Bones, joints, Cartilage
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
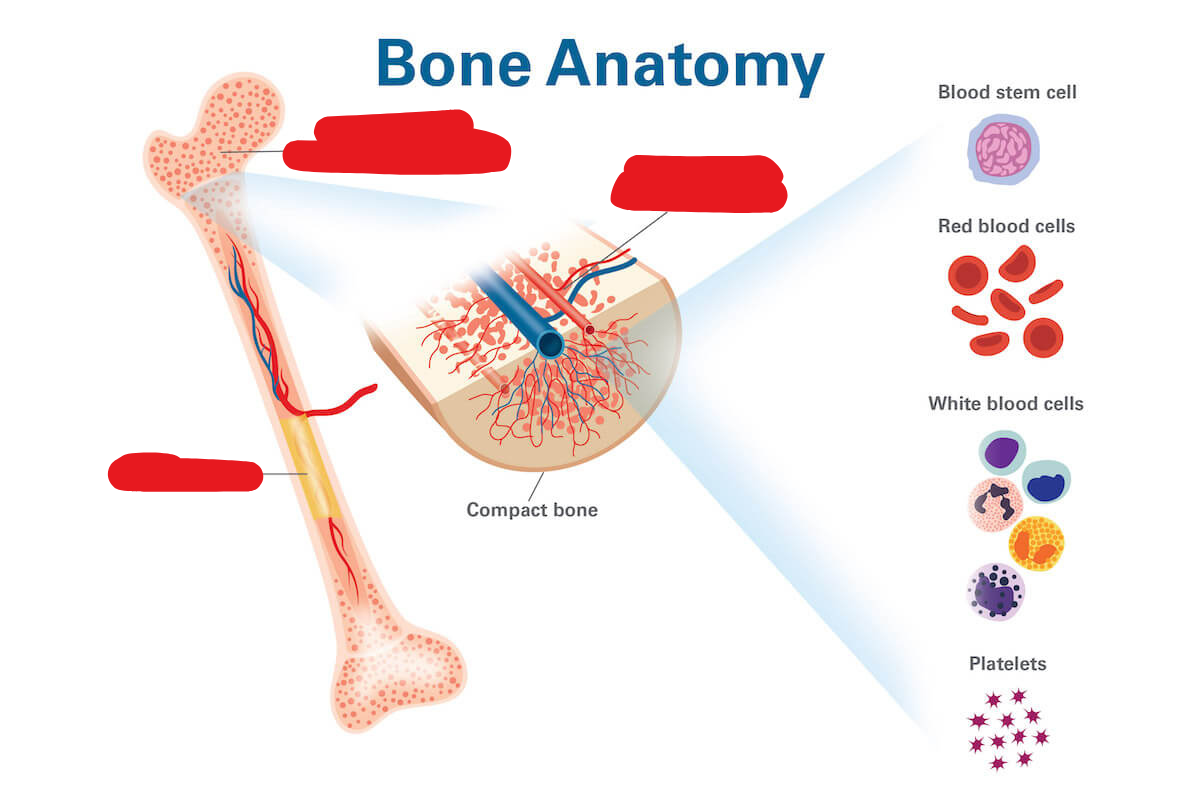
The soft, sponge like tissue in the center of most bones containing stem cells of red or white blood cells or platelets.
Bone marrow
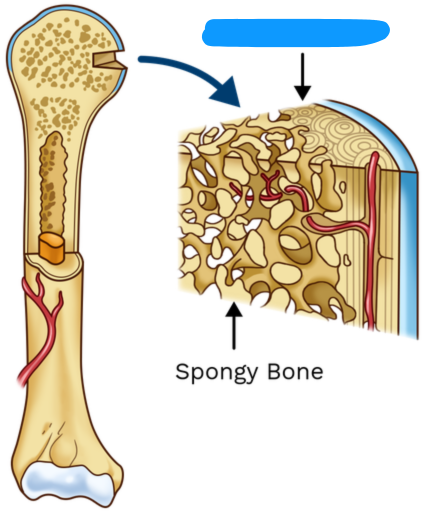
The meshwork of spongy tissue (trabeculae) of mature adult bone, typically found at the core of vertebral bones and the ends of the long bones.
Cancellous bone
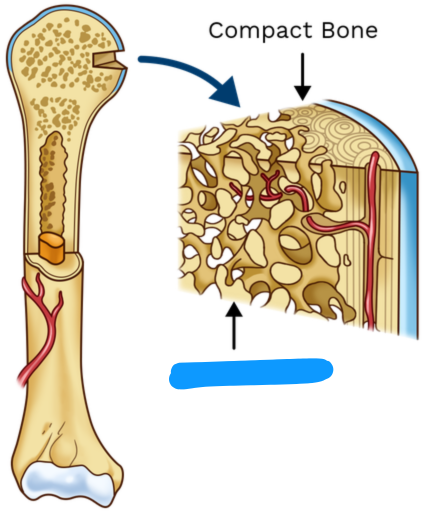
A denser material, also known as cortical bone, making up the hard structure of the skeleton.
Compact bone
The process of bone formation or remodeling.
Osteogenesis
A condition when bone tissue forms within a muscle or other soft tissue as a result of trauma or injury.
Myositis ossificans
Firm, flexible connective tissue that pads and protects joints and structural components of the body.
Cartilage
The explanation for bone adaptations as a result of the loads placed on them.
Wolff’s law
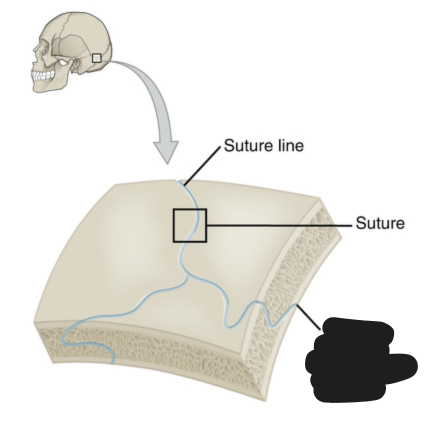
Points with fibrous connective tissue joining two bones that allow for very little movement.
Fibrous joints
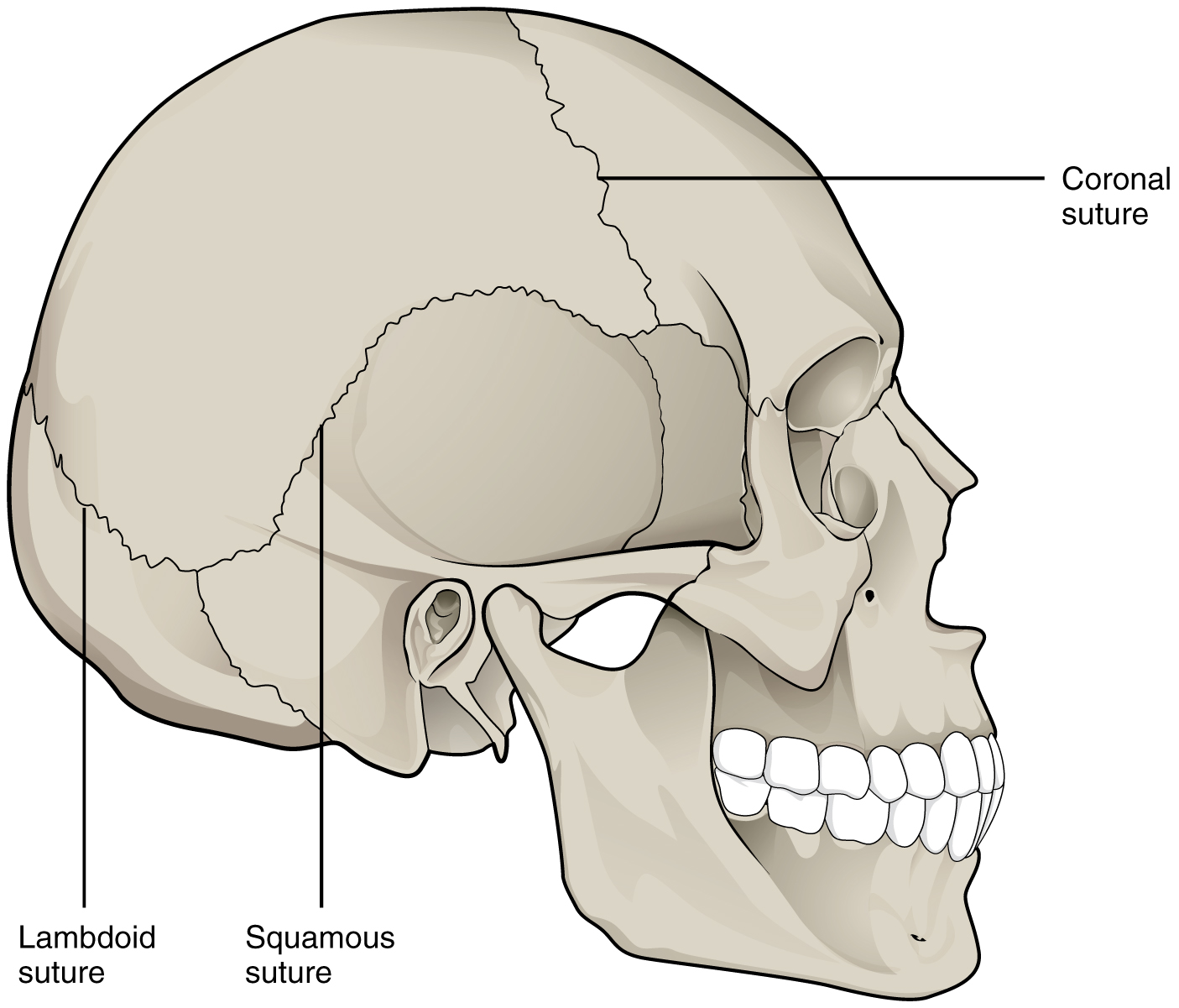
This type of joint is found in the skull. During birth, sutures are flexible to allow a baby to pass through the birth canal, and they become more rigid with age.
Sutures or synarthrodial joints
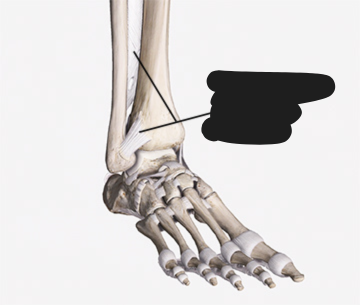
Found between some long bones such as the tibia and fibula.
Syndesmosis
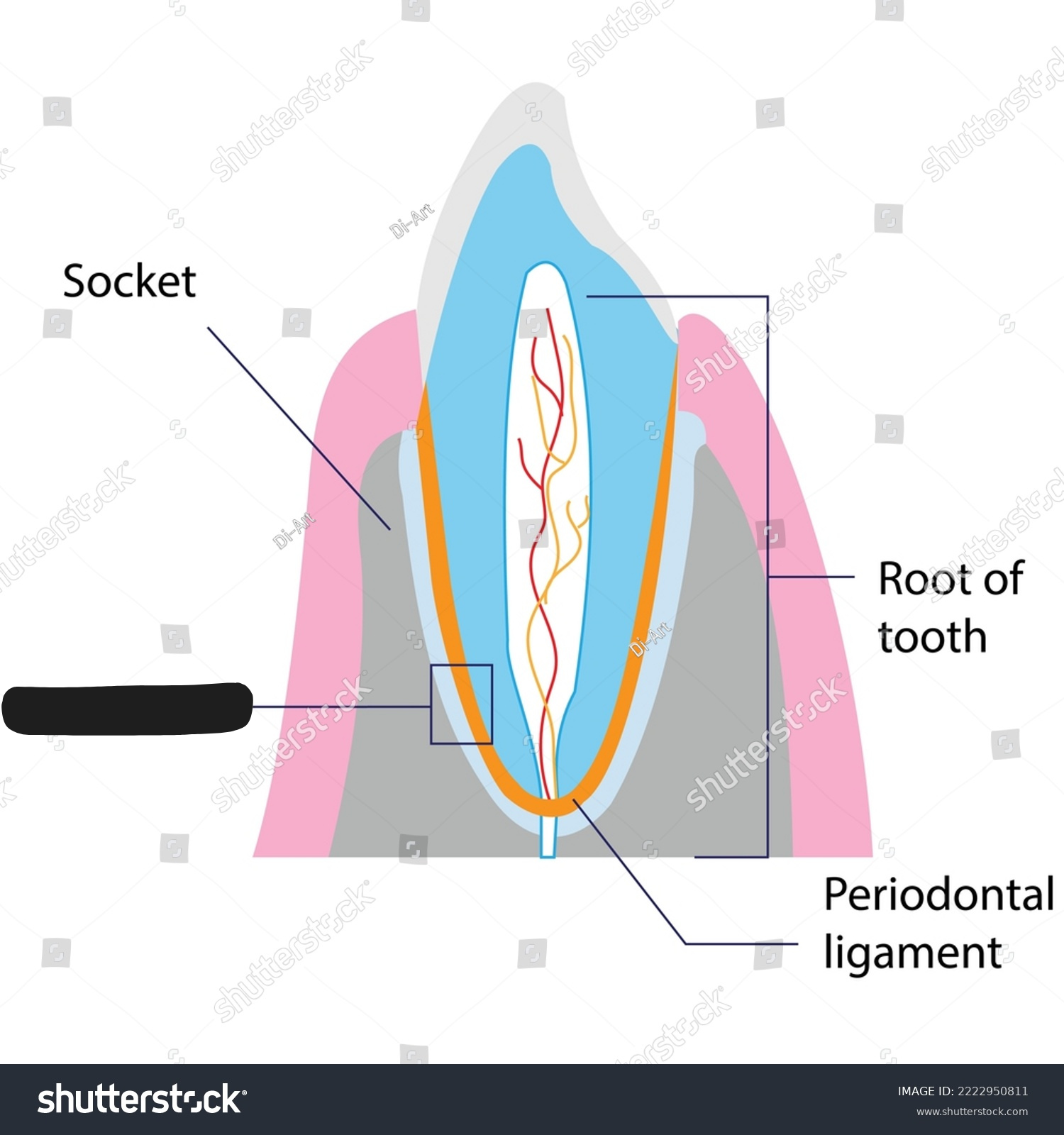
Attach teeth to the sockets of the maxilla and mandible.
Gomphosis joints
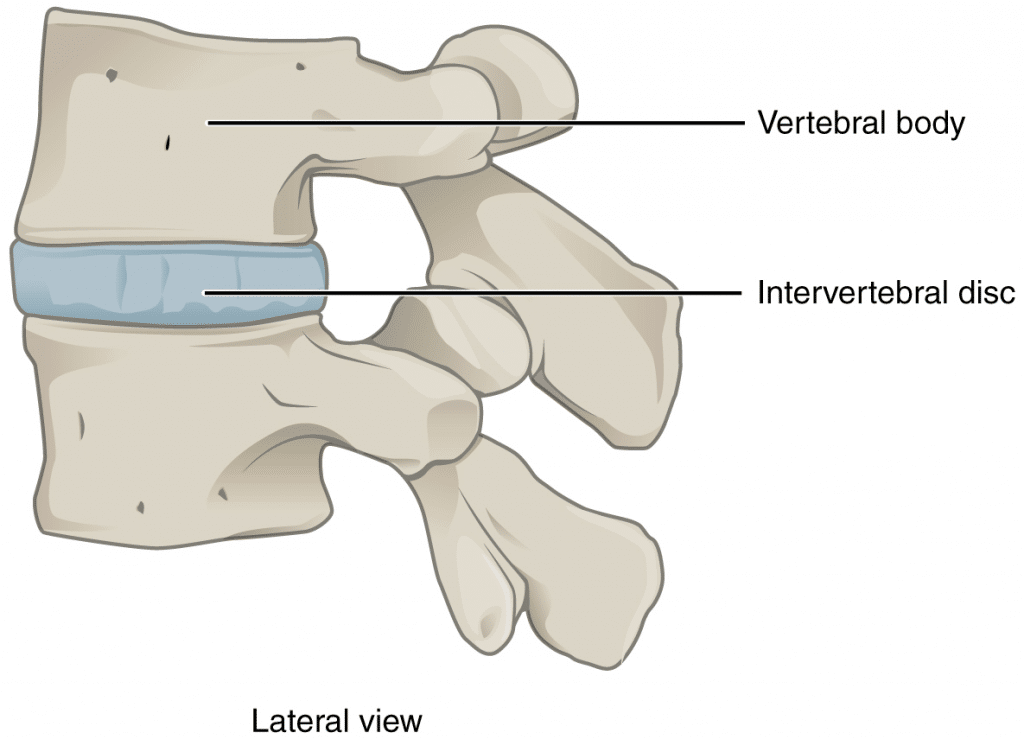
Moderately movable joints made of fibrocartilage or hyaline cartilage.
Cartilaginous joints
Epiphyseal (growth) plates.
Primary (Joint)
Intervertebral discs (layers of cartilage between vertebrae).
Secondary (Joint)
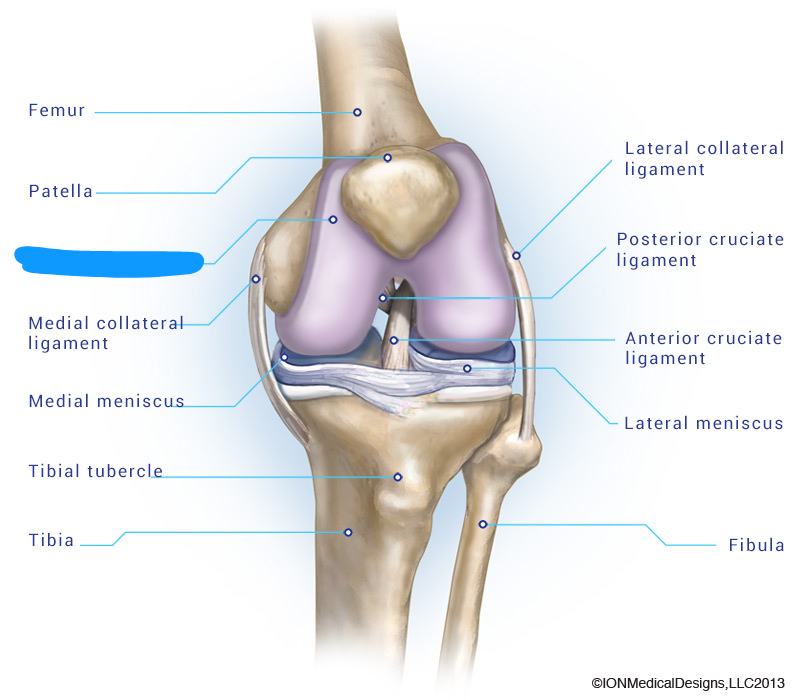
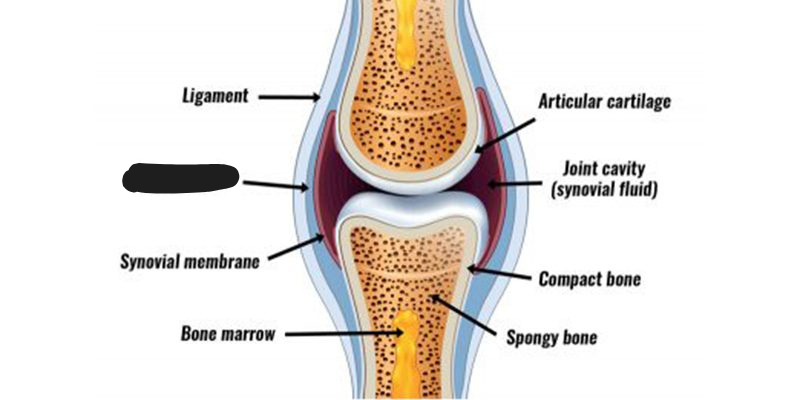
Fluid-filled joints found between bones that move against one another. The type of joint that allows movement.
Example: Knee
Synovial joints
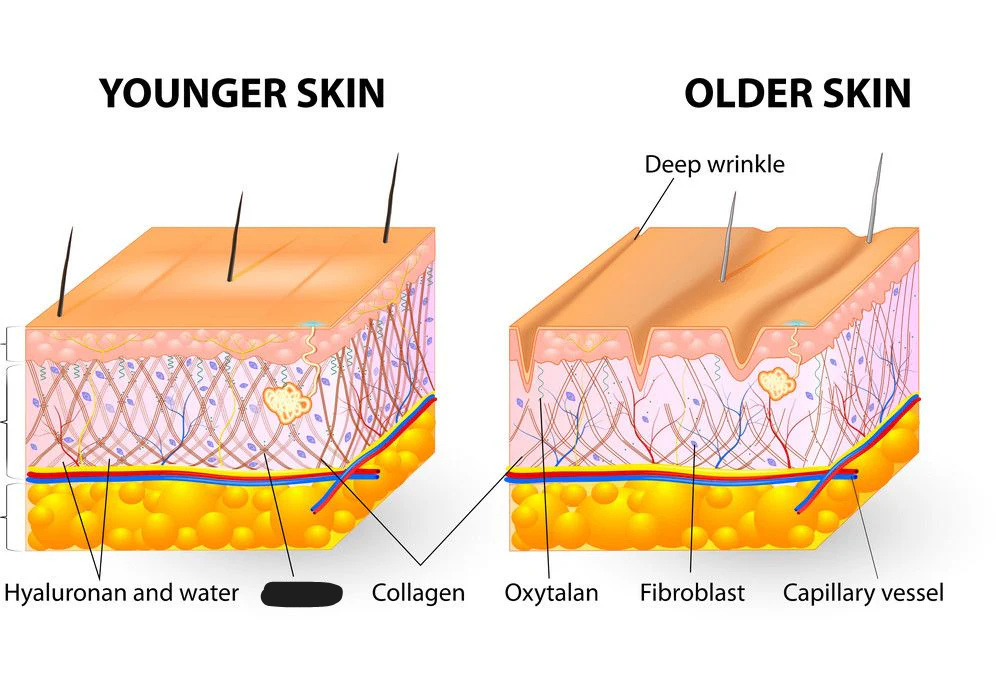
A highly elastic connective tissue allowing many tissues to retain their shape.
Elastin
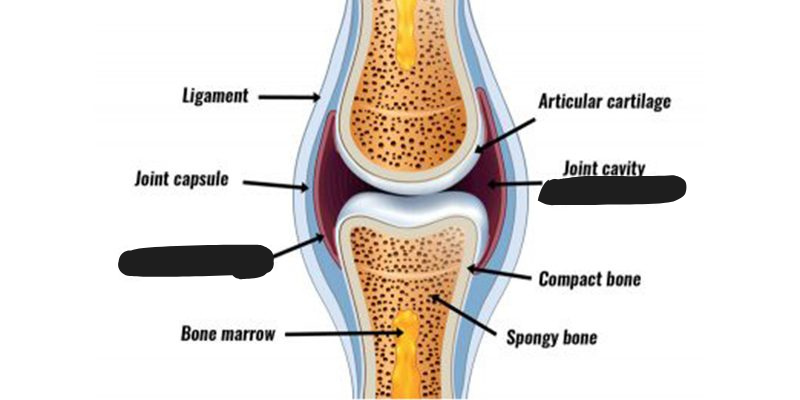
A thin, strong layer of connective tissue containing synovial fluid in freely moving join.
Joint capsule
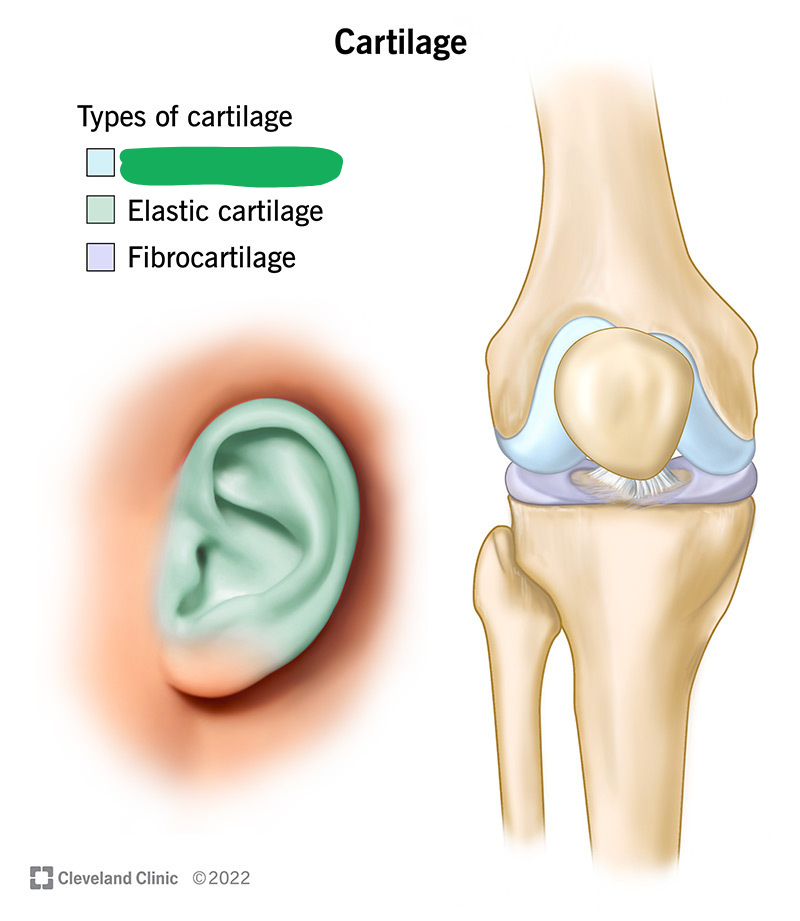
A transparent cartilage found on most joint surfaces and in the respiratory tract, which contains no nerves or blood vessels.
Hyaline cartilage
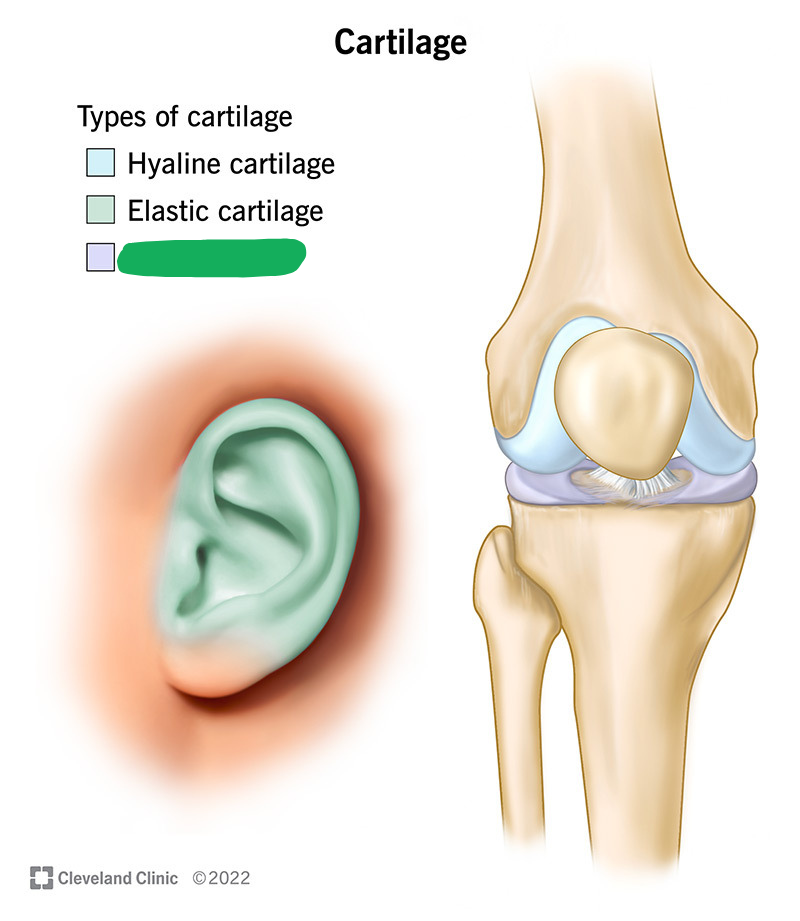
An elastic and tough tissue containing type I and type II collagen.
Fibrocartilage
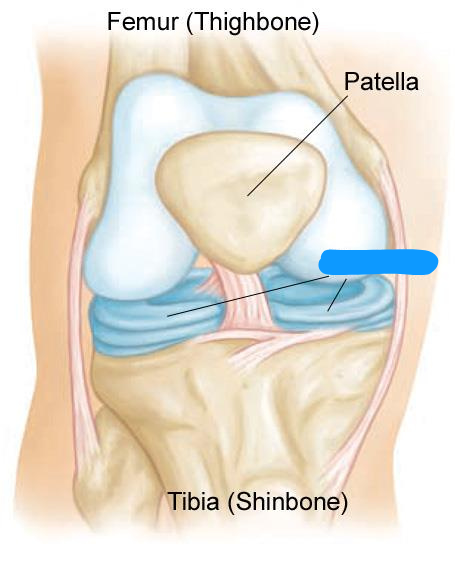
A form of fibrocartilage present in the knee, wrist, acromioclavicular, sternoclavicular, and temporomandibular joints.
Meniscus
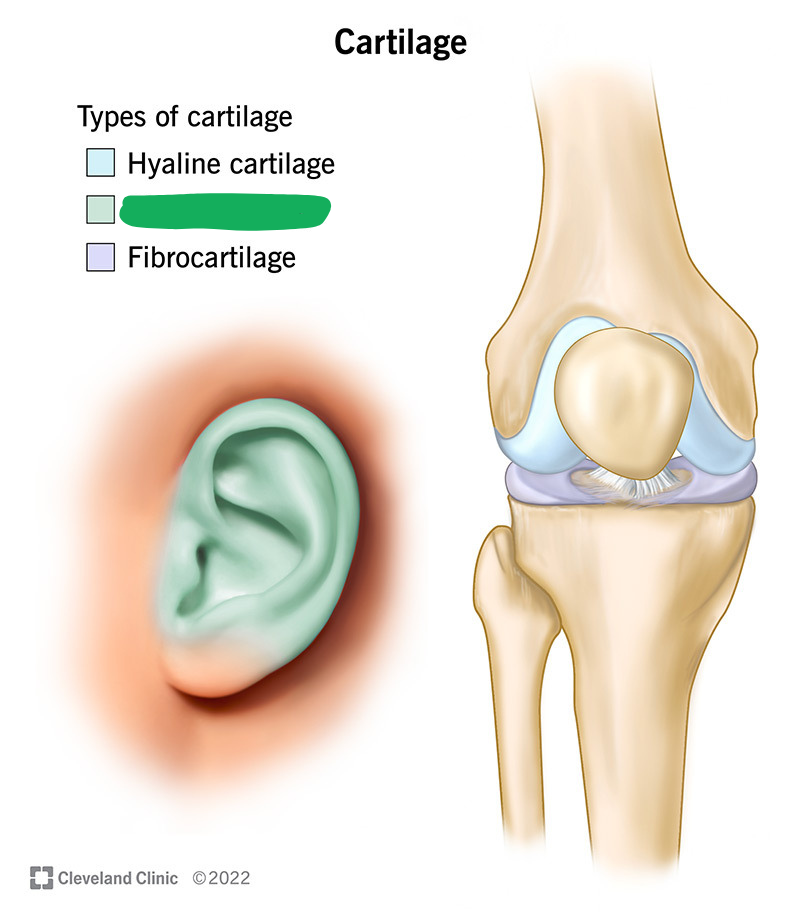
Flexible cartilage present in the outer ear, inner ear, and epiglottis.
Elastic cartilage

A piece of elastic cartilage in the throat that opens during breathing and closes during swallowing.
Epiglottis
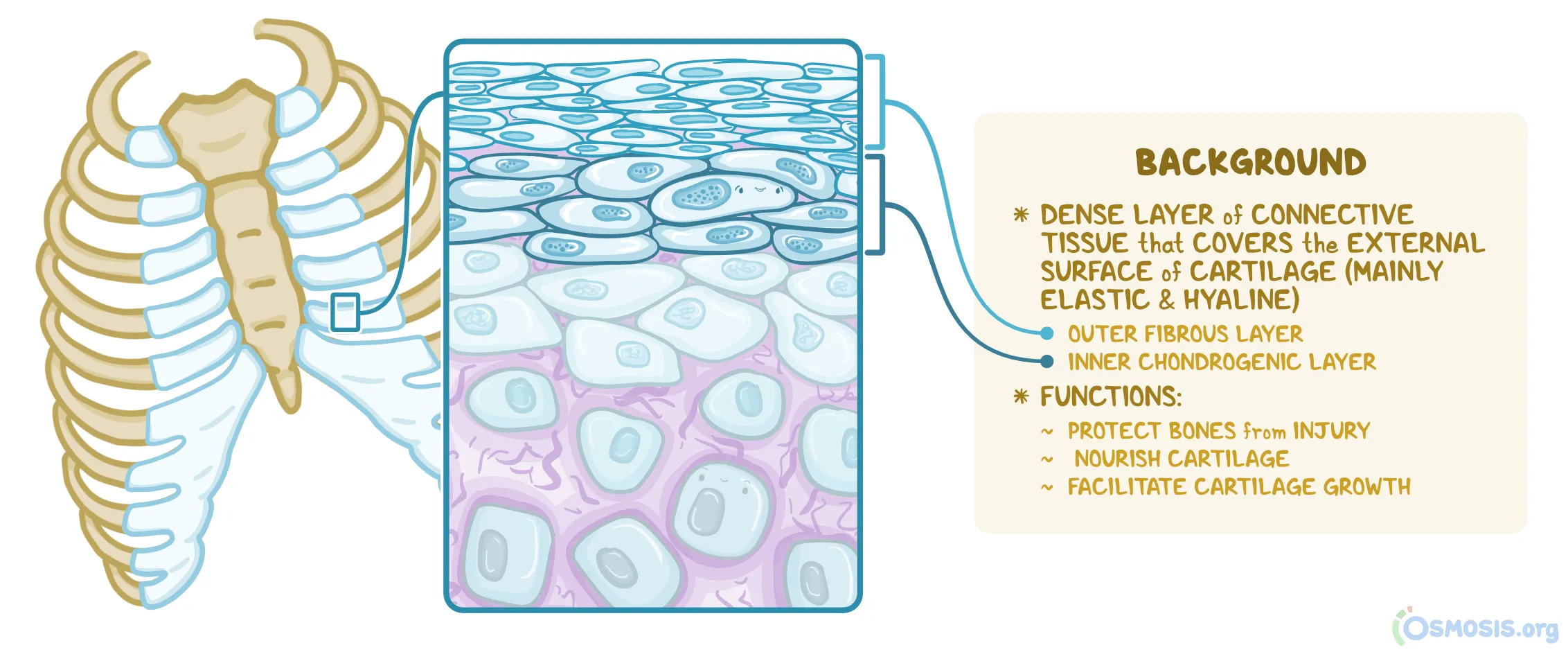
The connective tissue enveloping cartilage everywhere except at a joint.
Perichondrium

A form of hyaline cartilage located on the joint surface of bones.
Articular cartilage

Pain-sensitive nerve endings.
Nociceptors