Topic 6 - Waves
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
What is a transverse wave?
Vibrations are perpendicular to direction of energy transfer (e.g. light, water waves)
What is a longitudinal wave?
Vibration are parallel to direction of energy transfer (e.g. sound waves)
Define wavelength (λ)
Distance between identical points on waves - Crest-to-crest
Define frequency (f)
Number of waves per second
Measured in (Hz)
Define period (T)
The time it takes for one complete wave to pass a point
Define amplitude
Maximum displacement from undisturbed position
What is the wave speed equation?
v = f × λ
What is the speed of light in a vacuum?
3 × 10⁸ m/s
What is the speed of sound in air?
340 m/s
How to measure wave speed with a ripple tank?
Measure the wavelength: Use a metre rule to measure across 10 waves and then divide by 10
Measure the frequency: Count how many waves pass a point
in one second
Use equation: wave speed = wavlength x Frequency
How does the medium affect wave speed in solids?
Sound: Faster in solids > liquids > gases; because particles are tightly packed, allowing vibrations to transfer more quickly.
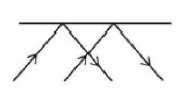
What is reflection?
Wave bounces off surface
What is specular reflection?
Smooth surface → clear reflection
What is diffuse reflection?
Rough surface → scattered rays
What is refraction?
Change in speed causes change in direction
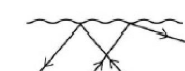
What happens when a wave enters a slower medium?
Bends towards the normal
How to investigate reflection and refraction?
Use light box, protractor, mirror/block; measure angle of incidence/reflection/refraction; trace rays
What are sound waves?
Longitudinal, travel through vibrations
Needs a medium
What is the range of human hearing?
20 Hz – 20,000 Hz
Why is hearing range limited?
Limited by size/shape of eardrum and cochlea sensitivity
WOrk plus how we hear
What is ultrasound?
High frequency sound waves with a frequency greater than 20 000 Hz, above limit of human hearing
Uses of ultrasound
Medical imaging, industrial testing
Explain why ultrasound can be used to measure the thickness of the layer of fat
-(ultrasound) waves reflected
-at boundary
Explain how ultrasonic waves are used to produce the image of an unborn baby.
Partly reflected when they hit a boundary between 2 different media
Time taken for reflected wave (to return) is used to produce the image
What are seismic waves?
Waves from earthquakes used to study Earth’s internal structure
What are P-waves?
Longitudinal, travel through solids & liquids
What are S-waves?
Transverse, only through solids
Explain why the study of seismic waves provides evidence for the structure of the Earth's core.
S-waves cannot travel through liquids
S-waves are not detected on the opposite side of the Earth, indicating the outer core is liquid
EM waves properties
All electromagnetic waves are transverse
All electromagnetic waves have the same speed in a vacuum.
Can be reflected, refracted, and diffracted
Order of EM spectrum (low to high frequency)
Radio → Microwaves → IR → Visible → UV → X-rays → Gamma
Raging martians invade venus using x-ray guns
Gamma rays
Kills cancer cells → used in cancer treatment, sterilising equipment
Causes: Mutation, killings living cells - Ionising radiation
X-rays
Very high frequency - absorbed by bone
Medical imaging
Mutations, cancer (ionising radiation)
Ultraviolet
Fluorescent lamps, Sun beds
Skin aging, cancer
Infrared
Cooking food, night vision
Microwaves
Cooking, satellite communication
Radio waves
Broadcasting, radio signals
Vsible light
Enables sight and is used in cameras, and fibre optics for communication
What causes different colours in visible light?
Each colour has a specific range of wavelengths.
What happens when light hits an object?
It is absorbed, transmitted, or reflected, depending on the object.
Why does a red object look red?
It reflects red light and absorbs other colours more strongly.
What do black and white objects do with light?
Black absorbs all visible wavelengths (appears black).
White reflects all visible wavelengths (appears white).
What do colour filters do?
They only let certain wavelengths (colours) through and absorb the rest
What happens when white light passes through a red filter?
It will appear red, because the red filter only lets red light through, and white paper reflects all colours that hit it.
What if red light hits a blue object?
The object will appear black, because blue objects only reflect blue. Since there’s no blue in red light, it absorbs all the red and reflects nothing.
Transparent
Translucent
Opaque
Transparent: Let all light through clearly (e.g. glass).
Translucent: Let some light through, but scatter it (e.g. frosted glass).
Opaque: Block all light; no transmission (e.g. wood).
Convex Lens (Converging):
Shape: Thicker in the middle, thinner at edges
Effect: Converges light rays to a point (principal focus)
Uses: Magnifying glasses, cameras, projectors, human eye lens
What do convex lenses do to parallel rays?
They converge them to the principal focus.
Concave Lens (Diverging):
Shape: Thinner in the middle, thicker at edges
Effect: Diverges light rays, rays appear to come from a point
Uses: Glasses for short-sightedness
What do concave lenses do to parallel rays?
They diverge them; rays appear to come from the principal focus on the same side.
What is the focal length?
The distance from the centre of the lens to the principal focus.
What is a real image?
Formed when rays meet; can be projected on a screen.
Produced by: Convex lenses
What is a virtual image?
Formed when rays appear to meet; cannot be projected.
Produced by: Convex and Concave lenses
Equation for magnification
Magnification = image height / object height
No units because it a ratio
What is a black body?
A perfect absorber and emitter of radiation
Perfect black body radiation
the object absorbs all of the radiation incident on it
Why is a perfect black body the best possible emitter of radiation?
● It is a perfect absorber since it absorbs all radiation incident on it ● A perfect absorber is also a perfect emitter
What happens to the quantity of infrared radiation emitted by an object as temperature increases?
The hotter the object, the more infrared radiation it will emit.
Dark, Matt Surfaces:
Good absorbers and emitters of radiation (e.g., black surfaces).
Absorb all colours of visible light, which is why they appear black when all wavelengths are absorbed.
Light, Shiny Surfaces:
Poor absorbers and emitters of radiation (e.g., white or reflective surfaces).
Reflect most visible light, making them appear white and emitting less radiation.
What can be said about the rates of emission and absorption for a body at constant temperature?
The body is absorbing and emitting radiation at the same rate.
What can be said about the rates of emission and absorption for a body increasing in temperature?
The body is absorbing radiation faster than it is emitting it.
What affects Earth's temperature?
1. The Earth's rate of absorption and emission of radiation
2. The amount of reflection of radiation into space
WORK ON 4 EXPERIMENTS DUMB SHI