AMSCO AP Human Geography - Unit 7.2: Economic Sectors and Patterns (copy)
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
primary sector
extracting natural resources from the earth. Examples include mining, farming, fishing, and forestry
secondary sector
making products from natural resources. Examples include manufacturing and building
tertiary sector
providing information and services to people. Examples include retail sales, medicine, and housekeeping
quaternary sector
managing and processing information. Examples include financial analysis, software development, and data sciences
quinary sector
creating information and making high-level decisions. Examples include research and top managers in corporations or government (Trumps’ tariffs?)
multiplier effect
the potential for a job to create more jobs. For instance, if a factory opens up, it brings in workers. Those workers make money, and spend it on necessities like clothes or food, leading to the opening of clothing markets or food stores.
least cost theory
an explanation by Alfred Weber about what key decisions businesses made about where to locate factories to minimize transportation costs (importing and exporting), labor costs (wages), and while maximizing agglomeration economies
agglomeration economies
the spatial grouping of several businesses to share costs, such as an access road to a public highway or development of a workforce with special skills
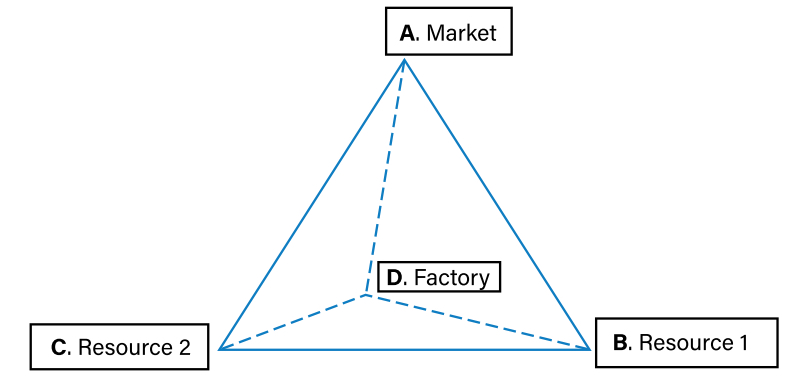
locational triangle
a model which shows Weber’s least cost theory. The three points of the model are the market for the good and two resources needed to make the good
bulk-reducing industries
a type of industry where raw materials lose weight during processing. Also known as a weight-losing, raw material-oriented, or raw material-dependent industry. These industries are usually located near the resource points
bulk-gaining industries
a type of industry where the good gains weight by processing. Also known as weight-gaining, market-oriented, or market-dependent industries, and they are usually located near the market point
labor-oriented industry / labor-dependent industry
an industry which is highly dependent on a workforce and therefore will be located near a source of specifically skilled workers (Pittsburgh?)
break of bulk
the procedure of transferring cargo from one mode of transportation to another
containerization
the system in which goods are loaded into a standardized shipping unit
intermodal
containers are able to be carried via plane, train, truck, or ship
footloose
a business which can “pack up and leave” for a new location quickly and easily
front offices
the expensive upper floors of a skyscraper for top executives. Usually designed to impress clients
back offices
an area where the rest of the employees of a business work; less expensive office space
core countries
countries which are highly industrialized and wealthy; highly developed. Includes the United States and Japan
semiperiphery countries
a mix of core and periphery countries. Countries are in the process of developing industries but less wealthy than core countries. Examples are China and Mexico
periphery countries
the least developed countries. More reliant on producing raw material (primary sector) than on industry. Includes Ethiopia and Bangladesh