Biology Midterm
1/177
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
178 Terms
Amino Acid
Monomers of proteins, 20 amino acids. Can be acidic or basic, hydrophilic or hydrophobic.
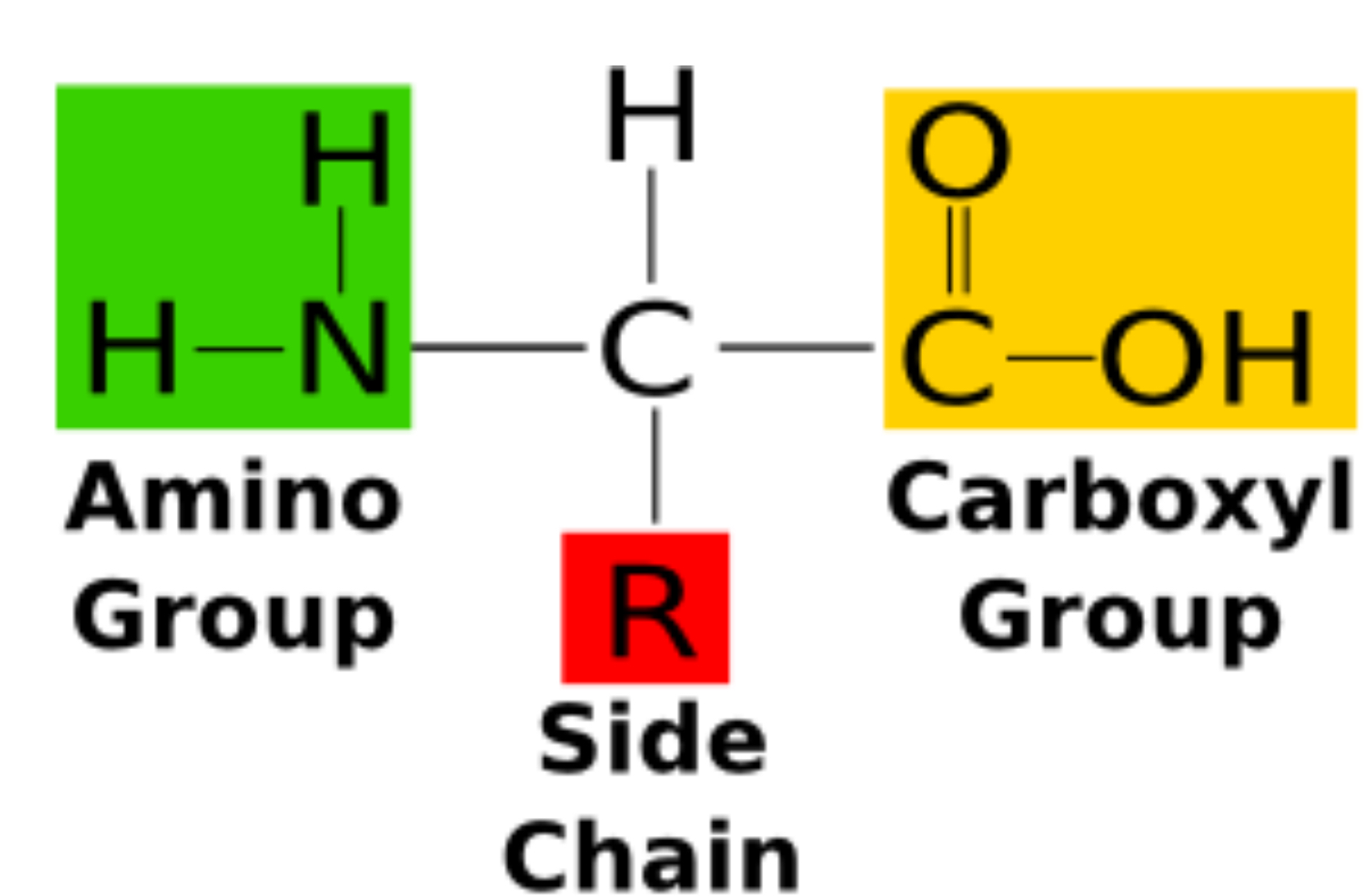
R Group
Part of an amino acid that differs and gives amino acid different properties
Peptide Linkage
Covalent bond between carboxyl group and amino group of 2 amino acids. Formed through condensation.
Tripeptide
Three amino acids bonded together
Nutrient
A chemical substance found in food used by the body
Essential Amino Acids
Cannot be synthesized by the body
Non-essential Amino Acids
Can also be through metabolism if necessary. This process is called transamination
Denaturation
When a protein folds incorrectly because of a change in temperature of pH
Primary structure
Linear sequence of amino acids
Secondary structure
Protein folds open itself through hydrogen bonds in backbone, no interaction between R groups (ex: alpha helices and beta sheets)
Tertiary structure
Interactions between R groups
Quaternary structure
2+ polypeptide chains come together to form a complex bioactive molecule
Integral proteins
Proteins attached to membrane
Conjugated protein
Has a non-protein prosthetic group.
Non-conjugated structure
Has no non-protein group.
Insulin
Hormone made in the pancreas that promotes the synthesis and storage of glycogen in the liver and muscle cells
Hemoglobin
Protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen
Collagen
A non-conjugated protein
-Three polypeptide molecules, triple helix
-Every third amino acid is glycine
-Stacks of the triple helices form fibers
Cell Theory
Cells can only arise from preexisting cells
Living organisms are comprised of cells, the smallest unit of life
Unicellular organisms carry out all functions of life in one cell
Unicellular
Single cell organisms
Multicellular
Organisms made of many cells
Protists
Single cell eukaryotes
Prokaryote
Unicellular, no nucleus or membrane bound organelles
Very small
Nucleoid instead of nucleus
70s ribosomes
2 types: Eubacteria and archaea
Bacteria
Unicellular organisms with a cell wall (made of peptidoglycan), plasma membrane, cytoplasm, naked DNA (sans histones) , 70s ribosomes
Sometimes have pilli and/or flagella
Pilli
Little ‘hairs’ on some bacteria that enable attachment to other bacteria
Flagella
A tail that allows bacteria to move around
Gram positive bacteria
thick cell wall, stains red/pink
Gram negative bacteria
thin cell wall, stains purple
Differentiation
Process by which cells become specialized, some genes/proteins are expressed more than others
Eukaryotes
Cells with membrane bound organelles and a nucleus, 80S ribosomes
Organelles
‘Little organs’ with specialized functions in cells
Cytoplasm
Fluid in cells, contained by plasma membrane
Plasma membrane
semi permeable membrane made of lipids and proteins
Nucleus
Control center where DNA is stored
Nuclear envelope
Double layered membrane that surrounds nucleus
Nuclear pores
Small holes in nuclear envelope that allow materials (such as RNA and proteins) in/out of nucleus
Chromosome
Length of DNA that carries specific genes
Condensed during mitosis and meiosis
Contained within nucleus
Chromatin
Nuclear material made of DNA and histone proteins, contained in nucleus
Nucleolus
Sited of ribosome synthesis, in nucleus
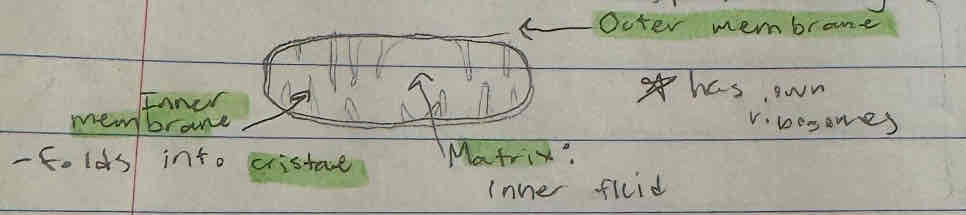
Mitochondria
Organelle, site of Krebs Cycle and Electron Transport Chain
Produces ATP, number depends on cell type/activity
Endoplasmic reticulum
Network of folded tubes, sacs and sheets
Transports stuff throughout cell
Made up of proteins, connected to nuclear envelope
Can have ribosomes (Rough ER) or not (smooth ER)
Golgi Apparatus
Modifies, sorts, and packs proteins for shipment
Stack of flattened membranous sacs (‘pancakes’)
Lysosomes
Spherical vesicles surrounded by a single membrane
Hydrolytic enzymes break down waste and foreign materials
Involved in autolysis and apoptosis (cell suicide)
Gene mutation
Change in the sequence of bases of a gene, more likely to occur in areas with less accessory proteins
Substitution
Swapping one base for another
Insertion
Adding a base to the DNA sequence
Deletion
Removing a base from the DNA sequence
Frameshift
Mutation (insertion or deletion) that ‘messes up’ (shifts) 3 base pair codons
Every codon is affected by mutation
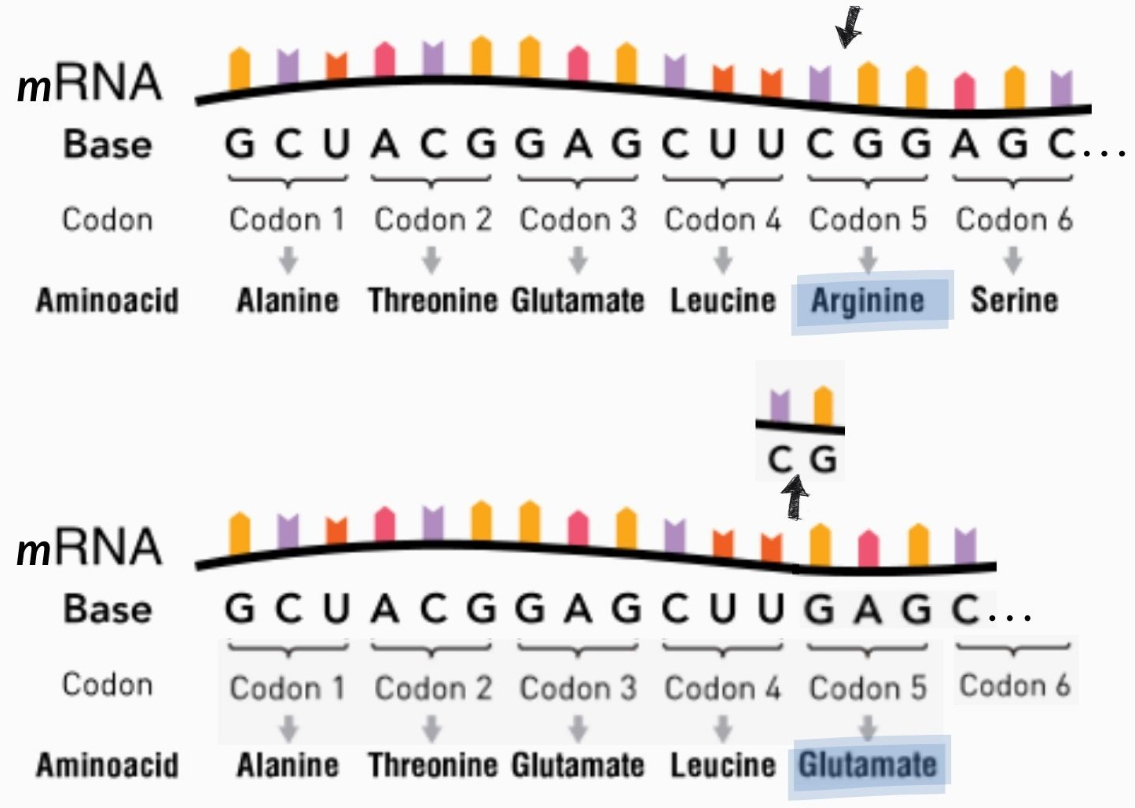
Degeneracy
AKA redundancy
Different codons can encode for same amino acid
Means that mutations sometimes have no impact
Mutagen
Agent that causes a genetic mutation
Can cause cancer (ex: radiation, bacterial infection, carcinogens, hpv)
Not all mutations are caused by mutagens
Transition
A substitution with a base of the same shape (Ex: Purine —> purine), less likely to change amino acid
Transversion
A substitution with a different shape of base, (ex: purine —> pyrimidine)
Germaine mutations
Occur in germ (reproductive) cells, passed down to offspring
Somatic mutations
Occur in somatic (non-reproductive) cells, passed down as cells divide in body
Genetic knockout
Deactivation or removal of a specific gene
Mutant
A genetically modified organism with 2 knockout alleles
Model Organisms
Non-human species that scientists use in the lab to investigate and understand biological processes
CRISPR
Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats, used as microbial immune system to remember and fight viruses
Used for gene editing
Cas
CRISPR associated protein
CRISPR Cas9
Gene-editing technology derived from bacterial CRISPR system. Cuts specific DNA then DNA repair mechanisms fix it in a way that modifies genetic sequence.
Cas9
Endonuclease that cuts strands of DNA at a specific site
Protospacer adjacent motif (PAM)
DNA sequence where Cas9 binds, downstream of target sequence
Non-homologous end joining (NHEJ)
Repair stage of CRISPR Cas9. Enzymes reconnect ends of broken DNA
Risky and can lead to mutations
Homology directed repair
Repair stage of CRISPR Cas9
Researchers design an RNA template to patch the breaK. A complementary DNA strand is created during repair.
Transcription
Synthesis of mRNA from DNA template, carried out by RNA polymerase
Promoter
A DNA sequence that is recognized by RNA polymerase to promote transcription
Template strand
Used to transcribe mRNA
AKA antisense/non-coding strand
3’-5’
Non-template strand
AKA coding/sense strand
5’-3’
Enhancer regions
Areas of DNA that increase transcription rates when a protein binds to them
Repressor regions
Areas of DNA that decrease transcription rates when a protein binds to them
Transcription initiation complex
Proteins and enzyme (RNA polymerase) that start transcription
Transcription factors
Factors that help initiate transcription, different factors can activate different genes
Gene expression
How the information is a gene directs protein synthesis
Ex: Housekeeping genes (always expressed), developmentally expressed, expressed in mature cells, signal based expression
Reverse transcription
RNA is converted to DNA, carried out by reverse transcriptase
RT-PCR
reverse transcriptase PCR
Introns
Non-coding sequences that interrupt coding sequences, transcribed but not translated
Exons
Coding sequences, transcribed and translated
Telomeres
Found at the ends of chromosomes, prevent degradation, attaching to other chromosomes, and apoptosis (programmed apoptosis)
VNTRs
Variable number tandem tandem repeats— short sequences of repeating bases, used in genetic profiling
Post transcriptional
Changes to newly transcribed mRNA, occurs in eukaryotic cells before translation
Transcription Steps
Initiation, elongation, termination
5’ capping
Modified guanine nucleotide added to 5’ end of mRN to prevent nuclear transport and degradation as well as promote translation
3’ polyA tail
100-250 bp chain of adenines added to 3’ end to increase stability
Intron splicing
Introns cut out
Alternative splicing
Splicing to create different combinations of exons
Translation
Synthesis of mRNA to protein, occurs on ribosomes in cytoplasm
Ribosome
Macromolecules used for translation, made of protein and RNA
Have a large and small subunit that come together around RNA
tRNA binding sites
Sites on ribosome where tRNA binds
A site: 1st site, where tRNA and mRNA bind
P site: Peptide strand is transferred on to amino acid
E site: Exit site
tRNA activation
An enzyme facilitated process that produces charged tRNA (tRNA with an amino acid attached)
Enzyme binds to ATP+amino acid
Amino acid/AMP complex forms and specific tRNA molecule is recruited
Amino acid and tRNA bind, AMP released
Translation Initiation
mRNA binds with small ribosomal subunit on 5’ end
Initiator tRNA (w/ methionine) binds to AUG sequence
Moves to P site
peptide linkage
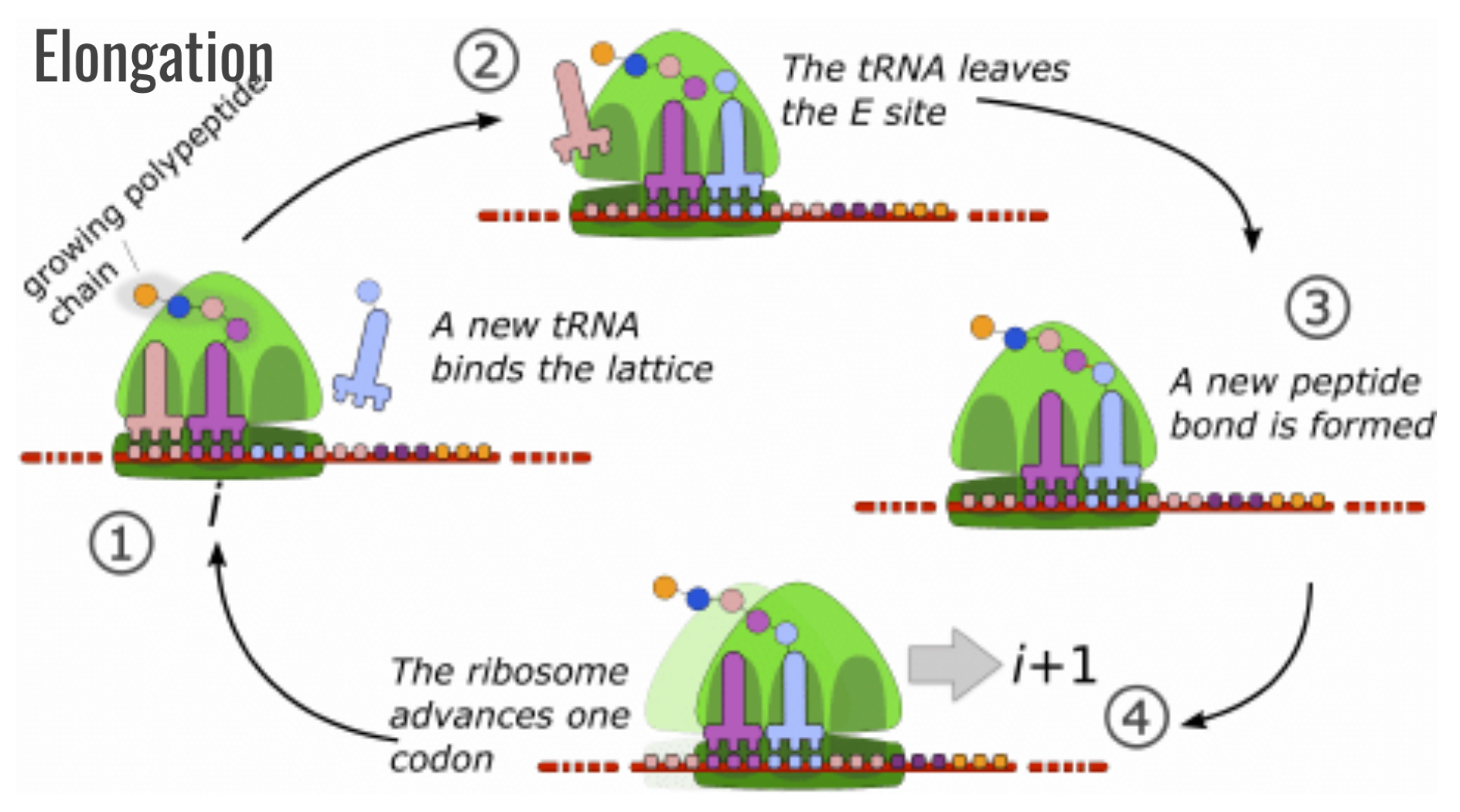
Translation elongation
New activated tRNA moves to A site
Old tRNA leaves E site
Peptide linkage forms in A site
Ribosome advances one codon, tRNAs shift down the line
Process repeats
Post-translational modification
Modification of proteins, ex: glycosilation to create glycoprotein
Ubiquitination
Post translational modification that involves the addition of the protein ubiquitin, prevents degradation
Proteolysis
Breakdown of proteins by hydrolysis, enzyme catalyzed, occurs in proteosomes
Translation termination
When a stop codon (UAA, UAG, UGA) is reached the polypeptide is released from the ribosome
DNA replication
Process by which DNA is copied. Occurs during synthesis phase of interphase.
Semi-conservative replication
Results in two DNA molecules with one original strand and one new strand
Helicase
1st step of replication, peels apart DNA and creates replication fork
Polymerase III
Reads primers and then synthesizes nucleotides
Polymerase I
Removes primers and switches them with nucleotides