Topic 6 - plant structures and their functions
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
- photosynthesis - factors affecting photosynthesis- plant cell organisation - transpiration and translocation- plant hormones (auxins and commercial uses)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
What substance absorbs energy required for photosynthesis
Chlorophyll
In what part of the plant/cell does photosynthesis take place
Leaves, chloroplast
What is the word equation for photosynthesis
Carbon dioxide + water = glucose + oxygen
What is the chemical equation for photosynthesis
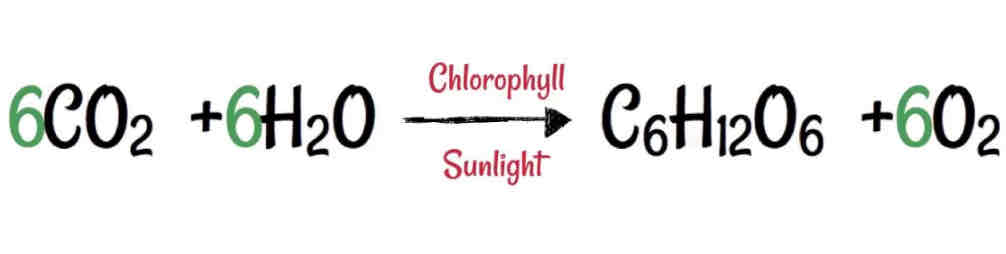
What type of reaction is photosynthesis
Endothermic
What can glucose made in photosynthesis be used for
Cellular respiration (break down glucose to release energy)
Make cellulose (used to make strong cell walls)
Make starch (used to store glucose)
Make amino acids (used to make proteins)
Make lipids (store energy as fats or oils)
How do plants get carbon dioxide for photosynthesis
Diffuses from the air into the leaves via stomata
How do plants get water for photosynthesis
Diffuses from soil into root hair cells by osmosis
What makes starch a useful long term storage molecule
easily broken down when needed
Compact
Insoluble in water
What else do plants need to make amino acids other than glucose
Nitrate ions
Which useful energy transfer happens overall in photosynthesis
Light → chemical
Why may plants not produce enough chlorophyll
lack required nutrients
Have a disease
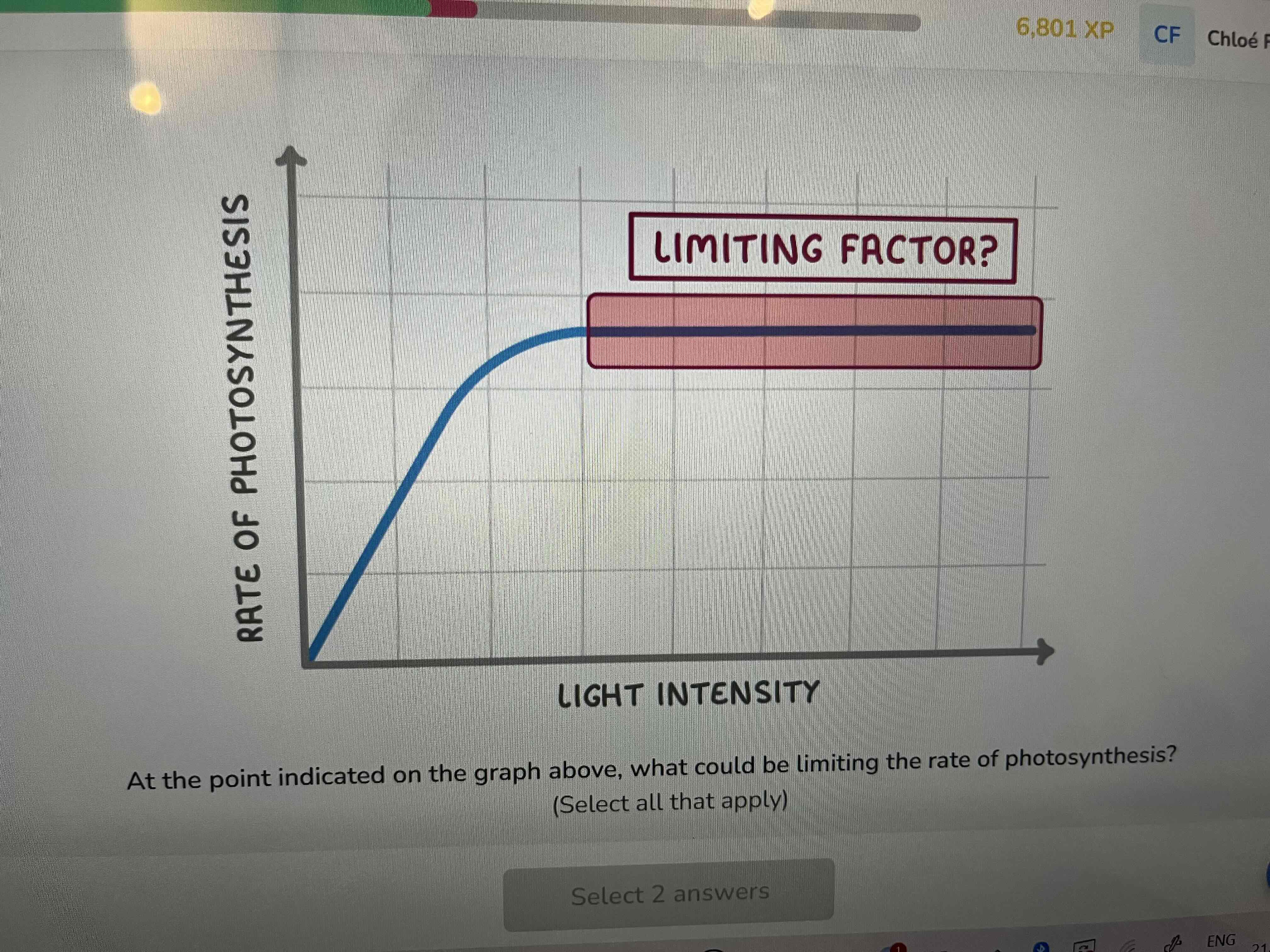
List three environmental factors that effect the rate of photosynthesis
light intensity
Temperature
amount of carbon dioxide
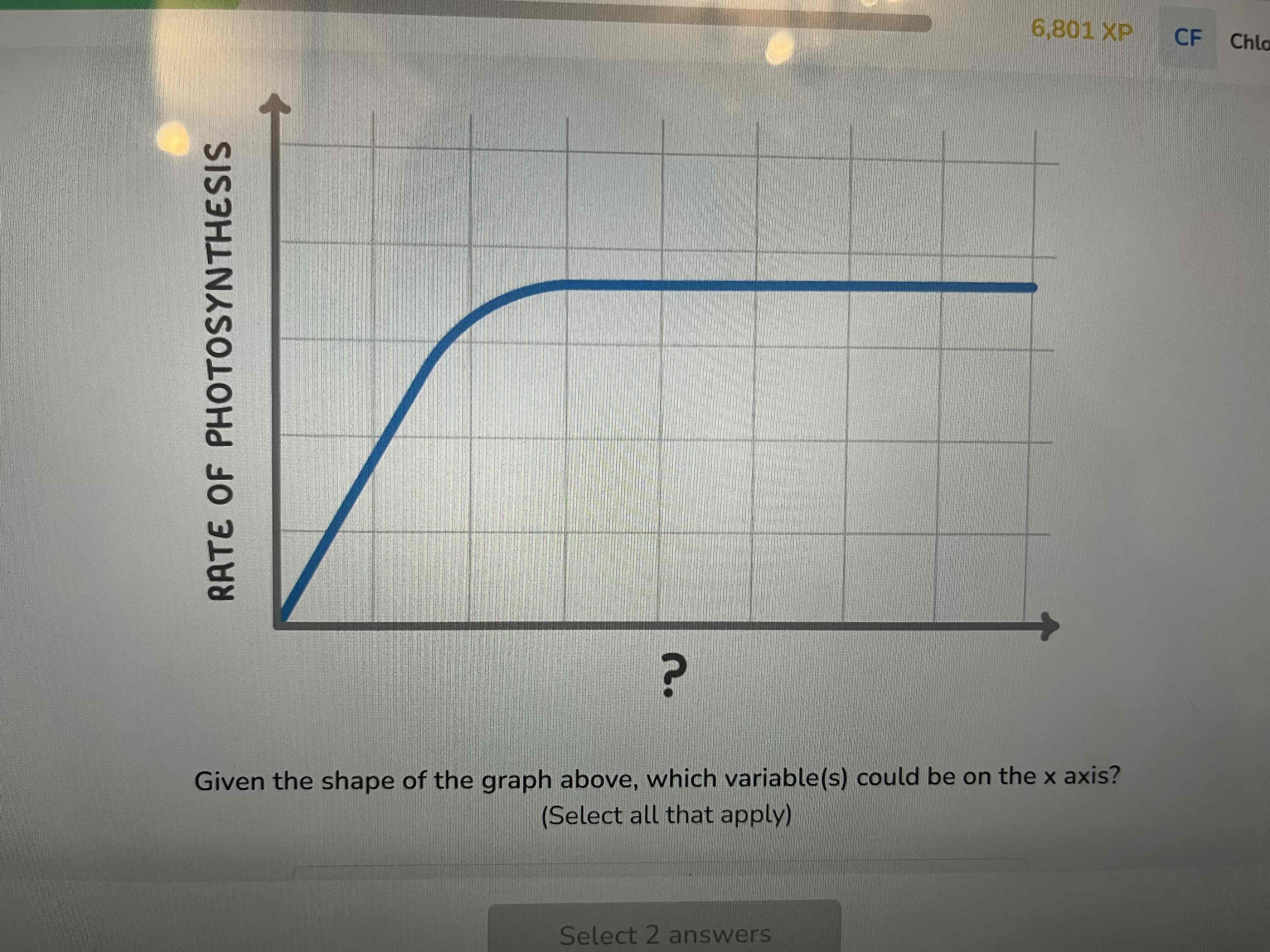
Carbon dioxide concentration
Light intensity
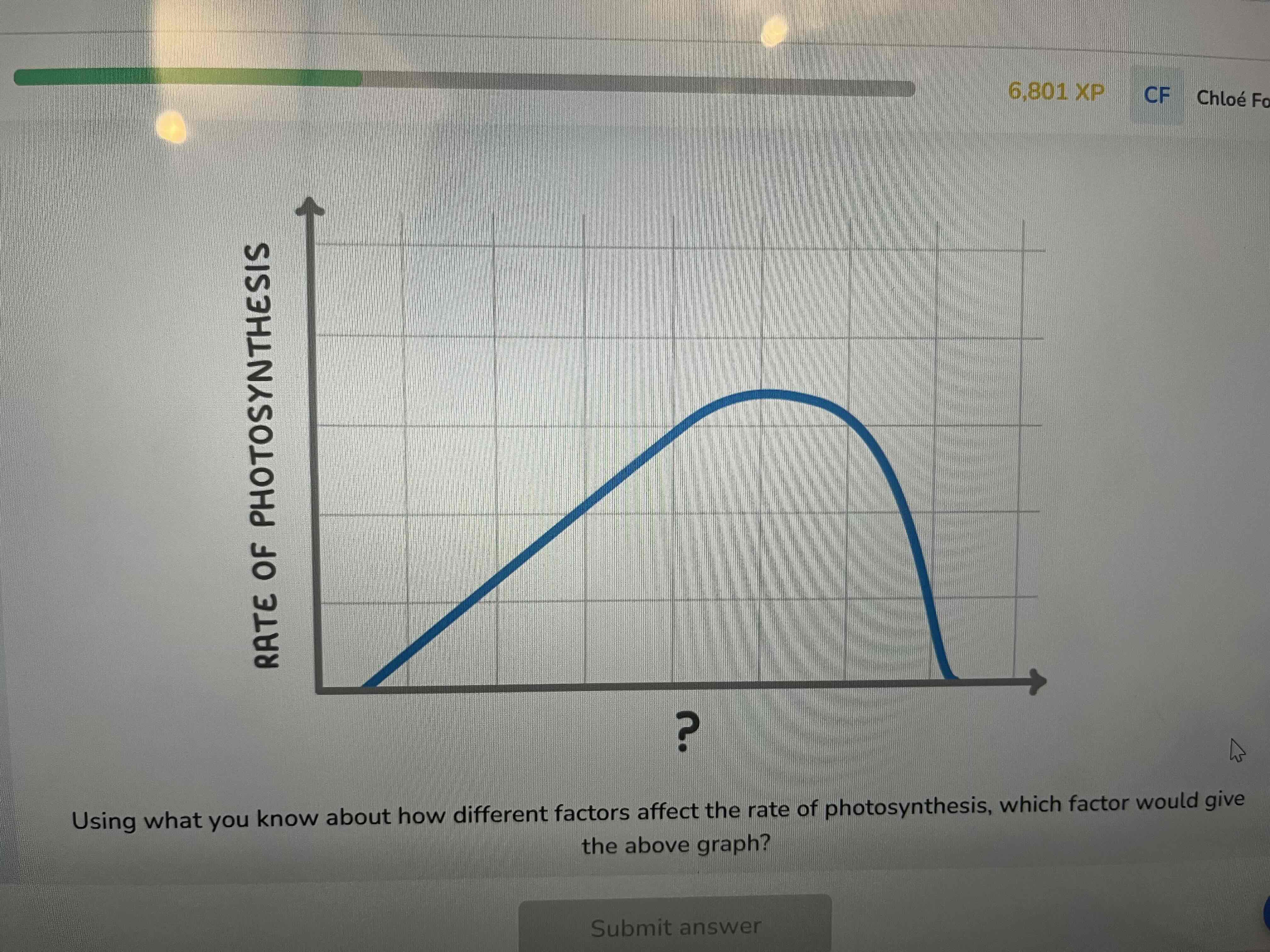
Temperature
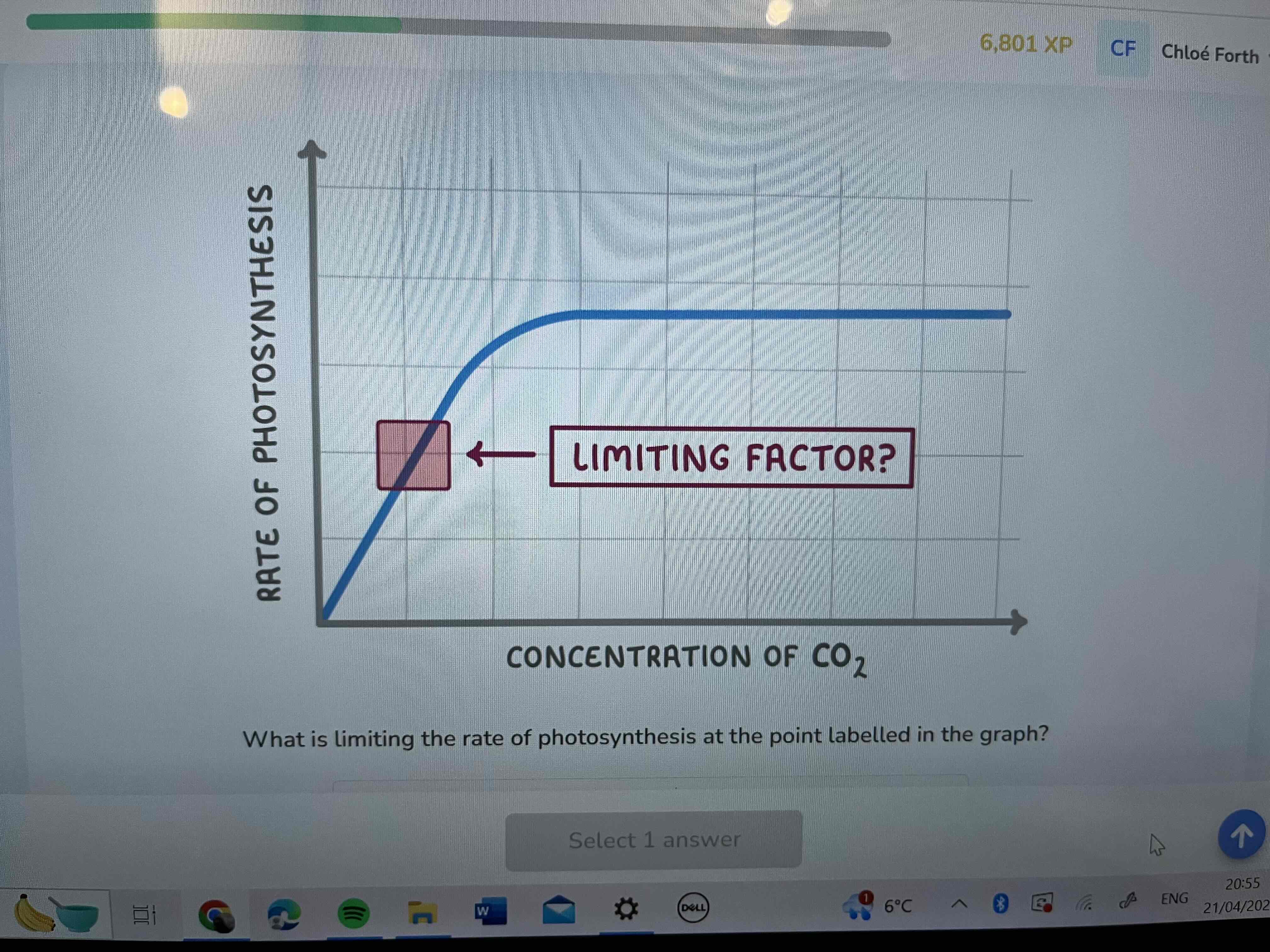
Carbon dioxide concentration
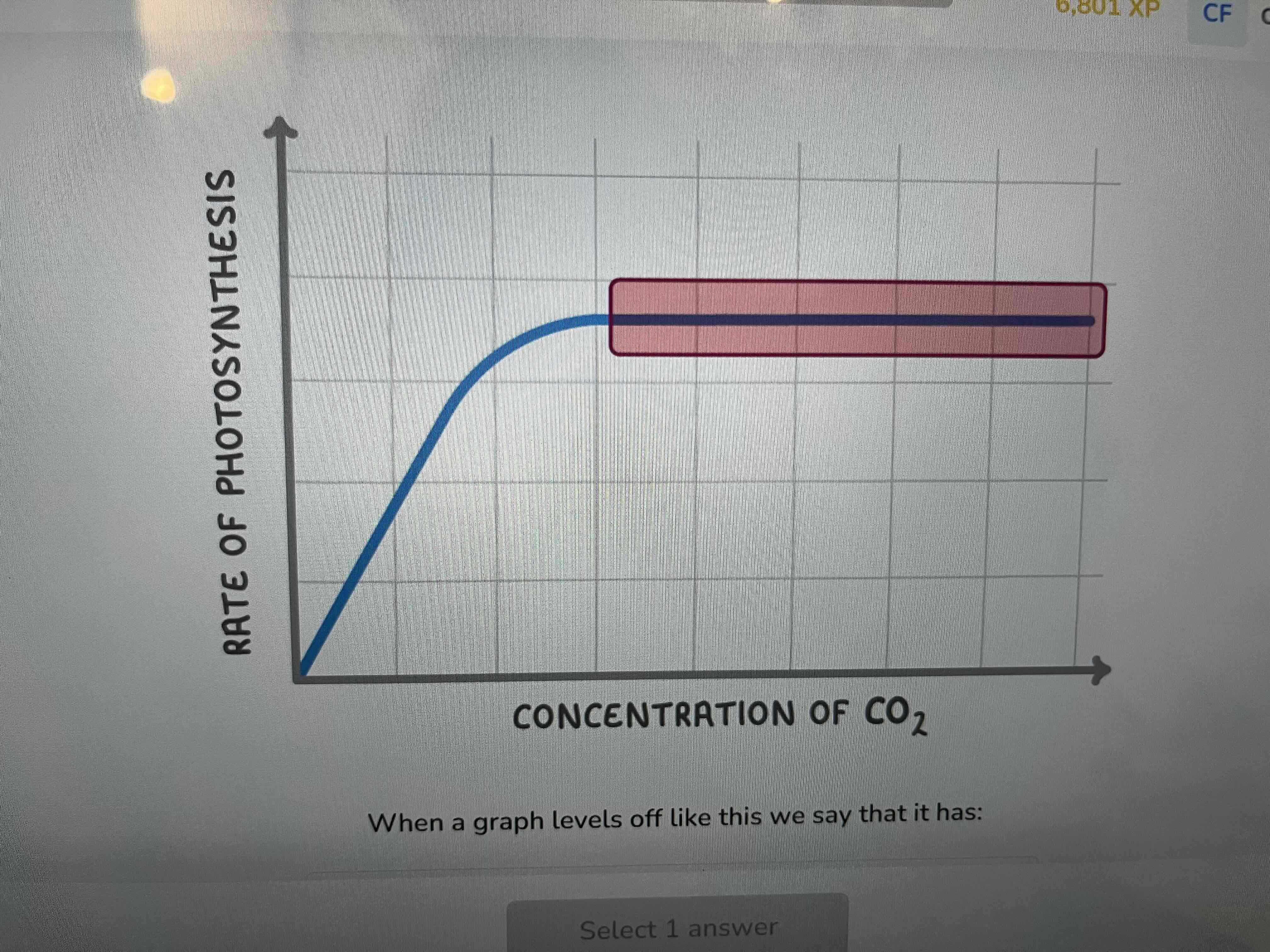
Plateaued
temperature
Light intensity
Describe and explain how the rate of photosynthesis varies with temperature
rate initially increases with temperature
Because particles have more energy and move faster so react more frequently
Highest rate is at optimum temp for enzyme action
At higher temps the rate decreases as bonds holding the enzyme together being to break and so the enzyme changes shape
Rate falls to zero as enzymes denature
How can farmers ensure that photosynthesis takes place 24 hours a day
Use artificial lighting
What are the two benefits of paraffin heaters
heat
Carbon dioxide
What are the four levels of plant organisation
Cells → tissues → organs → organ systems
Give an example of an organ on a plant
Leaf
The root, stem and leaves make up what
Organ system
What is a guard cell and example of
Cell
The palisade mesophyll layer is an example of what
Tissue
Draw and label/ name the parts of a cross section of a leaf
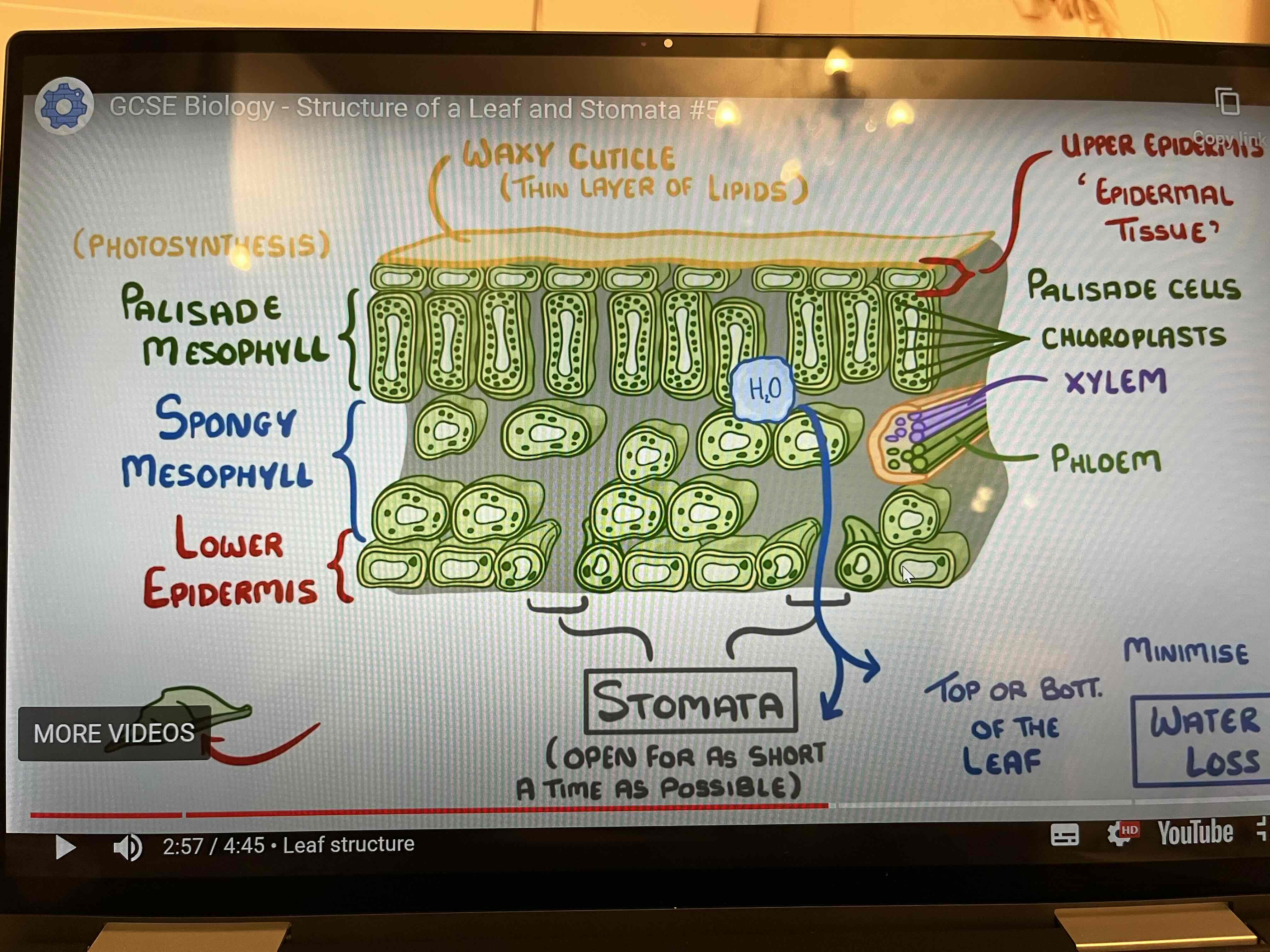
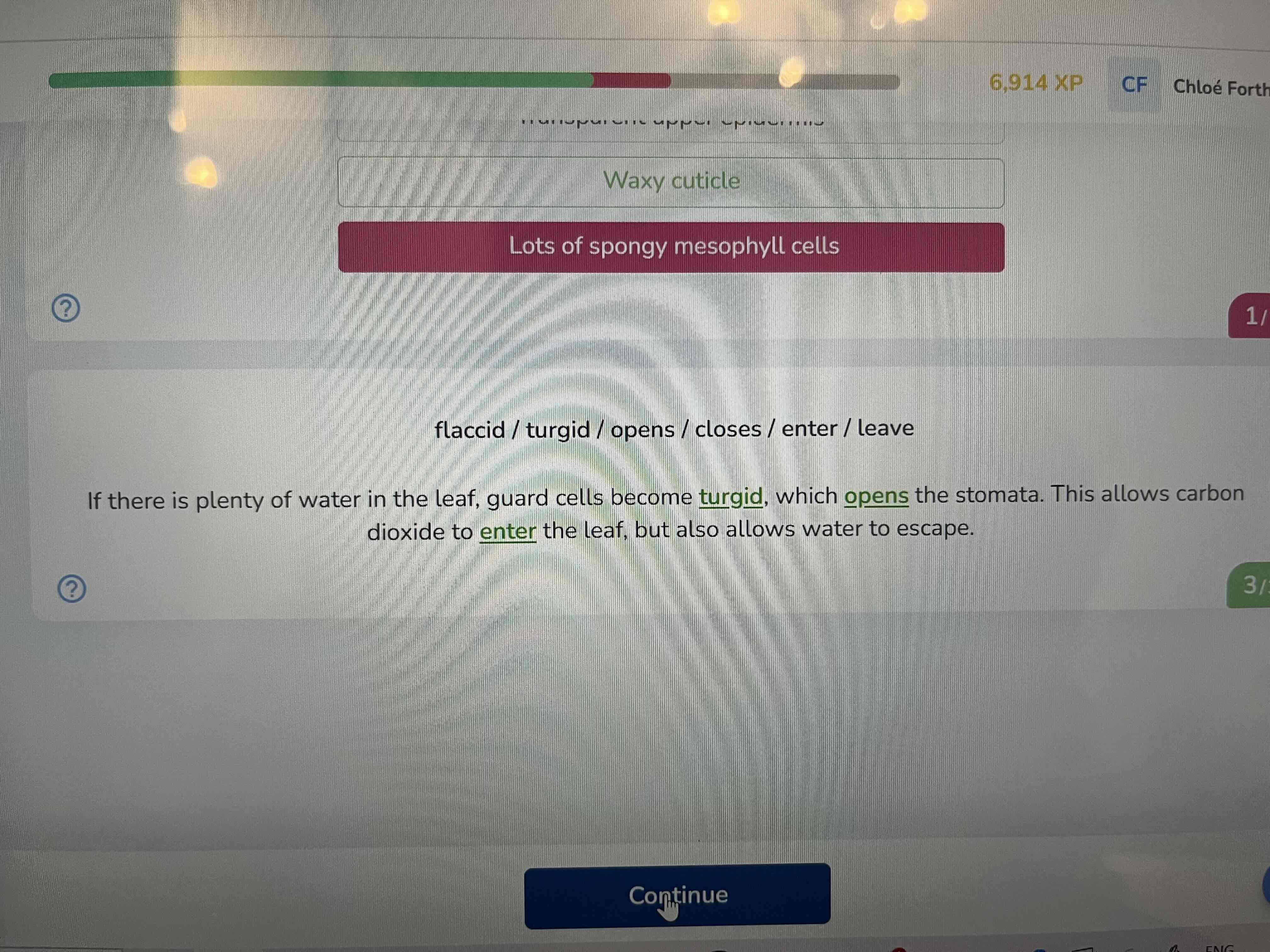
Which structures help minimise water loss
Guard cells that close stomata
Waxy cuticle
At night time is the stomata open or closed
Closed
What is Meriden tissue and where is it found
stem cells helping plant growth
Tips of roots and shoots
What part of the leaf is glucose produced in
leaf
What is the movement of sap up and down the plant called
Translocation
What do phloem cells have in their end walls to allow cell sap to pass along the phloem tube
Pores
What does xylem transport in a plant
Water and dissolved mineral ions
How do root hair cells absorb water from the soil
Osmosis
How do root hair cells absorb mineral ions from the soil
Active transport
Which substance are xylem cells reinforced with to make them stronger
Lignin
What is transpiration
Evaporation of water form leaves
What happens to the transpiration rate as the temp increases
Increases
Are stomata open or closed during the night
Closed
Why does the rate of transpiration increase if the light intensity is increased
The stomata is open wider to let more carbon dioxide into the leaf for photosynthesis
What happens to the rate of transpiration if the wind increases
Increases
Why does water loss slow down is a plant is pour into a plastic bag
Humidity increases
What influences rate of transpiration to vary
humidity
Temp
Light intensity
Air flow
What stimuli can plants detect
gravity
Touch
Light
Do plants have a nervous system
No
Do plant hormones act locally (a certain area)
Yes
What is a family of plant hormones produced in the tips of roots and shoots called
Auxins
Which way do auxins diffuse
Backwards from the tip of shoots and roots
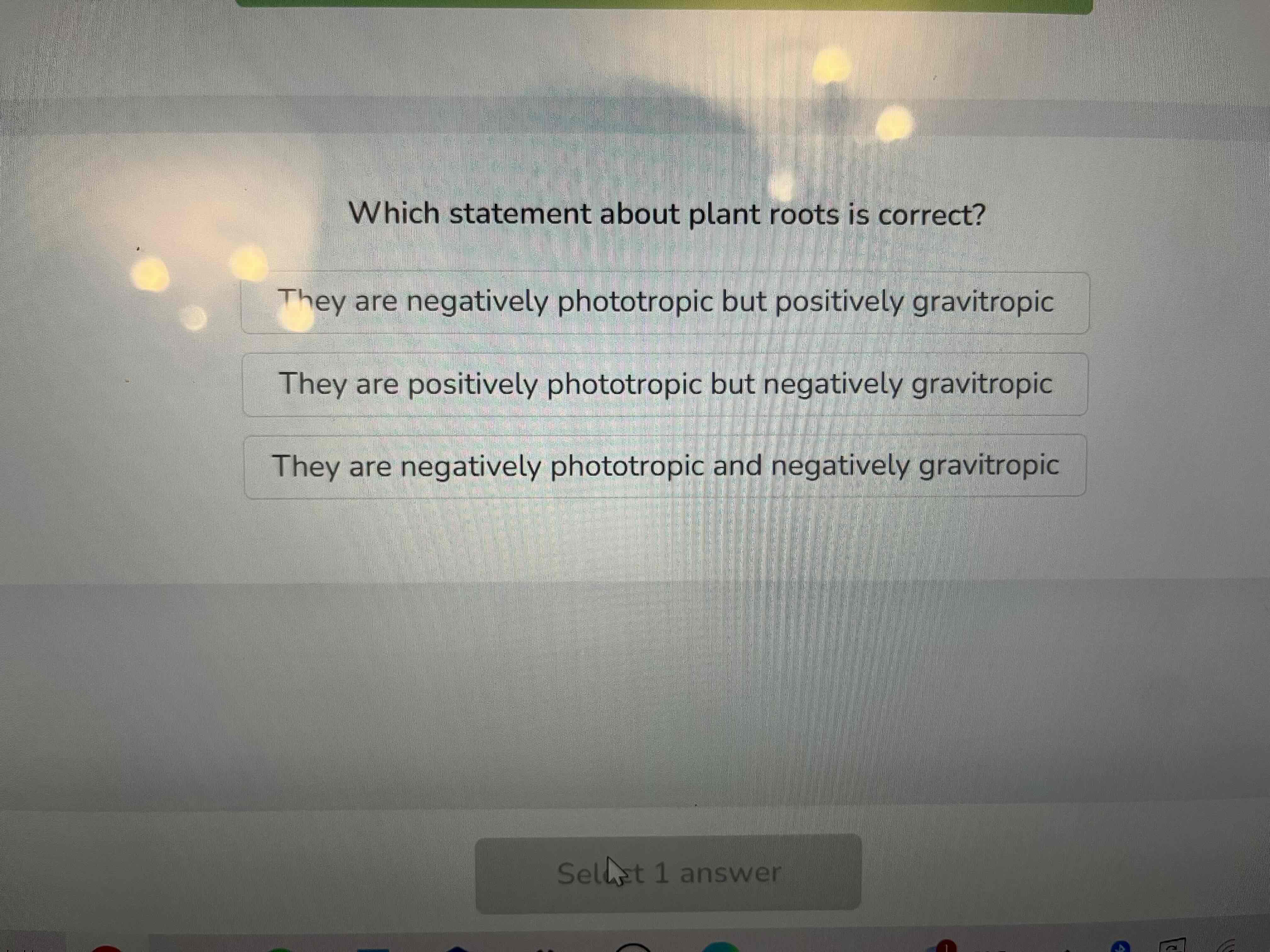
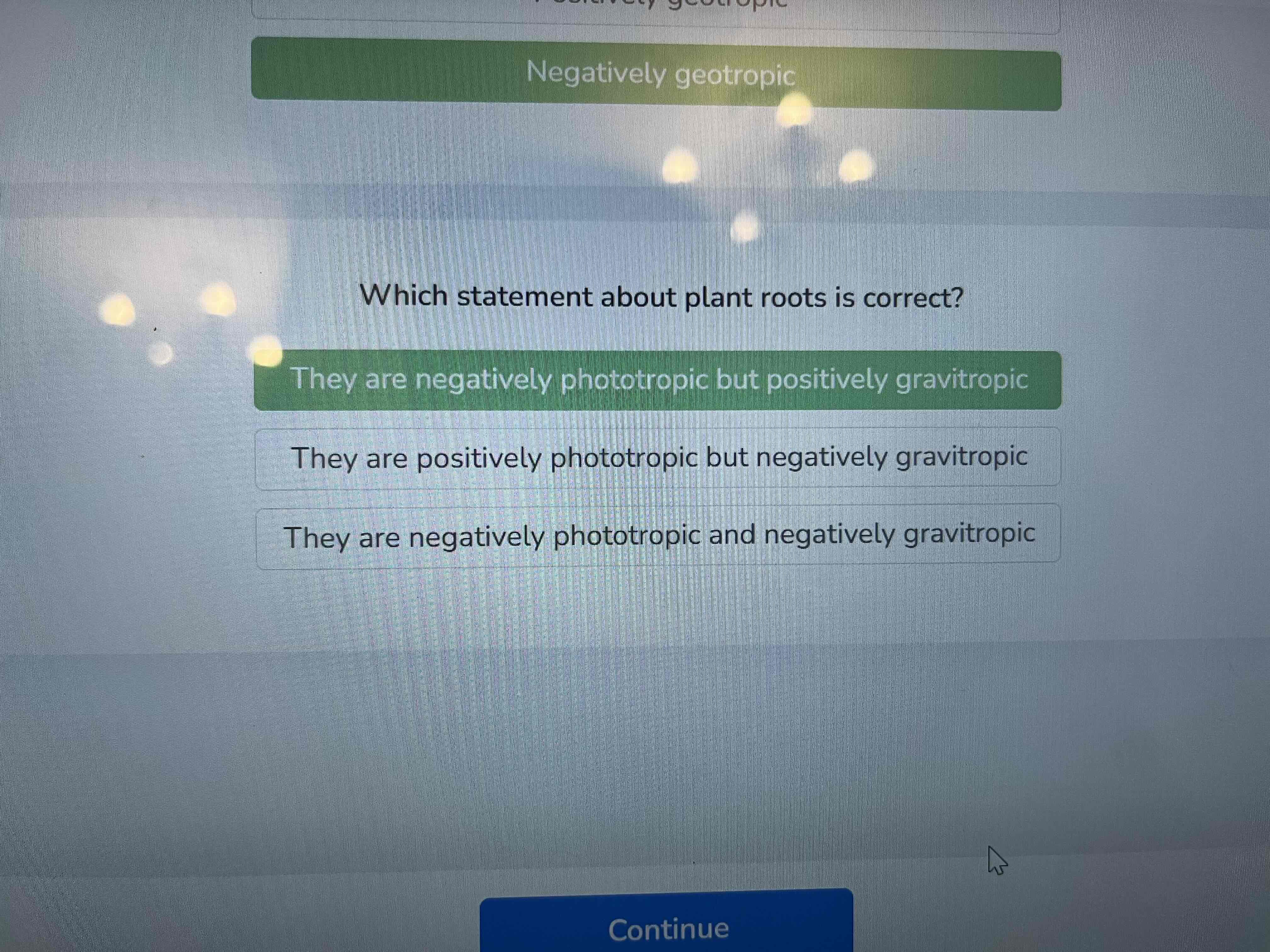
What refers to the growth of plants in response to gravity
Geotropism/ gravitropism
What side do auxins accumulate on
lower side
Shaded side
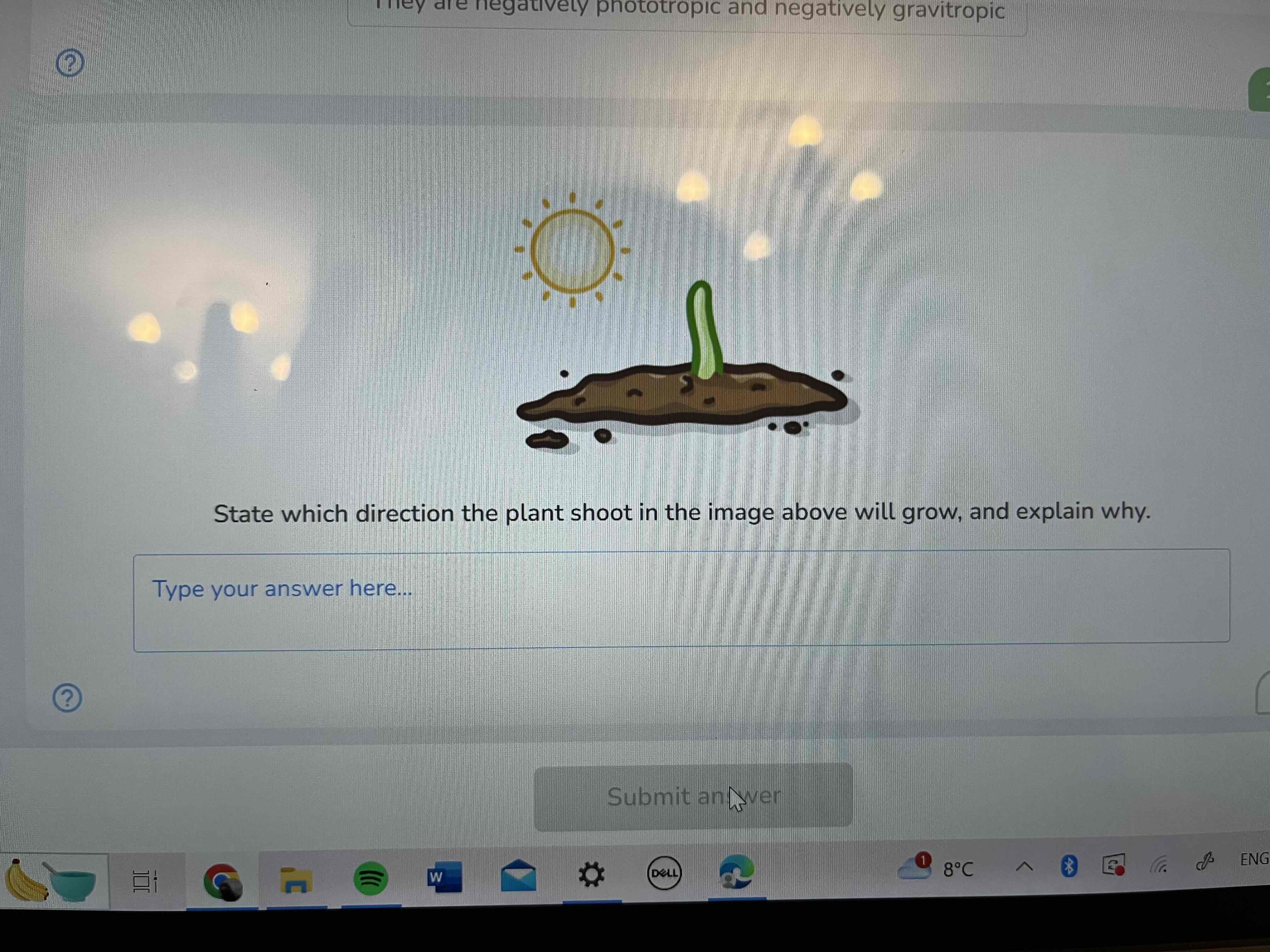
Shoots are considered
positively phototropic
Negatively geotropic
What is phototropism
A response to light
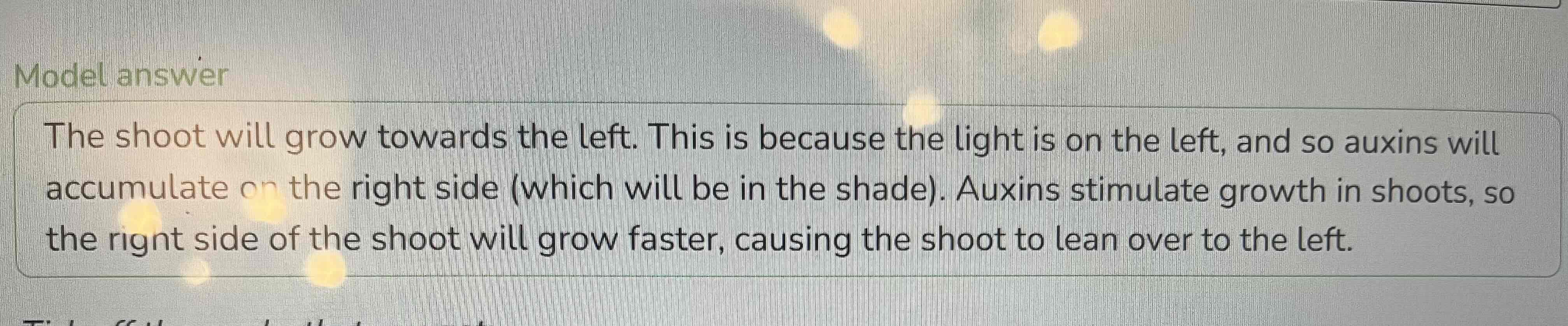
What happens to make a root grown in the direction of the force of gravity
Top side grows more than the bottom side
What is positive phototropism
Plants grow towards light source
What effects do auxins have on plants
Shoot cell growth and root cell inhibition
Name the plant hormones
Gibberellin
Auxins
Ethene
What are auxins
A family of plant hormones
What are three uses of auxins in agriculture and horticulture
In weed killers, rooting powders and to promote growth in tissue
Auxins stimulate cells to grow and divide so how can they be used as weed killers
Stimulated too much growth, disrupting growth process and kills the plant when too much is used.
What is the benefit of selective weedkillers
kill some plants but not all
What is dormancy
Seeds are inactive and don’t grow or develop
What is the process of germination
Seeds develop and grow
Which pant hormone can stimulate a plant to germinate in
Gibberellin
Which hormone is responsible for inducing fruit to ripen
Ethene
Explain how ethene is used in the transport of food
Ethene stimulates fruit to ripen
Fruit is picked unripe so it’s still hard and isn’t damaged during transport or storage
Ethene used to ripen fruit for sale