DAT Cellular Respiration
4.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/27
Earn XP
Last updated 10:43 PM on 5/26/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
1
New cards
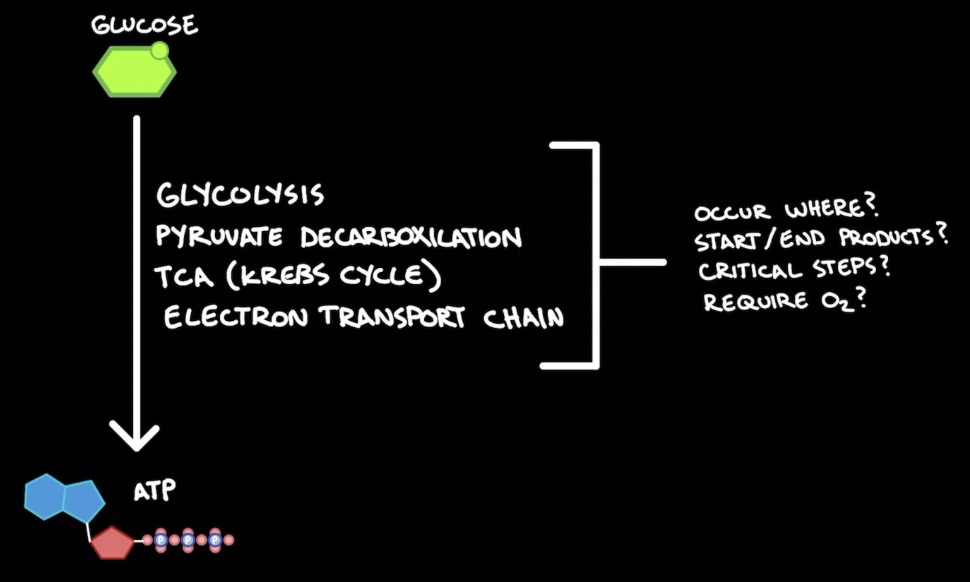
Glucose → ATP
1. Glycolysis
2. Pyruvate decarboxylation
3. TCA (Krebs cycle)
4. Electron transport chain
2
New cards
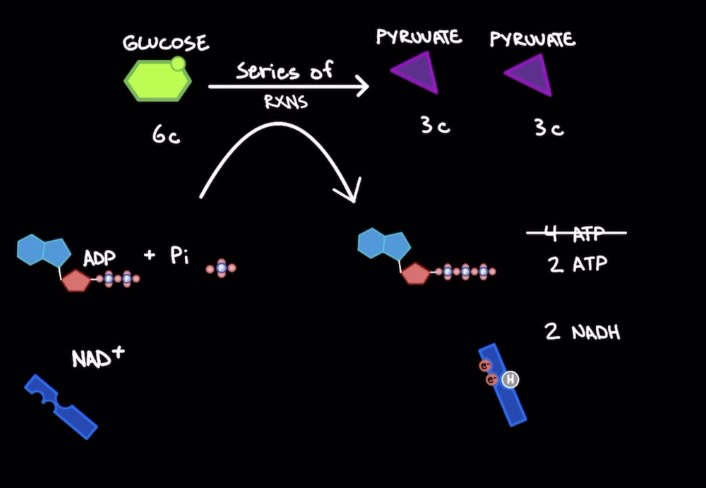
Glycolysis
* Break down of glucose
\
* Anaerobic (no O2)
\
* 1 glucose mol. (6 Carbons) → 2 pyruvate mols. (3 Carbons)
* 2 ATP input → 4 ATP output & 2 NADH = ==2 net ATP mols. & 2 NADH==
\
* Occurs in cytosol (not in organelle)
\
* Steps:
1. ==**Hexokinase:**== phosphorylates glucose → __**Glucose-6-phosphate**__ → irreversible rxn
\
2. ==**Phosphofructokinase (PFK):**== phosphorylates Glucose-6-phosphate → __**Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate**__ → rate limiting step
\
* Anaerobic (no O2)
\
* 1 glucose mol. (6 Carbons) → 2 pyruvate mols. (3 Carbons)
* 2 ATP input → 4 ATP output & 2 NADH = ==2 net ATP mols. & 2 NADH==
\
* Occurs in cytosol (not in organelle)
\
* Steps:
1. ==**Hexokinase:**== phosphorylates glucose → __**Glucose-6-phosphate**__ → irreversible rxn
\
2. ==**Phosphofructokinase (PFK):**== phosphorylates Glucose-6-phosphate → __**Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate**__ → rate limiting step
3
New cards
Most oxidized form of Carbon
* CO2
* Waste product of cellular respiration (occurs via oxidation)
* Waste product of cellular respiration (occurs via oxidation)
4
New cards
Oxidation rxns
* ADP + Pi → ATP (oxidized)
* NAD+ + FAD+ → FADH2 + NADH (oxidized)
* NAD+ + FAD+ → FADH2 + NADH (oxidized)
5
New cards
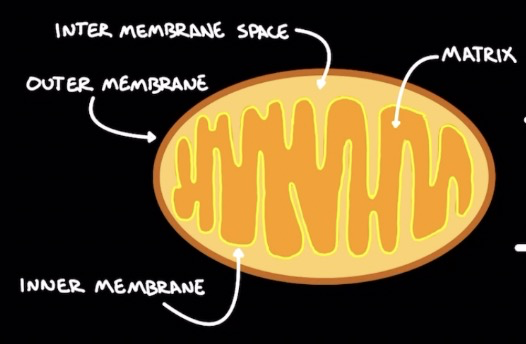
Mitochondria
* Double layered
\
* Outer membrane
\
* ==**Intermembrane space:**== H+ build up
\
* ==**Matrix:**==
* Krebs cycle → produces ATP
* β-oxidation to break down fatty acids
\
* ==**Inner membrane**==: many folds to ↑ surface area → ↑ electron transport chain output
\
* Outer membrane
\
* ==**Intermembrane space:**== H+ build up
\
* ==**Matrix:**==
* Krebs cycle → produces ATP
* β-oxidation to break down fatty acids
\
* ==**Inner membrane**==: many folds to ↑ surface area → ↑ electron transport chain output
6
New cards
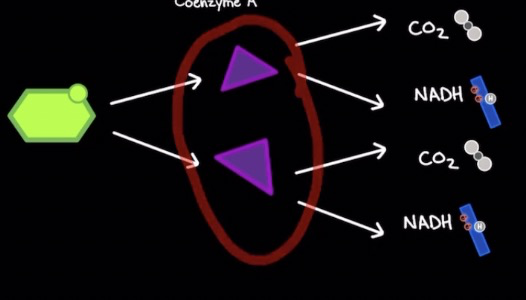
Pyruvate decarboxylation
* Occurs in mitochondrial matrix
\
* Aerobic process
\
* 2 pyruvate molecules from glycolysis transported into matrix via ==**secondary active transport**== **using protons** (doesn’t directly use ATP)
\
* 1 Pyruvate + Coenzyme A → Acetyl CoA + 1 NADH + 1 CO2
* ==**Pyruvate decarboxylate complex (PDC)**== catalyzes rxn
\
* Aerobic process
\
* 2 pyruvate molecules from glycolysis transported into matrix via ==**secondary active transport**== **using protons** (doesn’t directly use ATP)
\
* 1 Pyruvate + Coenzyme A → Acetyl CoA + 1 NADH + 1 CO2
* ==**Pyruvate decarboxylate complex (PDC)**== catalyzes rxn
7
New cards
How many CO2 and NADH yield from the breakdown of 1 glucose?
2 CO2 + 2 NADH
8
New cards
TCA (Krebs cycle) / Citric Acid Cycle
* Occurs in mitochondrial matrix
\
* Aerobic process
\
* 1 Acetal CoA + oxaloacetate → citrate
* Citrate further oxidizes until oxaloacetate is formed and the cycle repeats
\
* Full cycle yields: ==3 NADH + 1 FADH2 + 1 GTP (ATP) + 2 CO2==
\
* Aerobic process
\
* 1 Acetal CoA + oxaloacetate → citrate
* Citrate further oxidizes until oxaloacetate is formed and the cycle repeats
\
* Full cycle yields: ==3 NADH + 1 FADH2 + 1 GTP (ATP) + 2 CO2==
9
New cards
Electron transport chain (ETC)
* Occurs in **inner membrane / cristae** of mitochondria
\
* Aerobic process
\
* Removes e- from glucose, pyruvate and Acetyl CoA
\
* ==**Oxidative phosphorylation**== occurs here
\
* ==**Carrier proteins (I, II, III, IV)**== **in inner membrane (electron acceptors):** receive electrons from electron transporters (NADH, FADH2) → pump protons against \[ \] gradient into intermembrane space to supply energy to ATP synthase
* Highly acidic environment in intermembrane space
* ==CoQ (Ubiquinon):== can be fully oxidized and reduced during passing of electrons b/w protein complexes
* Soluble carrier
* ==Cyt C (Cytochrome C):== bound to Iron atom which transfers electrons b/w **Complex III and Complex IV** for redox rxns
* Protein carrier
* Used for genetic relations
\
* Final electron acceptor (after electrons have passed though all proteins): ==**Oxygen**== → combines w/ H+ to form H2O
\
* ==**ATP Synthase:**== drives protons down the gradient towards matrix (high \[ \] → low \[ \]) to catalyze ADP + Pi → ATP
* pH + Electrical Gradient: **Proton Motive Force**
* If pH of intermembrane space is higher than normal → less H+ → less cellular respiration occurring
\
* NADH creates more ATP (3x) than FADH2 (2x)
* NADH pumps more protons to carrier proteins than FADH2 because NADH enters the protein complex earlier than FADH2 and it enters Complex I (FADH2 enters Complex II)
\
* Total glucose produced = 36 ATP in eukaryotes and 38 in prokaryotes (no mitochondria so don’t need to pump NADH into matrix → saving 2 ATP during glycolysis)
\
* Aerobic process
\
* Removes e- from glucose, pyruvate and Acetyl CoA
\
* ==**Oxidative phosphorylation**== occurs here
\
* ==**Carrier proteins (I, II, III, IV)**== **in inner membrane (electron acceptors):** receive electrons from electron transporters (NADH, FADH2) → pump protons against \[ \] gradient into intermembrane space to supply energy to ATP synthase
* Highly acidic environment in intermembrane space
* ==CoQ (Ubiquinon):== can be fully oxidized and reduced during passing of electrons b/w protein complexes
* Soluble carrier
* ==Cyt C (Cytochrome C):== bound to Iron atom which transfers electrons b/w **Complex III and Complex IV** for redox rxns
* Protein carrier
* Used for genetic relations
\
* Final electron acceptor (after electrons have passed though all proteins): ==**Oxygen**== → combines w/ H+ to form H2O
\
* ==**ATP Synthase:**== drives protons down the gradient towards matrix (high \[ \] → low \[ \]) to catalyze ADP + Pi → ATP
* pH + Electrical Gradient: **Proton Motive Force**
* If pH of intermembrane space is higher than normal → less H+ → less cellular respiration occurring
\
* NADH creates more ATP (3x) than FADH2 (2x)
* NADH pumps more protons to carrier proteins than FADH2 because NADH enters the protein complex earlier than FADH2 and it enters Complex I (FADH2 enters Complex II)
\
* Total glucose produced = 36 ATP in eukaryotes and 38 in prokaryotes (no mitochondria so don’t need to pump NADH into matrix → saving 2 ATP during glycolysis)
![* Occurs in $$**inner membrane / cristae** of mitochondria$$
\
* Aerobic process
\
* Removes e- from glucose, pyruvate and Acetyl CoA
\
* ==**Oxidative phosphorylation**== occurs here
\
* ==**Carrier proteins (I, II, III, IV)**== **in inner membrane (electron acceptors):** receive electrons from electron transporters (NADH, FADH2) → pump protons against \[ \] gradient into intermembrane space to $$supply energy to ATP synthase$$
* Highly acidic environment in intermembrane space
* ==CoQ (Ubiquinon):== can be fully oxidized and reduced during passing of electrons b/w protein complexes
* $$Soluble carrier$$
* ==Cyt C (Cytochrome C):== bound to Iron atom which transfers electrons b/w $$**Complex III and Complex IV**$$ for redox rxns
* $$Protein carrier$$
* Used for genetic relations
\
* $$Final electron acceptor$$ (after electrons have passed though all proteins): ==**Oxygen**== → combines w/ H+ to form H2O
\
* ==**ATP Synthase:**== drives protons down the gradient towards matrix (high \[ \] → low \[ \]) to catalyze ADP + Pi → ATP
* $$pH + Electrical Gradient: **Proton Motive Force**$$
* If pH of intermembrane space is higher than normal → less H+ → less cellular respiration occurring
\
* NADH creates more ATP (3x) than FADH2 (2x)
* NADH pumps more protons to carrier proteins than FADH2 because NADH enters the protein complex earlier than FADH2 and it enters Complex I (FADH2 enters Complex II)
\
* $$Total glucose produced = 36 ATP in eukaryotes and 38 in prokaryotes (no mitochondria so don’t need to pump NADH into matrix → saving 2 ATP during glycolysis)$$](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/cc5a296811364aa5a49731ec032ed53f.jpeg)
10
New cards
Oxidative phosphorylation
Process of ADP → ATP from NADH and FADH2 via passing of e- through various carrier proteins in the electron transport chain
11
New cards
Electron carriers
NADH and FADH2
12
New cards
What are the products of 1 Glucose molecule that has __**only**__ undergone the Krebs cycle?
1 glucose → 2 pyruvate → 2 acetyl CoA → 6 NADH + 2 FADH2 + 2 GTP + 4 CO2
13
New cards
Fermentation
* Occurs when \[O2\] is too low to carry out aerobic processes in mitochondria
\
* NAD+ formation prioritized to form NADH
\
* Alcohol fermentation
* Lactic Acid fermentation
\
* NAD+ formation prioritized to form NADH
\
* Alcohol fermentation
* Lactic Acid fermentation
14
New cards
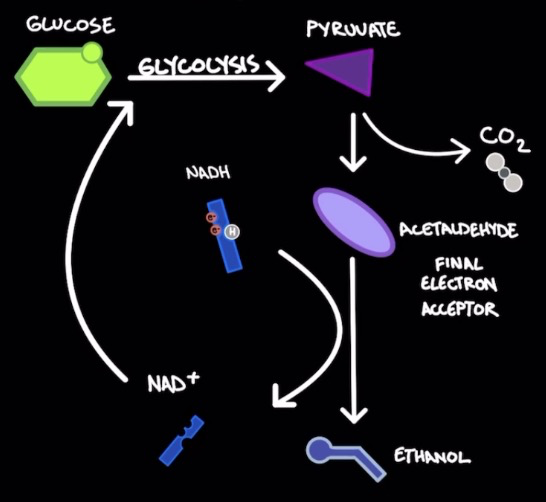
Alcohol fermentation
* Fungi (yeast), bacteria, plants
\
* Reduces pyruvate (from glycolysis) → ==acetaldehyde== + CO2 → ==ethanol== (by product) in a process that oxidizes NADH → NAD+
\
* Acetaldehyde is the final e- acceptor from NADH
\
* Reduces pyruvate (from glycolysis) → ==acetaldehyde== + CO2 → ==ethanol== (by product) in a process that oxidizes NADH → NAD+
\
* Acetaldehyde is the final e- acceptor from NADH
15
New cards
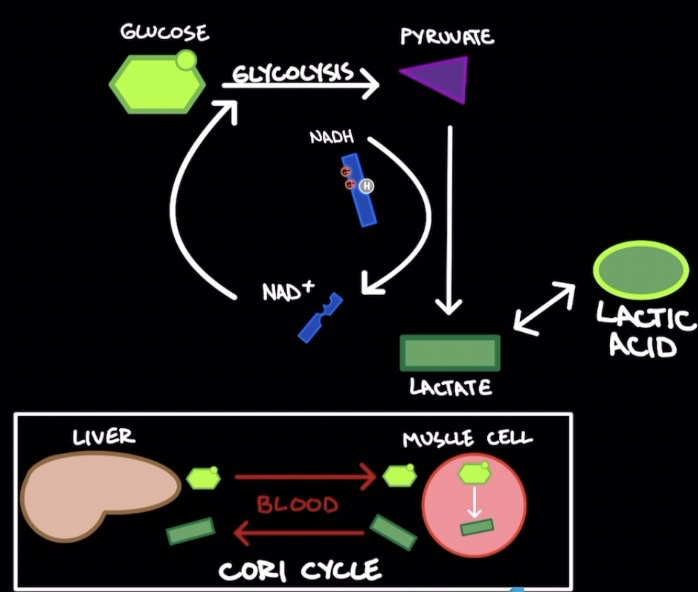
Lactic Acid Fermentation
* Occurs in muscle cells
\
* Use glycolysis to produce 2 pyruvate mols.
\
* Pyruvate reduced to lactate (by-product) → oxidizes NADH → NAD+
* Lactate (weak base) → Lactic acid (strong acid)
\
* ==**Cori Cycle:**== lactate from muscle cells transported into blood stream → liver → converted to glucose → blood stream → used to generate ATP through glycolysis
\
* Use glycolysis to produce 2 pyruvate mols.
\
* Pyruvate reduced to lactate (by-product) → oxidizes NADH → NAD+
* Lactate (weak base) → Lactic acid (strong acid)
\
* ==**Cori Cycle:**== lactate from muscle cells transported into blood stream → liver → converted to glucose → blood stream → used to generate ATP through glycolysis
16
New cards
Catabolic rxns
Releases energy by breaking down large molecules into smaller molecules
17
New cards
Anabolic rxns
Requires energy to build molecules from smaller molecules
18
New cards
Cellular metabolism
Anabolic & Catabolic rxns
19
New cards
What happens if a cell does not have glucose?
1. Uses other carbohydrates
2. Lipids
3. Proteins (last resort)
20
New cards
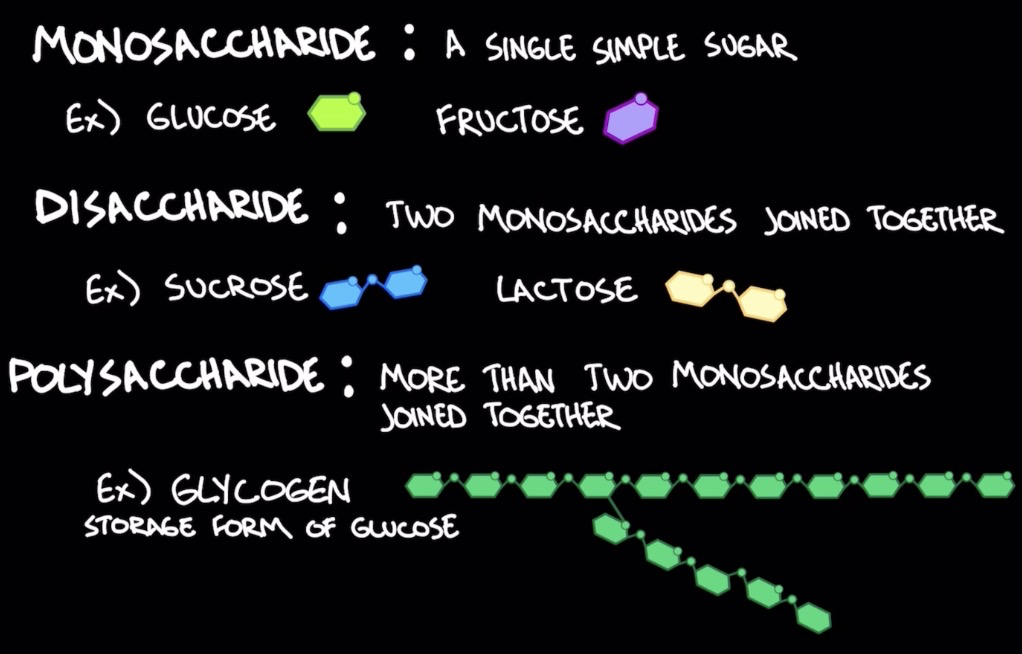
Carbohydrates as a source of energy
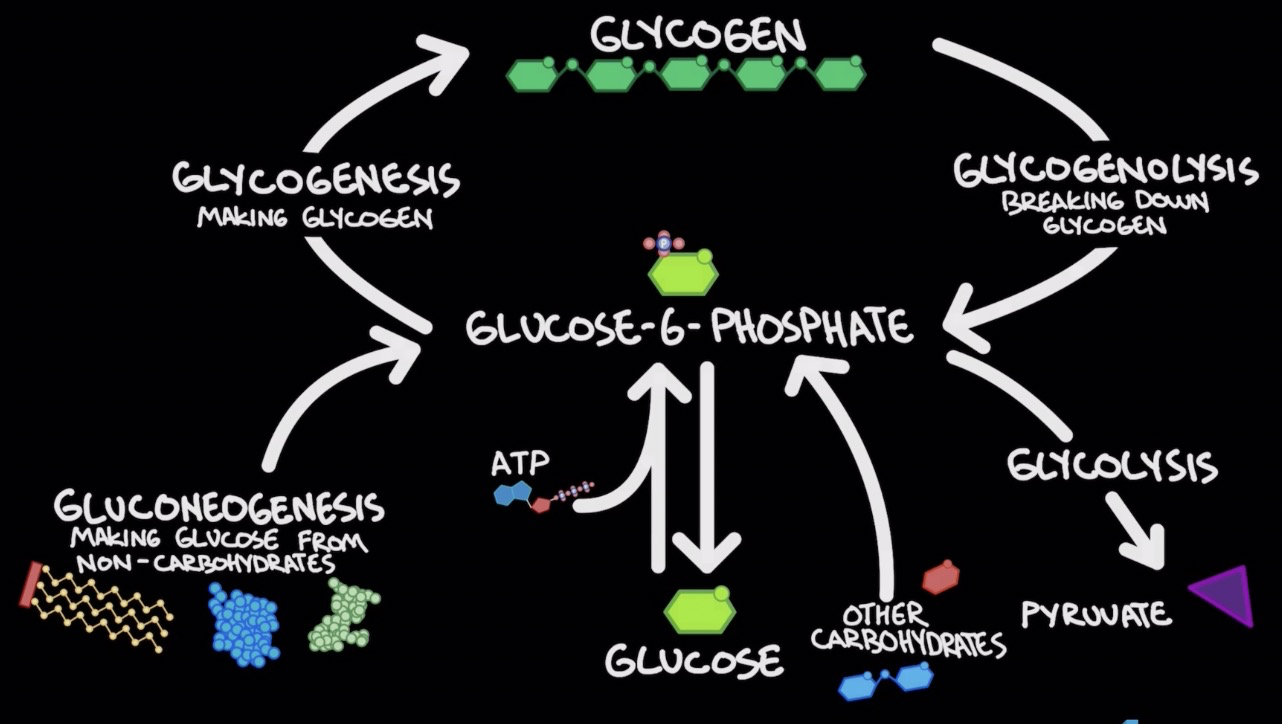
* Glycogen (polysacc.): storage for glucose
* found mainly in muscle and liver cells
\
* ==**Glycogenesis:**== formation of glycogen (glucose → glycogen)
\
* ==**Glycogenolysis**==: break down of glycogen (glycogen→glucose)
\
* Glucose-6-phosphate main molecule for rxn
\
* Regulated by Insulin and glucagon
\
* First broken down in mouth → stomach → duodenum → small intestine
\
* Disaccharides hydrolyzed into monosaccharides → converted to glucose or glycolytic intermediates
\
* All cells can store glycogen but only skeletal muscle and liver cells can store large amounts
* found mainly in muscle and liver cells
\
* ==**Glycogenesis:**== formation of glycogen (glucose → glycogen)
\
* ==**Glycogenolysis**==: break down of glycogen (glycogen→glucose)
\
* Glucose-6-phosphate main molecule for rxn
\
* Regulated by Insulin and glucagon
\
* First broken down in mouth → stomach → duodenum → small intestine
\
* Disaccharides hydrolyzed into monosaccharides → converted to glucose or glycolytic intermediates
\
* All cells can store glycogen but only skeletal muscle and liver cells can store large amounts
21
New cards
Gluconeogenesis
* Forming glucose from non-carbs
* Occurs in liver and kidney
* Occurs in liver and kidney
22
New cards
Why is phosphate added to a glucose molecule?
To keep the molecule w/n the cell and prevent it from diffusing out of the cell
23
New cards
Insulin
* Endocrine hormone
* Released by pancreas when glucose ↑
* Triggers cells to:
* make glycogen from glucose for storage
* undergo glycolysis to form ATP → activates ==**Phosphofructokinase**== (R.D.S)
* Released by pancreas when glucose ↑
* Triggers cells to:
* make glycogen from glucose for storage
* undergo glycolysis to form ATP → activates ==**Phosphofructokinase**== (R.D.S)
24
New cards
Glucagon
* Released by pancreas when glucose ↓
* Similar to epinephrine (triggers formation of glucose)
* Triggers cells to:
* ==**Glycogenolysis**== to form glucose
* Inhibit ==**glycogenesis**== to inhibit glycogen production
* Similar to epinephrine (triggers formation of glucose)
* Triggers cells to:
* ==**Glycogenolysis**== to form glucose
* Inhibit ==**glycogenesis**== to inhibit glycogen production
25
New cards
Lipids as a source of energy
* Long hydrocarbon chains that are highly reduced → have more energy than carbs
\
* ==**Triglycerides:**== 1 glycerol backbone bound to 3 fatty acid chains
\
* ==**Lipases**== in adipose tissue are hormone sensitive (e.g., to glucagon)
\
* ==**Lipolysis:**== break down of lipids into glycerol and the fatty acids by **lipase enzymes**
* Glycerol → ==**Glyceraldehyde 3 Phosphate**== (DAP/G3P/PGAL) → enters glycolysis
* Fatty acid chains activated by 2 ATP → ==**β-oxidation of** __**saturated**__ **FA in mitochondrial matrix**== (breaks 2 carbons at the β position) → 1 NADH + 1 FADH2 and 1 Acetyl CoA → citrate in Krebs cycle → 120 ATP generated
* ==**β-oxidation of** __**unsaturated**__ **FA**== → 1 less FADH2 for each double bond
\
* Lipids combine w/ soluble proteins → ==**lipoproteins (contain Apoproteins)**==
* Classified by density (fat : protein ratio)
* B/w meals, most lipids in plasma are in the form of lipoproteins
\
* Lipoproteins large and less dense when ratio is also large
* ==**Chylomicrons:**== first fat transporters to leave enterocyte and enter lacteals (small lymphatic vessels)
\
* ==**LDL (low protein density):**== unhealthy due to high fat content
* ==**HDL (high protein density):**== healthy cuz transport fat away from tissues → liver → cholesterol for bile → expelled during digestion
\
* ==**Triglycerides:**== 1 glycerol backbone bound to 3 fatty acid chains
\
* ==**Lipases**== in adipose tissue are hormone sensitive (e.g., to glucagon)
\
* ==**Lipolysis:**== break down of lipids into glycerol and the fatty acids by **lipase enzymes**
* Glycerol → ==**Glyceraldehyde 3 Phosphate**== (DAP/G3P/PGAL) → enters glycolysis
* Fatty acid chains activated by 2 ATP → ==**β-oxidation of** __**saturated**__ **FA in mitochondrial matrix**== (breaks 2 carbons at the β position) → 1 NADH + 1 FADH2 and 1 Acetyl CoA → citrate in Krebs cycle → 120 ATP generated
* ==**β-oxidation of** __**unsaturated**__ **FA**== → 1 less FADH2 for each double bond
\
* Lipids combine w/ soluble proteins → ==**lipoproteins (contain Apoproteins)**==
* Classified by density (fat : protein ratio)
* B/w meals, most lipids in plasma are in the form of lipoproteins
\
* Lipoproteins large and less dense when ratio is also large
* ==**Chylomicrons:**== first fat transporters to leave enterocyte and enter lacteals (small lymphatic vessels)
\
* ==**LDL (low protein density):**== unhealthy due to high fat content
* ==**HDL (high protein density):**== healthy cuz transport fat away from tissues → liver → cholesterol for bile → expelled during digestion
26
New cards
What carries fatty acids in blood?
Albumin
27
New cards
Lipid digestion
* Stored as ==**adipose tissue**==
\
* Only broken down in duodenum:
1. ==Bile== released from gall bladder to emulsify fats & ==pancreatic lipase== to break down lipids into FA chains and monoacylglycerides
\
2. Absorbed into enterocytes of small intestine
\
3. Reassembled into triglycerides, and then, along with cholesterol, proteins or phospholipids → packaged into ==**chylomicrons**==
\
4. Chylomicrons move to lymph capillary → circulatory system
\
* Only broken down in duodenum:
1. ==Bile== released from gall bladder to emulsify fats & ==pancreatic lipase== to break down lipids into FA chains and monoacylglycerides
\
2. Absorbed into enterocytes of small intestine
\
3. Reassembled into triglycerides, and then, along with cholesterol, proteins or phospholipids → packaged into ==**chylomicrons**==
\
4. Chylomicrons move to lymph capillary → circulatory system
28
New cards
Proteins as a source of energy
* Excess amino acids used for energy
\
* ==**Oxidative deamination:**== removal of amino group to form metabolic intermediates (Acetyl CoA, pyruvate, Oxaloacetate)
* Directly removes ammonia from AA
* Deamination in liver
* **By-product:** NH3 (ammonia) → ==**urea**== → excreted as urine in mammals
* Uric acid in insects, birds, reptiles
\
* Digestion occurs in stomach: ==**pepsin**== breaks down proteins into polypeptides
\
* In the small intestine: ==**trypsin**== breaks down specific polypeptides into amino acids
\
* ==**Oxidative deamination:**== removal of amino group to form metabolic intermediates (Acetyl CoA, pyruvate, Oxaloacetate)
* Directly removes ammonia from AA
* Deamination in liver
* **By-product:** NH3 (ammonia) → ==**urea**== → excreted as urine in mammals
* Uric acid in insects, birds, reptiles
\
* Digestion occurs in stomach: ==**pepsin**== breaks down proteins into polypeptides
\
* In the small intestine: ==**trypsin**== breaks down specific polypeptides into amino acids