11b: Cell-Cell Interactions
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
cell-cell signaling
cells communicate through signal molecules to produce coordinated cell responses
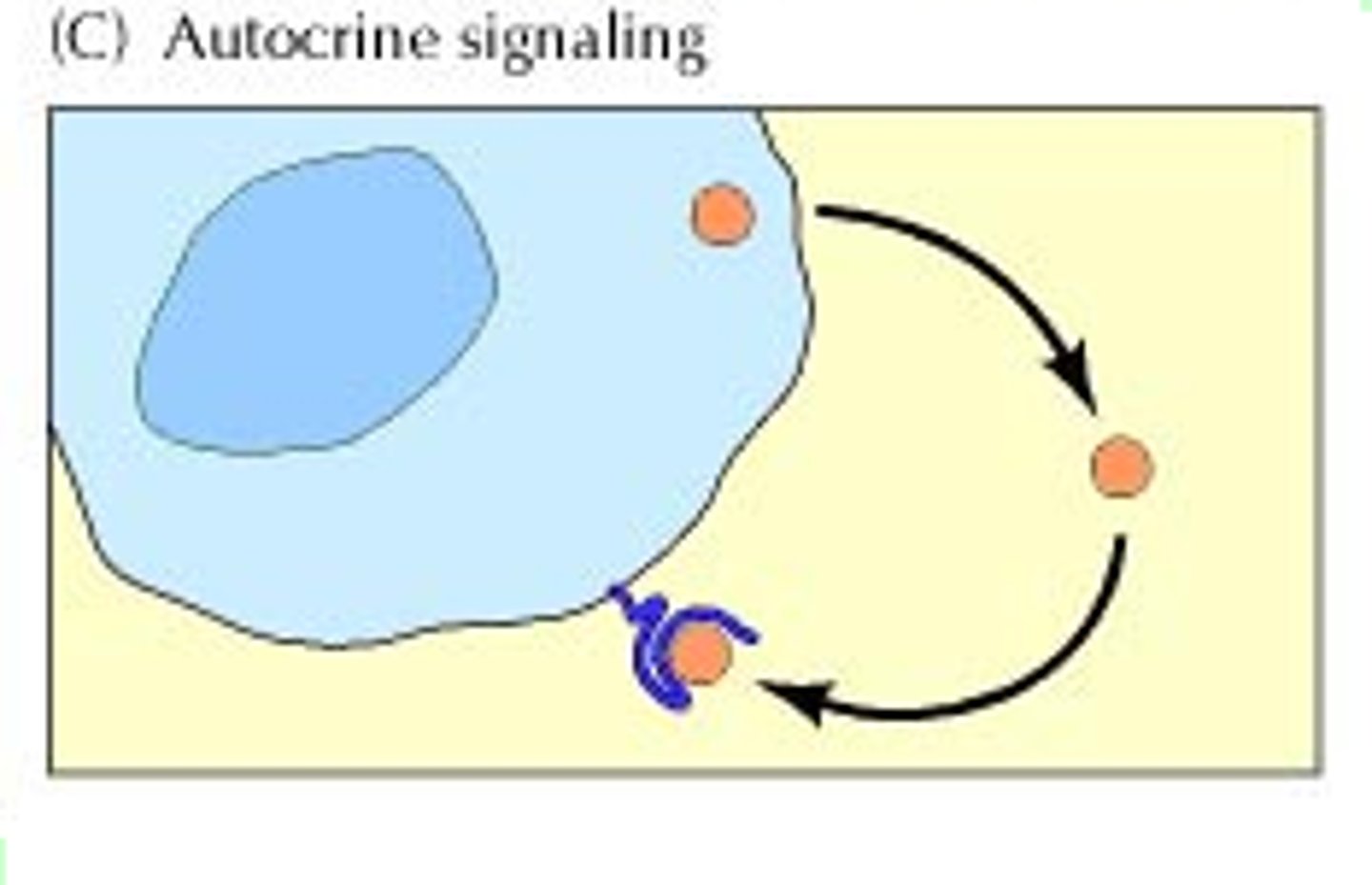
autocrine signals
acts on the same cell that secretes them
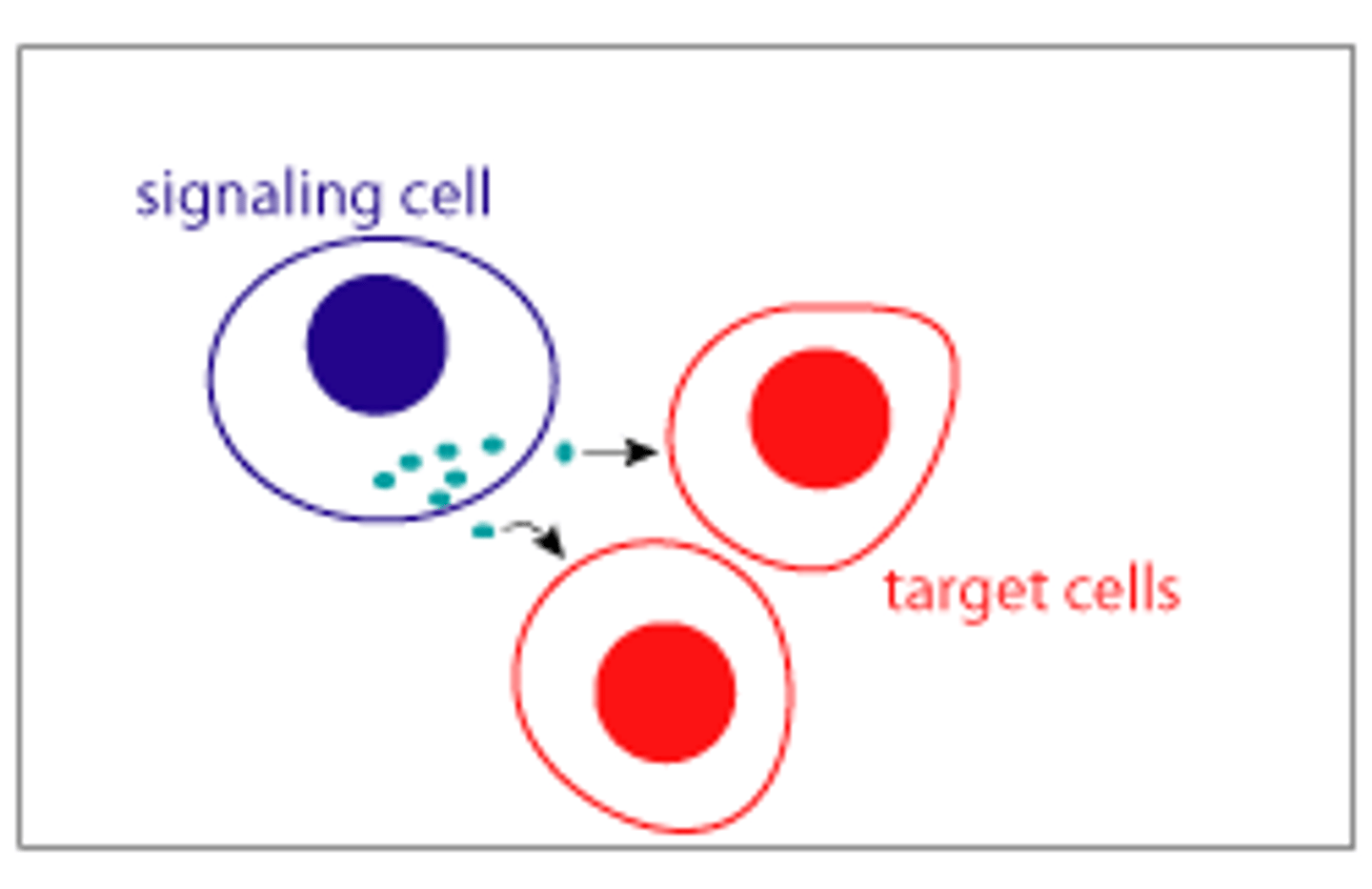
paracrine signals
diffuse locally and act on nearby cells
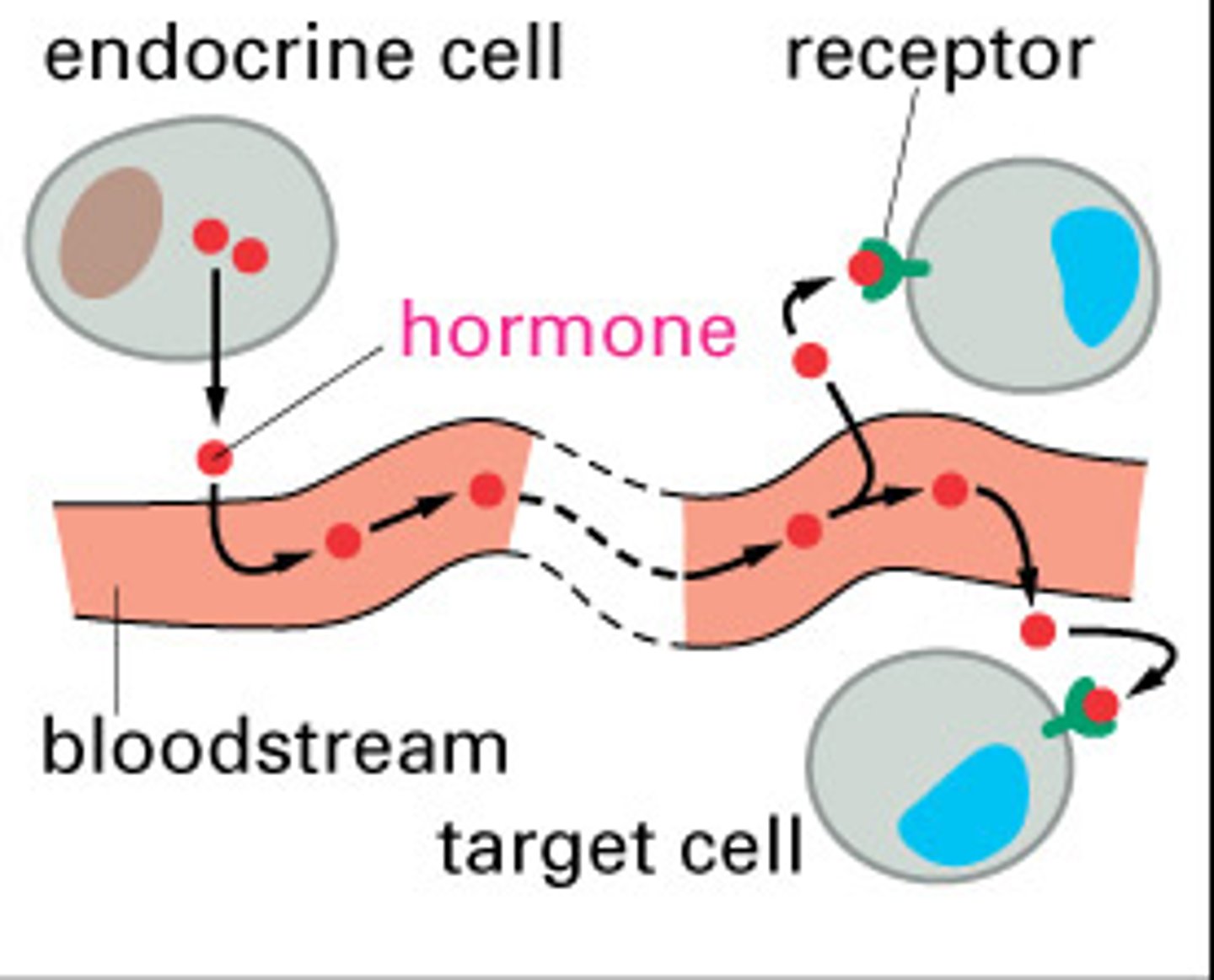
endocrine signals
are hormones carried between cells by blood or other body fluids
neuronal signals
neurotransmitters diffuse a short distance between neurons
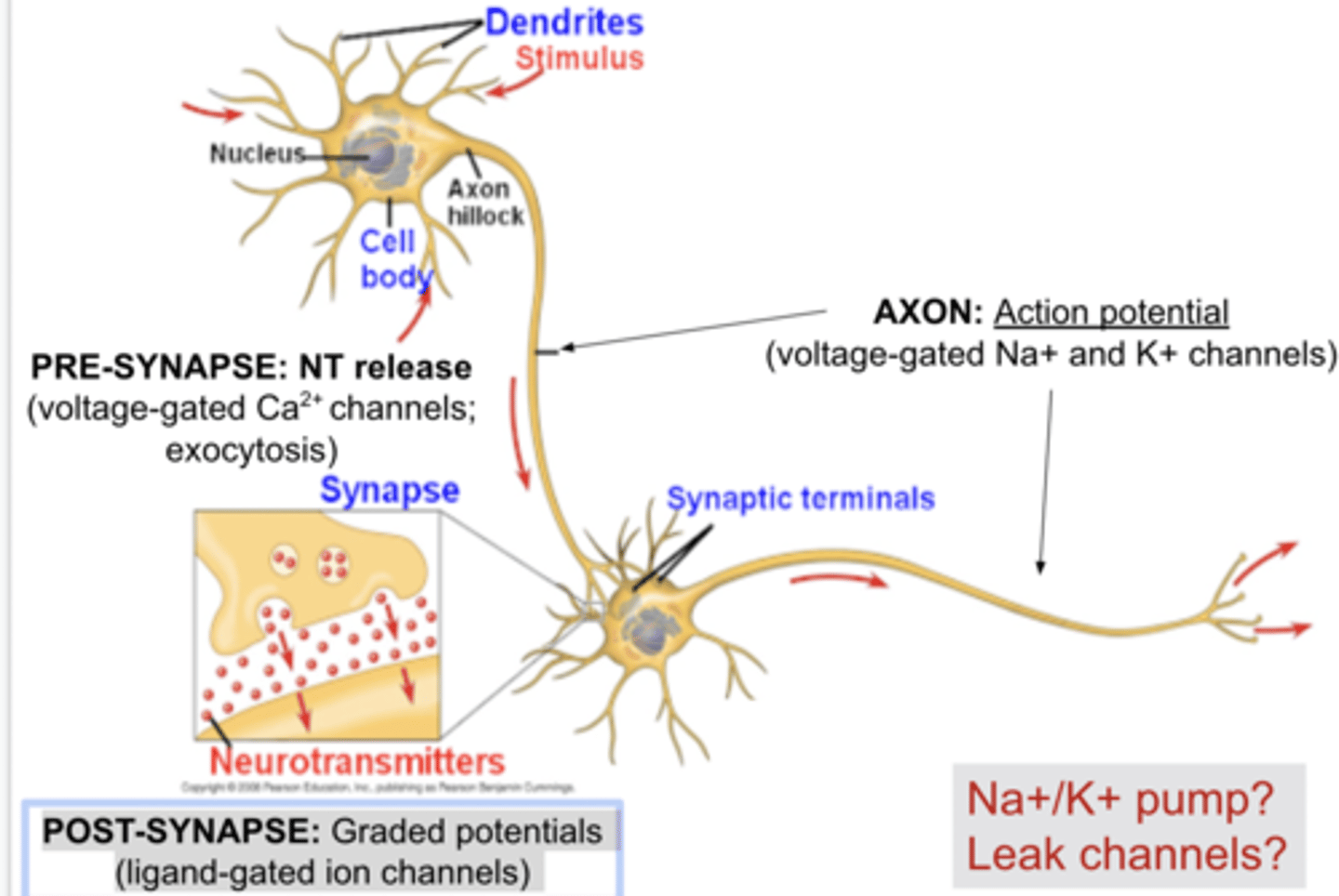
neuroendocrine signals
neurohormones are hormones from neurons
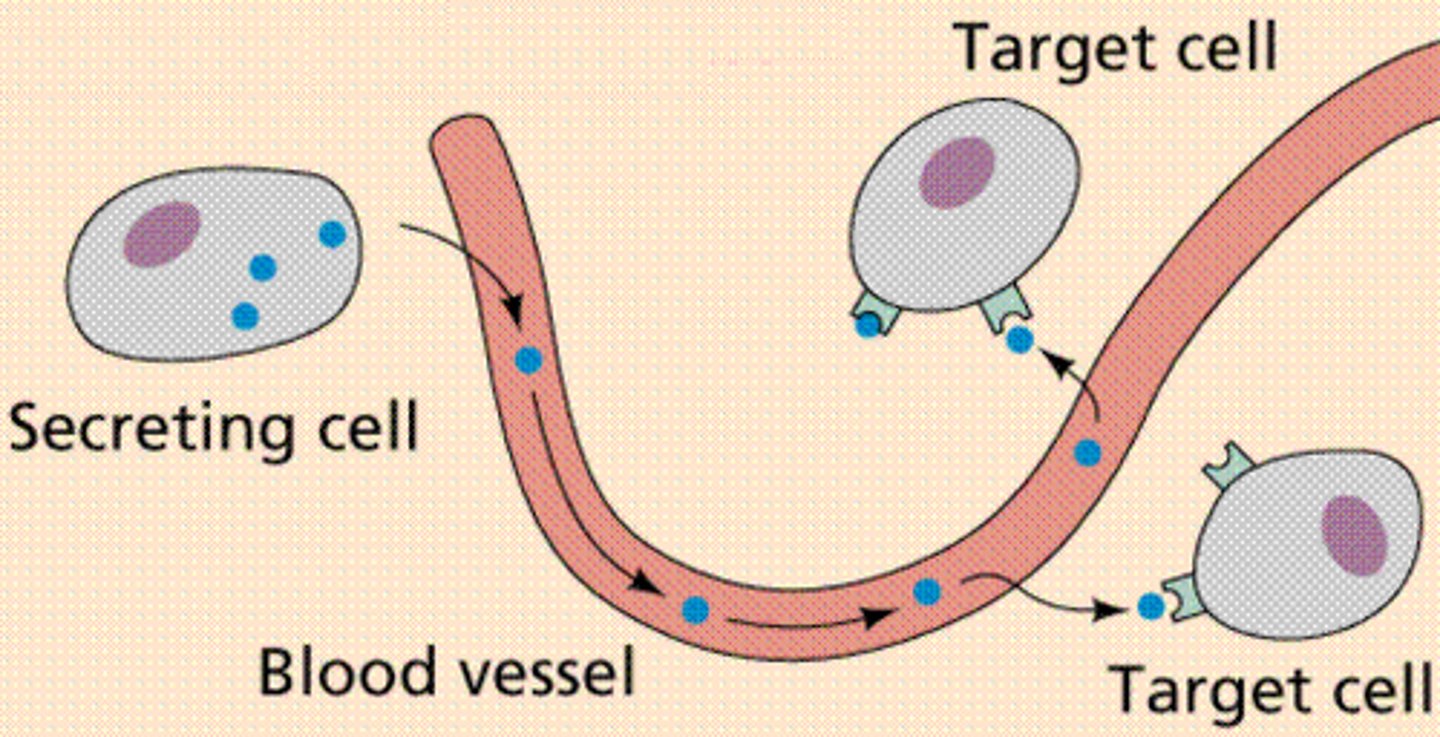
hormones
-secreted from a cell and circulated in the body (travels in blood)
-usually steroids, peptides, or gases
-bind to signal receptor molecules
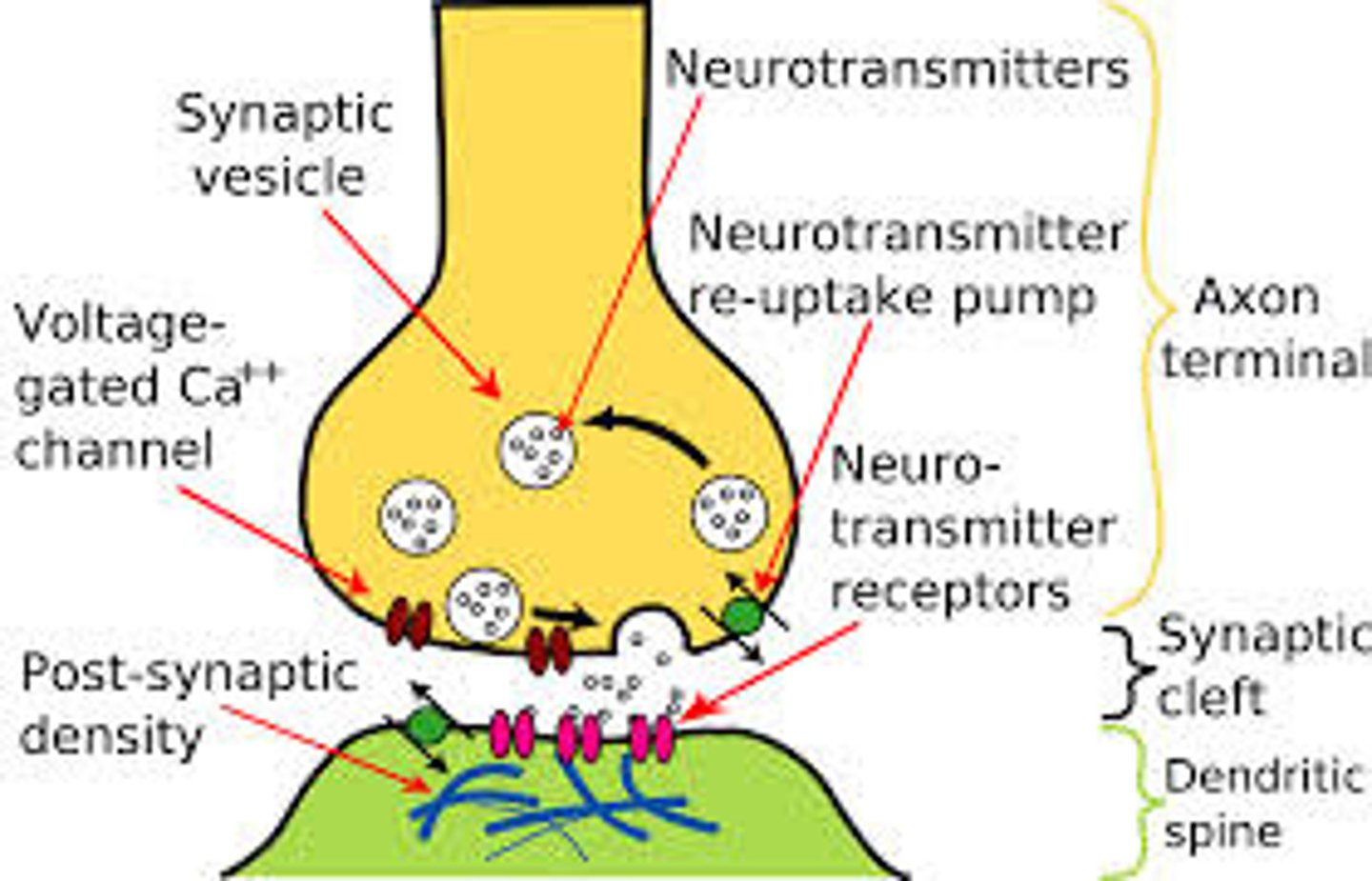
neurotransmitters
may open or close ion channels in a neighboring cell
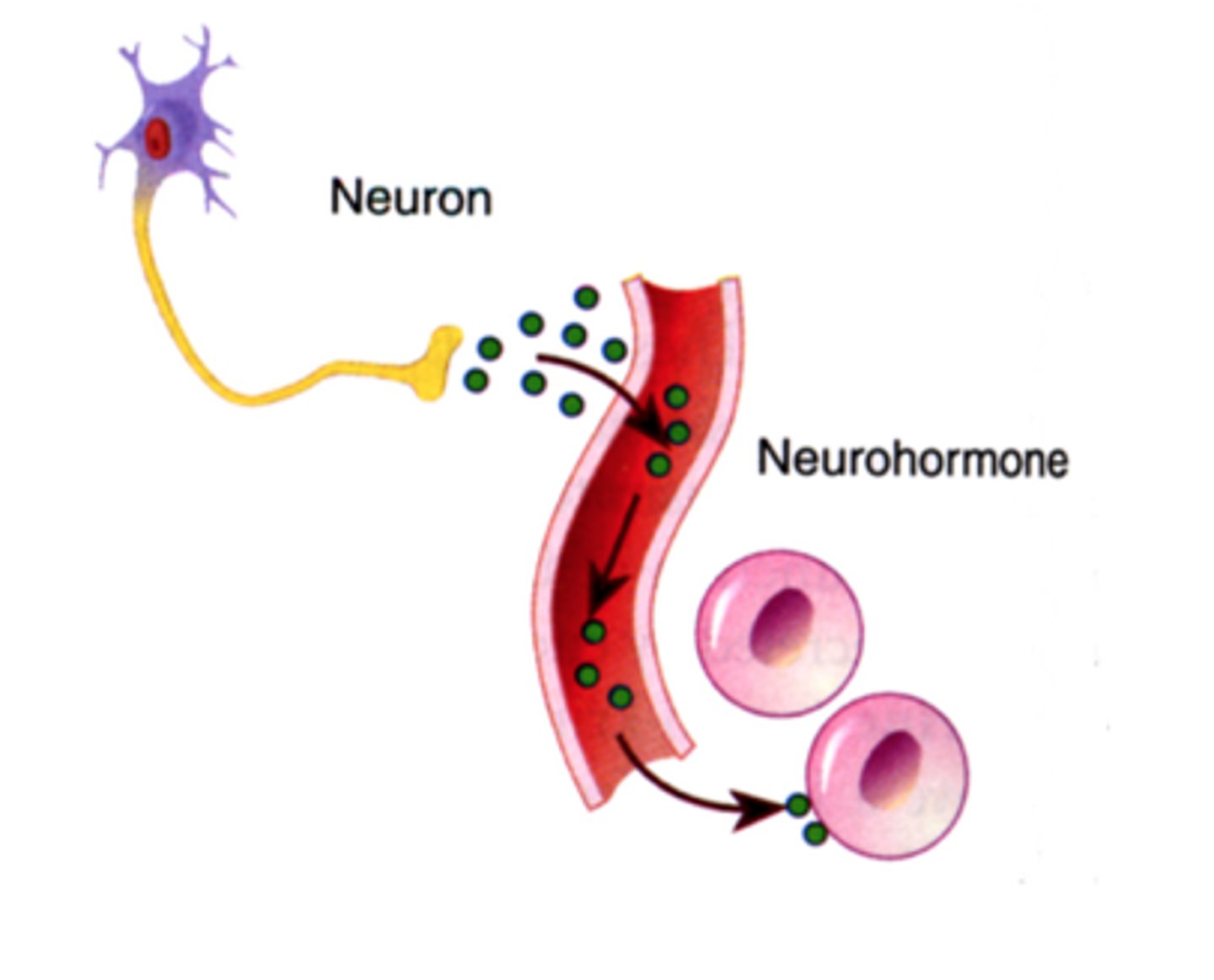
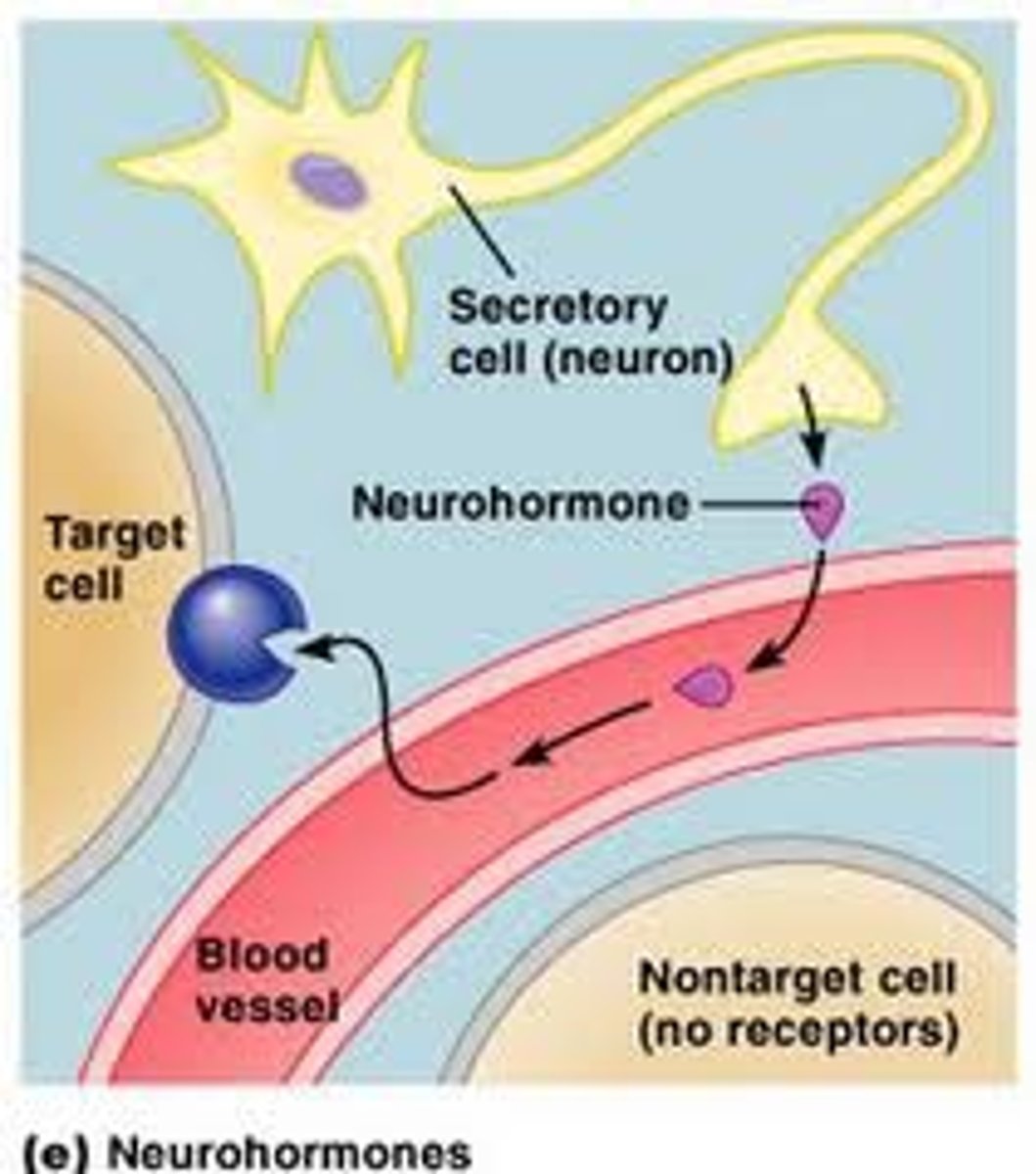
neurohormones(oxytocin)
hormones released from neurons, travel long distances
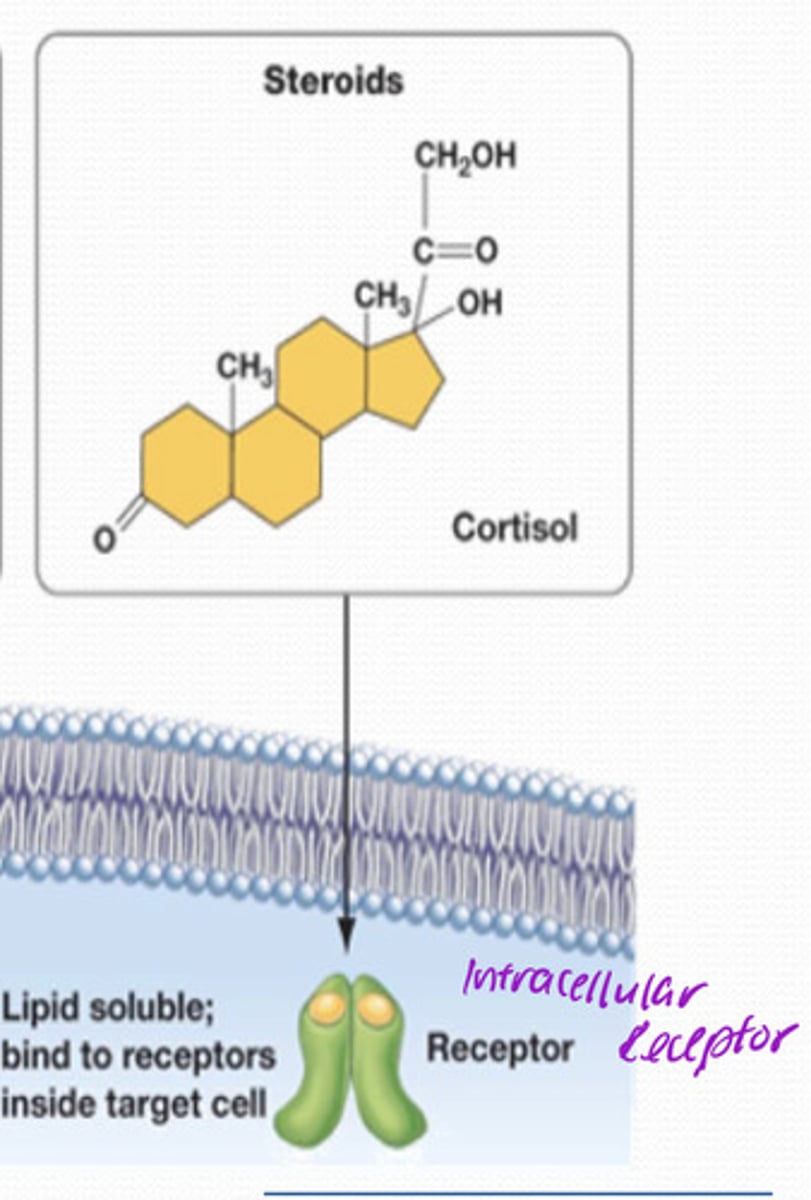
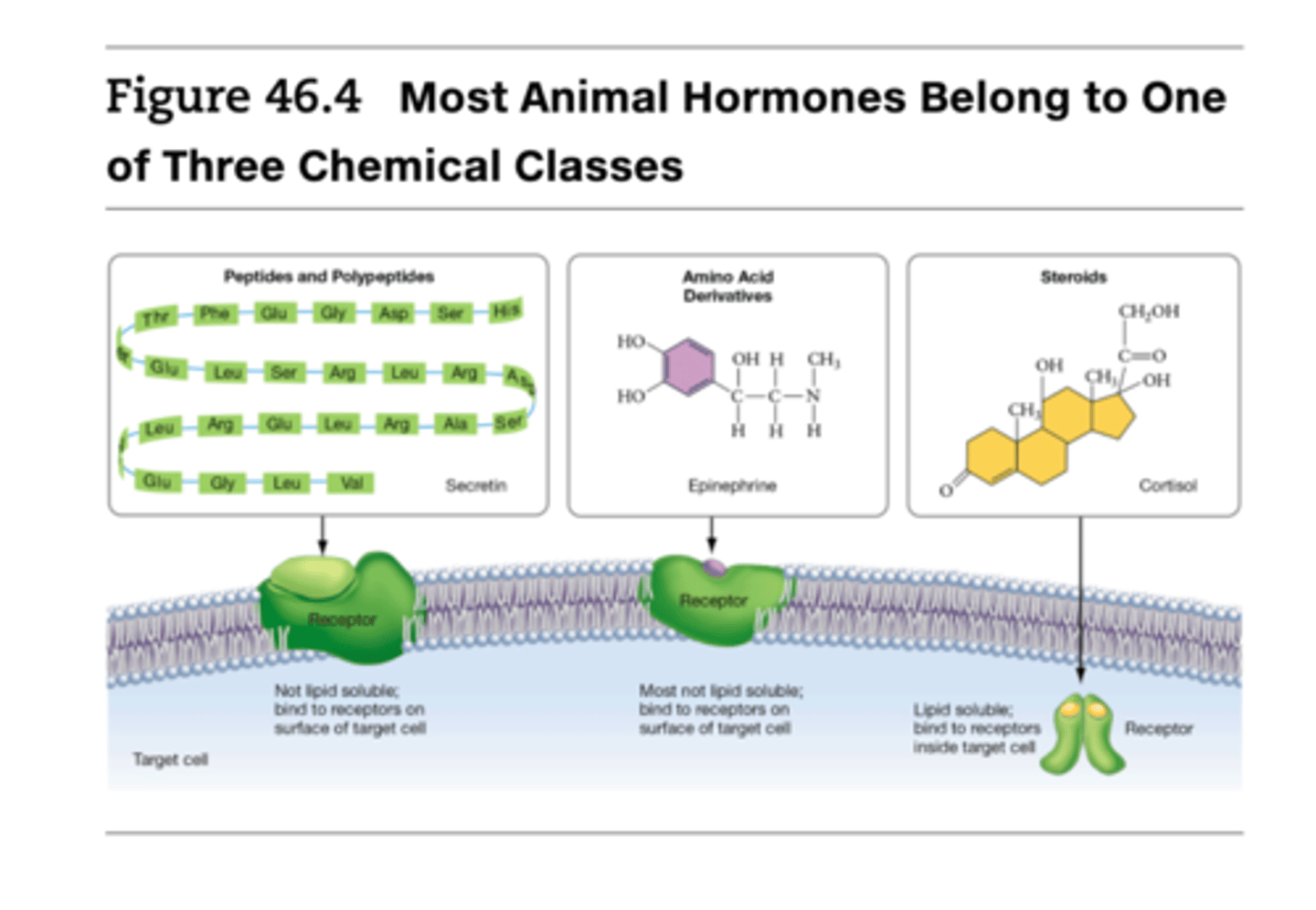
steroids bind to...
cytoplasmic receptor due to their ability to cross the lipid bilayer
peptides, polypeptides, and amino acid derivatives bind to...
can't cross lipid bilayer and bind to integral membrane receptor
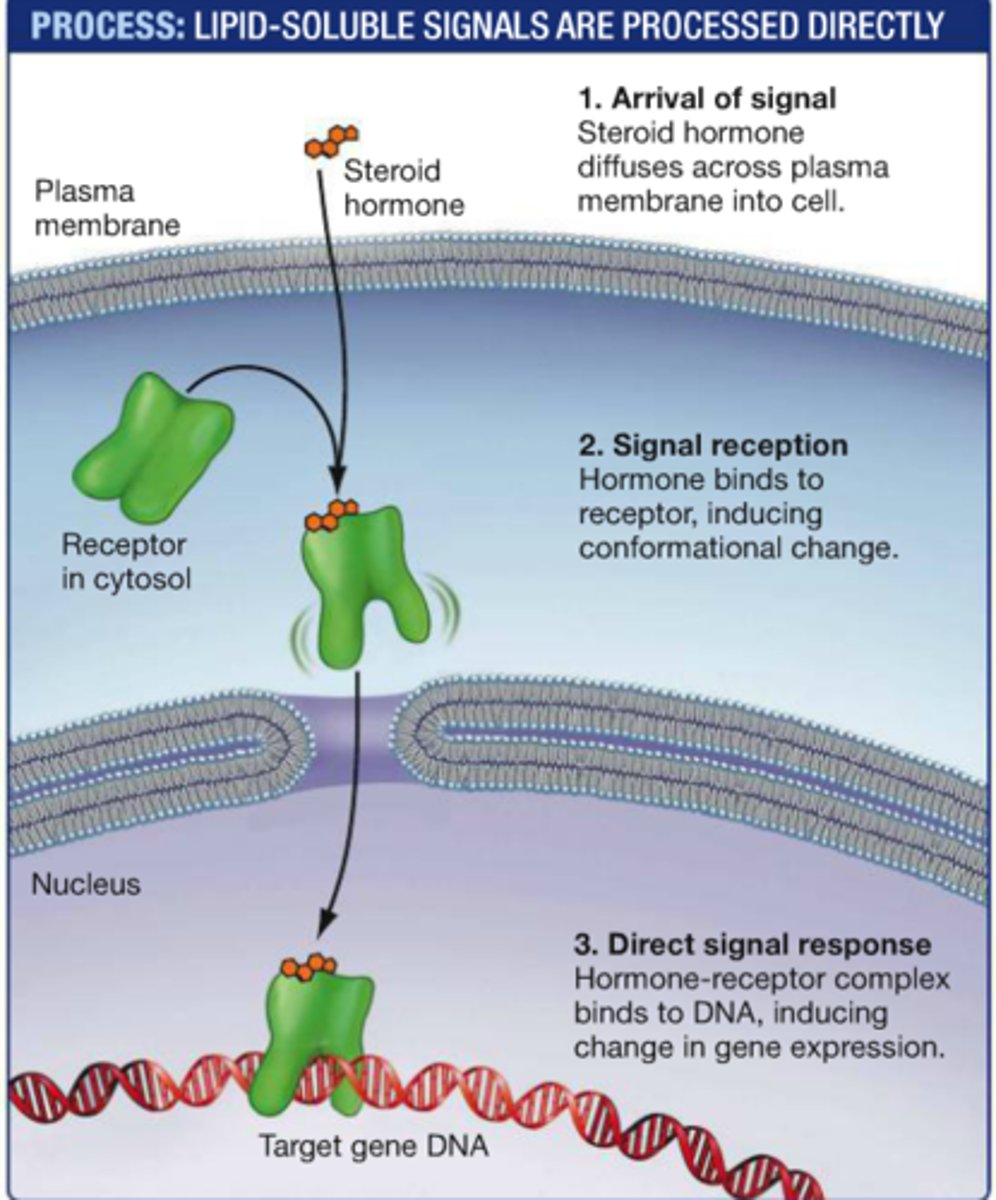
lipid soluble signals
enter the cell and bind to receptors in the cytosol
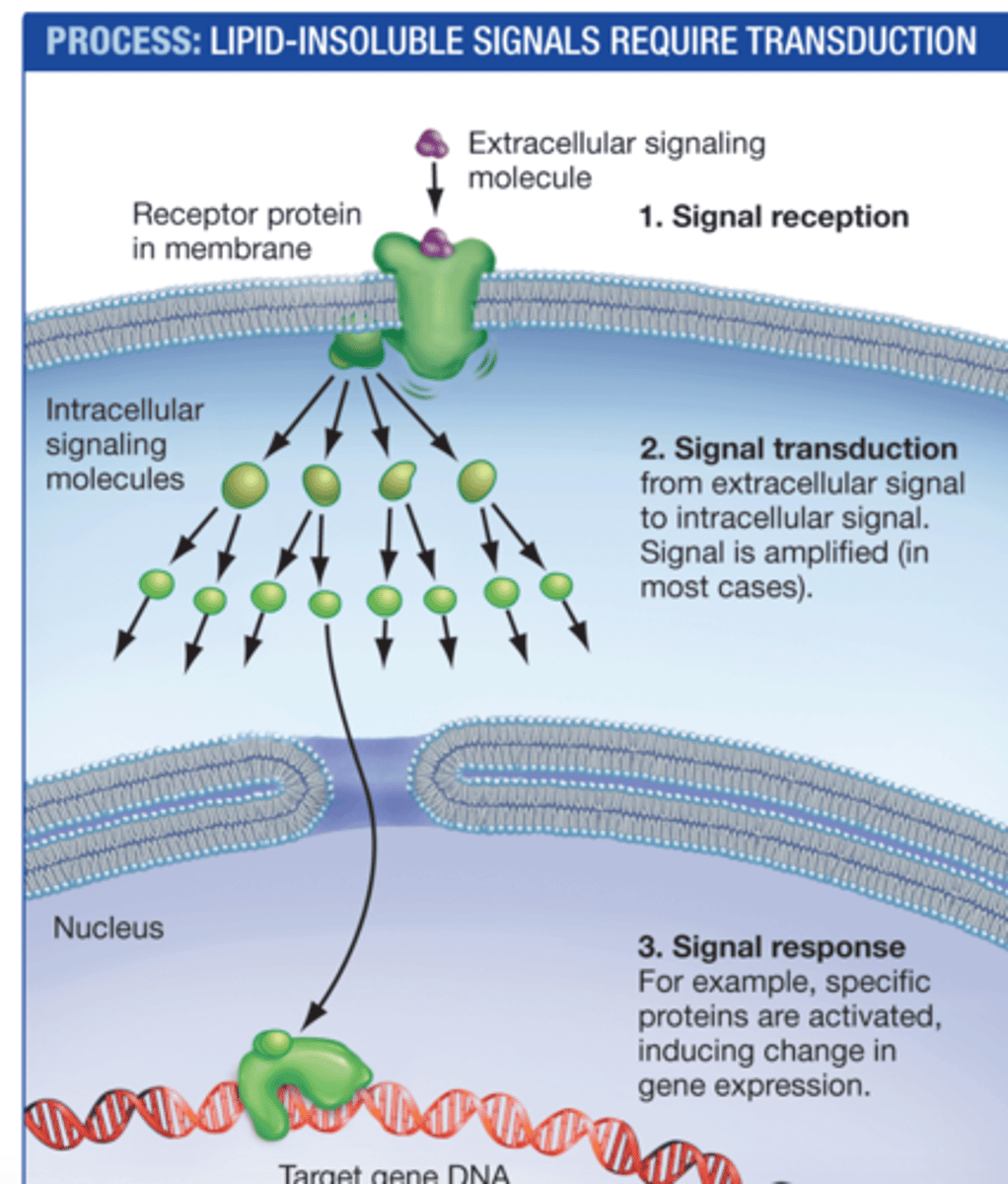
lipid insoluble/large hormones
-bind to receptors on the plasma membrane
-signal then transduced and amplified inside cell using 2nd messengers
-leads to enzyme activity, cytoskeletal organization, or gene expression
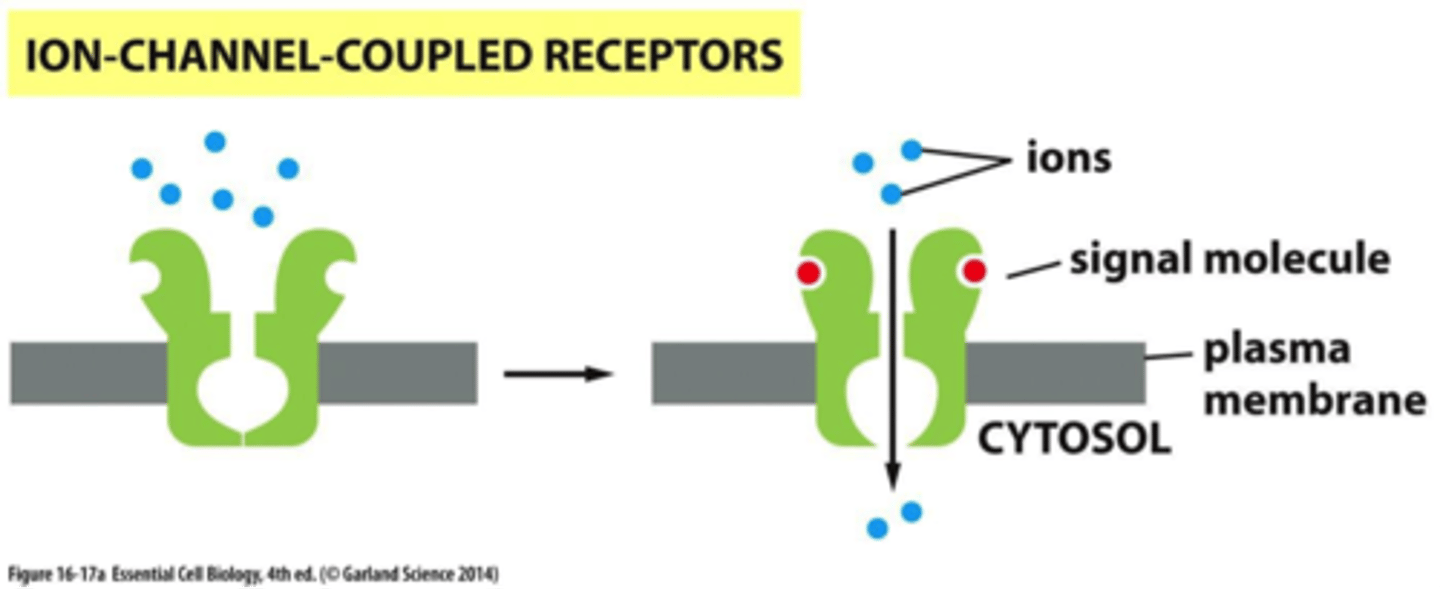
ion channel-coupled receptors (ligand-gated ion channels)
-ion channels opens when small molecule binds to it
-allows ions to move down gradient across membrane
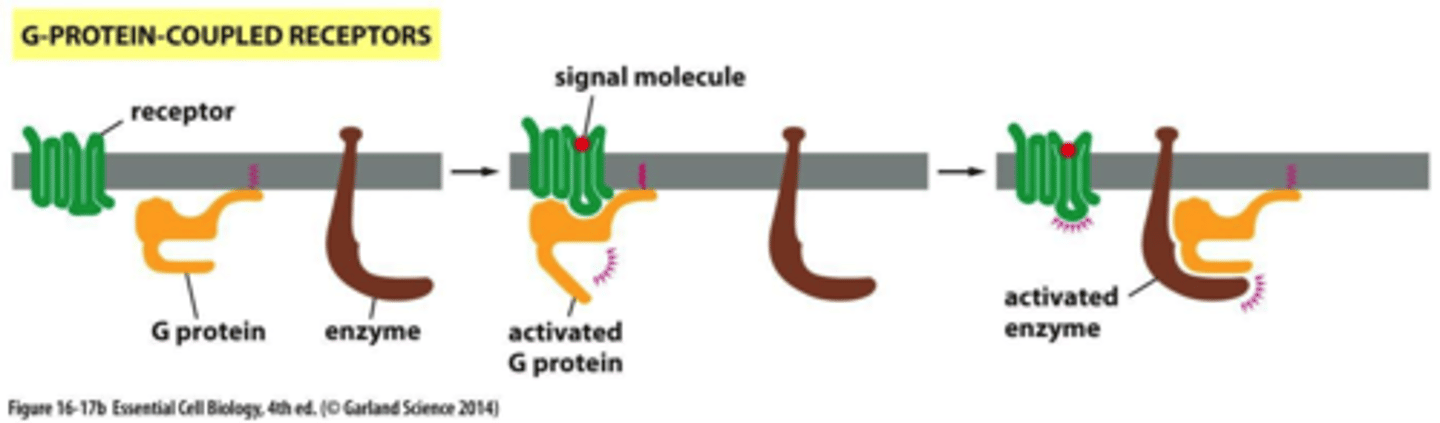
G-protein coupled receptors
consists of: receptor in the membrane, G-protein that is anchored to membrane, and target enzyme
-only on when GTP is bound
second messengers
-diffuse rapidly throughout the cell
-can be produced in large quantities
-amplify the hormone signal
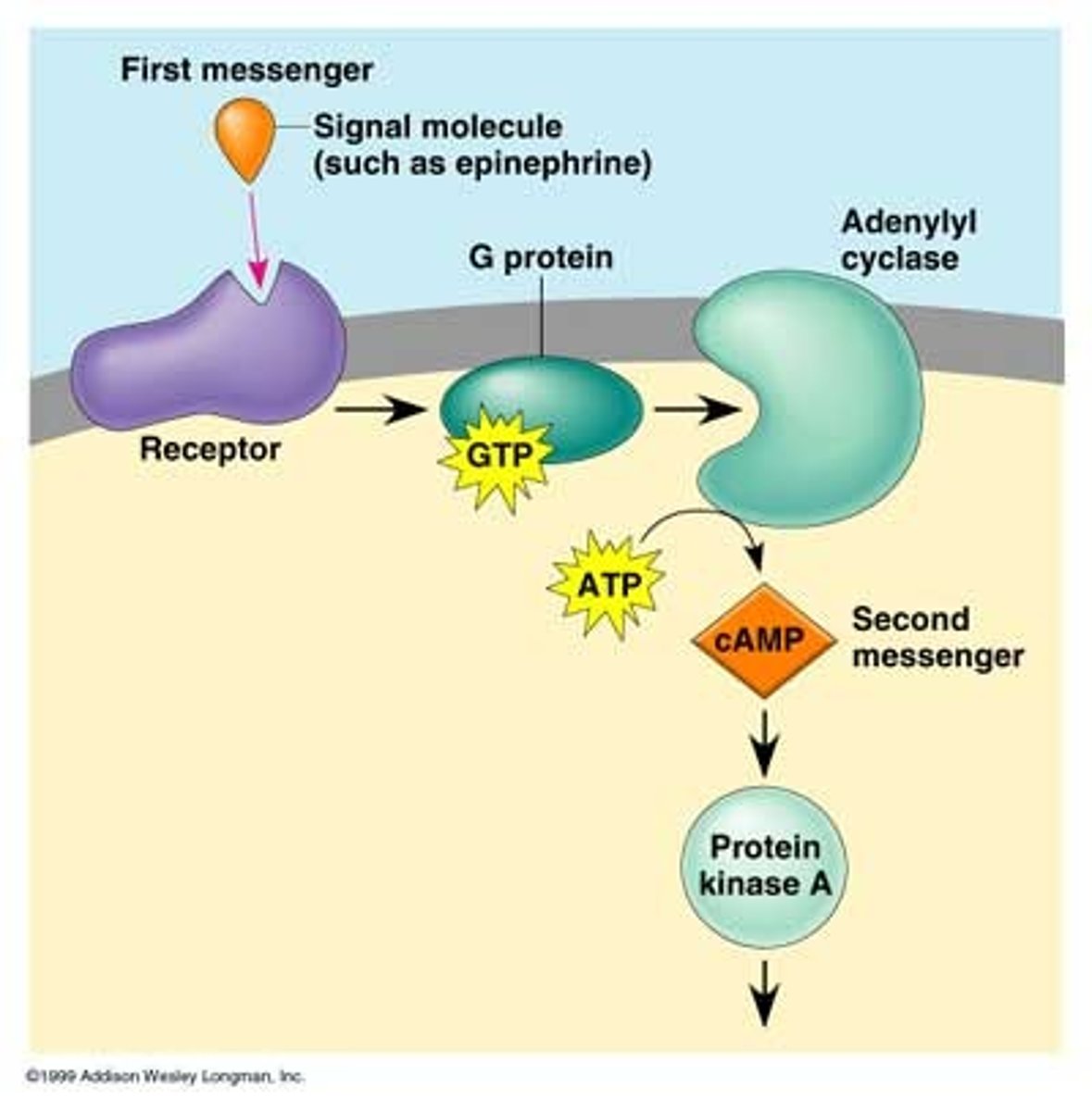
cAMP
2nd messenger produced from ATP that activates protein kinases
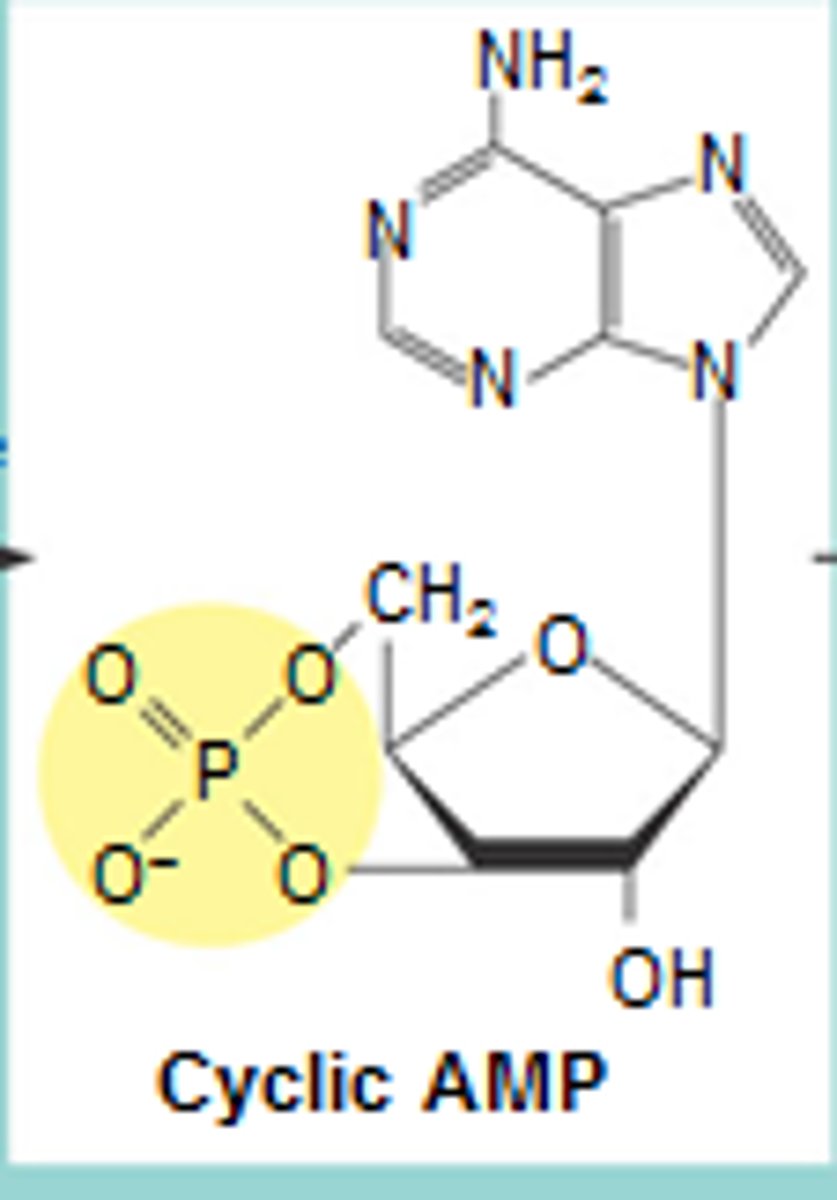
other 2nd messengers that activate protein kinases
PKA, phosphorylates other proteins
enzyme-linked receptors
-transmembrane proteins
-bind dimerized hormone signal(receptor is enzyme)
-enzymes phosphorylate each other
-bridging proteins activate RAS by switching out GDP for GTP
-then phosphorylation cascade
exp: receptor tyrosine kinases
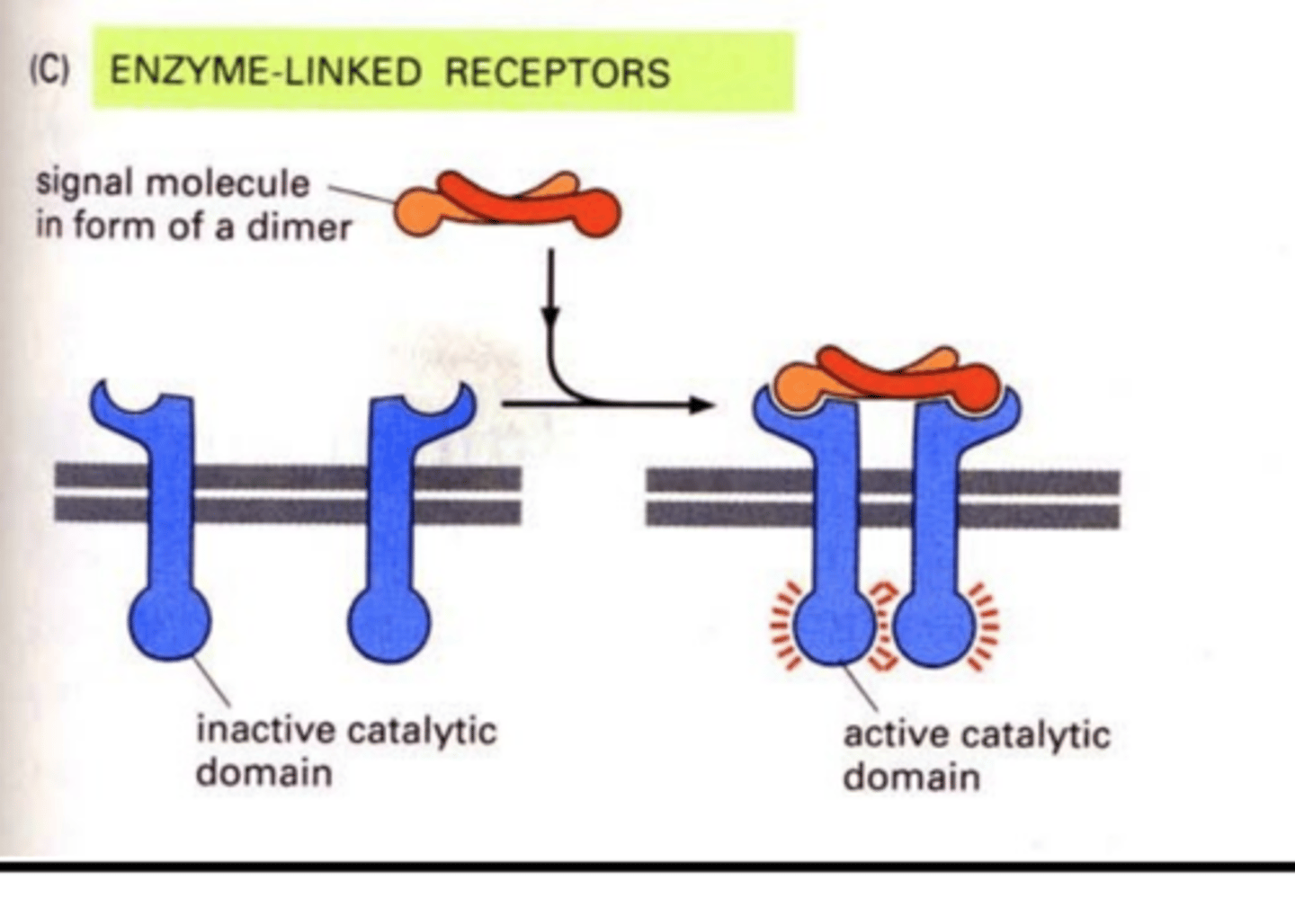
Why do target cells respond in different way to same hormone?
-signal transduction pathways are diverse
-diff 2nd messengers and enzyme systems
-diff amplification steps, protein kinases, or active genes
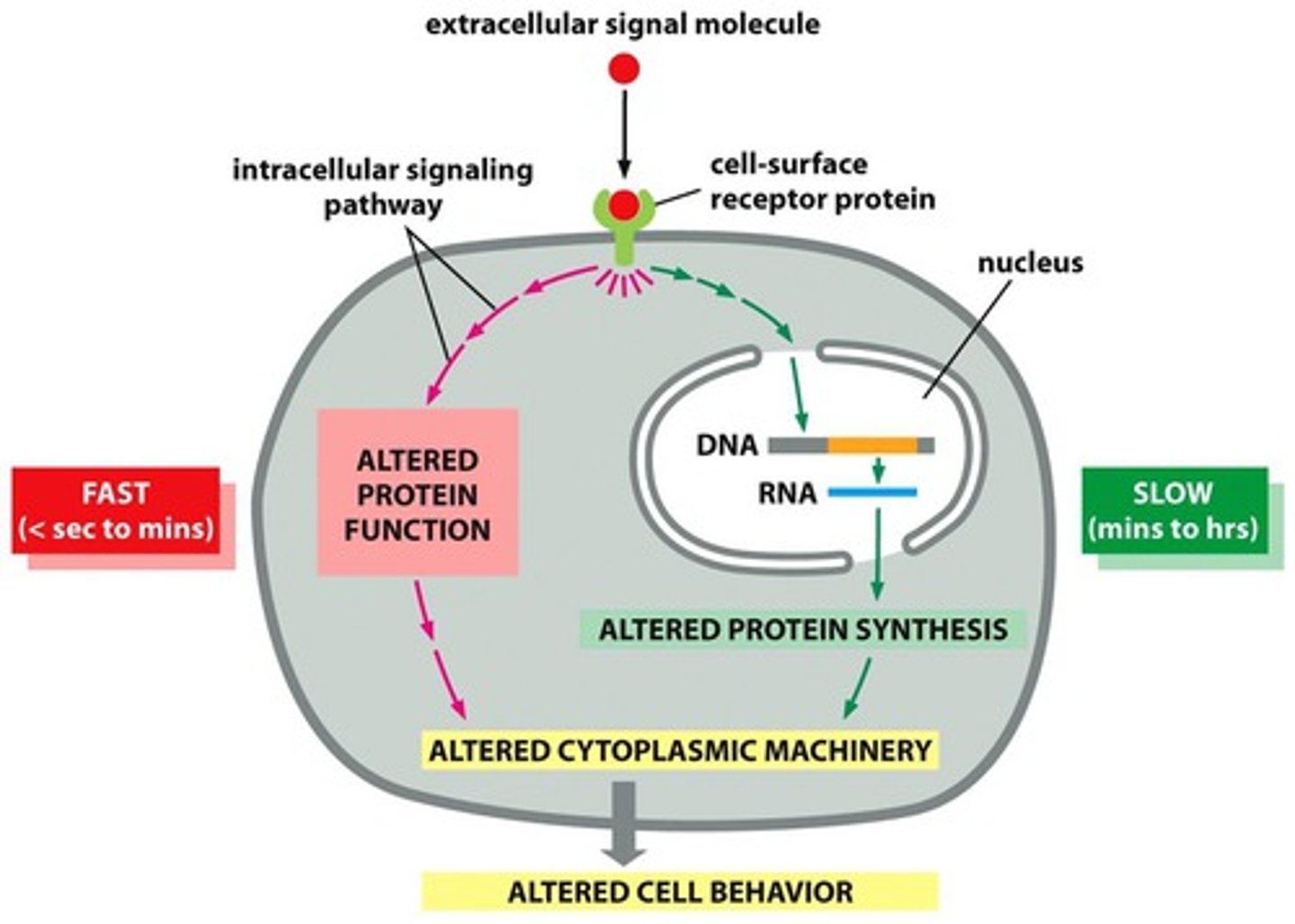
fast signal responses
a change in activation of a particular target protein that already exists in the cell (involves 2nd messengers)
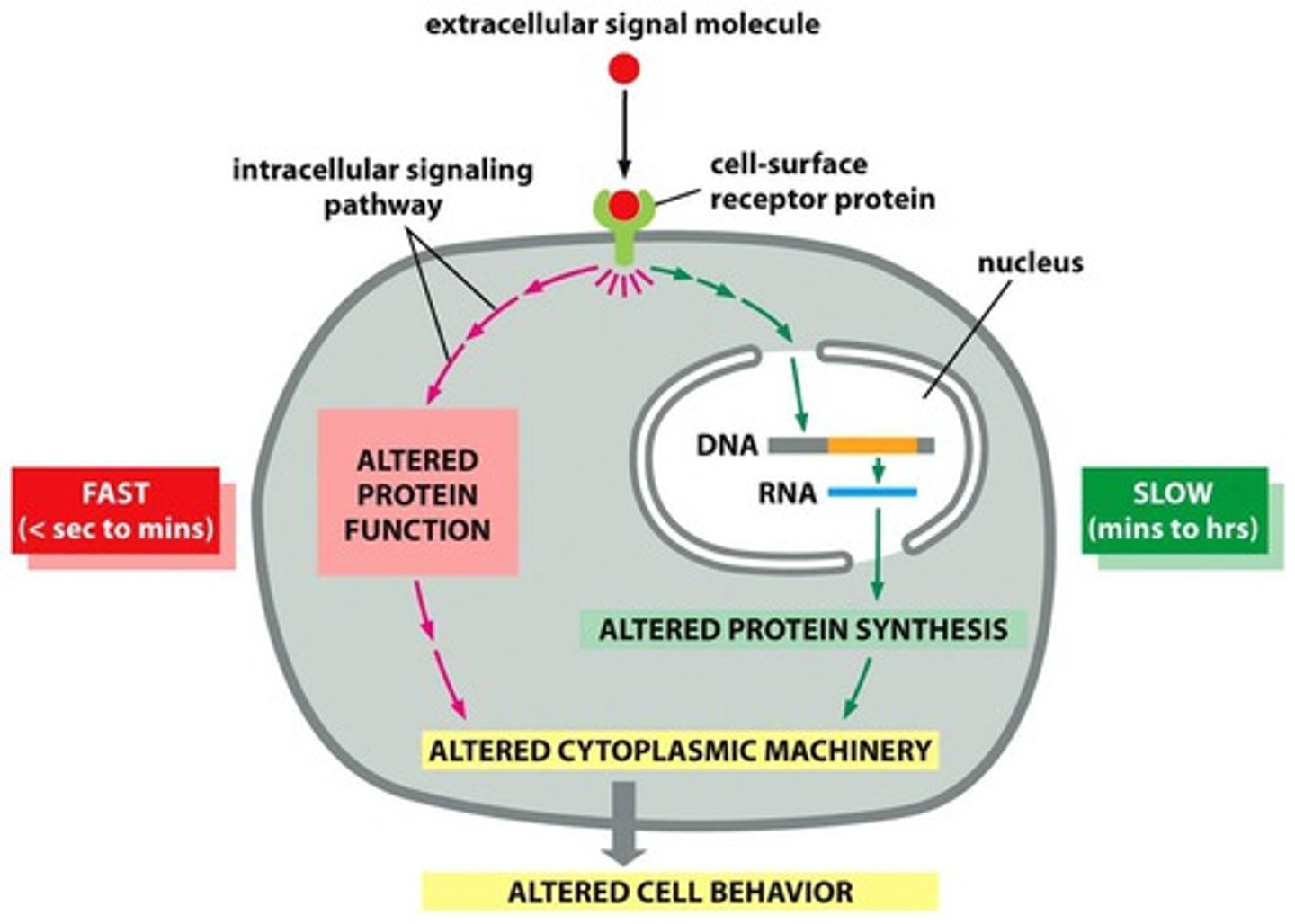
slow signal responses
a change in which genes are being expressed in the target cell
signal deactivation
cells have automatic and rapid mechanisms for signal deactivation
phosphatase
deactivates signal by removing a phosphate
hydrolysis of GTP
deactivates signal in paths involving G-proteins
phosphodiesterases cleave cAMP
deactivates signal by turning off 2nd messenger
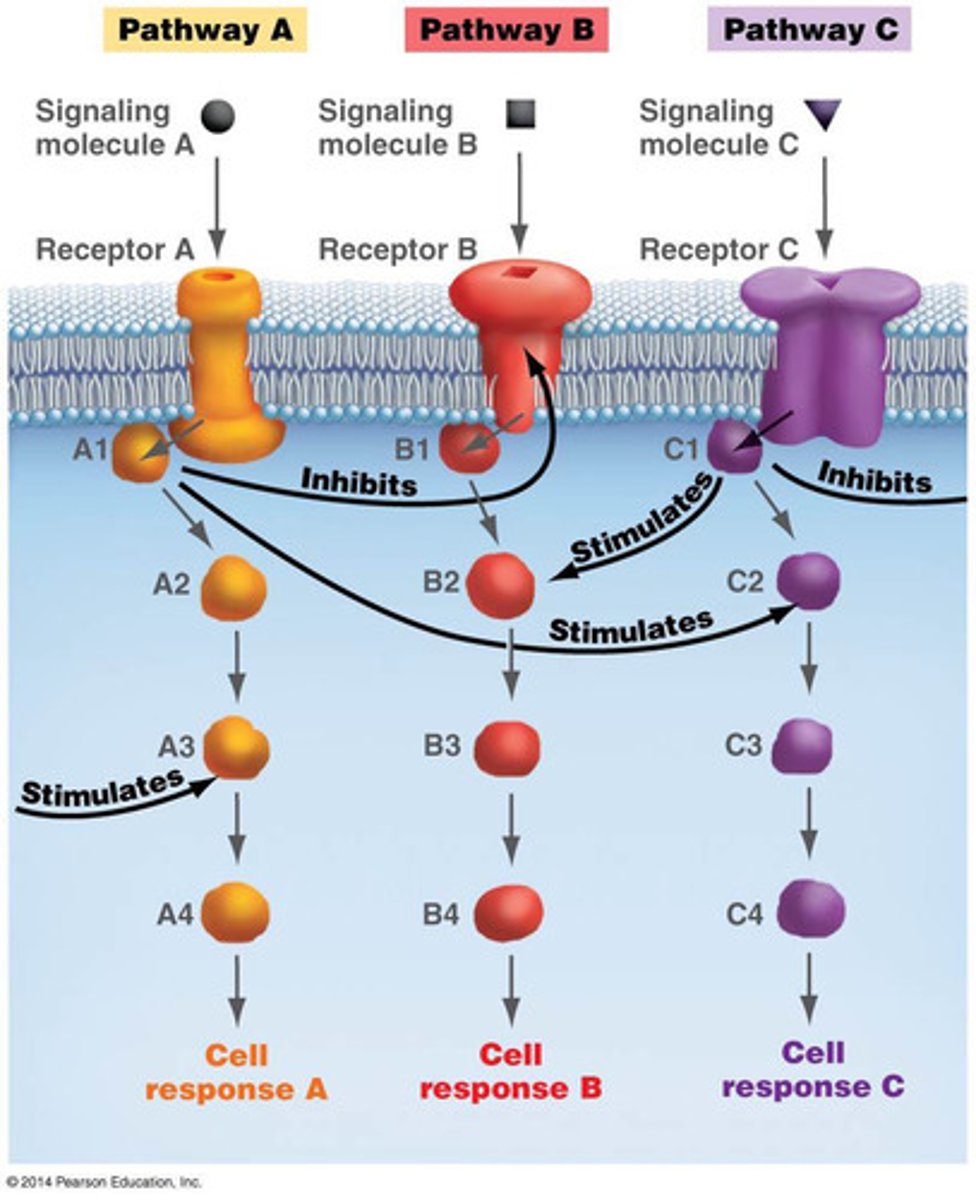
crosstalk
-signaling pathways interact using this
-a pathway can inhibit or stimulate another
-there are multiple potential points for crosstalk