PSYC 207 MIDTERM 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/123
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:09 AM on 11/15/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
1
New cards
Internal Reactions
combinations of intuitive valuation (fast & unconscious) + deliberate evaluation (careful, conscious, deliberate) of situation
2
New cards
Associative memory
your implicit model of the world, how you learn to create associations/ relationships between things
-> remembering someone's name
-> not always easy to describe, you just think it
-> culture is a major source of associative learning
-> remembering someone's name
-> not always easy to describe, you just think it
-> culture is a major source of associative learning
3
New cards
Semantic memory
your explicit model of the world, your general knowledge (facts, ideas, meanings, concepts)
- conscious connections & concepts
- conscious connections & concepts
4
New cards
Exposure
repeated exposure strengthens some associations & lack of exposure weakens others
5
New cards
Implicit & explicit
Implicit= we're unaware - not expressed directly, explicit= we're aware - it's clearly expressed
6
New cards
Culture & intuititive valuations
culture determines our experiences & what we're exposed to which determines our associative memory which determines our intuitive valuations
7
New cards
Conditioning
the process of learning associations between environmental events and behavioural responses
8
New cards
Classical conditioning
a type of learning in which one learns to link two or more stimuli and anticipate events
- repeated pairing of a neutral & physiologically important stimulus
- neutral stimulus begins to elicit response similar to one by the important one
- repeated pairing of a neutral & physiologically important stimulus
- neutral stimulus begins to elicit response similar to one by the important one
9
New cards
Operant conditioning
repeated pairing of some action or behaviour with reward or punishment
- behaviour + positive / negative outcome
- behaviour + positive / negative outcome
10
New cards
Media eliciting emotions
- words
- dramatic music
- visually creating feels of danger
- dramatic music
- visually creating feels of danger
11
New cards
System 1
the intuitive, automatic, unconscious, and fast way of thinking (associative)
- much more influenced by physiological reactions
- much more influenced by physiological reactions
12
New cards
System 2
the deliberate, controlled, conscious, and slower way of thinking
13
New cards
How does system 1 & 2 react to "birth is dangeros"
system 1: immediate fear due to previously established connections
system 2: judges this assumption as true as it searches for examples of things that could go wrong during birth
system 2: judges this assumption as true as it searches for examples of things that could go wrong during birth
14
New cards
Availability heuristic
estimating the likelihood of events based on their availability in memory; if instances come readily to mind (perhaps because of their vividness), we presume such events are common
-> "it's easy to think of complications during childbirth so it must be common..."
-> "it's easy to think of complications during childbirth so it must be common..."
15
New cards
Fluency heuristic
believing something because it is easy for your mind to process it
16
New cards
Processing fluency
the ease with which something is processed or comes to mind
- high fluency (availability) of something to come to mind makes us thing its frequency is also high
- high fluency (availability) of something to come to mind makes us thing its frequency is also high
17
New cards
Attribute substitution
occurs when individuals must make judgments that are complex but instead they substitute a simpler solution or apply heuristic
- subsituiting attribution of danger for attribution of frequency
- subsituiting attribution of danger for attribution of frequency
18
New cards
Micromort
a one-in-a-million chance of death
- dangers of giving birth roughly around 100 micromorts 1/ 10,000
- dangers of giving birth roughly around 100 micromorts 1/ 10,000
19
New cards
Judgement
The act of judging people and their actions based on associative memory & heuristics
20
New cards
Systematic distortions with birth
- overestimating the risk of not intervening
- underestimating the risk of intervening
- underestimating the risk of intervening
21
New cards
Culturally dominant representations of birth avoid...
- physiological reality: blood, bodily fluids, organs etc.
- vulnerability & dependency of newborns on mothers
- animalism & emotionality of birth
- vulnerability & dependency of newborns on mothers
- animalism & emotionality of birth
22
New cards
Accuracy motive
people are motivated to believe what is right and to avoid believing what is wrong
- makes us expand more cognitive effort, process info. more deeply, use more complex thinking strategies
- makes us expand more cognitive effort, process info. more deeply, use more complex thinking strategies
23
New cards
Directional motive
motive to arrive at a particular, directional explanation
- leads us to try & justify a conclusion in a rational, convincing manner
- leads us to try & justify a conclusion in a rational, convincing manner
24
New cards
The self-serving bias
the tendency for people to take personal credit for success but blame failure on external factors
* satisfies human need to sustain positive self image
* satisfies human need to sustain positive self image
25
New cards
Culture serving bias
created by self-serving bias that; positive outcomes are dominant cultural values & negative outcomes are non-dominant
(leads us to reaffirm our cultures)
(leads us to reaffirm our cultures)
26
New cards
Labour induction
intervening to end pregnancy
27
New cards
Due date
280 days (40 weeks) after 1st day of last period
28
New cards
Term pregnancy
between 37 and 42 weeks
29
New cards
Preterm pregnancy
before full 37 weeks of pregnancy
30
New cards
Postterm pregnancy
after 42 weeks of pregnancy (overdue)
31
New cards
Nulliparous
a woman who has never given birth
32
New cards
Multiparous
An woman that has given birth multiple times.
33
New cards
Membrane sweeping
A manual separation of the fetal membranes from the uterus intended to stimulate labour, usually preformed around 38-41 weeks to induce labour naturally
- presumed to cause the release of endogenous prostaglandins
- presumed to cause the release of endogenous prostaglandins
34
New cards
Pros & cons of membrane sweeping
pros:
- may decrease length of pregnancy
- may reduce rate of formal induction
cons:
- can be very painful
- can cause bleeding or irregular contractions
- possibility of rupture of amniotic sac
- may decrease length of pregnancy
- may reduce rate of formal induction
cons:
- can be very painful
- can cause bleeding or irregular contractions
- possibility of rupture of amniotic sac
35
New cards
Prostaglandins
hormone like lipid compounds known to play partial role in initiation of labour
36
New cards
Induction of labour methods
- artificial oxytocin
- prostaglandins
- mechanical methods
- prostaglandins
- mechanical methods
37
New cards
Artificial oxytocin
continuous oxytocin administration throughout labour & after delivery through IV drip, thought to induce & strengthen contractions
38
New cards
Prostaglandins induction of labour
in the hope to release during membrane sweeping, more effective in bringing vaginal delivery within 24 hrs
- more likely to cause uterine hyperstimulation (local administration cannot be done)
- if contractions are too strong there is higher likelihood of uterine rupture
- more likely to cause uterine hyperstimulation (local administration cannot be done)
- if contractions are too strong there is higher likelihood of uterine rupture
39
New cards
Balloon catheters
Saline-filled balloon inserted through the cervical canal to mechanically dilate the cervix
- increased infection for mother & baby
- increased infection for mother & baby
40
New cards
Amniotomy
incision into the amnion (rupture of the fetal membrane to induce labor; a special hook is generally used to make the incision)
- increased infection for mother & baby
- increased infection for mother & baby
41
New cards
Base rate neglect/ fallacy
a common fallacy in which a person ignores the overall frequency of some behaviour or characteristic in making a decision
- ignoring important background info.
- failing to take into account multiple probabilities (shyness & math example)
- ignoring important background info.
- failing to take into account multiple probabilities (shyness & math example)
42
New cards
Representativeness heuristic
judging the likelihood of things in terms of how well they seem to represent, or match, particular prototypes; may lead us to ignore other relevant information
- based on automatic attribute substitution (representativeness = likelihood of occurrence bias)
- based on automatic attribute substitution (representativeness = likelihood of occurrence bias)
43
New cards
What makes us over and underestimate risks of intervention?
the representativeness heuristic + our model about birth = overestimating risk of not intervening & underestimating risk of intervening
44
New cards
Precautionary principle
assumed unsafe until proven otherwise (anti-intervention)
45
New cards
Anti-cautionary principle
assumed safe until proven otherwise (intervention is good)
- often applied to new medical technologies
- often applied to new medical technologies
46
New cards
Medical reversals for pregnancy
- routine x-rays (found to cause cancer)
- thalidomide for nausea (found to cause severe birth defects)
- routine pubic area shaving (found to cause infection rather than prevent it)
- routine episiotomy (found to cause tearing rather than prevent it)
- thalidomide for nausea (found to cause severe birth defects)
- routine pubic area shaving (found to cause infection rather than prevent it)
- routine episiotomy (found to cause tearing rather than prevent it)
47
New cards
Cord clamping / cutting
stops the function of cord (no more blood or oxygen from it)
- if cord isn't cut immediately it actually enables a gradual transition to breathing & allow lungs to inflate & begin to learn how to work
- if cord isn't cut immediately it actually enables a gradual transition to breathing & allow lungs to inflate & begin to learn how to work
48
New cards
Wharton's jelly
a gelatinous substance within the umbilical cord that protects blood vessels
- changes structure with cooler temps.
- changes structure with cooler temps.
49
New cards
Umbilical cord
a tube containing the blood vessels connecting the fetus and placenta
- contains 2 veins & 1 artery
- contains 2 veins & 1 artery
50
New cards
Placental transfusion
transfer of residual placental blood to baby within first few minutes of age
51
New cards
Immediate cord clamping
within 30 seconds of delivery, first records date from late 1600s
- early explanations were to avoid blood loss from baby before closure of umbilical blood vessels or to spare bed linen
- early explanations were to avoid blood loss from baby before closure of umbilical blood vessels or to spare bed linen
52
New cards
Apgar score
a scale of 1-10 to evaluate a newborn infant's physical status at 1 and 5 minutes after birth
53
New cards
Standard of care
Written, accepted levels of emergency care expected by reason of training and profession; written by legal or professional organizations so that patients are not exposed to unreasonable risk or harm.
54
New cards
Active management of 3rd stage of delivery
1. administration of pitocin
2. early cord clamping & cutting
3. controlled traction of umbilical cord to help deliver placenta
2. early cord clamping & cutting
3. controlled traction of umbilical cord to help deliver placenta
55
New cards
Evidence of practices
- immediate cord clamping doesn't decrease post partum hemorrhage rates
- cord traction may not be important
- only pitocin may be associated with reduced hemorrhage
- cord traction may not be important
- only pitocin may be associated with reduced hemorrhage
56
New cards
Post partum hemorrhage
when a woman has abnormal excessive bleeding after birth
57
New cards
Cord clamping guidelines
WHO: delay umbilical cord clamping for 1-3 mins
Canada: the risk of jaundice is weighed against physiological benefits of delayed clamping
UK: delay clamping earlier than necessary (unless circumstances of heavy maternal blood loss or need for immediate neonatal resusicitation take priority)
Canada: the risk of jaundice is weighed against physiological benefits of delayed clamping
UK: delay clamping earlier than necessary (unless circumstances of heavy maternal blood loss or need for immediate neonatal resusicitation take priority)
58
New cards
Practice gap
it takes a long time for science to influence medical practice & if it does its only done partially
59
New cards
Archie Cochrane
Called for efforts to make research summaries about interventions available to health care providers
Efforts led to the development of Cochrane Center in Oxford and the Cochrane Collaboration.
- helped lay foundation for evidence-based medicine
Efforts led to the development of Cochrane Center in Oxford and the Cochrane Collaboration.
- helped lay foundation for evidence-based medicine
60
New cards
Levels of evidence
1. systematic reviews (view stats)
2. critical appraisal evidence synthesis & guidelines
3. critical appraisal article synopses
4. randomized controlled trials
5. cohort studies (compare already existing outcomes)
6. case-controlled studies/case series (1 person outcome)
7. expert opinion
2. critical appraisal evidence synthesis & guidelines
3. critical appraisal article synopses
4. randomized controlled trials
5. cohort studies (compare already existing outcomes)
6. case-controlled studies/case series (1 person outcome)
7. expert opinion
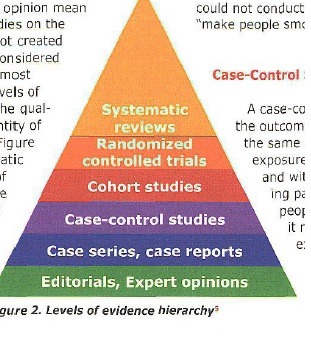
61
New cards
Evidence based medicine
medical care based on the latest and most accurate clinical research
- involves clinical judgement, relevant scientific evidence & patients values/ preferences
- involves clinical judgement, relevant scientific evidence & patients values/ preferences
62
New cards
Semantic knowledge
forms & changes based on the evidence we are exposed to
63
New cards
Procedural knowledge
forms & is based on what we frequently do (habits)
64
New cards
Medical knowledge
mostly procedural and only some semantic knowledge that serves procedural (explains why certain practices are adopted or not)
65
New cards
Scientific knowledge
mostly semantic and procedural knowledge is only used to determine what to do to update & improve
66
New cards
What influences the practice of obstetrics?
- personal "I wanna help"
- professional (duty of care)
- financial
medico-legal
- professional (duty of care)
- financial
medico-legal
67
New cards
Emotional salience
the emotional significance of percepts, thoughts, or other elements of mental experience, which can draw and sustain attention through mechanisms outside of cognitive control (system 1)
68
New cards
Cognitive control
deliberate guidance of current thoughts, perceptions or actions (system 2)
- conscious thoughts or actions
- imposed in goal-directed manner by currently active top-down executive processes
- conscious thoughts or actions
- imposed in goal-directed manner by currently active top-down executive processes
69
New cards
Amygdala
integrative center for emotions, emotional behaviour & motivation -> detects emotional salience, not threat
- located deep in the anterior inferior temporal lobe
- analogy: a smoke detector detects smoke not fire
- the stronger the emotional salience the more active
- located deep in the anterior inferior temporal lobe
- analogy: a smoke detector detects smoke not fire
- the stronger the emotional salience the more active
70
New cards
Amygdala activation & emotions
detects highest:
- disgust
- fear
- sad
- happy
- anger
fear + disgust = highly motivating
- disgust
- fear
- sad
- happy
- anger
fear + disgust = highly motivating
71
New cards
The insula
- Primary Gustatory Cortex
- taste identification & intensity
- damage can lead to the inability to identify taste experiences
- taste identification & intensity
- damage can lead to the inability to identify taste experiences
72
New cards
Orbifrontal cortex
- secondary gustatory cortex
- A region of the brain which converts sensory information into thoughts and actions
- the motivational value (approach / avoid) of taste experience
- A region of the brain which converts sensory information into thoughts and actions
- the motivational value (approach / avoid) of taste experience
73
New cards
Ventromedial prefrontal cortex (VMPFC)
involved in controlling emotional responses from the amygdala and decision-making
- very important for automatic reasoning / judgements
- very important for automatic reasoning / judgements
74
New cards
Somatic markers
bodily reactions that arise from the emotional evaluation of an action's consequences
- "gut feelings" or a tight stomach can indicate feelings of nervousness
- arise through unconscious process
- different markers created by different stimuli are integrated into VMPFC to produce a net somatic state
- "gut feelings" or a tight stomach can indicate feelings of nervousness
- arise through unconscious process
- different markers created by different stimuli are integrated into VMPFC to produce a net somatic state
75
New cards
When we are in conflict with our values...
- we need to recruit cognitive control & the lateral prefrontal cortex
- increased cognitive difficulty
- increased cognitive difficulty
76
New cards
When we do something that agrees with our values...
- we recruit the VMPFC
- relatively high processing fluency
- relatively high processing fluency
77
New cards
The Georgia Case
- hospital sought a court order authorizing to perform a c-section should she enter the hospital & refuse
- based on ultrasound stating she had placenta previa
- 99% chance fetus would die during delivery
- 50% chance mother would die
- based on ultrasound stating she had placenta previa
- 99% chance fetus would die during delivery
- 50% chance mother would die
78
New cards
Placenta previa
implantation of the placenta over the cervical opening or in the lower region of the uterus
79
New cards
Ultrasounds
the use of ultrasonic waves to see inside the body without performing surgery.
- sends pulses of waves into tissue using a probe & when these sound waves encounter material with different density part is rejected back to probe & detected as an echo (creating image)
- sends pulses of waves into tissue using a probe & when these sound waves encounter material with different density part is rejected back to probe & detected as an echo (creating image)
80
New cards
What causes a baby to loose oxygen?
- if umbilical cord is stretched, punctured or pressed on
81
New cards
Electric fetal monitoring (EFM)
- uses ultrasound 'belts' to produce info. about the baby's heart rate & record the intensity of contractions
- gives info. about baby's distress
- introduced in 1960's with the promise to reduce 50% incidence of cerebral palsy (no evidence to back up)
- interpretations are highly subjective
- higher contractions = lower heart rate for baby
- gives info. about baby's distress
- introduced in 1960's with the promise to reduce 50% incidence of cerebral palsy (no evidence to back up)
- interpretations are highly subjective
- higher contractions = lower heart rate for baby
82
New cards
Brain injury litigation (legal action)
- EFM records used during law suites
- main tool of blame
- heavily relied on to support counterfactual claims
- main tool of blame
- heavily relied on to support counterfactual claims
83
New cards
Counterfactuals
alternatives to what happened
- often activated automatically in response to negative events
- usually takes form of if/ then statements or questions
- often activated automatically in response to negative events
- usually takes form of if/ then statements or questions
84
New cards
Counterfactual reasoning
a method of testing claims for causality by asking what might have happened if one event had not occurred
85
New cards
Hindsight bias
the tendency to believe, after learning an outcome, that one would have foreseen it
- "I knew it all along"
- linked to availability heuristic (makes all related info. come to mind)
- an overconfidence of one's judgement
- "I knew it all along"
- linked to availability heuristic (makes all related info. come to mind)
- an overconfidence of one's judgement
86
New cards
Cerebral Palsy causes
damage to the brain before, during, or shortly after birth
- rarely due to events during childbirth
- a major cause of c-section eseclation
- rarely due to events during childbirth
- a major cause of c-section eseclation
87
New cards
Hypoxia
Low oxygen saturation of the body, not enough oxygen in the blood
88
New cards
Neonatal mortality
morality within 1st month of birth
89
New cards
Infant mortality
morality within 1st year of life
90
New cards
Stillbirth
the birth of a dead fetus, can happen during last 3 months of pregnancy or duirng labour
91
New cards
Intrapartum
the number of babies who die during labour or birth, very difficult to establish
92
New cards
Perinatal mortality
refers to death of a child under a week or stillbirth, also included intrapartum
93
New cards
Biggest causes of neonatal deaths
- premature baby complications (36%)
- infection (23%)
- intrapartum related conditions (23%)
- other/ not established (18%)
- infection (23%)
- intrapartum related conditions (23%)
- other/ not established (18%)
94
New cards
Can medical care reduce neonatal mortality?
- nearly impossible to decrease neonatal mortality, however the death of children under 6 decreases with resources (proper care)
95
New cards
Assimilation knowledge
adding new info. into our existing model & rejecting evidence if it doesn't fit
- wrong care, wrong data
- wrong care, wrong data
96
New cards
Accommodation knowledge
alternating our existing model as a result of new info. or experiences
- rejecting model of evidence doesn't fit
- wrong model, wrong thinking
- rejecting model of evidence doesn't fit
- wrong model, wrong thinking
97
New cards
Errors of judgement
based on dual-system models of reasoning
- automatic operations of system 1 generate a faulty intuition
- the controlled operations of system 2 fail to detect & correct
- automatic operations of system 1 generate a faulty intuition
- the controlled operations of system 2 fail to detect & correct
98
New cards
3 features of associative activation
- associative coherence
- attribute substitution
- processing fluency
- attribute substitution
- processing fluency
99
New cards
Judgement bias
an overweighting of some aspects of info. & an underweighting / neglect of others
- those given more weight are strongly activated & vice versa
-principles of associative activation help explain biases
- those given more weight are strongly activated & vice versa
-principles of associative activation help explain biases
100
New cards
Associative coherence
- a stimulus evokes a coherent & self-reinforcing pattern of reciprocal activation in associative memory
- "everything reinforces everything"
- high-level inferences evoked by a stimulus
- when an idea makes intuitive sense during 'fast-thinking mode' because it fits with associations we already made around something
- what does a cow drink? - many people will say milk
- "everything reinforces everything"
- high-level inferences evoked by a stimulus
- when an idea makes intuitive sense during 'fast-thinking mode' because it fits with associations we already made around something
- what does a cow drink? - many people will say milk