Unit 3 Psychology QCE
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
CNS
Brain and Spinal Cord
PNS
Somatic and Autonomic Nervous System
Somatic Nervous System
Carries messages from sensory receptors to CNS
Autonomic Nervous System
sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system
sympathetic nervous system
fight or flight
parasympathetic nervous system
rest and digest
spinal cord
connects brain and PNS
spinal reflex
involuntary response to stimuli without brain (reflex arc)
cerebral cortex
frontal, occipital, parietal, and temporal lobes
Broca's area
speech production
Wernicke's area
language comprehension
Broca's aphasia
non-fluent speech
Wernicke's aphasia
speech makes no sense
Geschwind's territory
connects Broca's and Wernicke's areas
Voluntary movement
coordinated from primary motor cortex, cerebellum, basal ganglis
emotions
limbic system, amygdala and prefrontal cortex
excitatory neurotransmitters
excites postsynaptic neurons into firing
inhibitory neurotransmitters
inhibits postsynaptic neurons from firing
Acetylcholine
Excitatory neurotransmitter that activates muscle contractions
epinephrine
adrenaline hormone responsible for flight or fight
Norepinephrine
cancels adrenaline and calms body
dopamine
carries messages between neurons to ensure initiation and maitenance of movements
Serotonin
regulates mood, memory, and sleep
Parkinson's disease
CNS disorder caused by lower levels of dopamine
Alzheimer's disease
Characterised by gradual widespread degeneration of brain neurons causing memory and cognitive decline
Visual reception
enables sensation and perception of external light stimuli
visual transduction
conversion of light to neural signals by visual receptors
Visual Transmission
sending sensory information to relavent areas of the brain
visual selection
feature detectors
visual perception process
stimulus, reception, transduction, transmission, interpretation
Visual perception principles
depth and visual cues
biological influences on vision
Ageing, genetics
perceptual set
past experience context
Hudson 1960
cultural evidence indicates importance of past experience on visual perception

Deregowski and Muldrow 1972
Lack of experience with 2D images influences the ability to identidy images
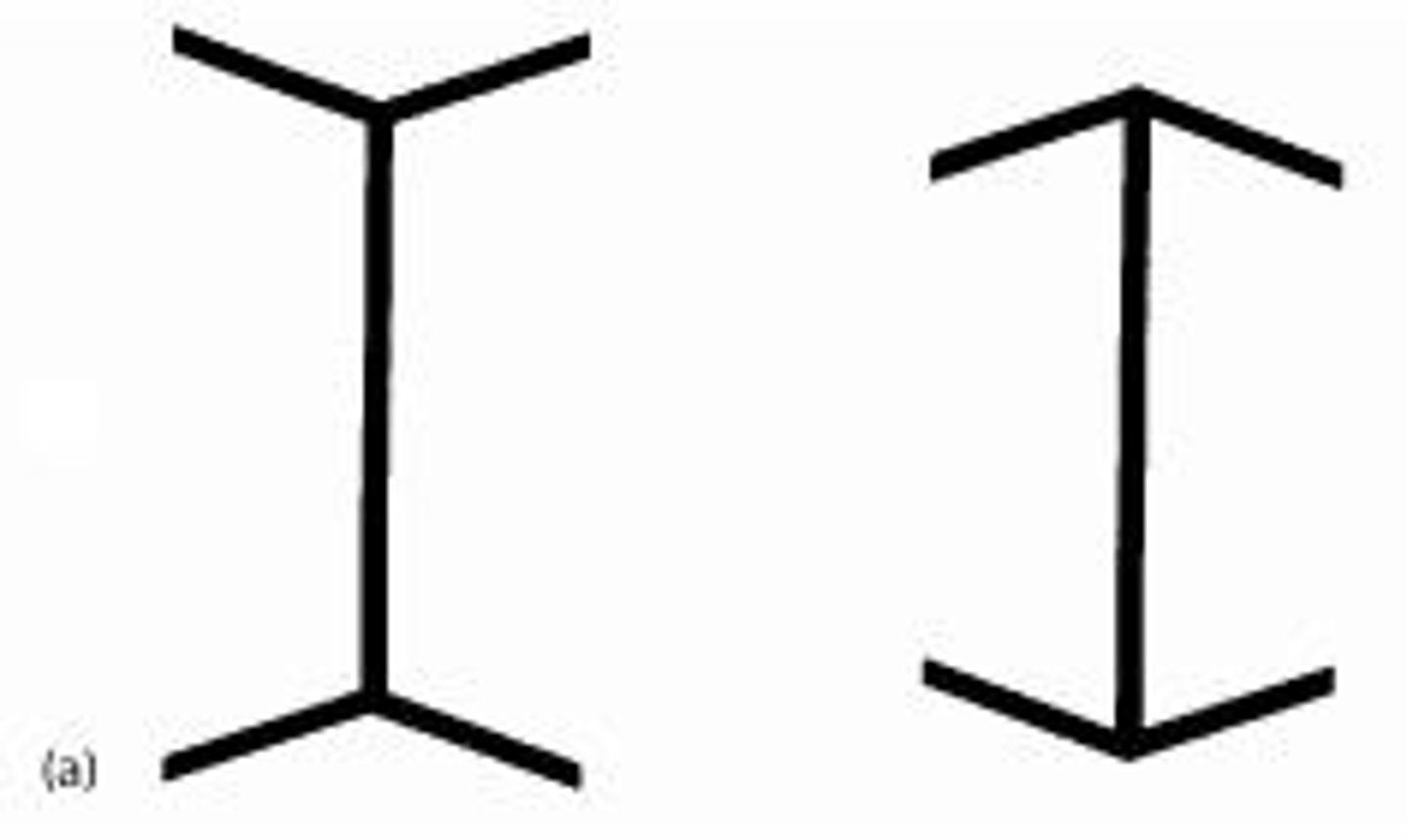
Muller-Lyer
Optical illusion of arrows
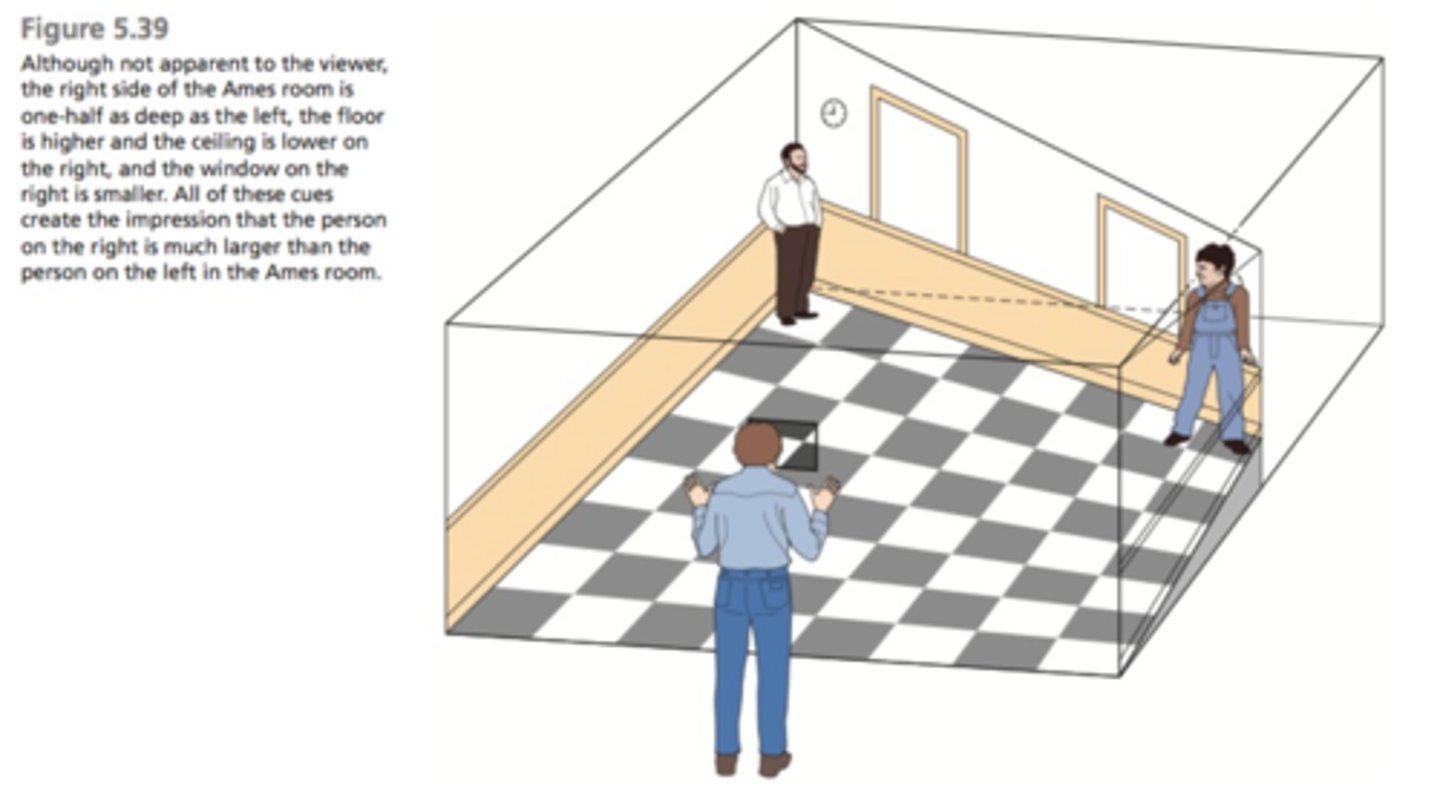
Ames room
optical illusion of a room that uses distoryed sizes
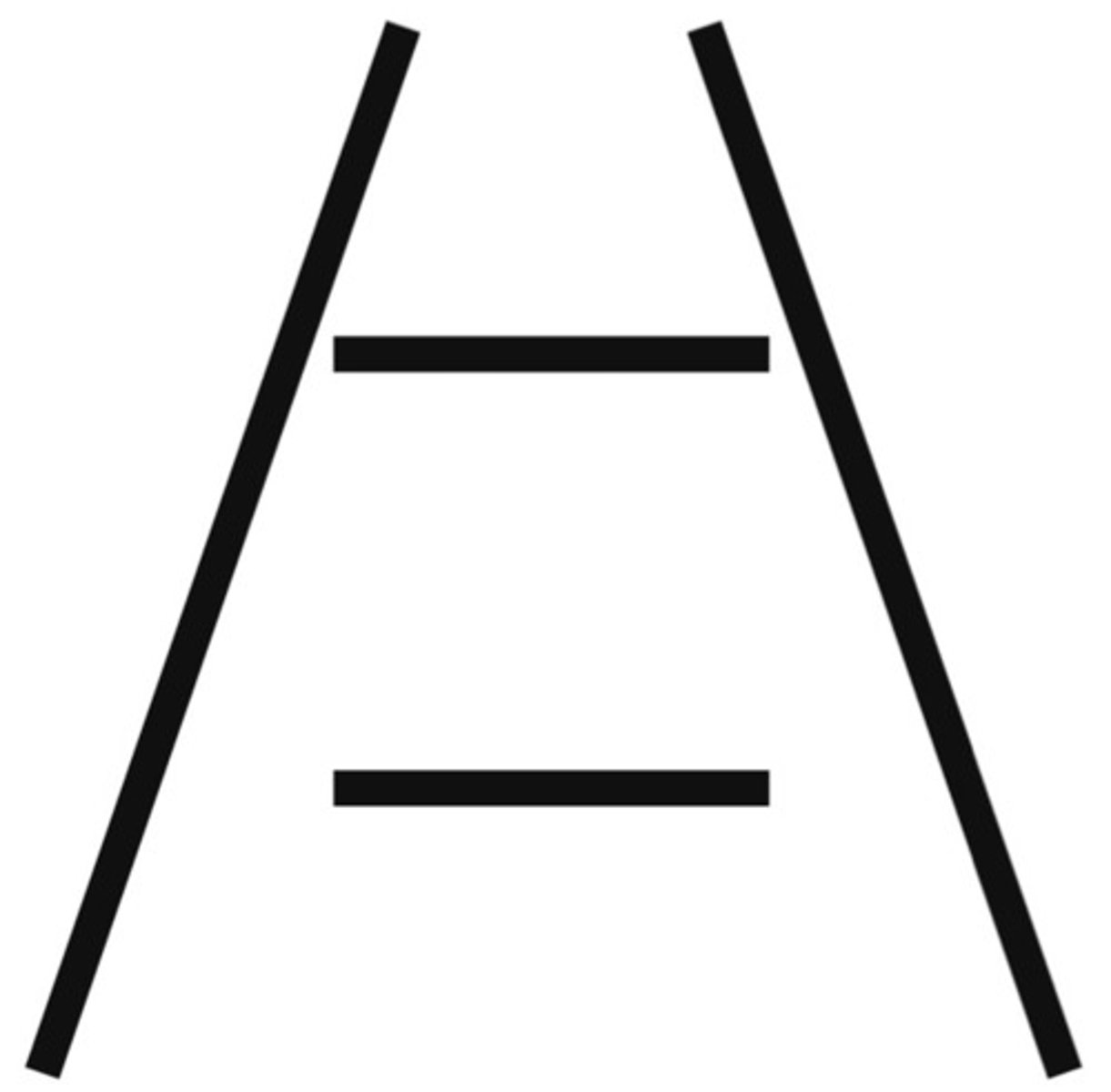
Ponzo Visual illusions
railway tracks that suggest hums will judge object size based on background
Sensory Memory
brief memory retaining impressions only
Short term memory
15-30 seconds with a capacity for 7 items
Long term memory
storage of info over an extended period
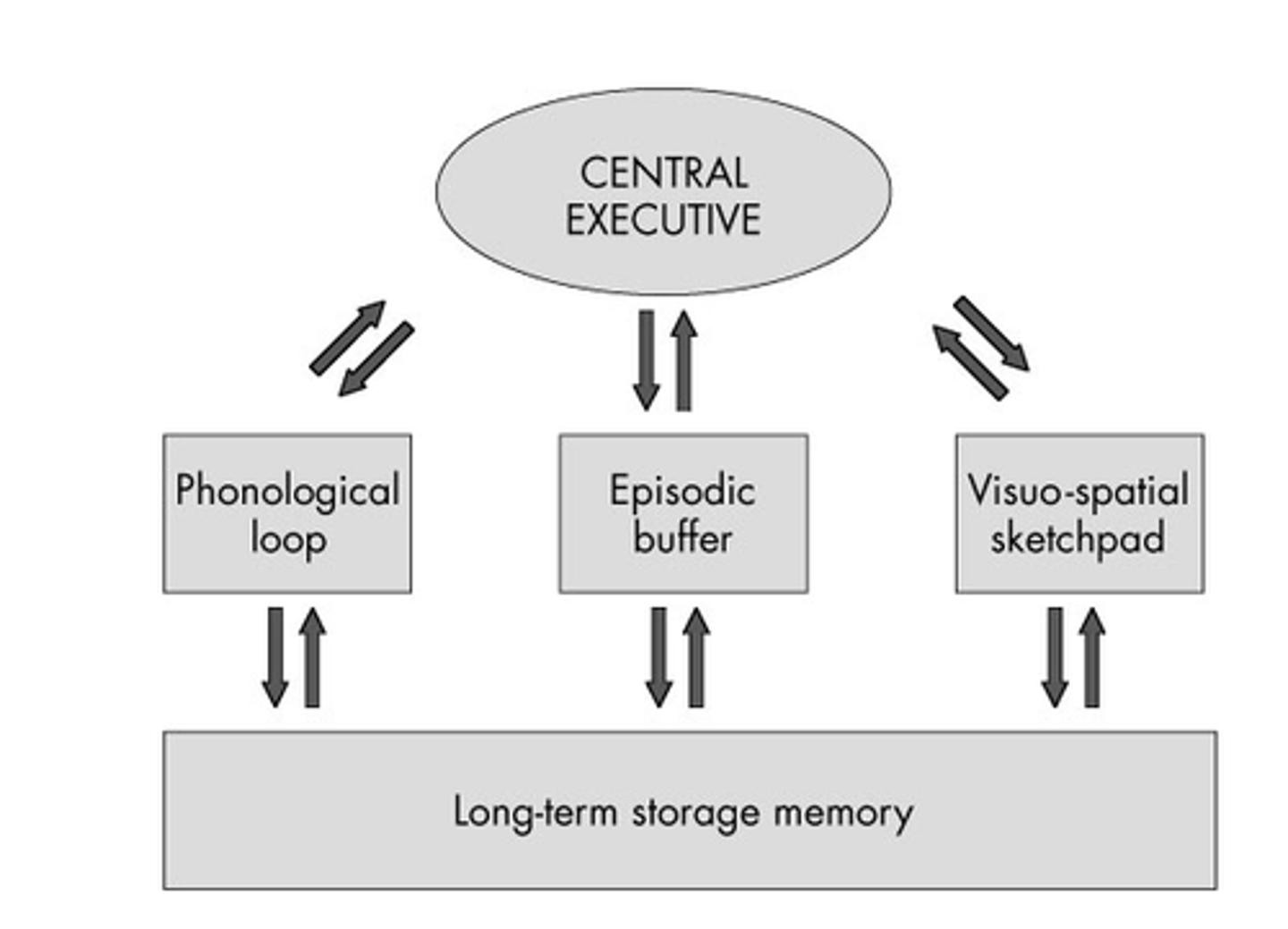
Baddeley and Hitch
Working memory model
LOP Model
Levels of processing memory including long term
implicit memory
procedural memory
explicit memory
episodic and semantic memory
Hippocampus
memory formation and storage
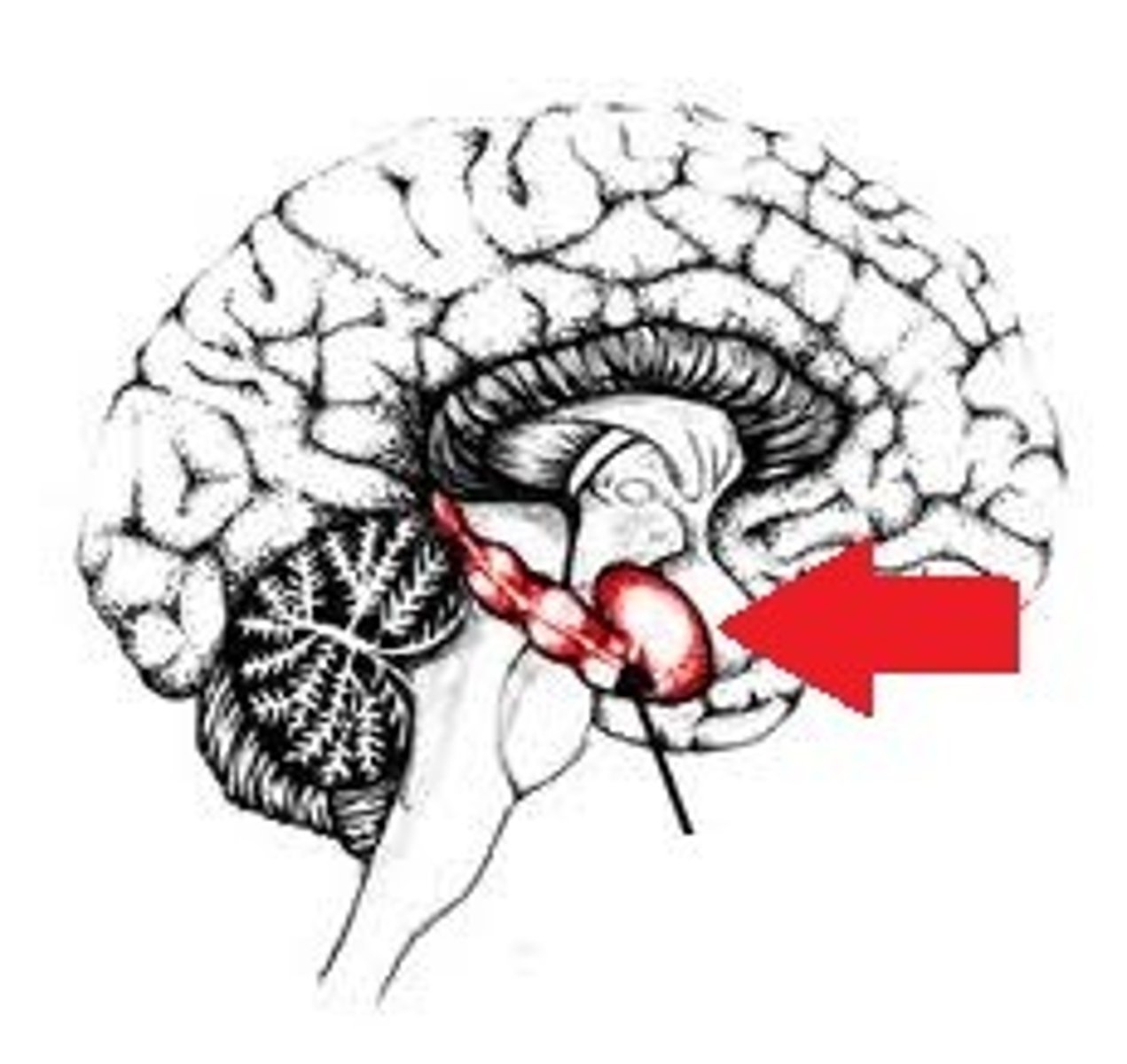
cerebellum
forming and storing implicit memory
chunking
breaking information into smaller sections to learn
rehearsal
maintenance and elaborative memory
Mnemonics
learning technique can be song, rhyme, or phrase
method of loci
mind palace way to store memory
SQ4R
survey, question, read, reflect, recite, and review
Grant et al. 1998
studying and being tested in same condition to improve memory
Classical Conditioning (Pavlov)
2 stimuli are repeatedly paired
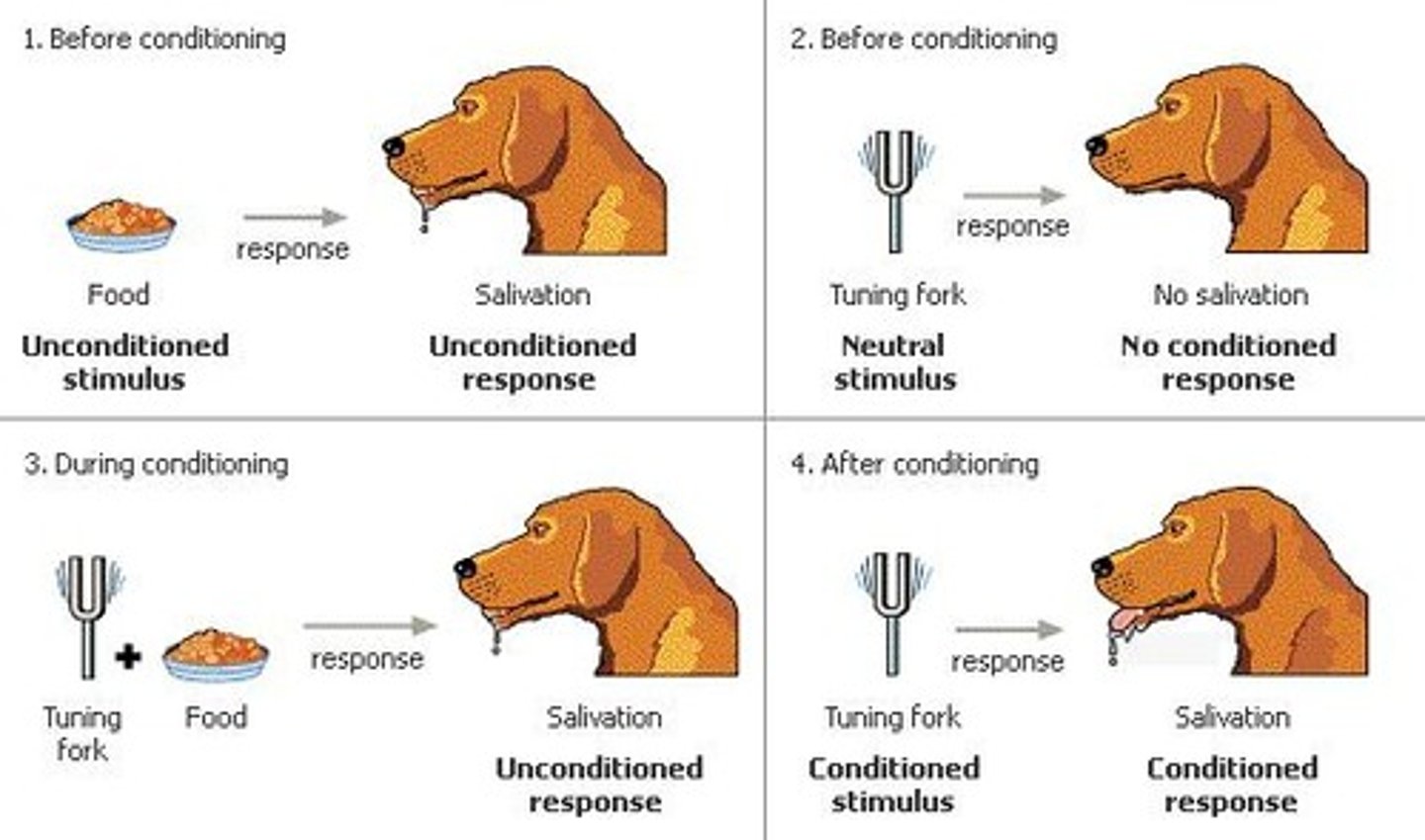
UCS
unconditioned stimulus
UCR
unconditioned response
NS
neutral stimulus
CS
conditioned stimulus
CR
conditioned response
Stimulus Generalisation
When a new stimulus evokes a similar response to another stimulus
Stimulus discrimination
when learnt to only respond to original stimulus
extinction response
response following consistent non-reinforcement of the response
spontaneous recovery
The reappearance of a conditioned response after apparent extinction
Watson and Rayner (1920)
Little Albert fear response to loud noise
positive reinforcement
Increasing behaviors by presenting positive stimuli, such as food.
negative reinforcement
the reinforcement of a response by the removal or avoidance of an unpleasant stimulus (not punishment)
punishment
unpleasant consequence or removal of pleasant consequence following a response
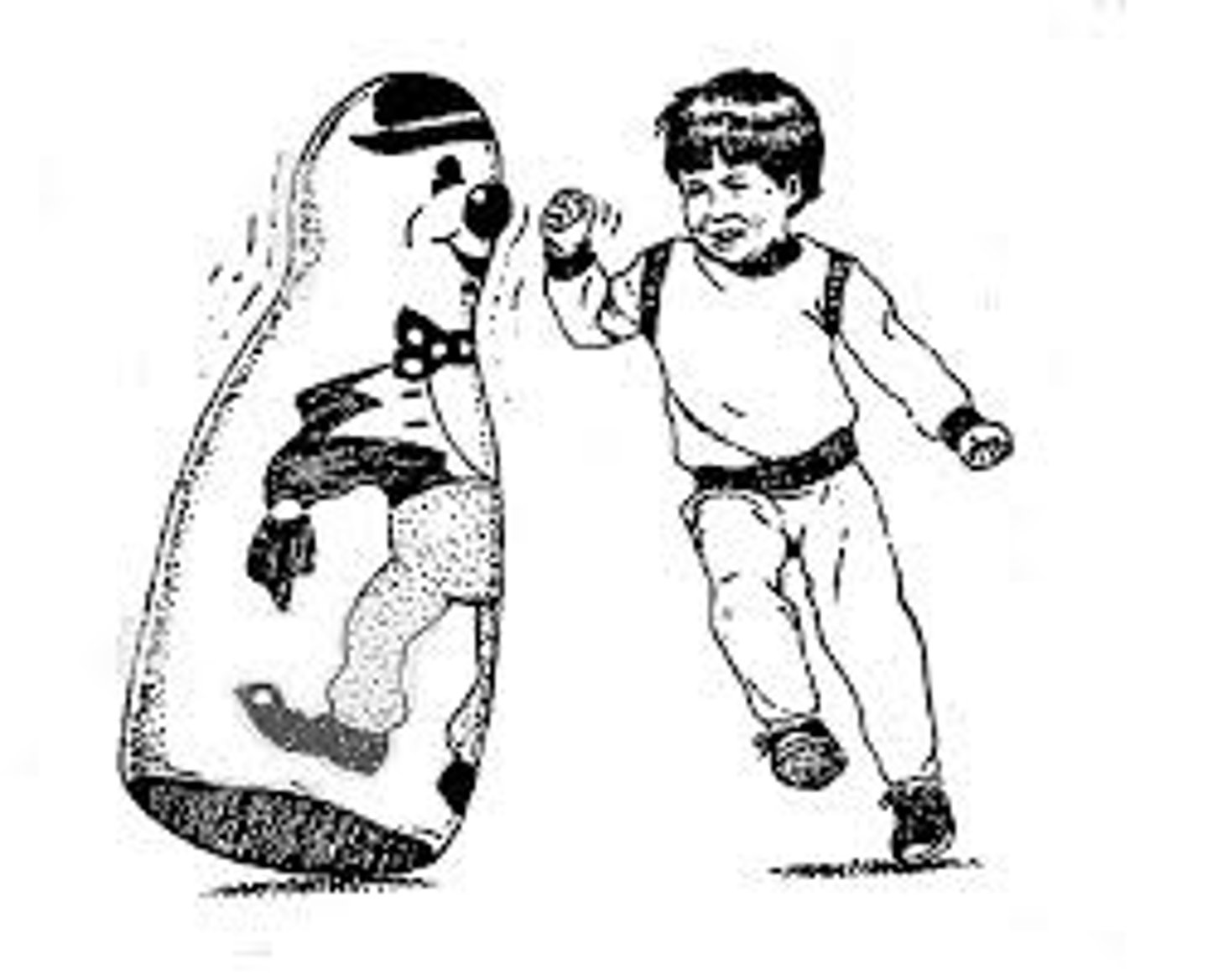
social learning theory
Replication of observed behaviour (Bandura's Bobo doll)

Vicarious conditioning
observing a model's behaviour being rewarded or punished and acting accordingly (e.g., seeing someone eat cake and get stomach pain so you dont eat the cake to avoid stomach pain)