Immunology
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 3 Bio 251 - rate my flashcard bixxxt!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What is immunology
Immunology is the study of immune system
3 Lines defense in the human body
Skin, mucous membrane, antimicrobial substance
Inflammation, fever, phagocytes
Humoral and cellular immunity
Innate Immunity
Present at Birth
Doesn’t change with use ( doesn’t improve)
Always available for rapid response to invade microbes
Does not recognize specific microbes
Adaptive Immunity
Developed over a lifetime
Develops more and improve with use ( memory response)
Extremely specific
1st line of Defense : Skin and Mucous membrane
Skin and mucous membrane are the first line of defense against pathogens that try to enter your body
Physical and chemical
Skin provides basic physical barriers
Epidermis (Physical) - not alive
Dermis ( Most alive ) ( Chemical - Sebum & Fatty Acid)
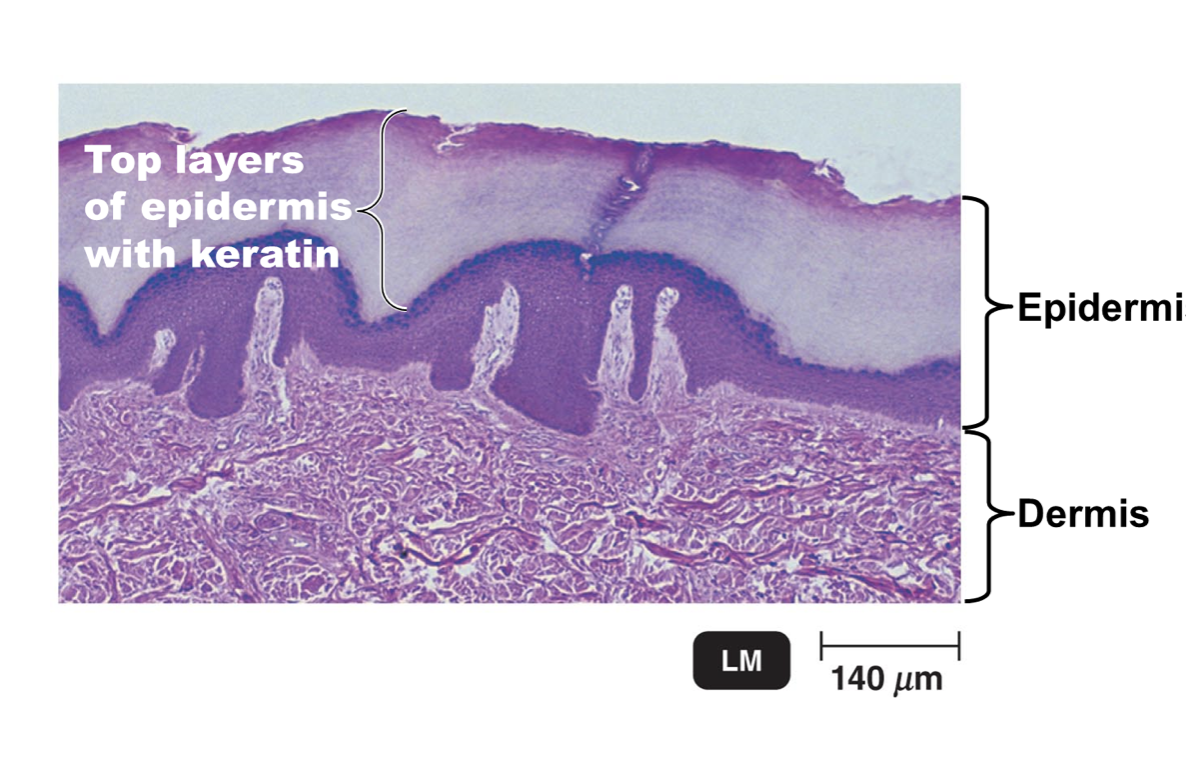
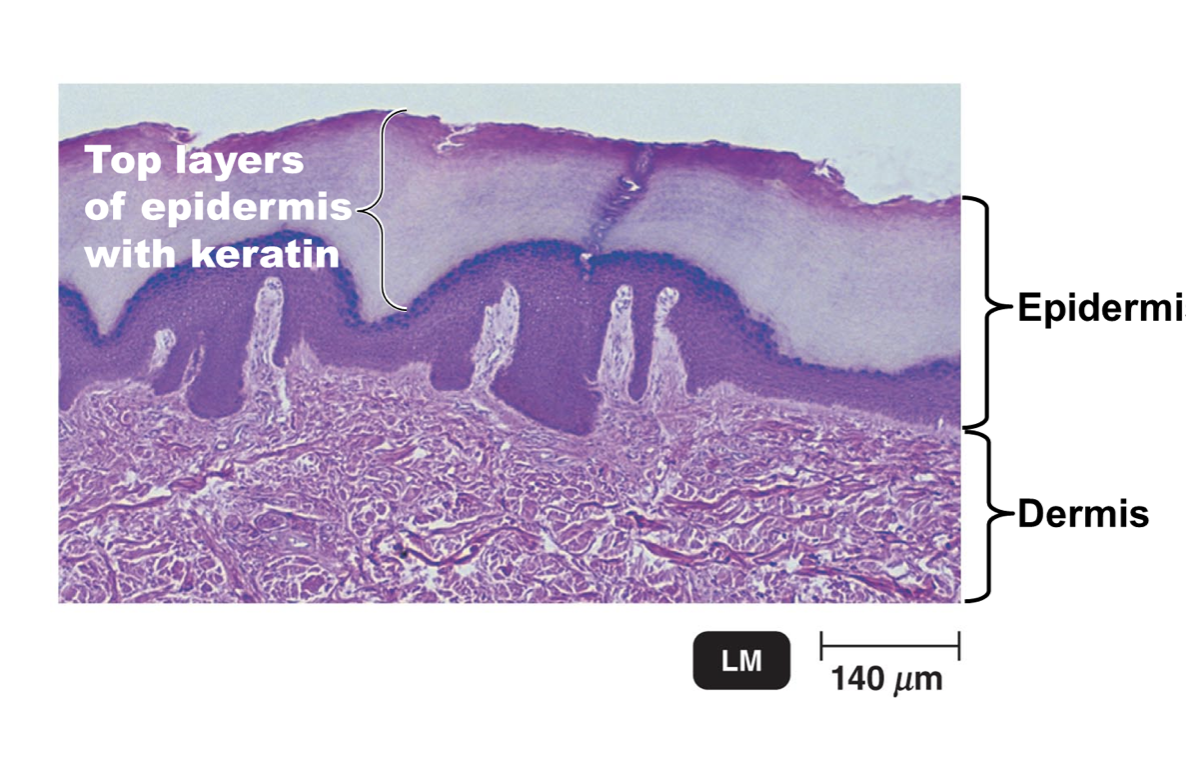
Epidermis
Outer, thinner portion of skin
Many layers of tightly packed cells
Topmost layer is dead and contains keratin (protective protein)
No Blood vessels
Dry
Periodic shedding
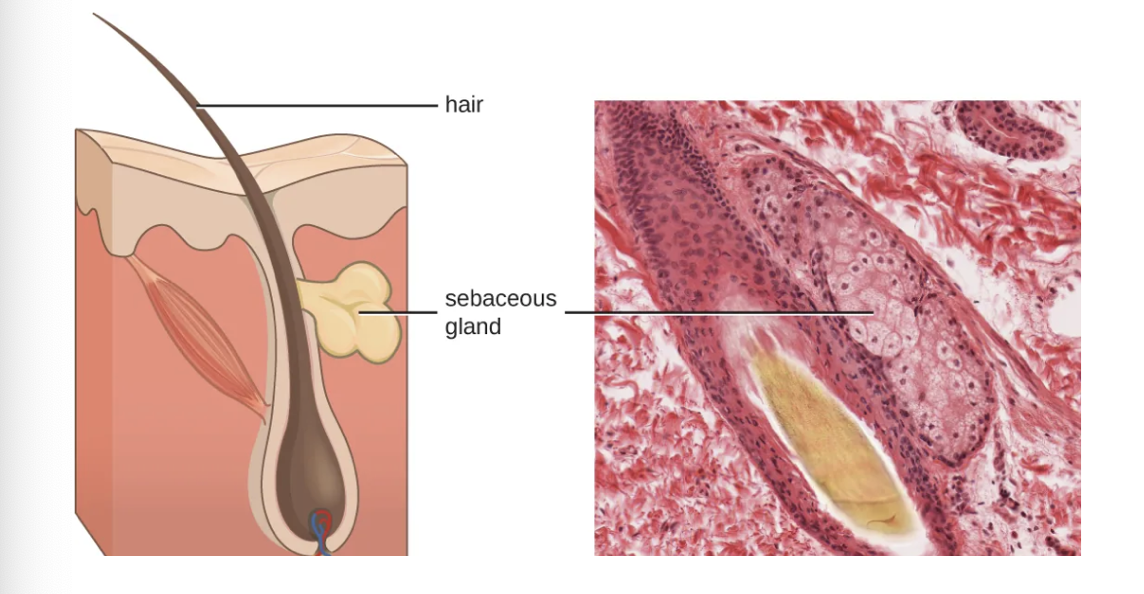
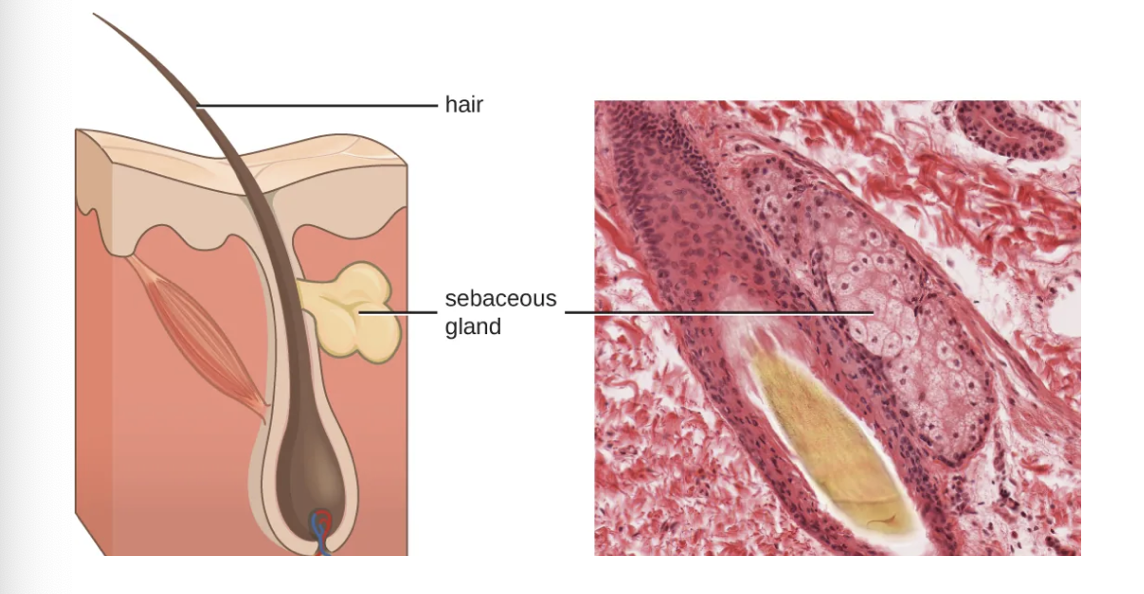
Skin - Chemical Protection
Skin Contains:
Sebaceous Gland - produces an oily substance called Sebum
Protective film over skin
Lowers pH ( 3-5)
Contains unsaturated fatty acid
Inhibits bacteria and fungi
Sweat Gland - Chemical Protection
Sweat Gland:
Perspiration to flush microbes from surface
Contains lysozyme - enzyme breaks down bacteria cell walls
Mucous membrane - Provide protections
Mucous membrane line the entire gastrointestinal (GI), respiratory and genitourinary tracts
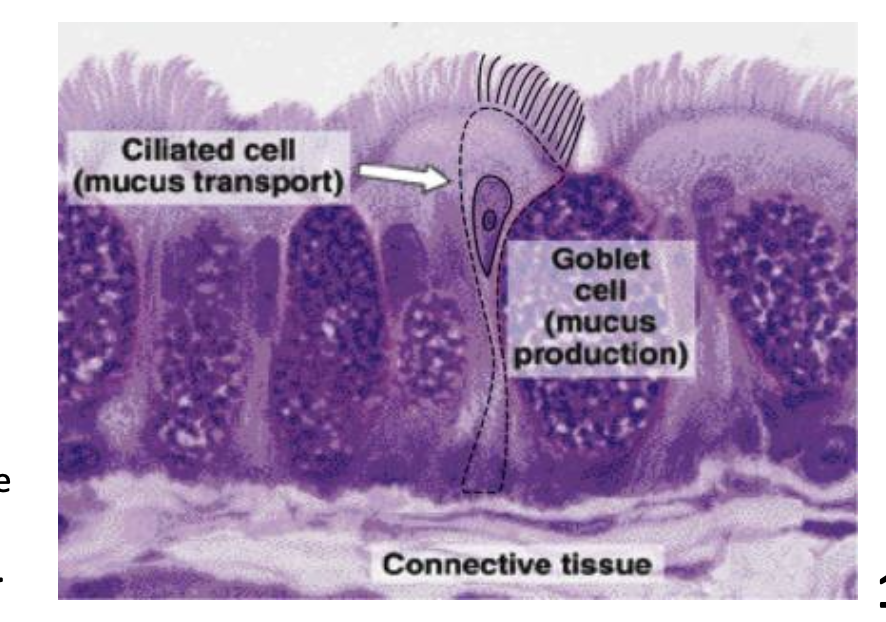
Goblet cells ( type of epithelial cell) secretes mucus, slightly viscous fluid composed of glycoproteins
Around orifices there’s a Mucous membrane secretes mucous viscous substance that helps trap things like microbes & dust ***
Function of Mucous Membrane
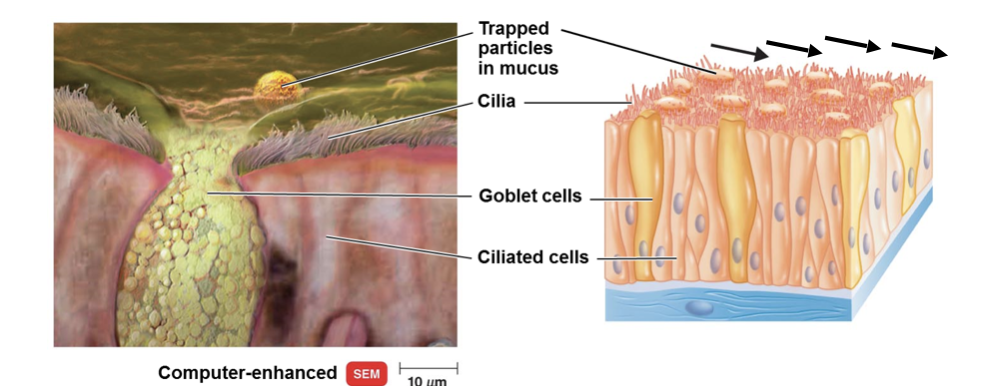
Mucus and mucous membrane provide several functions:
Mucus traps microbes
Mucous membrane of the nose has hairs that filter inhaled air
External canal has earwax and hairs that prevents entry
Cells of mucous membrane of lower respiratory tract are covered in cilia
Ways to EXPEL microbes
Release by: ** gotta know
Tears ( Lacrimation)
Saliva Production
Peristalsis ( Propels food along GI)
Defecation
Vomiting Diarrhea
Urine Flow
Microbiota Defense
Normal microbiota are not usually considered part of the first line of defense, but some of these microbes offer protection by preventing pathogens from colonizing the host by:
Competing with pathogens for nutrients.
Producing substances harmful to pathogens.
Altering external conditions (pH or oxygen availability).
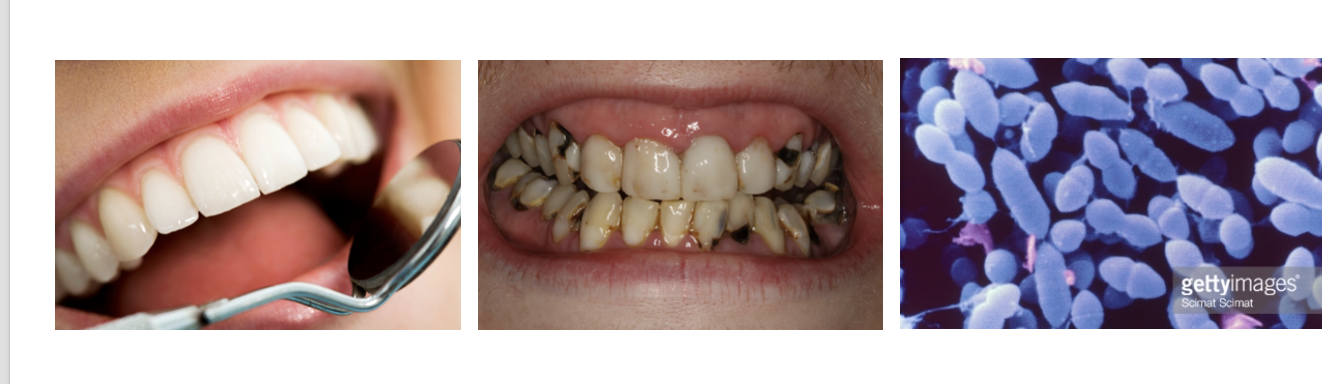
Oral Health
S. Mutans ( BAD) - a prominent cause of tooth decay ( produces lactic acid that dissolves teeth enamel and inhibits growth of other bacteria)
S. Sanguines ( GOOD ) - beneficial bacterium that competes with S. Mutans by producing hydrogen peroxide
Phagocytes
EAT for living
Phagocytosis: the ingestion of microorganism or other substance by cell
Phagocyte : Phago- to Eat
Cye : Cell
Invade Microbes
How do Phagocytes know what to eat?
Phagocytes can recognize self vs. Non Self
“Check” pat down cells to recognize parts that do belong and foreign cells
If contact with foreign cells ( virus) they can respond to them. With receptors called : TLR (Toll-Like Receptors) and PAMPS
PAMPS helps recognize pathogens by innate immunity * ENGULF It
many types of TLR & PAMPS
PAMPS
Pathogens-associated molecular patters are molecules found on pathogens recognized by the innate immunity
TLR
Toll-Like Receptors
are protien receptors on the surface of phagocytes that bind to PAMPS
Immune cells have pattern recognition receptors
4 Main Stages Phagocytosis
1 - Chemotaxis
2 - Adherence
3 - Ingestion
4 - Digestion
Chemotaxis
Chemical signals attract phagocytes to microorganism
sense it towards the gradient ( attraction)
Adherence
Attachment of phagocyte to the surface of the microorganism
attachment **
Ingestion
Plasma membrane extends pseudopods that engulfs the microorganism once engulfed, microbe is in phagosome
eats it **
Digestion
Microorganism is digested and broken down inside a phagolysosome
phagosome Fuse with lysosome
Release waste - on what’s not digestible ( poops it)
Where are phagocytes in the body
Circulatory System
Lymphatic System
Cardiovascular System
Runs parallel from cardio system
found around the same spots of arteries and veins
Phagocytes and other immune cells aggregate in lymphoid tissue and lymph nodes
Inflammation - 2nd line of Defense
Inflammation is a local defensive response to any type of cellular/tissue damage
Cause Damage:
Microbial Infection
Physical agents ( Heat, Radiation, Sharp Objects)
Chemical Agents ( Acids & Bases)
Function of Inflammation
Destroy the microbe and remove it’s by- products ( like toxins)
Damage control
Helps recruit cells & proteins to help repair cells & replace damaged tissue
Cellular Response during Inflammation
Damage cells signals chemicals
that cause vasodilation ( increase blood flow more leaky)
Increase permeability ( helps phagocytes move from blood vessel to the infection site)
Recruitment of phagocytes!!!
Chemical Signals
Cause vasodilation & permeability and attract phagocytes to Local site of inflammation
Cytokines ( Chemical Signal)
Important chemical signal to help recruit phagocytes to local site of inflammation
Interferons - Chemical Signal
Type of cytokine
Signals release when cell is infected by virus
Infected cells release interferons to alert neighboring cells - let them know they are infected!
2 Phases of migrations reach the infected area
Margination Phase
Phagocyte sticks to endothelium (lining) of blood vessel
Blood vessel → Tissue
(Rolling sicking*)
Diapedesis | Extravasation Phase
Phagocyte squeezes between endothelial cell to each infected area
Squeezing through the epithelium
Signs & Symptoms of Inflammation
Redness
Vasodilation
Swelling
Vasodilation
Blood vessel fluid leakage
Increase in cell number
Heat
Vasodilation
Increase in cell activity
Pain
Damage
Pressure
Increase nerve sensitivity
Complement - Antimicrobial Defense
Protein-Base antimicrobial defense system
Over 30 different proteins involved
Activation chain - 30 different protein involved
Like a cascade - one triggers another, amplifying the effect ( dominos effect)
MAC ( Membrane attack complex)
Complement system putting a hole in the membrane
Complement protein bind together to form a “ pore” in microbe cell membrane causing it to Cytolysis death
Outcome: Inflammation & Cytolysis
Cell - cuts