5 Intraoral Radiography (Digital and Extraoral 2D Radiography)
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Digital images are discrete and numeric in what 2 ways:
▪ In terms of spatial distribution of pixels
▪ In terms of different shades of gray of each of the pixels
what term refers to the matrix element/ picture element of a digital array which identifies a gray level at that point?
pixel
pixels can be processed and manipulated and are usually expressed in what numerical values?
0-255 values
A digital image is a large collection of ______ organized in a matrix of rows and columns
pixels
what are the 3 methods of digital image acquistion?
digital direct
digital indirect
indirect/hybrid
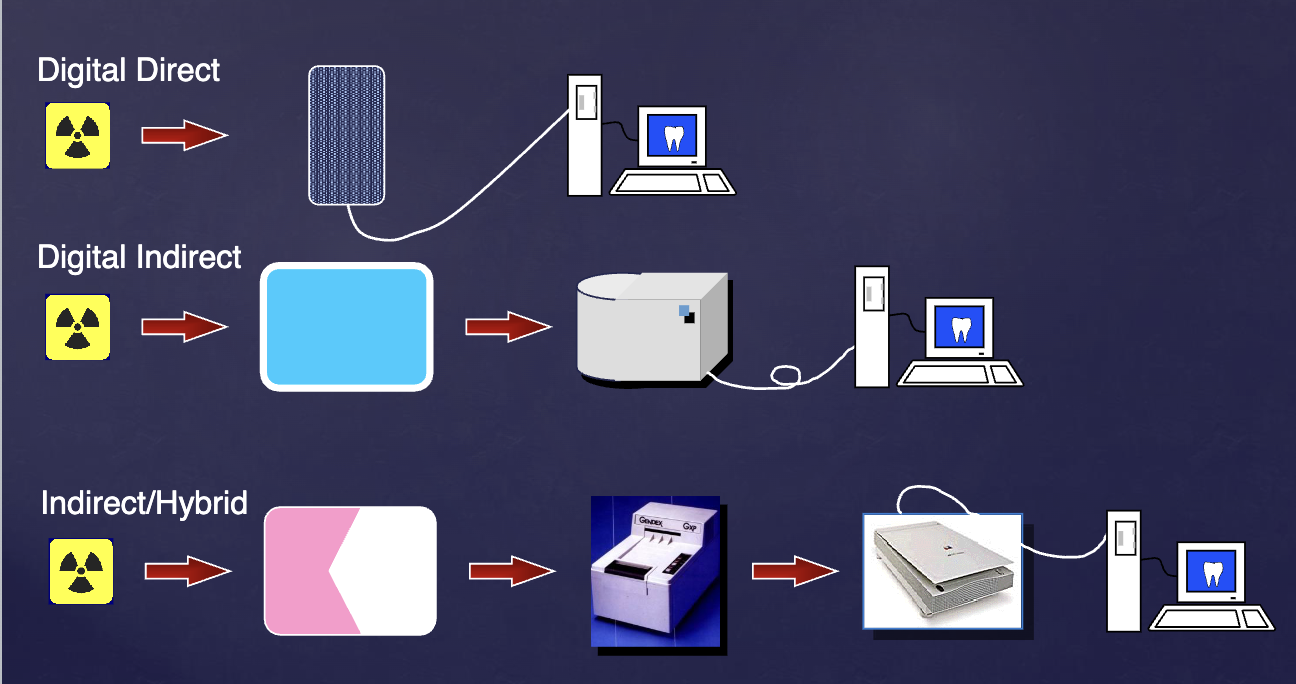
what digital receptors are available for direct image acquisition?
charge coupled device (CCD)
complementary metal oxide semiconductors (CMOS)
flat panel detectors
what digital receptors are available for indirect image acquisition?
photostimulable phosphors (PSP)
wireless
what are the CCD/CMOS-steps in image acquisition?

what are advantages of PSP imaging plates (indirect)?
100% re-usable
Same size as film
Flexible
Thin
No wires
Used with existing x-ray equipment
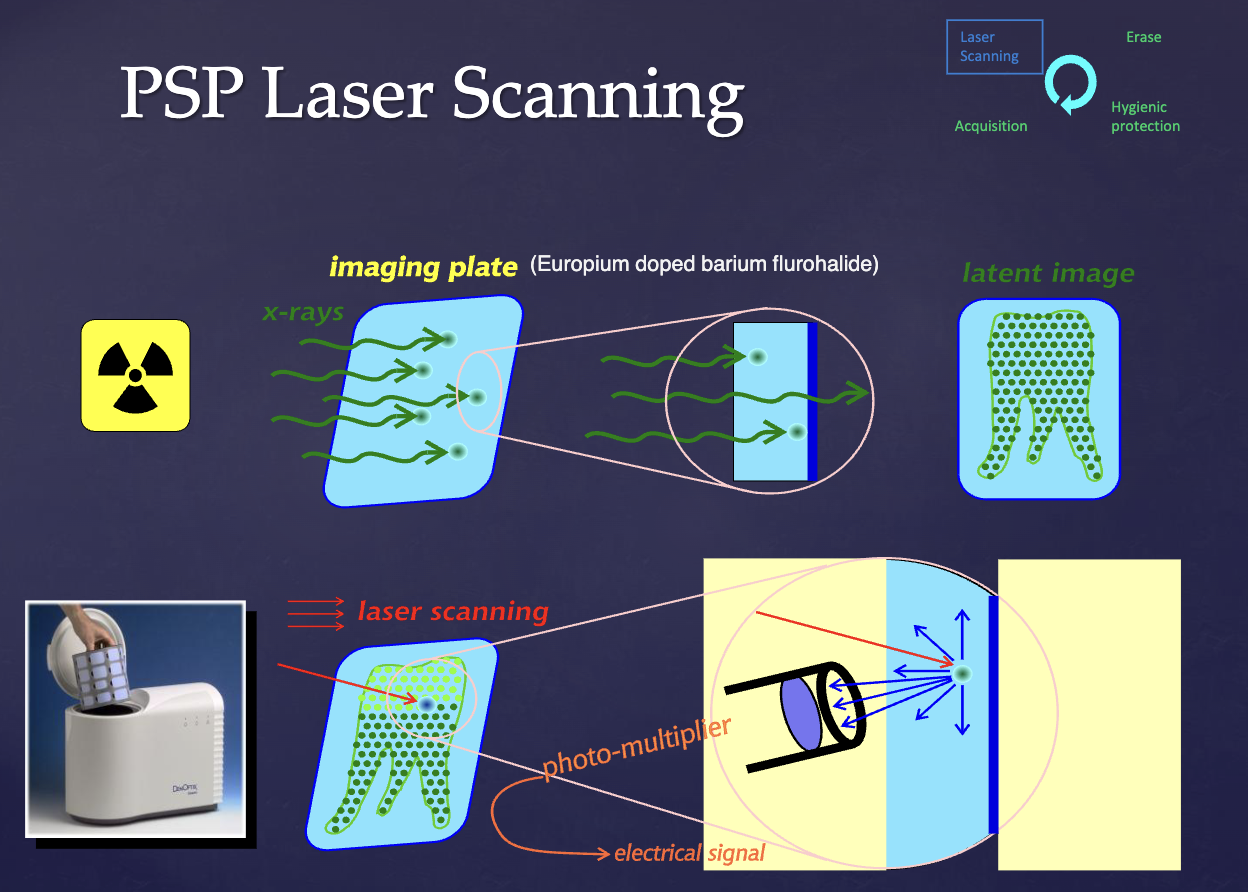
describe the PSP cycle
acquisition
laser scanning
erase
hygienic protection
describe the process of how PSP acquisition and laser scanning occurs.
Europium doped barium flurohalide absorbs and stores energy from x-rays
Release this energy when stimulated by another light of appropriate wavelength
describe the process of how PSP erasing occurs.
expose for 2 minutes (light source should be close and intense)
use view box to check laser erases images
ghose images appear if incomplete
what is used as hygienic protection for PSP?
barrier envelopes (sizes 0, 1, 2, 3, 4)
what do barrier envelopes do?
provide protection from light and cross contamination (PSP)
these are disposable

what are advantages of CCD/CMOS?
direct and fast (good for endodontics, urgent care diagnosis)
high spatial resolution
what are disadvantages of CCD/CMOS?
sensor dimensions
cable
smaller active surface area
small exposure latitude
expensive
what are advantages of PSP?
film-like (no cable)
larger active surface area
large exposure latitude
economical
what are disadvantages of PSP?
indirect
plate handling
lower spatial resolution
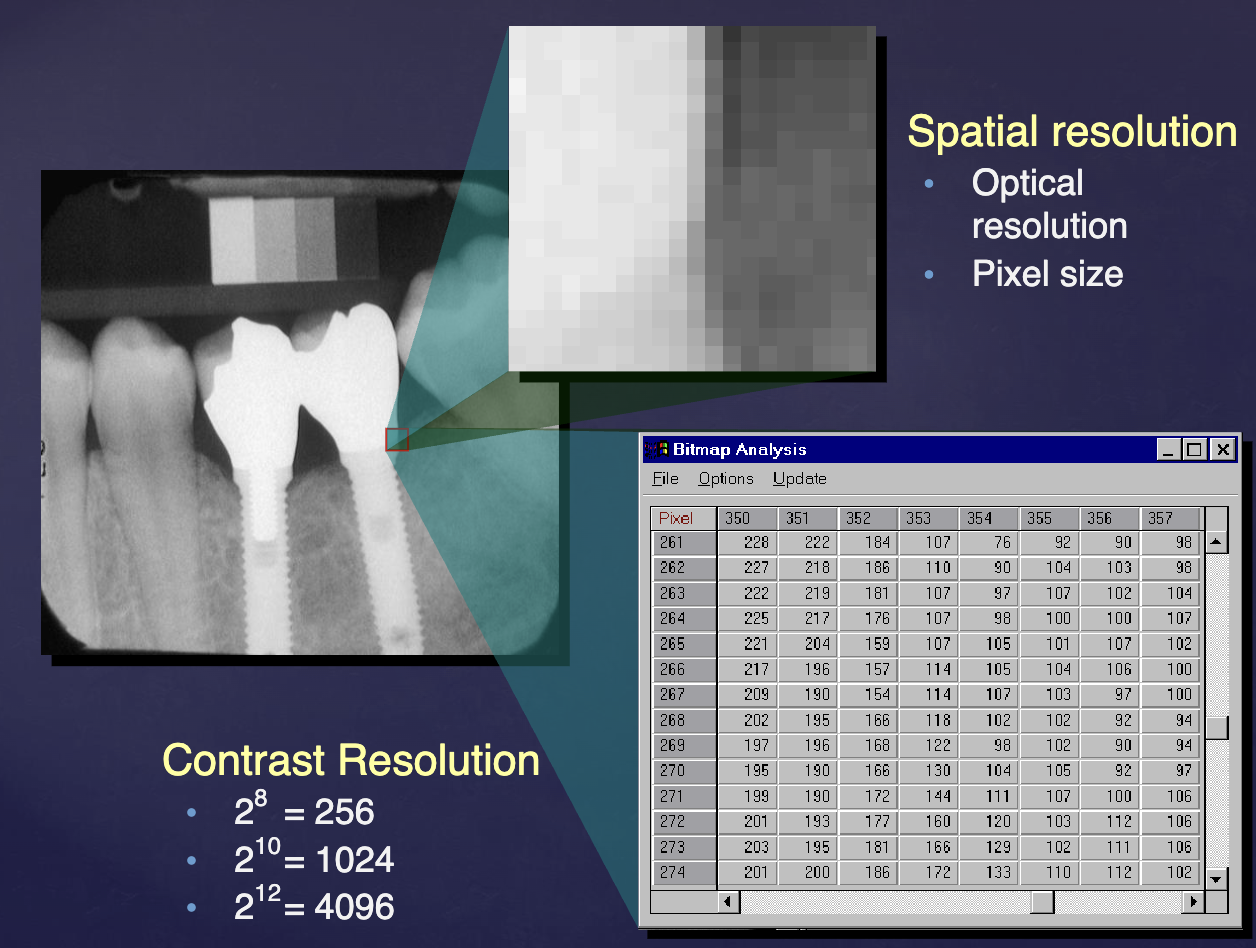
what term refers to the capacity to distinguish fine detail in an image?
spatial resolution
spatial resolution is defined and limited by ________
minimum pixel size.
in PSP system, spatial resolution is determined by…?
thickness of phosphor material
t/f: increase in quantity of radiation will not improve maximum spatial resolution
true
how is spatial resolution measured? (in units of…?)
in units of line pairs per mm (at least 2 pixels required to resolve a line pair)

what is the maximum spatial resolution of film? CCD/CMOS? PSP?
• Film: > 20 lp/mm
• CCD/CMOS: 25 lp/mm (20-μm pixels)
• PSP: >7 lp/mm
Human eye can distinguish __ lp/mm without benefit of mangnification
6 lp/mm
what term refers to the Ability to distinguish different densities in the radiographic image?
contrast resolution
what factors affect spatial resolution?
pixel (only)
what factors affect contrast resolution?
attenuation characteristics (density) of tissues imaged
capacity of detector/receptor to distinguish differences
ability of computer display to portray differences
ability of observer to recognize differences
what term refers to the different densities/shades of gray stored in a radiographic image?
bit depth
• 8, 10, 12, 16 bits
• 256 (28) to 65,536 (216) different densities
• In practice, limited by noise, computer display
what term refers to the ability of a detector to capture a range of x-ray exposures?
detector latitude (we want the ability to record a wide range of tissue densities from gingiva-enamel)
what term refers to the ability to respond to small amounts of radiation?
detector sensitivity (Detector efficiency, pixel size, system noise)
what term refers to the efficiency of a detector in converting incident x-ray energy into an image signal?
detective quantum efficiency
what does a high detective quantum efficiency value indicate?
less radiation needed to achieve identical image quality
what is any operation that acts to improve, correct, analyze, or in some way change a digital image called?
digital image processing
what is the goal of digital image processing?
improve image quality by:
optimizing contrast
reducing noise
removing technical artifacts
can spatial resolution be influenced by processing software?
no. because it is dependent on technical variables of the detector (eg; pixel size)
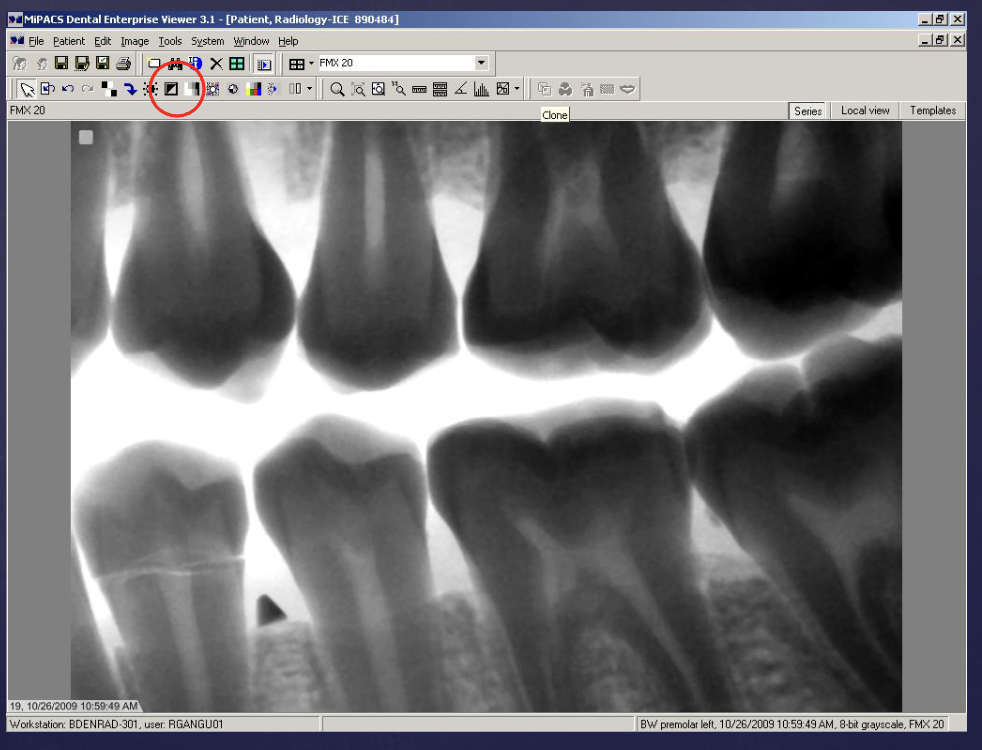
what type of digital processing is this?
edge enhancement
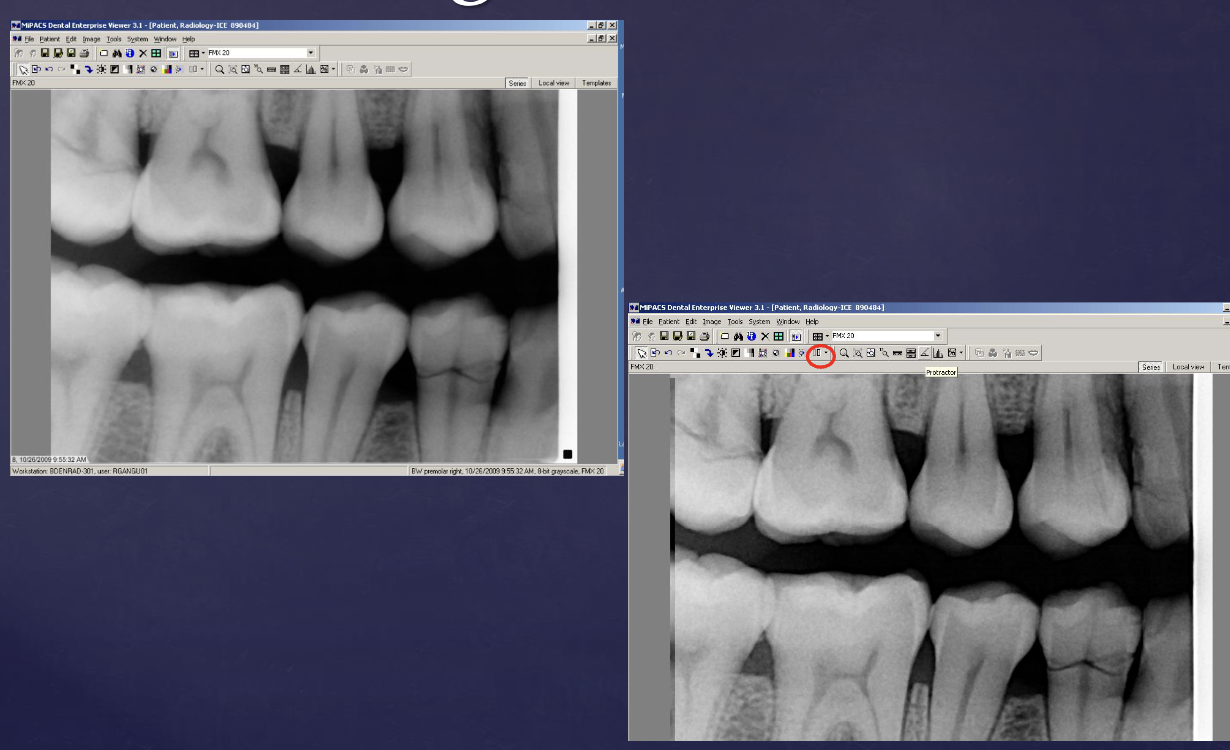
what type of digital processing is this?
magnification
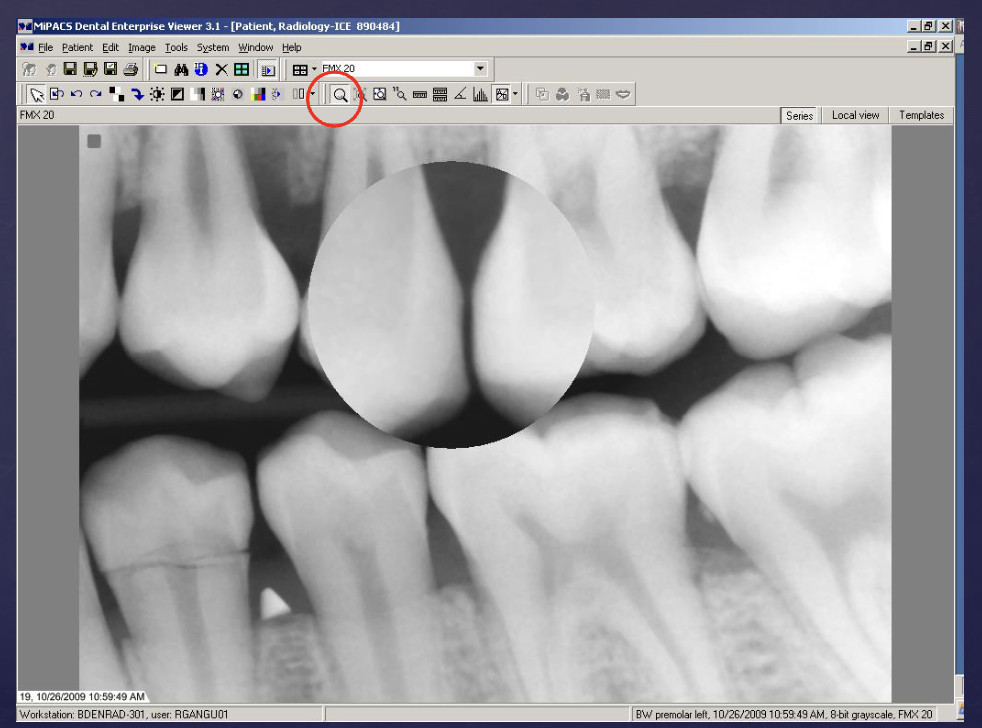
what type of digital processing is this?
inversion
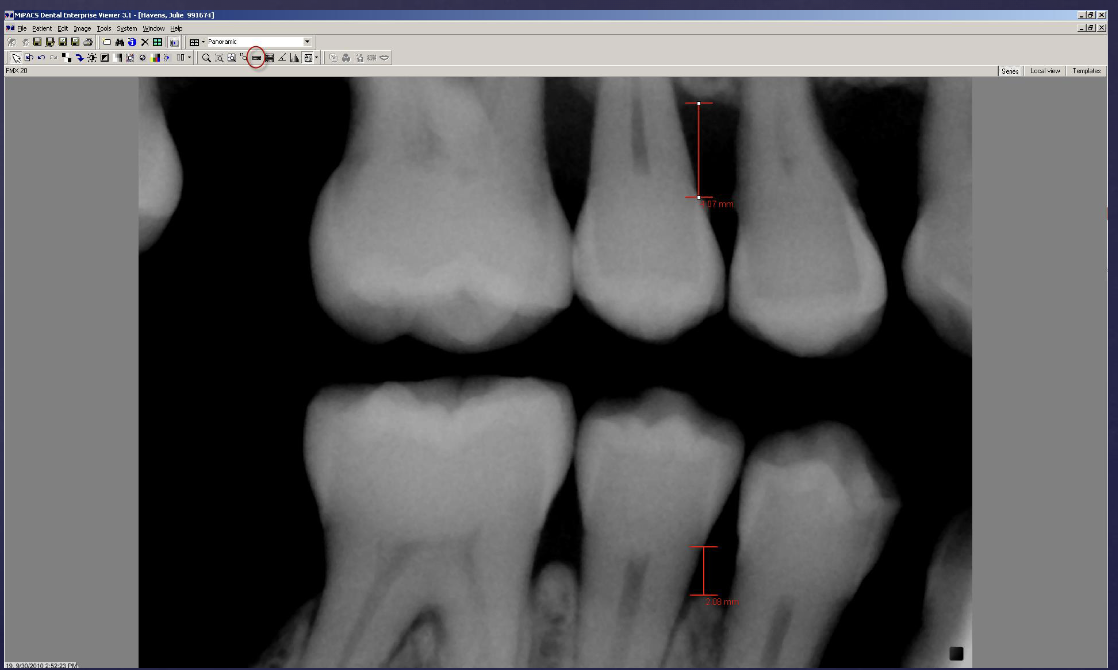
what type of digital processing is this?
linear measurement
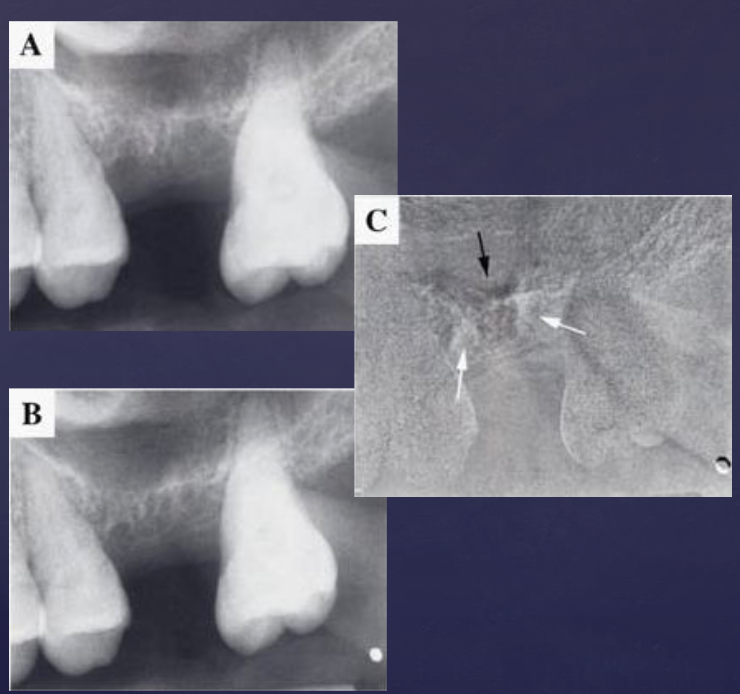
what is digital subtraction radiography?
• Image A-immediately after extraction
• Image B- one month later
• Image C- subtraction of figures A and B revealed areas of bone loss (black) and bone deposition (white)
Jpeg images cannot be manipulated because it is compressed. what file is standard practice?
Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM)
what guidelines should we follow for image storage?
accessibility and backup
what are the advantages of digital imaging?
instant image availability, storage, and retrieval
dose reduction (2-8 fold)
ability to process (contrast, magnify, etc.)
ability to transfer from one location to another (teleradiology)
ability to duplicate without loss of quality
better pt communication
what are the disadvantages of digital imaging?
high initial costs
sensor placement (inflexible, rigid, cable)
image quality
evolving technology
other
unfamiliarity
learning curve for staff
what are clinical applications of digital imaging?
anywhere film would be used
teleradiology
integration into e-records
pt education
what type of imaging is it when both the x-ray source and the image receptor are outside the patient’s mouth?
extraoral imaging
what are the components of a film cassette used in extraoral imaging?
screen film + intensifying screen
digital receptor (direct, PSP)

how do intensifying screens work in extraoral imaging?
Phosphor layer in the screen absorbs x ray photons and emits visible light (blue or green)
Visible light exposes the screen film
t/f: Significant reduction in patient exposure using screen film compared to intraoral film
true
standard intensifying screens are made of…?
calcium tungstate (blue light)
rare earth intensifying screens are made of …?
gadolinium or lanthanum (green light)
what are types of extraoral imaging?
Panoramic
Cephalometric (Lateral and PA)
PA (Postero-Anterior)
Lateral Oblique view
Waters’ projection
Submentovertex view
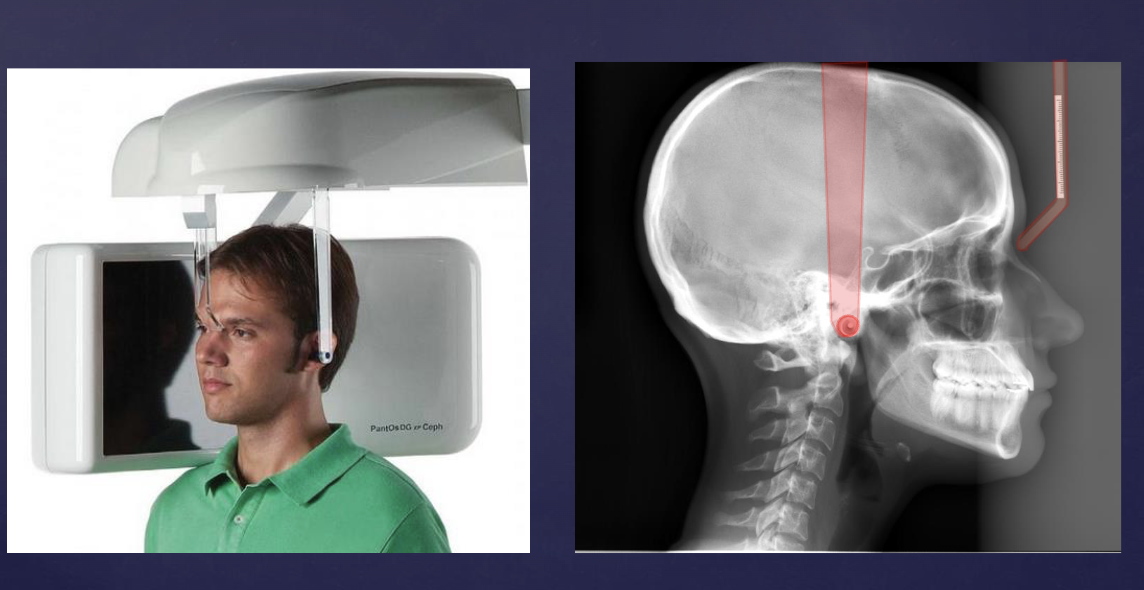
what type of extraoral image is this?
lateral Cephalometric projection
when are lateral Cephalometric projection useful?
orthodontics (cephalometric analysis)
survey of skull/facial bones (trauma, disease, developmental abnormality)
assessment of nasopharyngeal soft tissues, paranasal sinuses
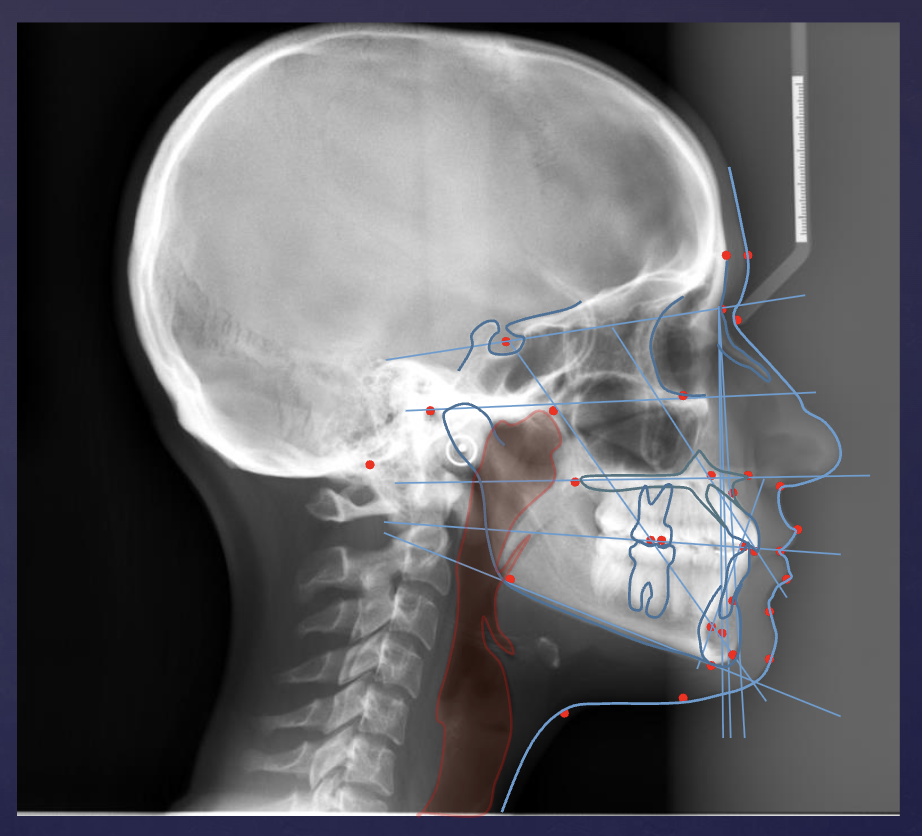
when are PA Cephalometric projection useful?
assess symmetry
evaluate skull for trauma, disease, developmental abnormality
assess frontal, ethmoid sinuses + nasal fossa and orbits
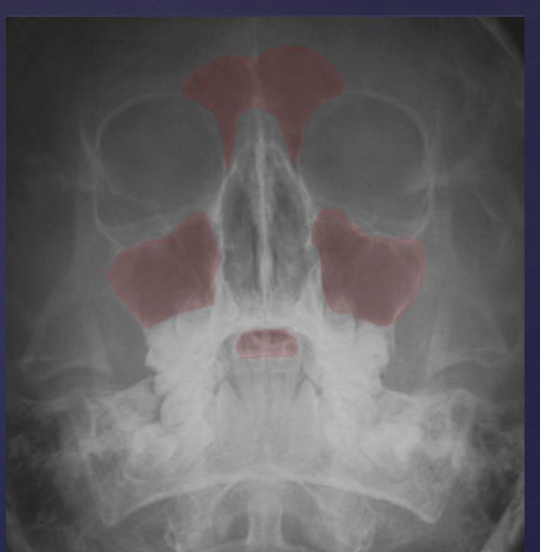
when are waters’ projection useful?
evaluating maxillary, frontal, ethmoid sinuses
orbit
zygomaticofrontal suture
nasal cavity