Sexual Reproduction
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
1
New cards
Sexual reproduction
* Germline cells give rise to gametes.
* each gamete only receives half the amount of genetic material (n)
* After fertilisation, this amount is restored to the full number of chromosomes (2n)
* each gamete only receives half the amount of genetic material (n)
* After fertilisation, this amount is restored to the full number of chromosomes (2n)
2
New cards
Gametes
* Male gametes are usually very small in size. They are usually motile – they can make their own way to the ovum.
* Female gametes are larger than the male, and cannot move on their own.
*
* Female gametes are larger than the male, and cannot move on their own.
*
3
New cards
Fertilisation
* Fertilisation occurs when the two gametes of the male and female fuse.
* Forms new, single cell = zygote.
* Cell undergoes mitosis = develop into embryo.
* Forms new, single cell = zygote.
* Cell undergoes mitosis = develop into embryo.
4
New cards
Meiosis
Meiosis is a process where a single cell divides twice to produce four cells containing half the original amount of genetic information. These cells are our sex cells – sperm in males, eggs in females
5
New cards
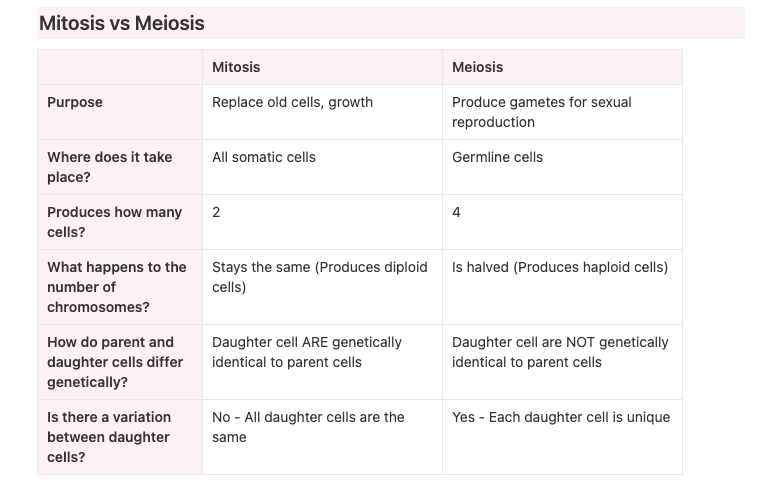
Mitosis vs Meiosis
6
New cards
Two divisions
* Meiosis I separates homologous chromosomes.
* Meiosis II separates sister chromatids (just like mitosis).
* Meiosis II separates sister chromatids (just like mitosis).
7
New cards
Crossing over
* In the early stages of meiosis, crossing-over happens.
* Homologous chromosomes (matching pairs of chromosomes) swap pieces.
* This increases the variation seen in offspring.
* Homologous chromosomes (matching pairs of chromosomes) swap pieces.
* This increases the variation seen in offspring.
8
New cards
Assortment
* resulting zygote contains a combination of genes arranged in an order that has never occurred before and will never occur again.
9
New cards
Stages of Meiosis 1
Prophase I
Metaphase I
Anaphase I
Telophase I
Metaphase I
Anaphase I
Telophase I
10
New cards
Prophase I
* Chromatin shortens and thickens, and chromosomes appear.
* Each chromosome has two chromatids attached at the centromere.
* Homologous chromosomes match up and crossing-over occurs.
* Each chromosome has two chromatids attached at the centromere.
* Homologous chromosomes match up and crossing-over occurs.
11
New cards
Metaphase I
* Random assortment occurs; homologs line up on equator.
* Nuclear membrane breaks down.
* Nuclear membrane breaks down.
12
New cards
Anaphase I
* Each homologue separates and moves to opposite poles of the cell; being pulled by the spindle fibres.
13
New cards
Telophase I
* New nuclear membranes form.
* Chromosomes decondense.
* Cytoplasm divides (cytokinesis).
* Chromosomes decondense.
* Cytoplasm divides (cytokinesis).
14
New cards
Stages of Meiosis 2
Prophase II
Metaphase II
Anaphase II
Telophase II
Metaphase II
Anaphase II
Telophase II
15
New cards
Prophase II
* Nuclear membranes break down.
* Chromosomes shorten and thicken.
* Centrioles move to poles.
* Spindle fibres form.
* Chromosomes shorten and thicken.
* Centrioles move to poles.
* Spindle fibres form.
16
New cards
Metaphase II
* Chromosomes line up along equator, not in homologous pairs.
17
New cards
Anaphase II
* Each sister chromatid is separated at the centromere, and they move to opposite poles of the cells.
18
New cards
Telophase II
* Nuclear membrane reforms.
* Chromosomes uncoil and lengthen.
* Spindle disappears.
* Nuclear envelopes reform.
* Cytoplasm divides in cytokinesis; 4 haploid daughter cells (gametes) are formed.
* Chromosomes uncoil and lengthen.
* Spindle disappears.
* Nuclear envelopes reform.
* Cytoplasm divides in cytokinesis; 4 haploid daughter cells (gametes) are formed.
19
New cards
Genetic Variation
* Each gamete is unique.
* Offspring will always be genetically different to the parents.
* This is due to crossing over and independent assortment.
* Offspring will always be genetically different to the parents.
* This is due to crossing over and independent assortment.
20
New cards
When Meiosis goes wrong
Chromosomal abnormalities are a major cause of spontaneous abortions.
21
New cards
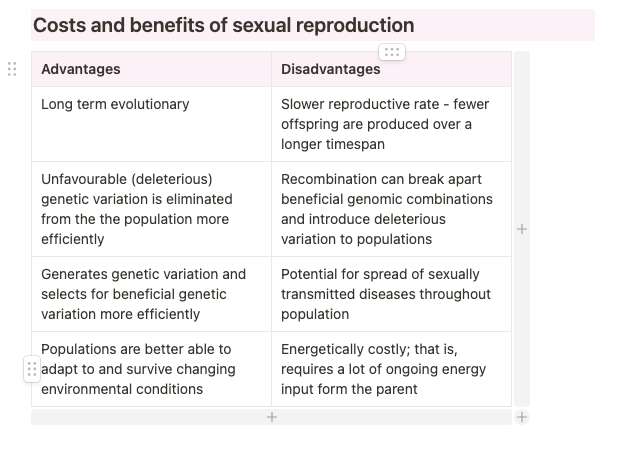
Costs and benefits of sexual reproduction