6. Human Resources
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Human Resources
The department or function within an organisation that is focused on activities related to employees.
Human resource management (HRM)
The management of people at work to assist the organisation in achieving its objectives.
Internal influences on HR objectives
Corporate objectives
Financial strategies
Operational strategies
Marketing strategies
External influences on HR objectives
Economic change
Social change
Technological change
Political and legal change
Market change
Effectively managing HR allows:
Add value through expertise and customer service
Control labout costs
Motivated employees
Identify and develop leaders
Soft HRM focuses on the needs of employees- their roles, rewards, motivation etc. What are examples of this?
Permanent work (PT/FT)
Acceptable remuneration
A nice work environment
Training
Chance for promotion
Hard HRM identify workforce needs of the business and recruit and manage accordingly. What are examples of this?
Zero-hour contracts
Minimum wage
Lack of training
Financial incentives to raise productivity
Cheap recruitment methods
Employee engagement
The degree of commitment shown by employees to their individual work as well as towards the business objective.
Employee involvement
The amount of contribution an employee can make to their working practises and decision making.
Talent development
Identifying exceptional talent in the business and developing and promoting the talent.
Benefits of training:
Better productivity
Improved motivation
More flexibility through better skills
Less supervision required
Better recruitment and retention
Easier to implement change in the business
Diversity
Ensuring the workforce is representative of the local area. Ie, ethnicity, gender, disability and religion.
What will an objective of diversity aim for?
To ensure that personal differences do not hinder progress in the workplace and that employees aren't discriminates against.
Protected characteristics under the Equality Act 2010:
Age
Disability
Gender reassignment
Marriage/ civil partnership
Pregnancy/ maternity
Race
Religion/ belief
Sex/ sexual orientation
Alignment of values
Ensuring all employees embrace and promote the values of the organisation.
Labour productivity
Concerned with the volume of output that is obtained from each employee.
Calculation for labour productivity
Divide the out over a time period by the number of employees.
Why does measuring and monitoring labour productivity matter?
Labour costs are usually a significant part of total costs.
Efficiency and profitability linked to productive use of labour.
Key measures of HR performance
Labour turnover and staff retention- % of staff who leave during a period
Labour productivity- Output per employee
Abstenteeism- % of staff who are absent from work
Productivity
The quantity of work produced by a team, business or individual.
Efficiency
The resources used to produce that work.
The more efficient and high- quality raw materials are... the higher level of productivity.
Why productivity matters?
Profits- labour costs significant part of total costs
Efficiency- closely linked to productive use of labour
Competitive advantage- keep unit costs down to remain competitive
Factors influencing labour productivity
Extent and quality of fixed assets
Skills, ability and motivation of the workforce
Methods of production within the organisation
External factors
How to improve labour productivity?
Measure- measure performance and set targets
Streamline- streamline production processes (remove unnecessary processes)
Invest in- invest in capital equipment (automation and computerisation)
Improve- improve the working conditions
Labour turnover
The proportion of a firm's workforce that leaves during the course of a year.
Internal causes of increased turnover
Poor recruitment and selection process
Ineffective motivation or leadership
Lower wages rates than competitors
External causes of increased turnover
More local vacancies arising
Better transport links- making a wider geographical area accessible for workers
Positive consequences of high labour turnover
New employees= new ideas and enthusiasm |
Workers with specific skills can be hired |
New perspectives for solving problems |
Negative consequences of high labour turnover
Cost of recruitment |
Cost of training |
Time taken for new staff to settle in |
Less productivity during this time |
Ways of improving employee retention
Financial incentives
Non- financial incentives
Improving the effectiveness of recruitment and selection process
Conduct research to understand why employees are leaving (eg exit survey)
Absenteeism
The habitual non-presence of an employee at his/ her job.
Eg. scheduled vacations, occasional illness and family emergencies.
What are the issues with absenteeism
Significant business cost- cover
Key to understand reasons
Often predictable
Possibly reduces motivation
May lose customers
How to decrease absenteeism
Show understanding
Set targets and monitor trends
Have a clear sickness and absence policy
Provide rewards for good attendance
Consider the wider issues of employee motivation eg personal life
Why use data for HR resource decision
Productivity and labour turnover data provides a company with information on its performance
Low productivity and high labour turnover might suggest poor management
Managers analyse the figures to identify- changes overtime, benchmarking, performance against targets
Organisational structure
Shows how people and management are organised in a business.
Factors that influence organisational structure:
Size of business- small business tend to have a flat structure and larger businesses have a more complex structure with different hierarchy's and departments.
Type of business- how many locations does the business have? Any overseas operations? Is the workforce skilled, unskilled or semi-skilled?
Management and leadership- a company with an autocratic leadership will have a very different structure to a company who likes to delegate tasks and responsibility.
Flat structure- pros
More opportunity for delegation
Flat structure- cons
Difficult to manage employees properly
Insufficient time to manage employees properly
Tall structure- pros
More opportunity for promotion
Tall structure- cons
Lines of communication may be slower
Less opportunity for delegation
Delegation
The passing down of authority through the organisation.
Delegation pros
Can speed up and improve the quality of decision making
Can reduce the workloads of senior and middle managers, allowing them to focus on key tasks
Delegation improves the skills of junior employees and prepares them for more senior roles in the organisation
Delegation cons
May require the business to spend more on training employees to ensure they have the necessary skill set
May be inappropriate in some organisations where leadership styles are authoritarian
Not a suitable strategy to adopt to manage a crisis
Job design
The process of grouping together or dividing up tasks and responsibilities to create complete jobs.
Labour productivity
Measures the output per employee per time period
Job enrichment
Occurs when employees' jobs are redesigned to provide them with more challenging and complex tasks.
Empowerment
Is a series of actions designed to give employees greater control over their working lives.
A centralised structure
Where business decisions are made at the top of the business or in a head office and distributed down the chain of command.
Centralised structure- pros
Rapid decision making
Should ensure business objectives that are set by senior managers are pursued
Economies of scale and overhead savings are easier to achieve
Centralised structure- cons
Demotivated staff, not given an opportunity to make decisions
More bureaucratic
Customer service often lacks flexibility
Decentralised structure
Where a business allows decisions to be made by managers and subordinates.
Decentralised structure- pros
Junior employees should be more motivated and empowered
Reduces workload off senior managers
Good way of training and developing junior management
Decentralised structure- cons
More variation at different branches- flaws in customer service
Decision making isn't necessarily "strategic"
harder to achieve tight financial control- risk of cost overruns
Internal influences on delegation, centralisation and decentralisation:
Leadership and management styles
The business' overall or corporate objectives
The skills of the workforce
External influences
The technological environment
The competitive environment
The economic environment
Why change the organisational structure?
Growth of the business means more formal structure is appropriate
Reduce costs and complexity
Employee motivation needs boosting
Customer service and/ or quality improvements
Challenges of changing the organisational structure
Employee resistance
Disruption and de motivation= potential staff retention problems
Costs
Negative impact on customer service or quality
Reasons a business may need to recruit
Start up
Increased demand
Business is relocating- not all existing staff are able to move
Skill shortage
Changes in employment patterns
Ageing population
Greater emphasis on flexible working hours
Technology allows employees to communicate more effectively when apart
People rarely stay in the same job for life
PT and flexible work- pros
Cheaper to employ as entitled to less benefits
More flexible work force
Wide range of potential recruits
PT and flexible work- cons
Employees feel less loyal to business and therefore less motivated
Harder for managers to control and coordinate workforce
Internal recruitment- pros
Business already aware of the person’s skill set
Cheaper
Quicker
Can be motivating if opportunity is present
Internal recruitment- cons
Leaves a vacancy that needs to be filled
Demotivating for staff who don’t get the job
External recruitment-pros
New skill set
Someone to motivate staff if current staff is demotivated
External recruitment-cons
Expensive
Time consuming
Ways to avoid costly redundancies
Freeze external recruitment
Put a stop on voluntary overtime
Offer voluntary redundancies
Consider career breaks
Review employee benefits
Redeployment
The moving of an employee from one job or role to another.
Redundancy
When you dismiss an employee because you no longer need anyone to do their job.
Benefits of redeployment
Maintains job security for employee
Business retains skills and experience
Labour resources are allocated more effectively
Reduced cost of recruitment and selection
Why do businesses need training?
To support new employees
Improve productivity
Increase marketing effectiveness
Support high standards of customer service and production quality
Introduction of new technology, systems, legislations
Support employee progression and promotion
Reasons why businesses neglect training
They fear employees will be poached by competitors
A desire to minimise short-term costs
They cannot make a justifiable investment case
Training takes time to have the desired effect
Sometimes the benefits of training are more intangible (eg morale) than tangible
Assuming that training is effective; then…
Employees feel more loyal to the firm
Shows that business is taking an interest in their workers
Provide employees with greater promotional opportunities
Enables employees to achieve more at work- possibly gaining financially from this
Motivation
The will to work- comes from the enjoyment of work itself and/ or the desire to achieve certain goals
Reasons why we go to work:
To earn money
Sense of achievement/ job satisfaction
To belong to a group
Sense of security
To obtain a feeling of self-worth
List the main financial incentives a business can offer
Wages
Salaries
Bonus system
Commission
Profit sharing
Performance related pay
Piece rate payment
Share option
Fringe benefits
Wages
Normally paid per hour worked and receive money at end of week
Salaries
Normally an annual salary which is paid at end of each month
Bonus system
Usually only paid when certain targets have been achieved. However, sometimes they are unachievable.
Commission
Often salespersons, partly paid according to number of products they sell
Profit sharing
A system whereby employees receive a proportion of company’s profits. Direct link between pay and performance.
Performance related pay
Paid to those employees who meet certain targets
Piece rate payment
Pay per item produced in a certain period of time
Share option
Incentive for senior managers who are given shares of the company rather than a straightforward bonus or membership of a profit sharing scheme
Fringe benefits
Items and employee receives in addition to their normal wage or salary
List the main non-financial incentives a business can offer
Empowerment
Praise
Promotion
Job enrichment
Job enlargement
Better communication
Working environment
Team working
Praise
Recognition for good work
Promotion
Promoting employees to a position of higher responsibility
Job enrichment
Giving employees more challenging and interesting tasks
Job enlargement
Giving employees more tasks of a similar level of complexity
Better communication
Employees have a chance to give feedback and advice to managers
Working environment
Providing a safe, clean, comfortable environment to work in
Team working
Offers employees an opportunity to meet their social needs and often accompanied by empowerment for team
What is the best mix of incentives?
The “market” largely determines the base financial rewards paid for most jobs
Offering flexibility to employees in choosing which incentives they get often works well
Influenced by what the business can afford
What are the three classic theories of motivation?
Taylor- scientific management
Maslow- hierarchy of needs
Herzberg- two-factor theory
What is Taylor’s theory of motivation
Managers should closely control their employees
Autocratic leadership style- managers making decisions themselves
Use piece-rate pay
What is Taylor’s approach?
Identify efficient methods of production
Spot the efficient workers
Train the remaining staff
Pay workers based on productivity
What is Maslow’s theory of motivation?
Softer approach than Taylor
Five levels of human needs that need to be fulfilled
Business should offer different incentives to workers in order to help employees fulfil each need and progress up the hierarchy
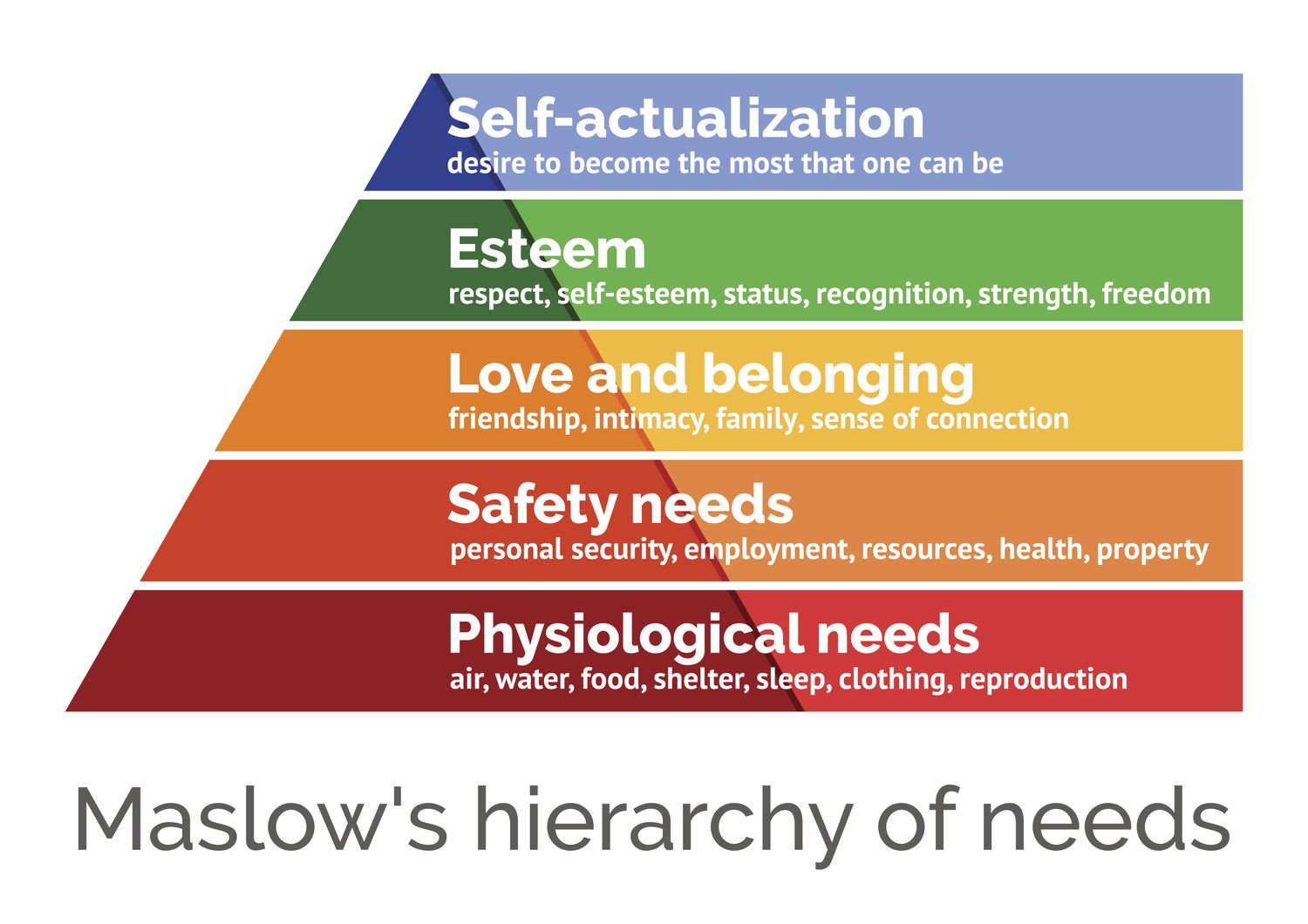
What is Herzberg’s theory of motivation?
Two-factor theory
Motivators- directly motivate people to work harder
Hygiene/ maintenance factors- can demotivate if not present but do not actually motivate employees
What are some examples of motivators and hygiene factors?
Motivators- Responsibility at work, meaningful and fulfilling work, recognition
Hygiene- Pay, working conditions, appropriate supervision and policies
What was Mayo’s theory?
Hawthorn effect
Concluded that scientific management could not explain the importance of people’s behaviour in the workplace
The type of job being carried out and type of supervision impacts motivation
Group relationships and sense of worth also impacts motivation