Paper 1 Quiz - Momentum
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
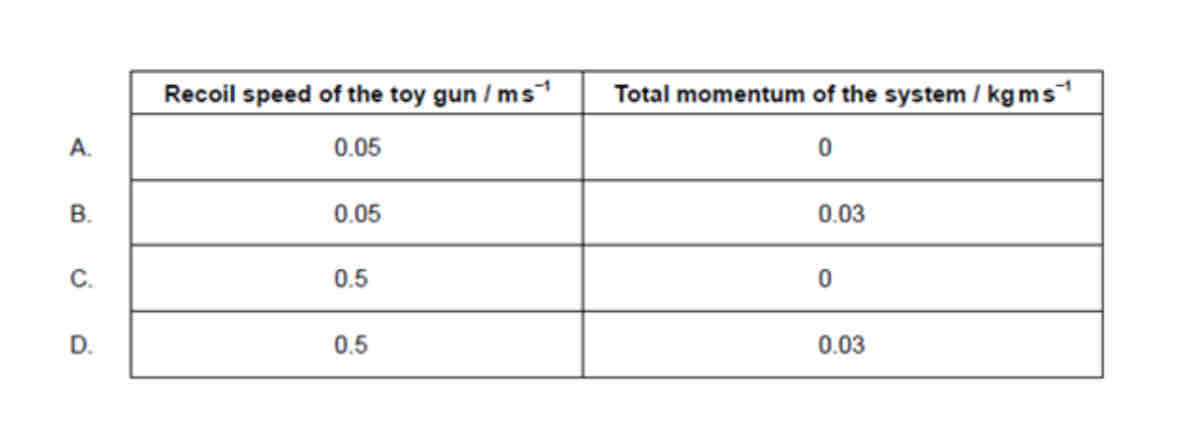
A table-tennis ball of mass 3 g is fired with a speed of 10 m s^-1 from a stationary toy gun of mass 0.600 kg. The gun and ball are an isolated system. What are the recoil speed of the toy gun and the total momentum of the system immediately after the gun is fired?
ANSWER: A
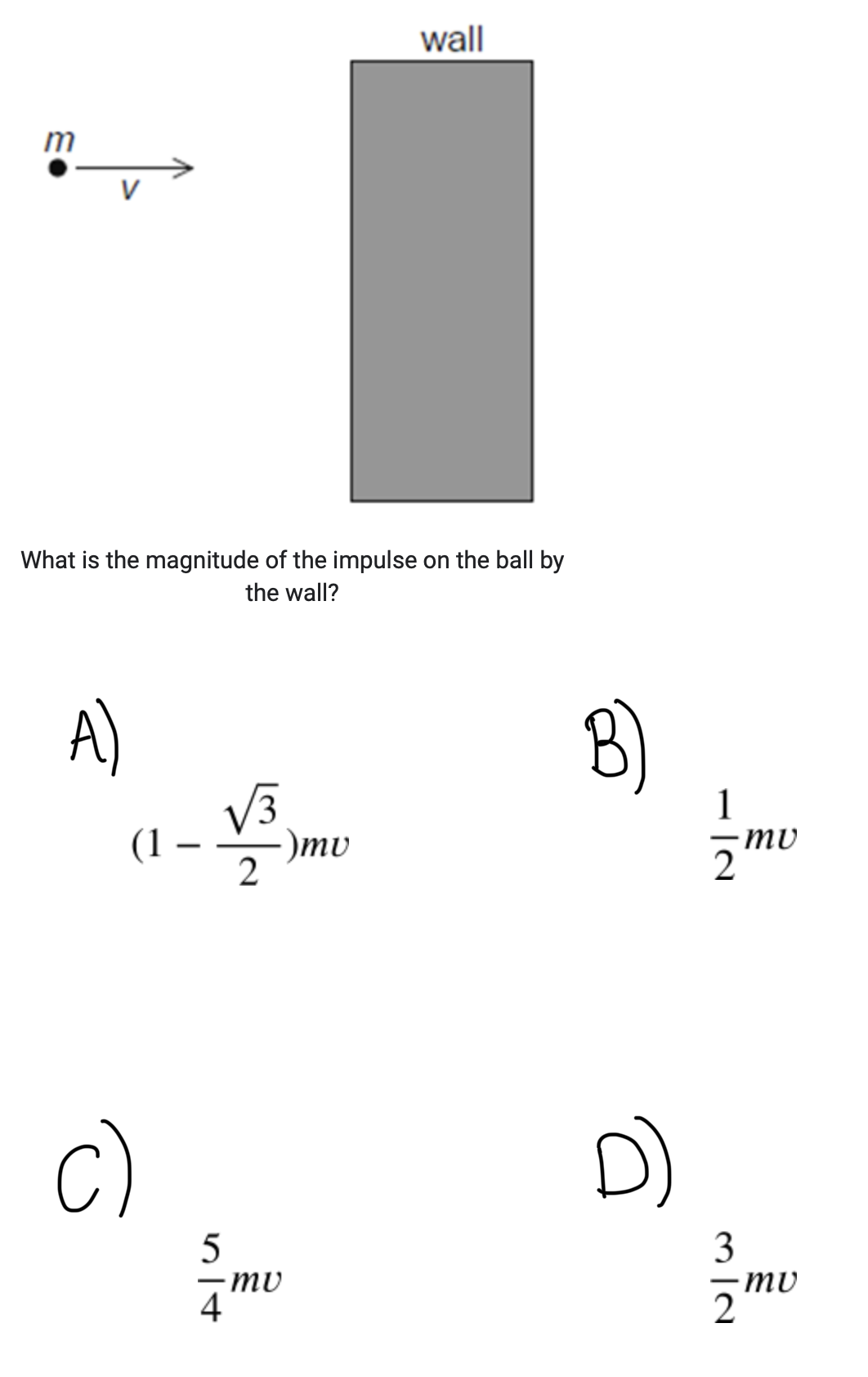
A ball of mass m collides with a wall and bounces back in a straight line. The ball loses 75 % of the initial energy during the collision. The speed before the collision is v.
ANSWER: D
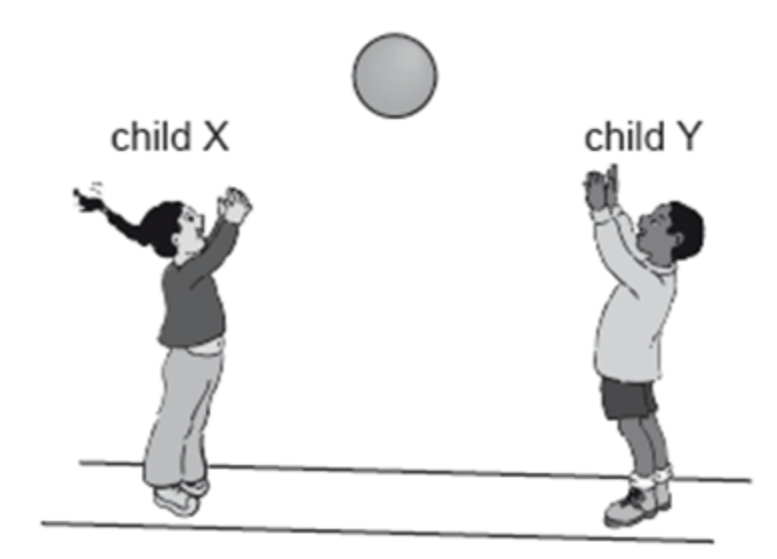
Child X throws a ball to child Y. The system consists of the ball, the children and the Earth. What is true for the system when the ball has been caught by Y?
A. The momentum of child Y is equal and opposite to the momentum of child X.
B. The speed of rotation of the Earth will have changed.
C. The ball has no net momentum while it is in the air.
D. The total momentum of the system has not changed.
ANSWER:D
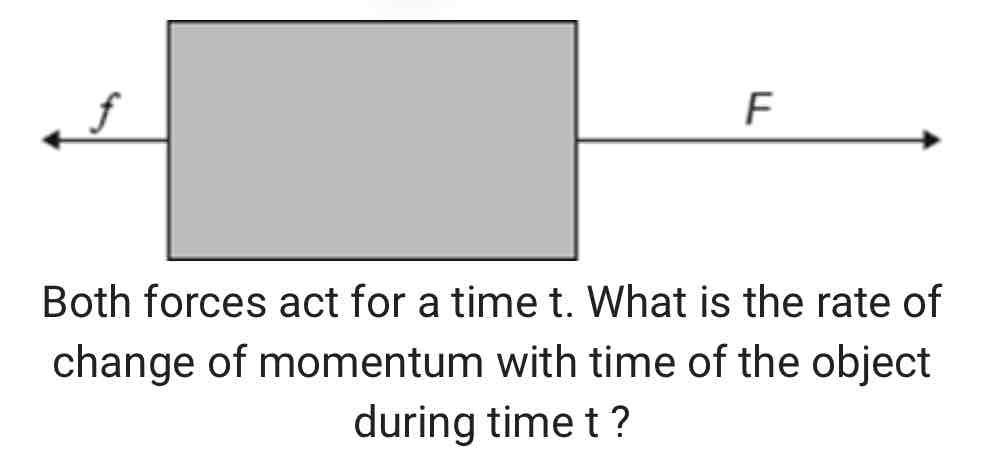
An object is moving in a straight line. A force F and a resistive force f act on the object along the straight line.
A. F + f
B. F – f
C. (F + f )t
D. (F – f )t
ANSWER: B
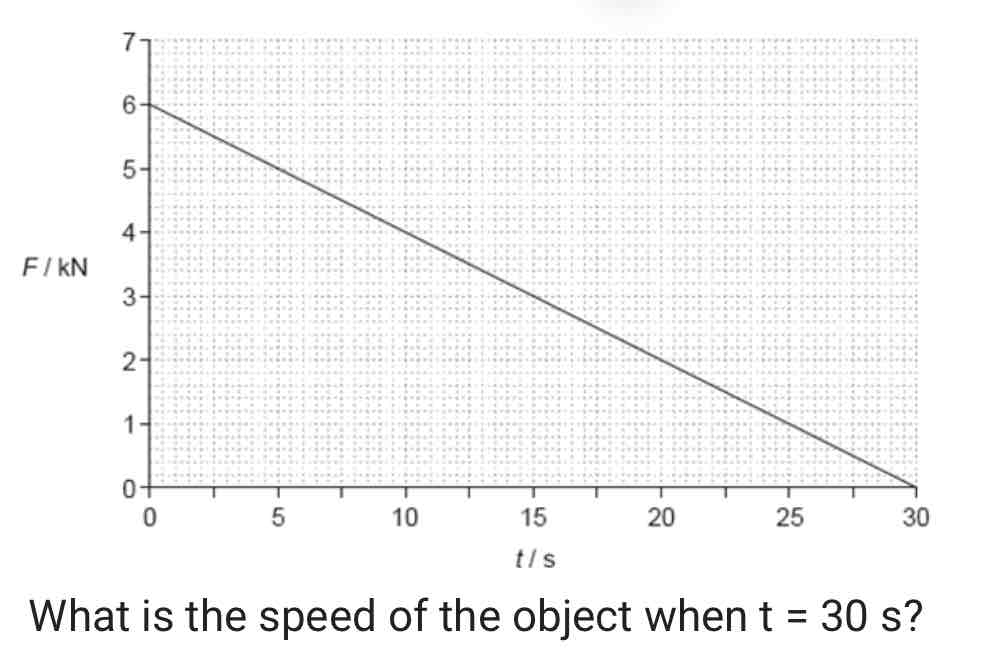
The graph shows the variation with time t of the force F acting on an object of mass 15 000 kg. The object is at rest at t = 0.
A. 0.18 m s^–1
B. 6 m s^–1
C. 12 m s^–1
D. 180 m s^–1
ANSWER: B
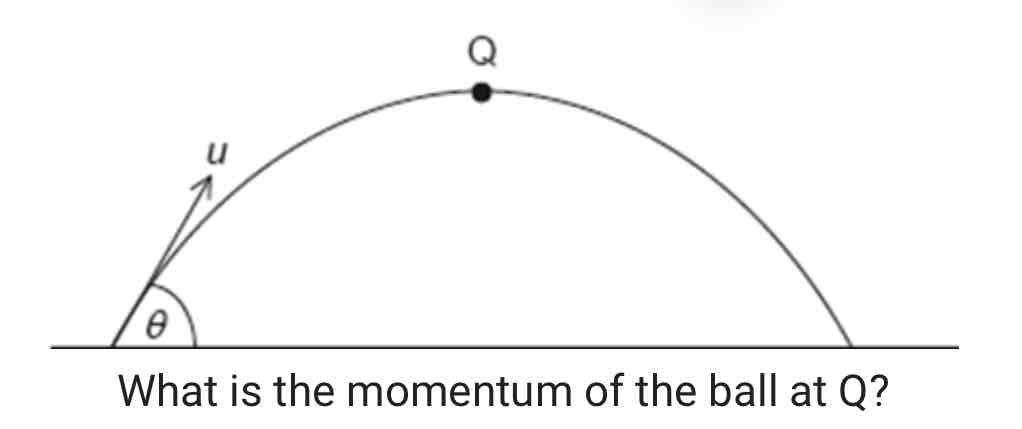
A ball of mass m is thrown with an initial speed of u at an angle θ to the horizontal as shown. Q is the highest point of the motion. Air resistance is negligible.
A. zero
B. mu cosθ
C. mu
D. mu sinθ
ANSWER: B
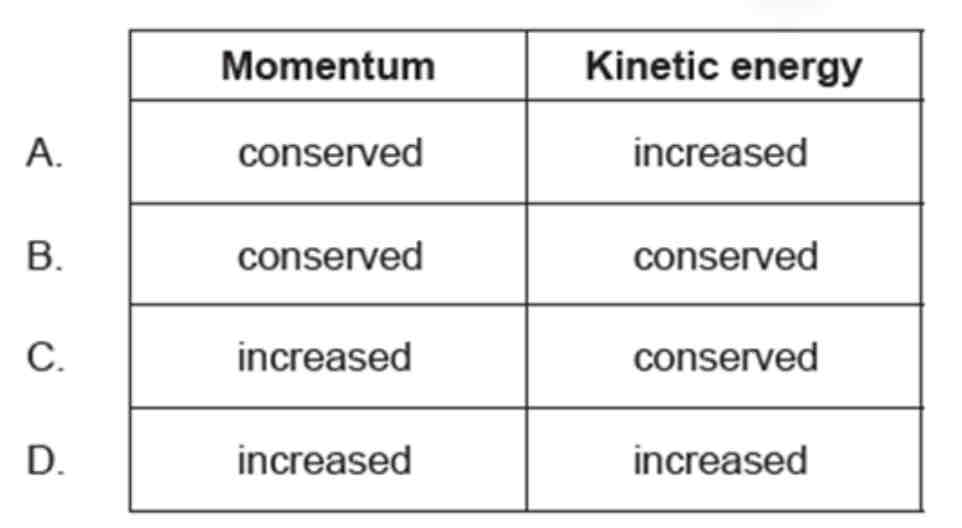
A moving system undergoes an explosion. What is correct for the momentum of the system and the kinetic energy of the system when they are compared immediately before and after the explosion?
ANSWER: A
An inelastic collision occurs between two bodies in the absence of external forces. What must be true about the total momentum of the two bodies and the total kinetic energy of the two bodies during this interaction?
A. Only momentum is conserved.
B. Only kinetic energy is conserved.
C. Both momentum and kinetic energy are conserved.
D. Neither momentum nor kinetic energy are conserved.
ANSWER: A
A net force acts on a body. Which characteristic of the body will definitely change?
A. Speed
B. Momentum
C. Kinetic energy
D. Direction of motion
ANSWER: B
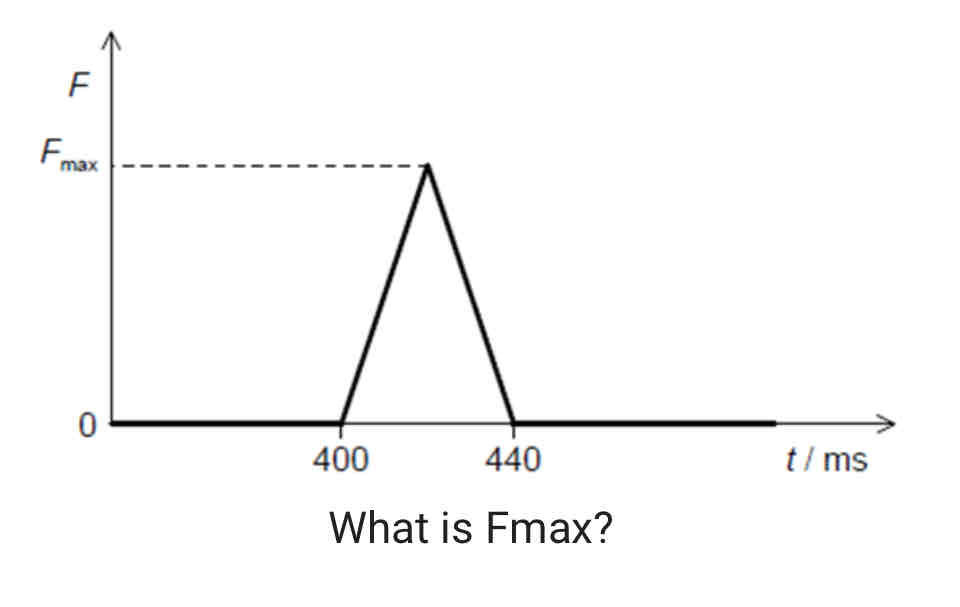
A ball of mass 0.2 kg strikes a force sensor and sticks to it. Just before impact the ball is travelling horizontally at a speed of 4.0 m s^–1. The graph shows the variation with time t of the force F recorded by the sensor.
ANSWER: 40N
A ball of mass m strikes a vertical wall with a speed v at an angle of θ to the wall. The ball rebounds at the same speed and angle. What is the change in the magnitude of the momentum of the ball?
A. 2 mv sin θ
B. 2 mv cos θ
C. 2 mv
D. zero
ANSWER: B
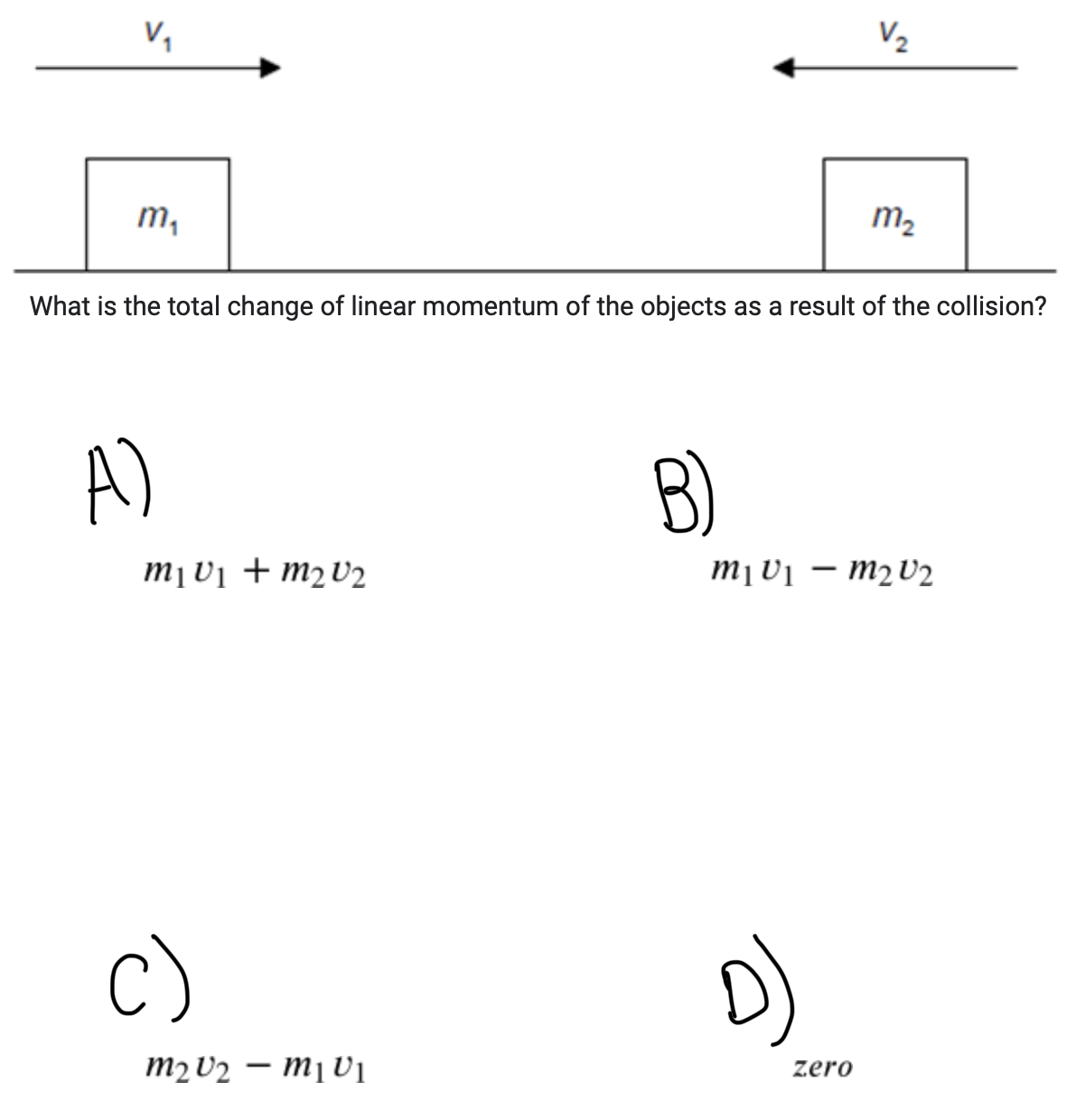
Two objects m1 and m2 approach each other along a straight line with speeds v1 and v2 as shown. The objects collide and stick together.
ANSWER: D
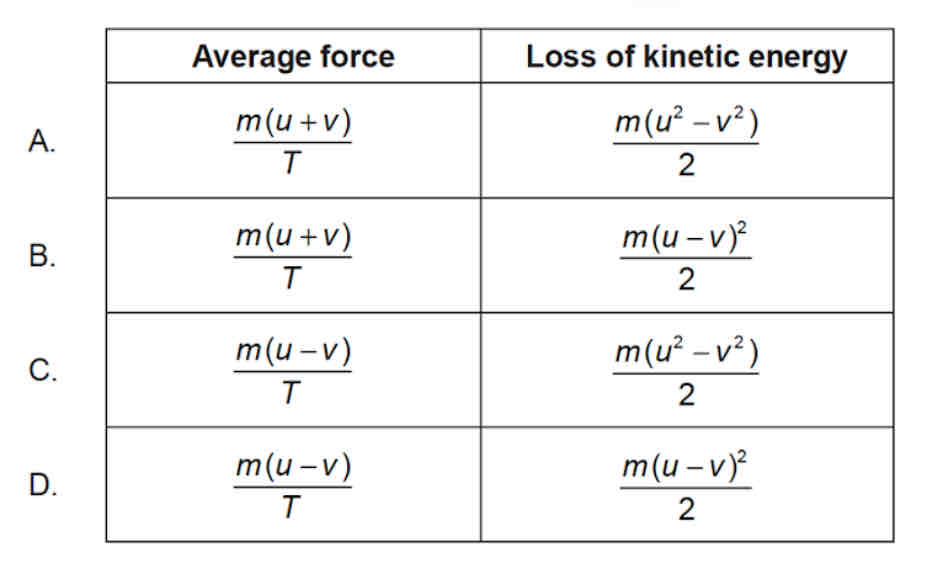
A ball with mass m moves horizontally with speed u. The ball hits a vertical wall and rebounds in the opposite direction with speed v<u. The duration of the collision is T. What are the magnitude of the average force exerted by the wall on the ball and the loss of kinetic energy of the ball?
ANSWER: A
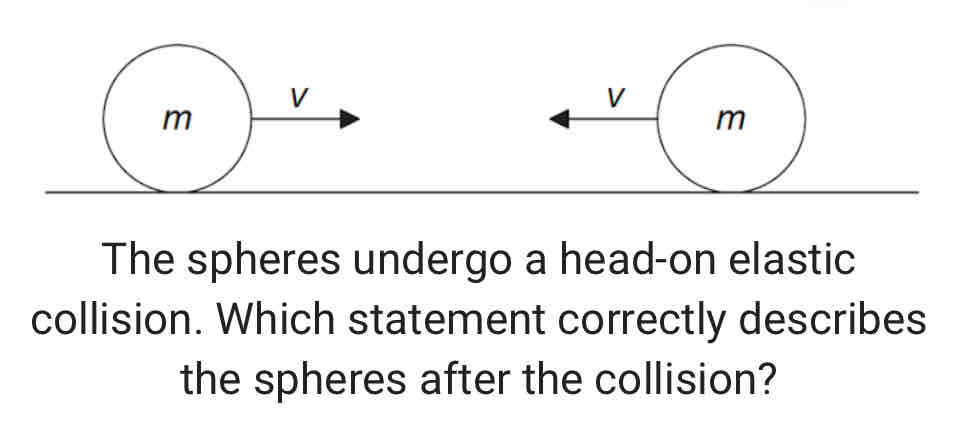
Two identical spheres, each of mass m and speed v, travel towards each other on a frictionless surface in a vacuum.
A. The total momentum of the spheres is 2mv.
B. Each sphere has zero momentum.
C. The total kinetic energy of the spheres is mv^2.
D. Each sphere has zero kinetic energy.
ANSWER: C
A block of mass 2.0 kg accelerates from a speed of 15 m s−1 to a speed of 20 m s−1 without changing its direction. What impulse acts on the block?
A. 2.5 N s
B. 5.0 N s
C. 10 N s
D. 17.5 N s
ANSWER: C
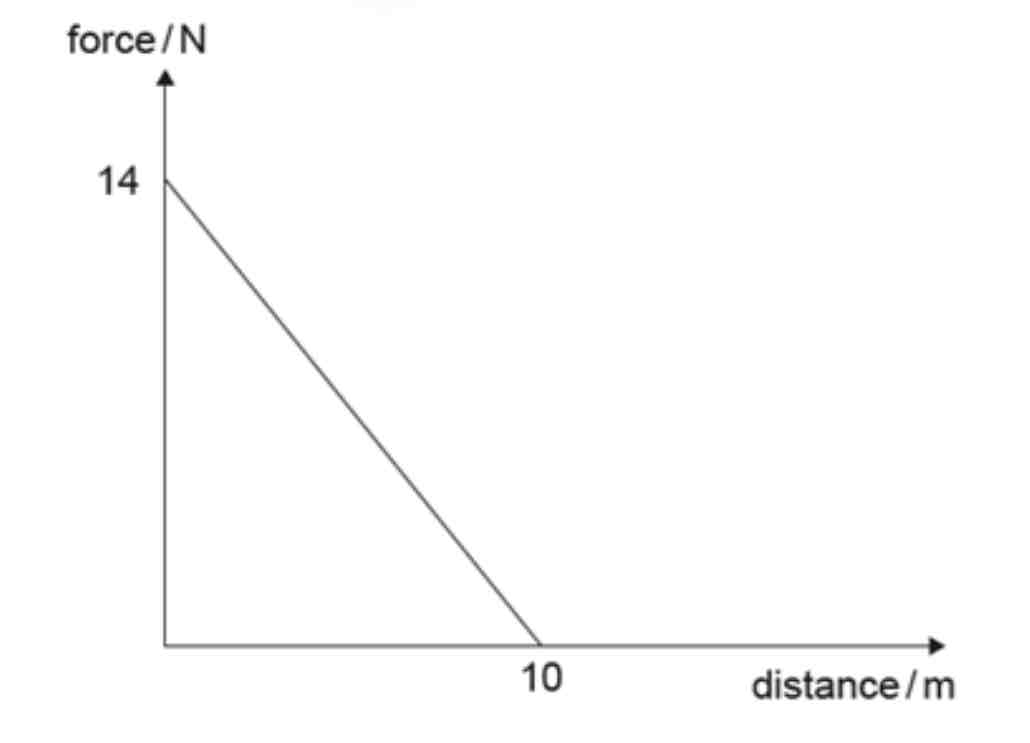
A mass of 4.0 kg moving with a velocity of 1.0 m s−1 is acted on by a net force which varies with distance as shown. What is the maximum speed of the mass?
A. √35 m s−1
B. 6 m s−1
C. √71 m s−1
D. 12 m s−1
ANSWER: B
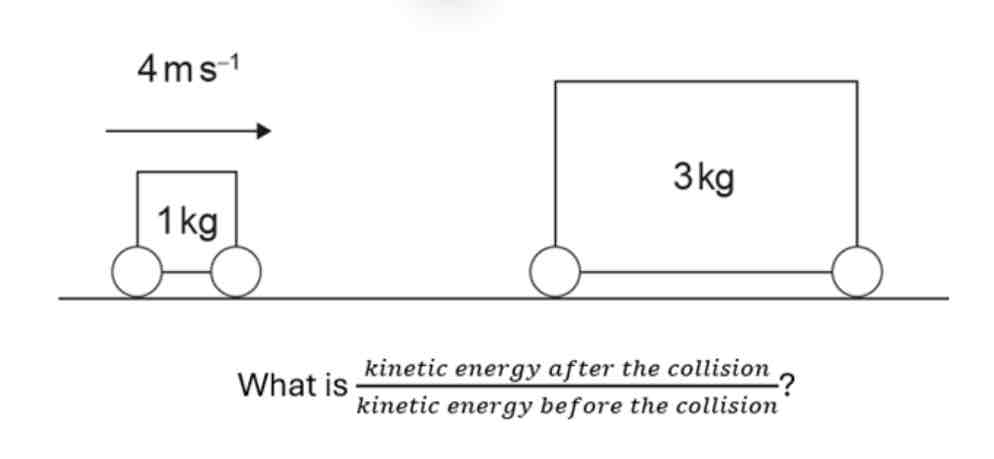
A cart of mass 1 kg moving at 4 m s−1 collides with a stationary cart of mass 3 kg. After the collision the carts stick together.
A. 1/16
B. 1/8
C. 1/4
D. 1/2
ANSWER: C