Psych Exam 3
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/117
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:08 AM on 11/17/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
1
New cards
binocular cues
depth perception
convergence: closer object = greater convergence
convergence: closer object = greater convergence
2
New cards
monocular cues
relative size, clarity, linear perspective
3
New cards
Perceptual constancy
interpretation of changing sensations as perception that is relatively consistent
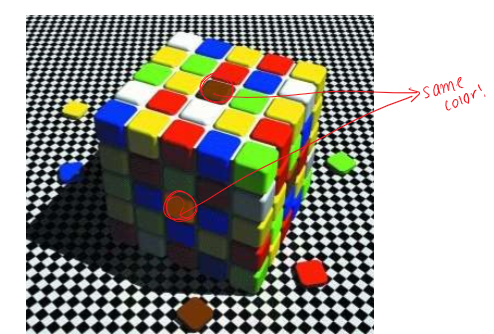
4
New cards
color constancy
consistent perception of color of objects although the amount of light changes (brain automatically adjusts for illumination)
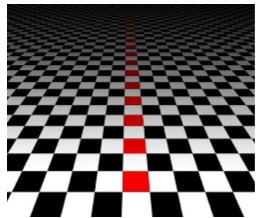
5
New cards
lightness constancy
consistent perception of shade of objects although the amount of light changes
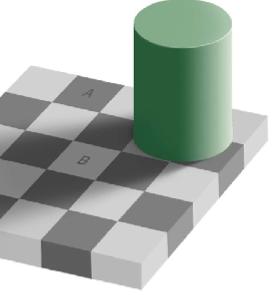
6
New cards
shape constancy
perception that object's shape remains constant despite changing shape of retinal image (ex: spinning coin)
7
New cards
size constancy
perception that the size of objects remains constant despite different sizes of images on retina
8
New cards
classical conditioning
learning to respond to a new stimulus that has been associated with another stimulus that normally produces the behavior (automatic responses) ex: Jim/Dwight prank
9
New cards
operant conditioning
learning behaviors due to experiences with their consequences (punishment/reward to behavior)
10
New cards
observational learning
learning via observation and imitation
11
New cards
neutral stimulus
stimulus that doesn't normally cause a response ex: bell
12
New cards
unconditioned stimulus
stimulus that automatically elicits response without prior conditioning (the thing you don't have to learn a response to) ex: food
13
New cards
unconditioned response
innate response to unconditioned stimulus ex: salivation
14
New cards
conditioned stimulus
previously NS that now elicits a conditioned response due to its association with a US ex: bell
15
New cards
conditioned response
learned response to a stimulus that did not originally elicit the response ex: salivation
16
New cards
acquisition
stage of conditioning in which the association between the 2 stimuli (US and CS) is being learned; need to happen closely together
17
New cards
generalization (classical)
conditioned response to stimuli that are not the conditioned stimulus (but similar to the CS) ex: if Pavlov blew a whistle, dog will salivate bc whistle is similar to a bell
18
New cards
discrimination (classical)
CR occurs only to a specific stimulus (the CS)
19
New cards
extinction (classical)
failure to exhibit the CR to the CS because the CS no longer predicts the US
20
New cards
spontaneous recovery (classical)
reappearance of the CR to the original CS after extinction
21
New cards
second order (higher-order) conditioning
new neutral stimulus becomes associated with previously conditioned stimulus - becomes new CS ex: light on, ring bell, light bell, then food, then light will also become associated with food
22
New cards
conditioned aversion
classically conditioned association between CS and US that causes an unpleasant response ex: bad experience with something once turns you away from it again
23
New cards
counterconditioning
replacing unwanted CR with wanted response ex: gradually introduced cookies to child scared of rabbits to make him not as afraid of them anymore
24
New cards
law of effect (Thorndike)
the tendency of an organism to produce a behavior depends on the effect the behavior has on the environment ex: cat puzzle box
25
New cards
skinner box (operant chamber)
hungry animal placed in box, press bar and they receive food which becomes the reinforcer, increasing bar pressing
26
New cards
reinforcement
consequence of behavior that increases the probability that the behavior will occur
27
New cards
punishment
consequence of behavior that decreases the probability that the behavior will occur
28
New cards
shaping
reinforcing closer and closer approximation of the desired response (break final behavior into parts such as teaching a dog a long trick, break it down into steps)
29
New cards
successive approximations
responses that are increasingly similar to the desired response
30
New cards
positive reinforcement
presentation of a pleasant stimulus after a behavior -> increases probability of that behavior
31
New cards
negative reinforcement
removal of an unpleasant stimulus after a behavior -> increases probability of that behavior
32
New cards
positive punishment
unpleasant stimulus follows behavior -> decreases probability of that behavior
33
New cards
negative punishment
removal of pleasant stimulus after a behavior -> decreases probability of behavior
34
New cards
generalization (operant)
after a behavior is reinforced in one situation, it is performed in a different situation
35
New cards
discrimination (operant)
a behavior that is reinforced in one situation is not performed in a different situation
36
New cards
extinction (operant)
after the reinforcer is withdrawn, the behavior decreases
37
New cards
spontaneous recovery (operant)
after extinction, the behavior reappears
38
New cards
continuous reinforcement
consequences are the same each time the behavior occurs (better for initial/fast learning)
39
New cards
intermittent (partial) reinforcement
consequences are given only some of the times the behavior occurs (better for long term learning)
40
New cards
ratio schedules of reinforcement
reinforcement is given after the behavior is exhibited a certain number of times
41
New cards
interval schedules of reinforcement
reinforcement is given after a certain amount of time
42
New cards
fixed-ratio
reinforcement for a fixed proportion of responses emitted
43
New cards
variable-ratio
reward for some percentage of responses, but unpredictable number of responses required before reinforcement (ex: going door-to-door to sell something, slot machines)
44
New cards
fixed-interval
reinforcement for responses after a fixed amount of time
45
New cards
variable-interval
reinforcement for responses after an amount of time that is not constant (ex: pop quizzes)
46
New cards
problems with punishment
difficult to identify which behavior is being punished, doesn't teach what not to do, the person may fear the one punishing, does not eliminate existing rewards for the behavior, can model aggression
47
New cards
extrinsic motivation
pursuit of a goal for external rewards (ex: to do it for something else)
48
New cards
intrinsic motivation
pursuit of activity for its own sake (ex: do it for your own good)
49
New cards
overjustification effect
too much reward undermines intrinsic motivation
50
New cards
modeling
imitating others' behavior
ex: Bandura experiments with Bobo doll
ex: Bandura experiments with Bobo doll
51
New cards
memory
information that has been stored and can be retrieved
52
New cards
3 steps of information processing model
encoding, storage, retrieval
53
New cards
encoding
getting info into memory
54
New cards
storage
maintaining encoded info over time
55
New cards
retrieval
pulling from previously encoded and stored info from memory
56
New cards
3 stages of memory formation
sensory, short-term, long-term
57
New cards
sensory memory
system that holds sensory info (visual, auditory) for a very brief time after the stimulus disappears
58
New cards
iconic memory
visual sensory memory (ex: double take)
59
New cards
echoic memory
auditory sensory memory
60
New cards
short-term memory
for info that is available to consciousness for about 20-30 seconds; capacity is about 5-9 items in memory
61
New cards
long-term memory
relatively permanent memory with unlimited capacity
62
New cards
explicit memory
conscious recollection of material from long-term memory (declarative)
63
New cards
semantic memory
memory of general knowledge and trivia
64
New cards
episodic memory
memory of personally experienced events
65
New cards
implicit memory
not brought to mind consciously, but expressed in behavior (nondeclarative)
66
New cards
procedural memory
memory for the performance of skills ex: riding a bike, skills, abilities
67
New cards
priming
prior exposure to a stimulus affects responses to a later stimulus (ex: read a story with rude words vs without, and then observed for rude behavior afterward)
68
New cards
recall
producing memories using minimal retrieval cues (ex: fill in the blank, short answer)
69
New cards
recognition
knowledge of whether one has previously been exposed to info (ex: multiple choice)
70
New cards
relearning
learning occurs more quickly the second time it is learned
71
New cards
chunking
organizing info into smaller meaningful pieces to facilitate memory
72
New cards
mnemonics
strategies and tricks for improving memory through acronyms or sounds
73
New cards
rehearsal
repeating some information
74
New cards
maintenance rehearsal
rote repetition of material
75
New cards
elaborative rehearsal
thinking about the meaning of the information and examples
76
New cards
levels of processing (Craik & Tulving)
information can be processed at different depths, from shallow to deep
77
New cards
shallow processing
superficial features, such as physical appearance (led to less memorization of list of words)
78
New cards
deep processing
meaning of the words (led to better memorization of list of words)
79
New cards
encoding specificity
specific cues are encoded with the memory
80
New cards
context-dependent memory
the environment in which something is learned serves as a cue for retrieval (ex: take the exam in the same room you learned the material)
81
New cards
state-dependent memory
physical or mental state in which something is learned serves as a cue for retrieval (ex: chew gum while studying so you chew gum during the exam)
82
New cards
encoding failure
memory fails to form due to lack of attention or processing
83
New cards
storage decay
after memory has been stored, may fade
84
New cards
ebbinghaus's forgetting curve
after forming a memory, majority of forgetting occurs initially
85
New cards
retrieval failure
stored memories cannot be accessed (ex: tip-of-the-tongue phenomenon)
86
New cards
anterograde amnesia
memory loss for info encountered after a head injury
87
New cards
retrograde amnesia
memory loss for info from before head injury
88
New cards
heuristics
simple rules for making complex decisions/judgements
89
New cards
representativeness heuristic
tendency to see someone or something as belonging to a particular group or category by evaluating how similar this person or thing is to a typical person or thing in that category
90
New cards
base-rate fallacy
using the representativeness heuristic means ignoring base rates
91
New cards
base rates
frequency with which given events or cases occur in the population
92
New cards
availability heuristic
strategy for making judgements based on how easily specific kinds of information can be brought to mind (what you can think of easily, vivid memory)
93
New cards
simulation heuristic (counterfactual thinking)
imagining alternative version of actual events shapes emotional response (thinking about how you could do something differently like 1st, 2nd, 3rd place)
94
New cards
perseverance effect (belief perseverance)
beliefs tend to persist in the face of disconfirming information
95
New cards
confirmation bias
tendency to search for and use information that is consistent with our existing beliefs (like listening to who you resonate with)
96
New cards
outcomes of biligualism
greater cognitive flexibility, think more creatively, higher academic achievement in upper grades
97
New cards
enriched experiences
increases IQ with more stimulus, spur brain development
98
New cards
Romanian orphanages
little contact and stimulation led to cognitive impairment
99
New cards
stereotype threat
threat felt when stereotype is salient to targets of negative stereotypes
ex: a girl being aware of the stereotype that girls are bad at math would cause her to perform worse at math
ex: a girl being aware of the stereotype that girls are bad at math would cause her to perform worse at math
100
New cards
4 counters to stereotype threat
-be aware of the stereotype threat
-be aware of role models to help
-recognize your values and affirmations
-know that skills are malleable
-be aware of role models to help
-recognize your values and affirmations
-know that skills are malleable