stereotypes 1
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
what are stereotypes?
generalised beliefs about or expectations from members of group
not necessarily fixed or inaccurate
difference between stereotyping, prejudice, and discrimination?
stereotyping - the cognitive component of attitudes towards a social group; beliefs about what a particular group is like
prejudice - the affective (feeling) component of attitudes towards a social group
discrimination - the behavioural (action) component of attitudes towards a social group
why do we form and use stereotypes?
schemas - cognitive frameworks for organising, interpreting and recalling information
categorising for efficiency - sometimes least cognitive effort is preferable
motivational purpose - feel positive about group identity in comparison to other social groups
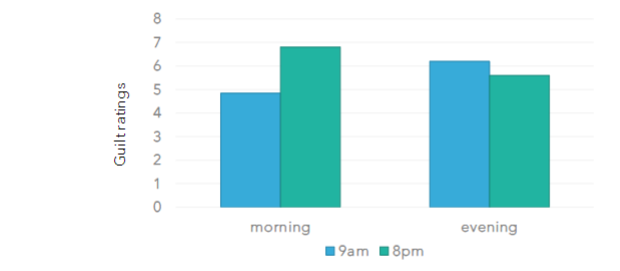
describe Bodenhausen (1990)
participants presented with info from a legal trial - designed to draw on stereotypes that suggest the defendant is guilty but objectively ambiguous
participants were either morning or evening people - tested in least preferred time of day so they have limited resources
stronger reliance on stereotypes when cognitive resources are scarce
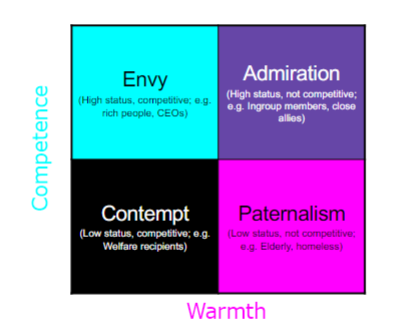
stereotype content model (Fiske et al., 2002)
stereotypes about most groups contain just two underlying dimensions: competence (status) and warmth (competition)
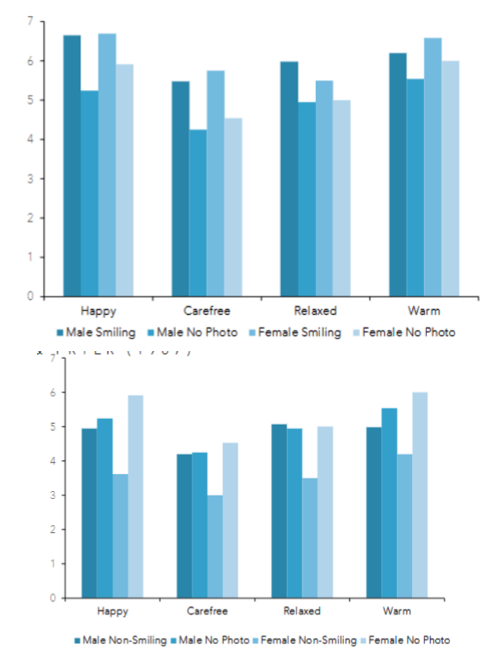
describe Deutsch, LeBaron, and Fryer (1987)
asked participants to rate how warm, happy, carefree and relaxed a number of people were based on verbal description accompanied by: no photo, smiling photo or non-smiling photo
women were perceived as less happy, carefree and relaxed than men when not smiling
non-smiling women were rated less happy, carefree and relaxed than woman with no photo - not found for men
evidence of negative consequences of ‘positive’ stereotypes
how do stereotypes influence cognitive processing?
where we direct attention - attend to stereotype-consistent info
how we interpret info - interpret ambiguous info in line with stereotypes
what we remember - recall more stereotype-consistent info
how we gather info - ask questions to confirm our beliefs
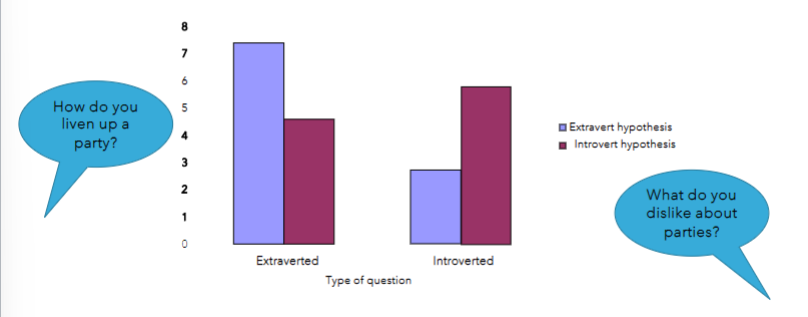
describe Snyder and Swann (1978)
participant ‘interviewers’ were led to believe that an interviewee that was either introverted or extroverted
they selected questions from a prepared list
they chose questions likely to confirm expectations