BIO 107: Unit 4 - Ch 16 Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Be sure to enable 'answer with term' in the Practice Test and Learn feature.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
What are sensory receptors?
What are specialized cells that monitor specific conditions in the body or external environment?
What are the general senses?
What type of senses are these:
Temperature
Pain
Touch
Pressure
Vibration
Proprioception
What are the special senses (sense organs)?
What type of senses are these:
Olfaction - smell
Vision - sight
Gustation - taste
Equilibrium - balance
Hearing - sound
What is sensation?
What is the information arriving from the general senses?
What is perception?
What is the conscious awareness of a sensation?
What are free nerve endings?
What are the branching tips of dendrites?
What are tonic receptors?
Which type of receptors:
Are always active
What are phasic receptors?
Which type of receptors:
Are normally inactive
Become active for a short time whenever a change occurs
What does adaptation reduce?
What is the reduction in sensitivity of a constant stimulus?
What are fast-adapting receptors?
Which adapting receptor type:
Response characteristic of phasic receptors
What are slow-adapting receptors?
Which adapting receptor type:
(Tonic) show little peripheral adaptation
Remind you of an injury long after
What are nociceptors of general sensory receptors?
Which general sensory receptor is:
PAIN
Common in:
Superficial portions of the skin
Joint capsules
Outside of bones
Around the walls of blood vessels
What is fast pain of nociceptors?
Which pain type of nociceptors is:
Prickling pain, such as that caused by an injection or a deep cut
What is slow pain of nociceptors?
Which pain type of nociceptors is:
Burning and aching pain
What are thermoreceptors of general sensory receptors?
Which general sensory receptor is:
Are temperature receptors
What are mechanoreceptors of general sensory receptors?
Which general sensory receptor is:
Sensitive to stimuli that physically distort their cell membranes
Stretching, compression, & twisting
What are tactile receptors of mechanoreceptors?
Which class of mechanoreceptors:
Provide the sensations of touch, pressure, and vibration
What are baroreceptors of mechanoreceptors?
Which class of mechanoreceptors:
Detect pressure changes in the walls of blood vessels
In portions of the digestive, reproductive, and urinary tracts
What are proprioceptors of mechanoreceptors?
Which class of mechanoreceptors:
Monitor the positions of joints and muscles
What is fine touch in tactile receptors?
Which touch type in tactile receptors:
Are extremely sensitive to location, shape, size texture, movement
What is crude touch in tactile receptors?
Which touch type in tactile receptors:
Provide poor localization, give little information about the stimulus
What are free nerve endings of tactile receptors?
Which type of tactile receptors:
Sensitive to pain & temp. tickle, itch & touch

What is root hair plexus of tactile receptors?
Which type of tactile receptors:
Monitor distortions and movements across the body surface wherever hairs are located
Adapt rapidly, so are best at detecting initial contact and movements
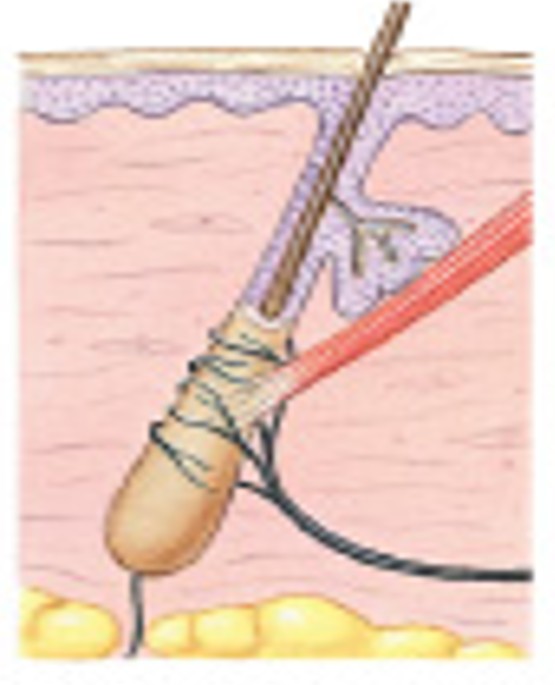
What are tactile discs of tactile receptors?
Which type of tactile receptors:
Also called Merkel’s discs
Fine touch and pressure receptors

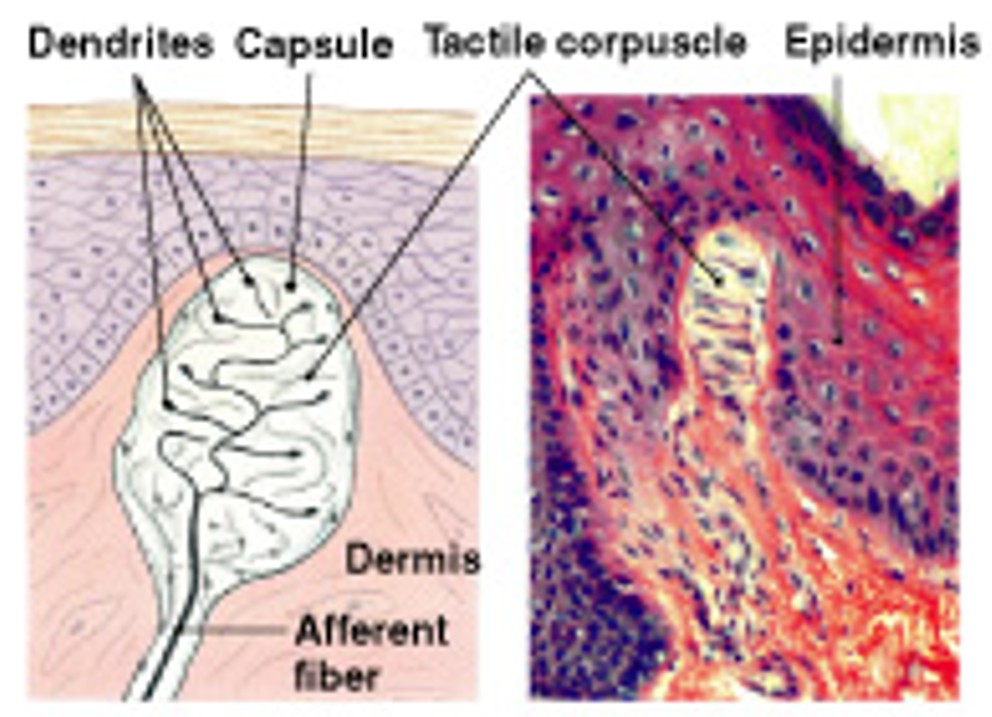
What are tactile corpuscles of tactile receptors?
Which type of tactile receptors:
Also called Meissner’s corpuscles
In eyelids, lips, fingertips, and genitalia
Fine touch
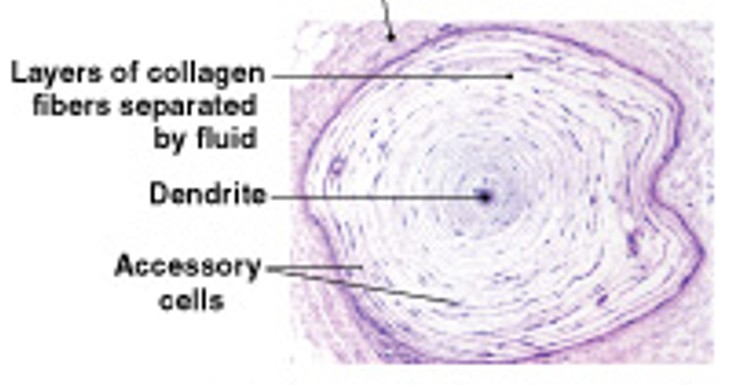
What are lamellated corpuscles of tactile receptors?
Which type of tactile receptors:
Also called Pacinian corpuscles
Sensitive to deep pressure
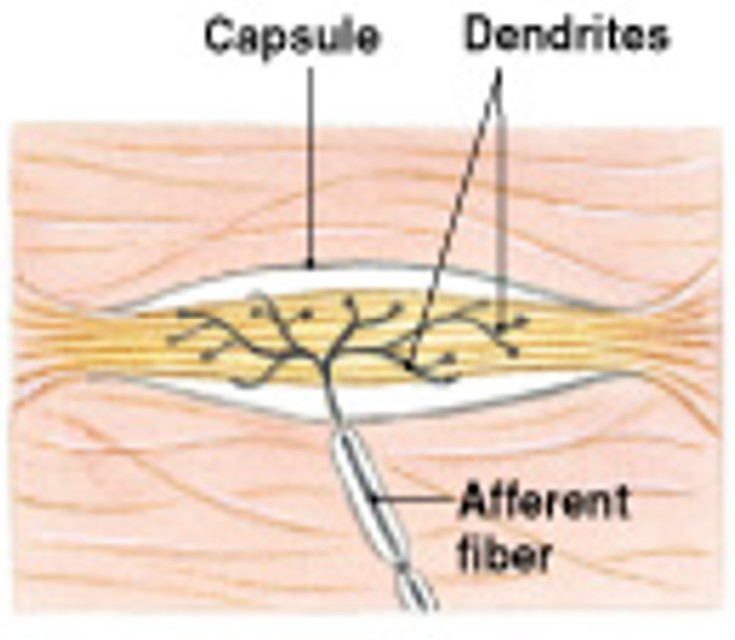
What are Ruffini corpuscles of tactile receptors?
Which type of tactile receptors:
Distortion of the skin
Located in the reticular (deep) dermis
What are muscle spindles of proprioceptors?
Which major group of proprioceptors:
Monitor skeletal muscle length
Trigger stretch reflexes
What are golgi tendon organs of proprioceptors?
Which major group of proprioceptors:
Monitor external tension developed during muscle contraction
Stimulated by tension in tendon
What are joint capsule receptors of proprioceptors?
Which major group of proprioceptors:
Free nerve endings detect pressure, tension, and movement at the joint
What are chemoreceptors?
What are receptors that monitor pH, carbon dioxide, and oxygen levels in arterial blood?
What are carotid bodies of chemoreceptors?
Which bodies of chemoreceptors are:
Near the origin of the internal carotid arteries on each side of the neck
What are aortic bodies of chemoreceptors?
Which bodies of chemoreceptors are:
Between the major branches of the aortic arch
What is first-order neuron?
Which neuron order type is:
Sensory neuron delivers sensations to the CNS
From somatic receptors → spinal cord or brain stem
What is second-order neuron?
Which neuron order type is:
From spinal cord or brain stem → thalamus
What is third-order neuron?
Which neuron order type is:
If the sensation is to reach our awareness, thalamus → cerebral cortex
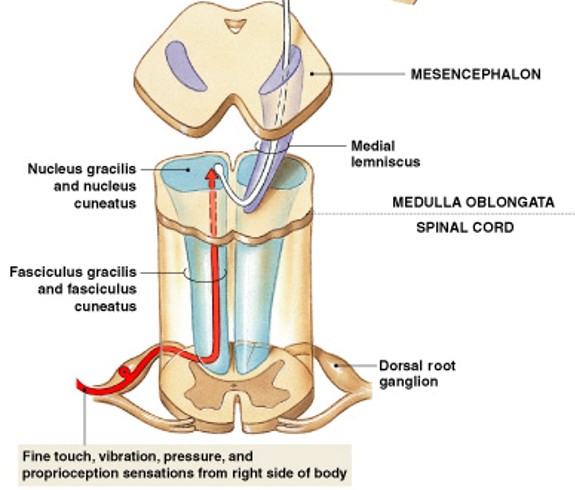
What is the posterior column pathway?
Which major somatic sensory pathway:
Carries sensations of highly localized (“fine”) touch, pressure, vibration, and proprioception
Decussation - crossing over
Medial lemniscus - tract from medulla to thalamus
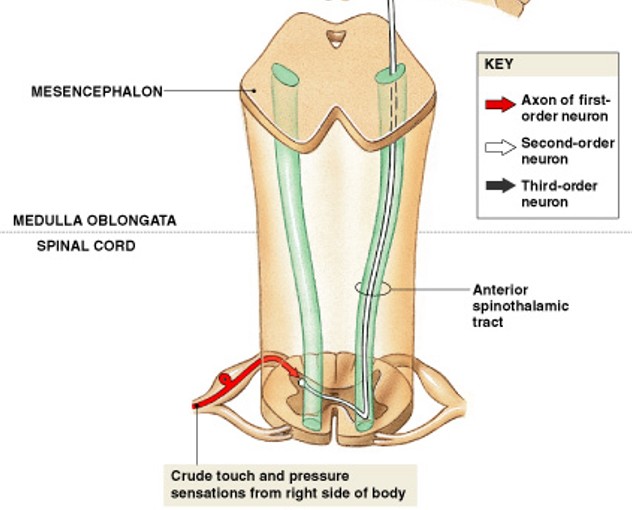
What are anterior spinothalamic tracts of anterolateral pathway?
Which tract of anterolateral pathway:
Carries crude touch and pressure sensations
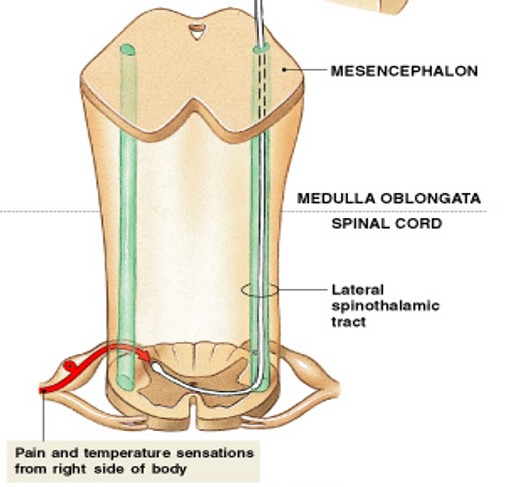
What are lateral spinothalamic tracts of anterolateral pathway?
Which tract of anterolateral pathway:
Carries pain and temperature sensations
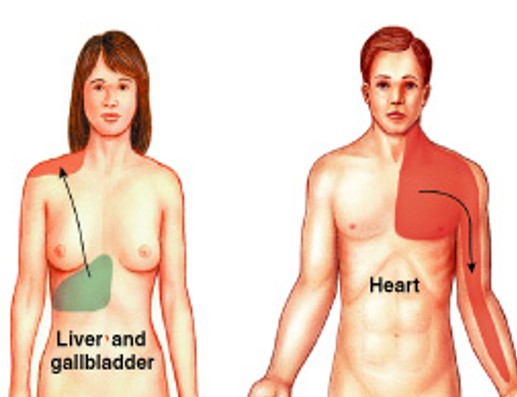
What is referred pain in the anterolateral pathway?
Which pain type in anterolateral pathway is:
Individual feels pain in specific part of body surface
What is the spinocerebellar pathway?
Which major somatic sensory pathway:
From spinal cord to cerebellum
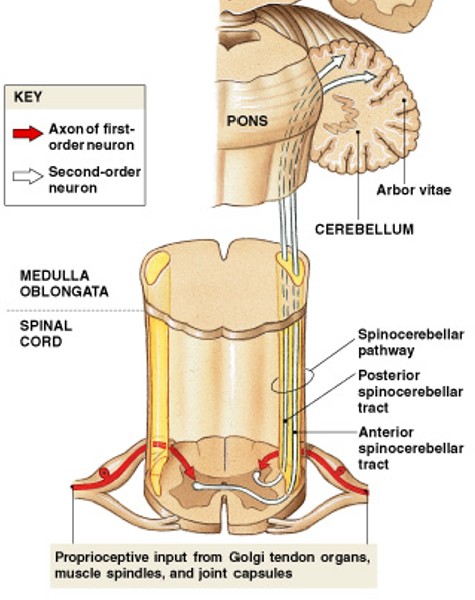
What are posterior spinocerebellar tracts of spinocerebellar pathway?
Which tract of spinocerebellar pathway:
Cerebellum receives same side trunk and lower limb proprioceptive information via the inferior cerebellar peduncle
What are anterior spinocerebellar tracts of spinocerebellar pathway?
Which tract of spinocerebellar pathway:
Cerebellum receives opposite side trunk and lower limb proprioceptive information via the superior cerebellar peduncle
What are visceral sensory pathways?
Which type of pathway:
Monitors visceral tissues and organs, primarily within the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities
What are solitary nucleus of visceral sensory pathways?
Which part of visceral sensory pathways:
Major processing and sorting center for visceral sensory information
Which cranial nerves carry visceral information?
What do cranial nerves V, VII, IX, and X carry?
What do somatic nervous system (SNS) controls in motor pathways?
What controls contractions of skeletal muscles in motor pathways?
What is upper motor neuron?
Which motor neuron is:
Cell body lies in a CNS processing center
Axon synapses with lower motor neuron
May facilitate or inhibit lower motor neuron
What is lower motor neuron?
Which motor neuron is:
Cell body lies in a nucleus of the brain stem or spinal cord
Only the axon extends outside CNS
Axon innervates skeletal muscles
What are corticospinal pathways?
Which type of pathway:
Provides voluntary control over skeletal muscles
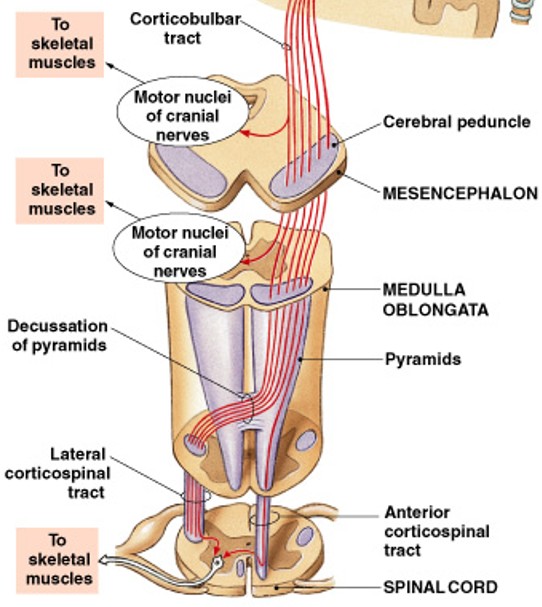
What are corticobulbar tracts of corticospinal pathways?
Which corticospinal tracts:
Provide conscious control over skeletal muscles (using cranial nerves)
Move the eye, jaw, face, and some muscles of neck and pharynx
What are lateral corticospinal tracts?
Which corticospinal tracts:
Activates skeletal muscles on the opposite side (90% cross high)
For fast & skilled movements (writing)
On lateral side
What are anterior corticospinal tracts?
Which corticospinal tracts:
Activates skeletal muscles on the opposite side (10% cross low)
For fast & skilled movements (writing)
On anterior side
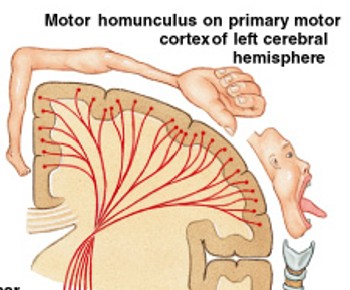
What is motor homunculus?
What provides indication of degree of fine motor control available?
What are medial pathways?
Which type of pathway:
Primarily concerned with control of muscle tone
Gross movements of neck, trunk, and proximal limb muscles
What are vestibulospinal tracts of medial pathways?
Which tract of medial pathway:
(CN VIII) monitor position and movement of the head
Maintain posture and balance
What are tectospinal tracts of medial pathways?
Which tract of medial pathway:
Moves head & eyes toward stimuli
What are reticulospinal tracts of medial pathways?
Which tract of medial pathway:
Controls muscle tone & visceral motor functions
What are lateral pathways?
Which type of pathway:
Primarily concerned with muscle tone and more precise movements of distal parts of limbs
What are rubrospinal tracts of lateral pathways?
Which tract of lateral pathway:
Govern precise movements of distal parts of limbs
What does the cerebellum monitors?
What monitors:
Proprioceptive (position) sensations
Visual information from the eyes
Vestibular (balance) sensations from inner ear
What does basal nuclei provides?
What provides background patterns of movement involved in voluntary motor activities?