Biology Topic 2 - Foundations in Biology
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
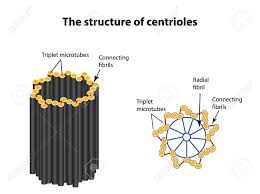
Centrioles
Structures in the cytoplasm, are hollow cylinders containing microtubules arranged at right angles to each other. Involved in cell division as they produce the spindle fibres during mitosis.
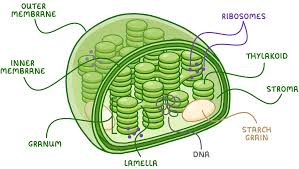
Chloroplasts
Organelles found in plants and algae, are the site of photosynthesis. Sometimes found in protoctists. Surrounded by double membrane. Sacks of flattened membrane sacs called thylakoids contain chlorophyll. (each stack of thylakoids is called a granum (singular) and grana (plural)). Fluid-filled matrix called stroma. Contains loops of FNA and starch gains.
Cilia
Small hair-like structures. Project from surface of cells. They:
Move fluid past cells (e.g. mucus in the airway - in lungs, cilia beat in a wave-like motion to move mucus, germs and other foreign particles up and out of the airway).
Transducing (converting something into a different form like energy, a message or genetic material) sensory stimuli (including chemical concentrations, osmolarity, light intensity and fluid flow).
Transporting eggs - cilia in the fallopian tube
Locomotion - beat in a rhythmic, coordinated fashion to create movement
Confocal microscopy
A type of microscopy that uses lasers to scan specimen point by point to produce an image.
Cytoskeleton
A mesh/network of protein fibres found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells used for structural support and intracellular transport. Consist of rod like microfilaments that give support and mechanical strength, keep cell shape stable, allow cell movement. Help substance and organelles move through cytoplasm within cell (by walking and dragging). Form spindle before cell division. Microtubules make up cilia.
Differential staining
Using multiple different stains to distinguish different parts of a specimen.
Eosin
A stains that stains cytoplasm pink.
Methylene blue
stains DNA and RNA blue
What are adenine, thymine, cytosine and guanine examples of.
Nitrogenous bases