comparative advantage
the ability of a country to produce a good or service at a lower opportunity cost than others
Entrepot
a port, city or trading post
Gender parity
ensuring that both genders have equal opportunities
Absolute advantage
when a country has absolute advantage over international trade than any others