9- reactive lesions
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
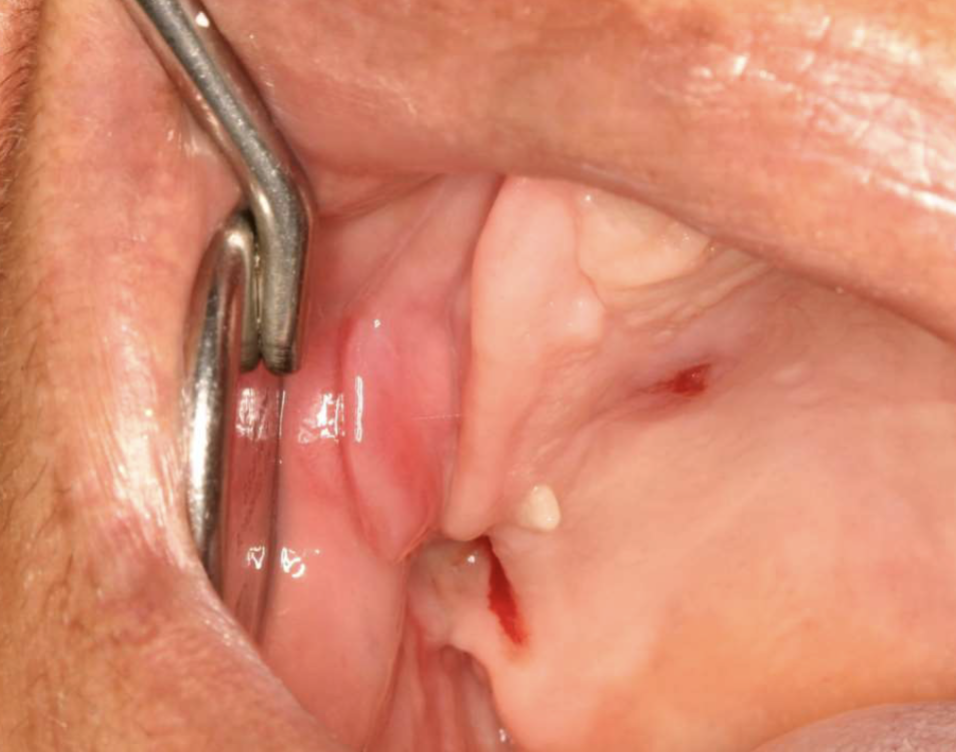
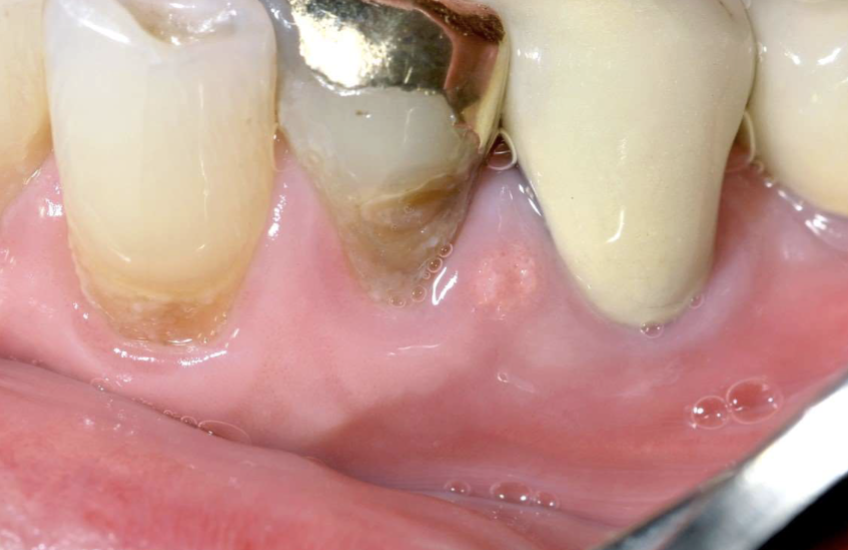
2 types of denture-related lesions
epulis fissuratum
inflammatory papillary hyperplasia
definition of epulis
tumor of gingiva or alveolar mucosa
2 clinical features of epulis fissuratum
single/multiple folds of hyperplastic in alveolar vestibule
fibroepithelial polylp/leaf-like denture fibroma may be seen along palatal mucosa
3 histopathologic features of epulis fissuratum
hyperparakeratosis/hyperorthokeratosis
papillary hyperplasia and/or pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia
hyperplasia of CT
2 tx options for epulis fissuratum
surgical removal
remake denture to prevent recurrance
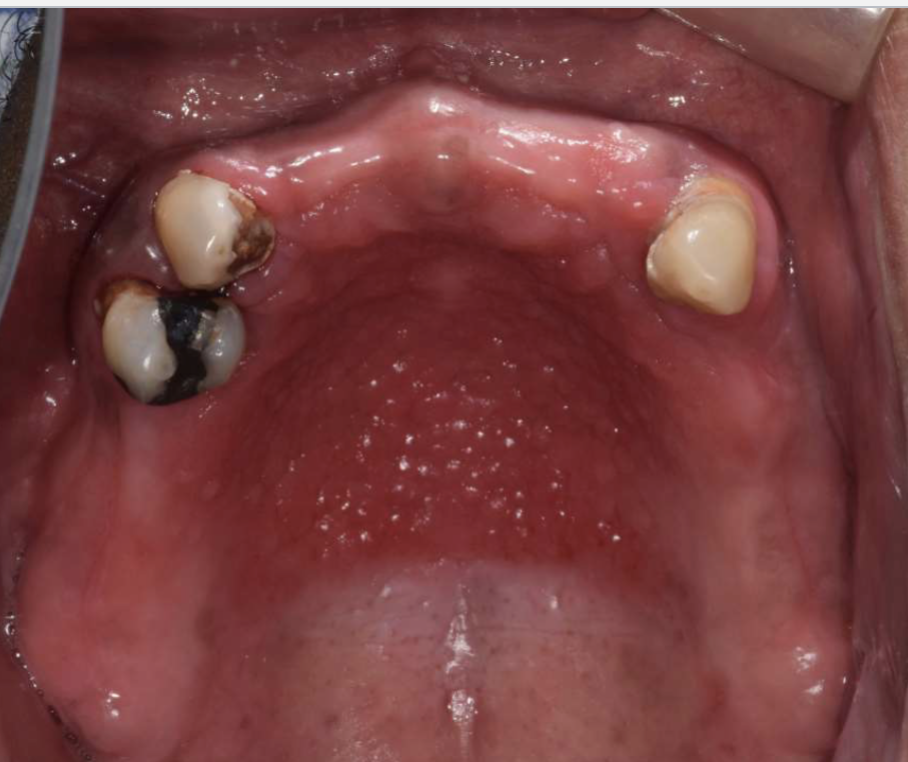
3 clinical features of inflammatory papillary hyperplasia
hard palate beneath denture base
pink/red pebbly mucosa
erythema suggests secondary candidal infection
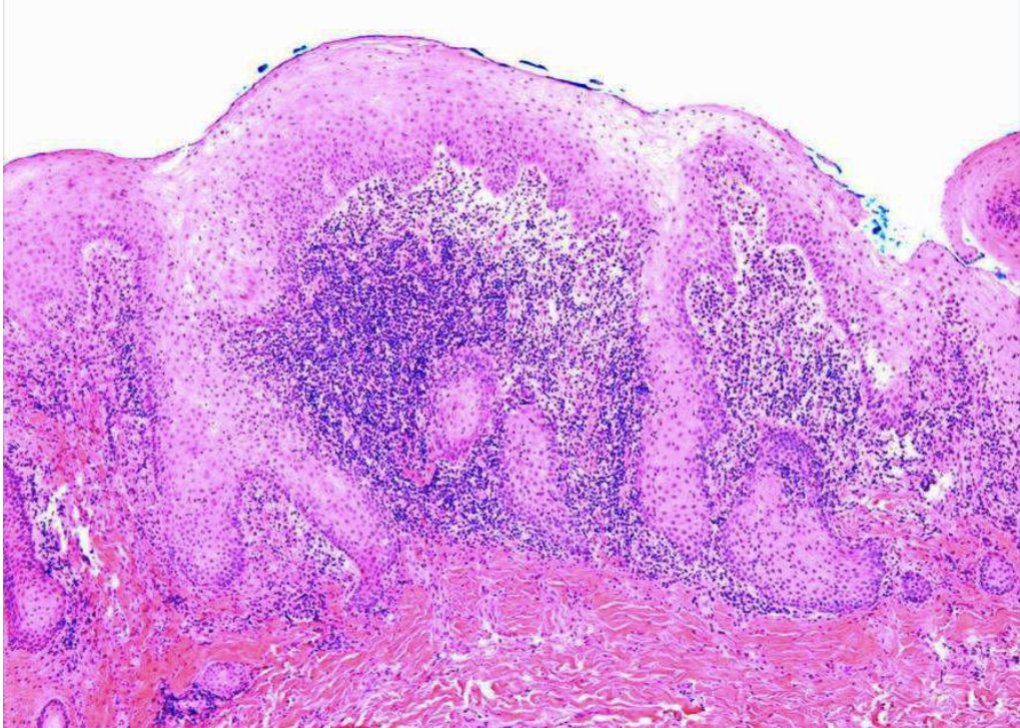
3 histopathologic features of inflammatory papillary hyperplasia
papillary growths on surface
may show pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia
sialadenitis
tx for inflammatory papillary hyperplasia
mild cases: remova denture
established cases: excision → relining/refabricating denture
antifungals if needed
what’s a common oral pathology associated w/ trauma
traumatic ulcers
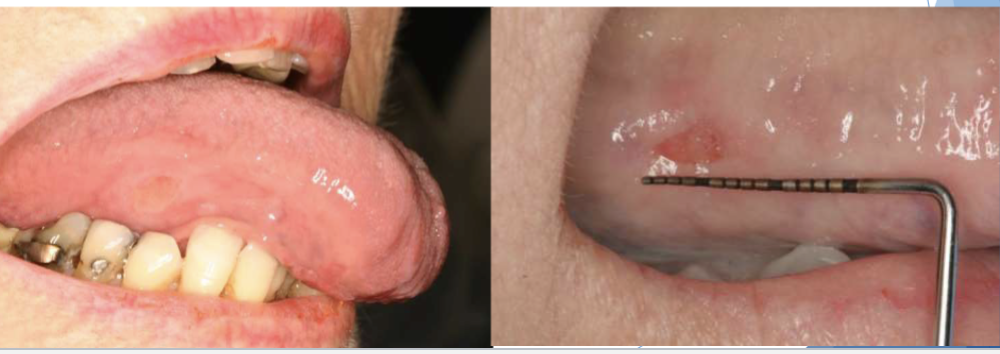
3 histopathologic features of traumatic ulcers
ulcerated surface w/ fibrin membrane
granulation tissue
variable amounts of inflammation
what’s traumatic ulcerative granuloma
penetrating ulcer that takes weeks-months to resolve
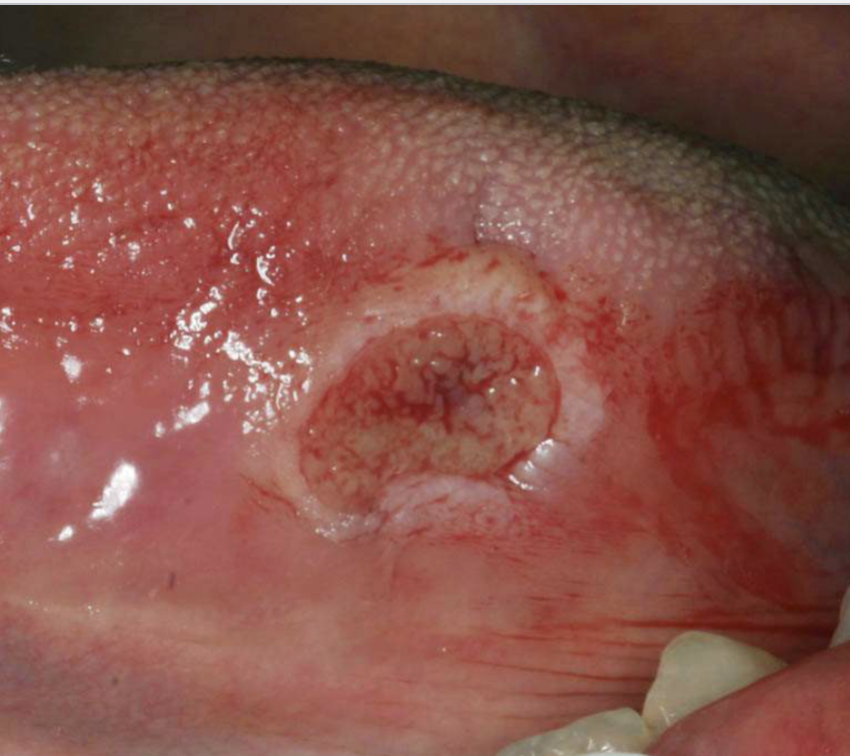
clinical features of traumatic ulcerative granulomas
commonly on tongue
often surrounded by white hyperkeratotic rim
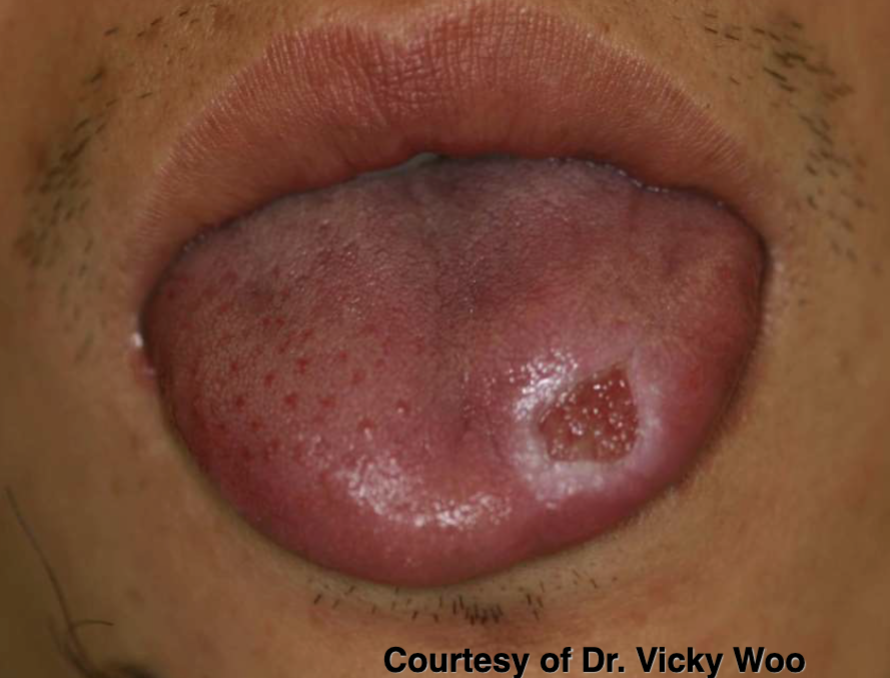
traumatic ulcerative granulomas affect men or women more
men
3 histopathological features of traumatic ulcerative granulomas
numerous eosinophils
inflammation of skeletal muscle
granulation tissue
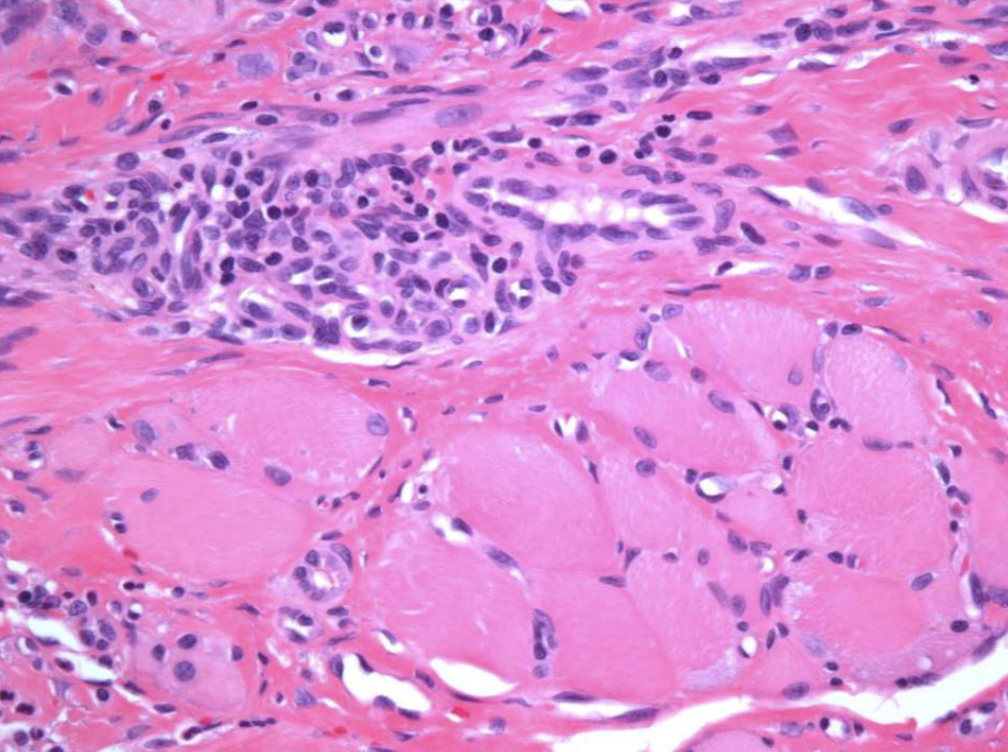
3 tx options for traumatic ulcerative granulomas
remove irritant
excision of excess tissue
topical/intra-lesional steroids
name of pathology that involves hyperplasia of mouth, skin, genitalia epithelium
verruciform xanthoma
4 clinical features of verruciform xanthoma
50% of oral lesions on gingiva/alveolar mucosa
may be pink, white, red, yellow, orange
well-demarcated verrucous mass
may resemble squamous papillomas or early carcinomas
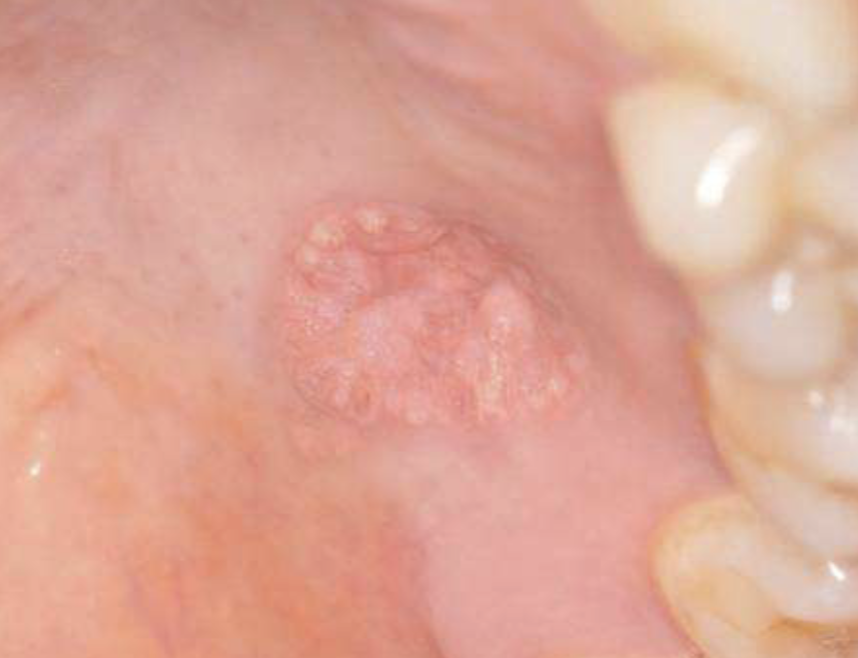
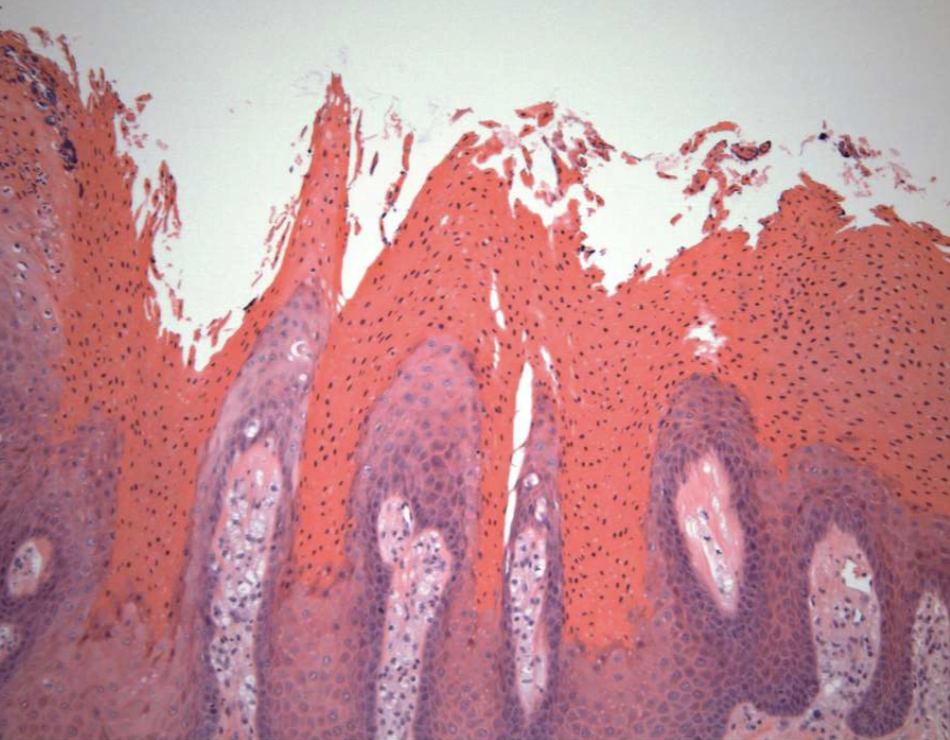
2 histopathologic features of verruciform xanthoma
papillary, acanthotic surface covered by parakeratin
large macrophages w/ foamy cytoplasm
tx option for verruciform xanthoma
excision
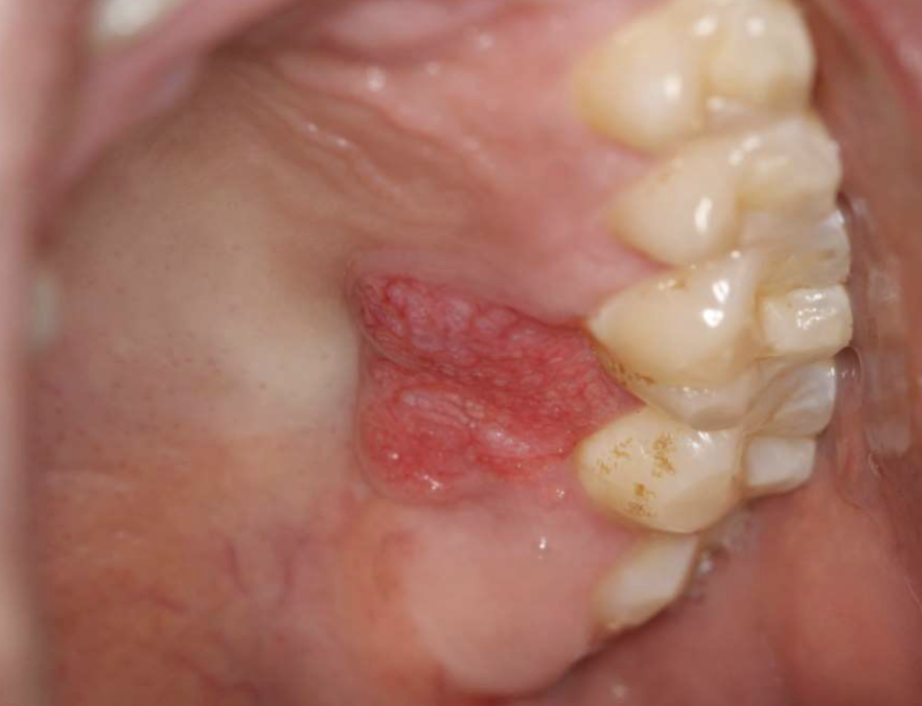
what is this
verruciform xanthoma
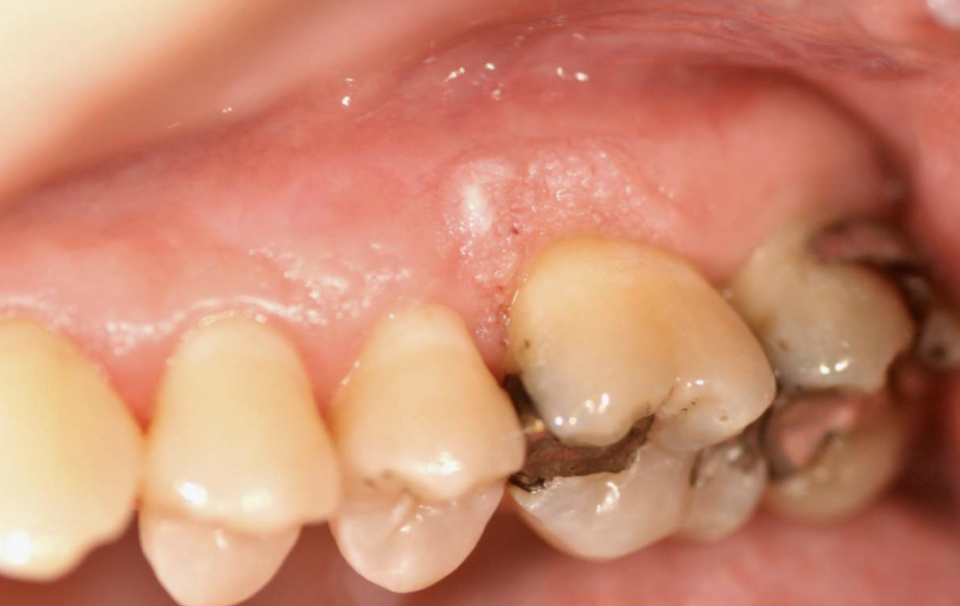
what is this
verruciform xanthoma
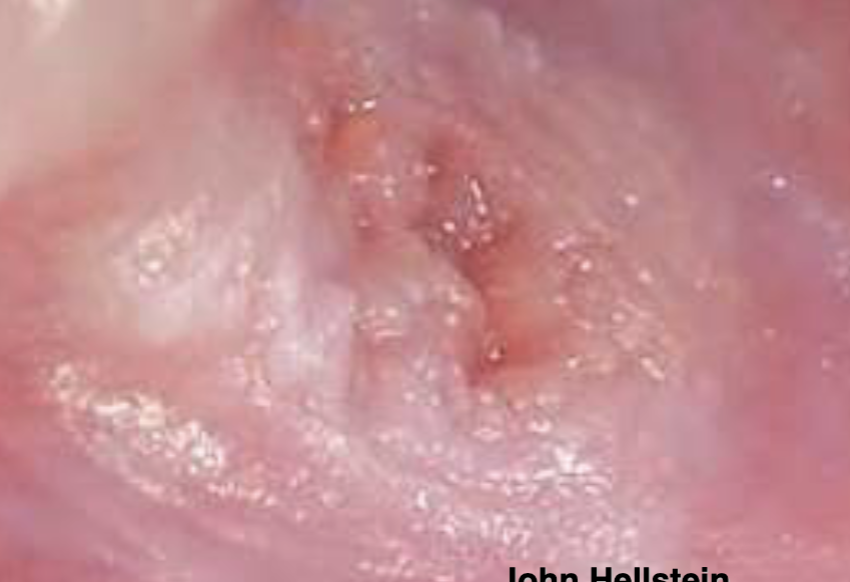
what is this
verruciform xanthoma
what is this
verruciform xanthoma
2 types of chemical injuries
medicament:
factitial (self-inflicted)
iatrogenic (by provider)
3 causes of factitical medicament chemical injuries
aspirin
mouthwashes/hydrogen peroxide
tooth-whitening products
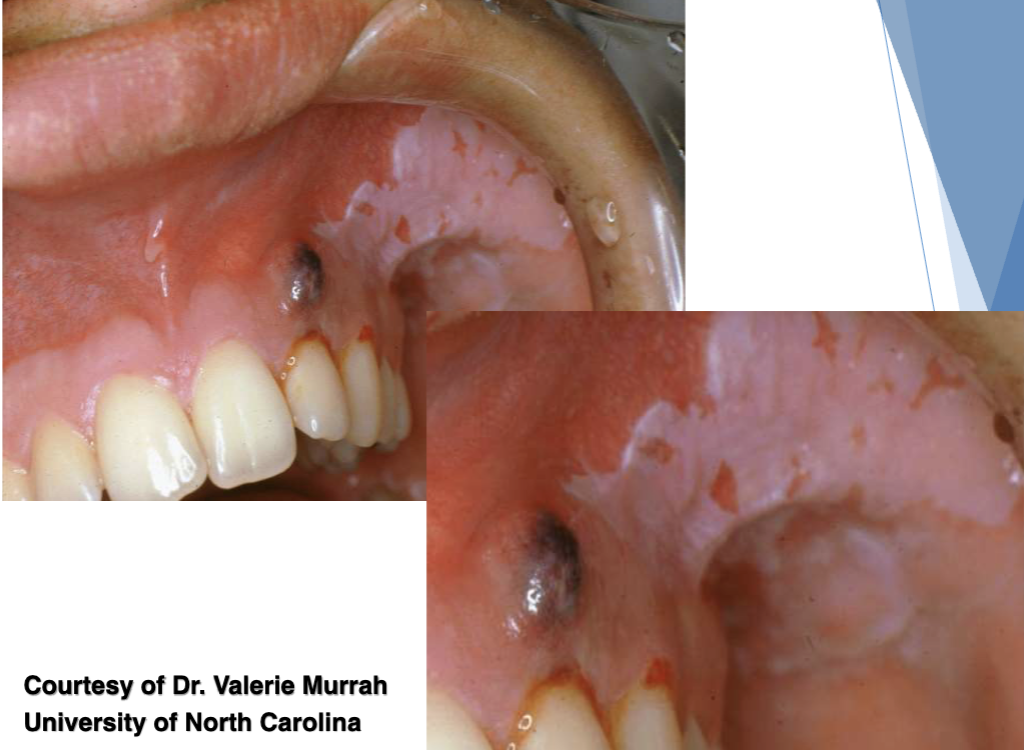
what is this
aspirin burn
what is this
aspirin burn
what is this
aspirin burn
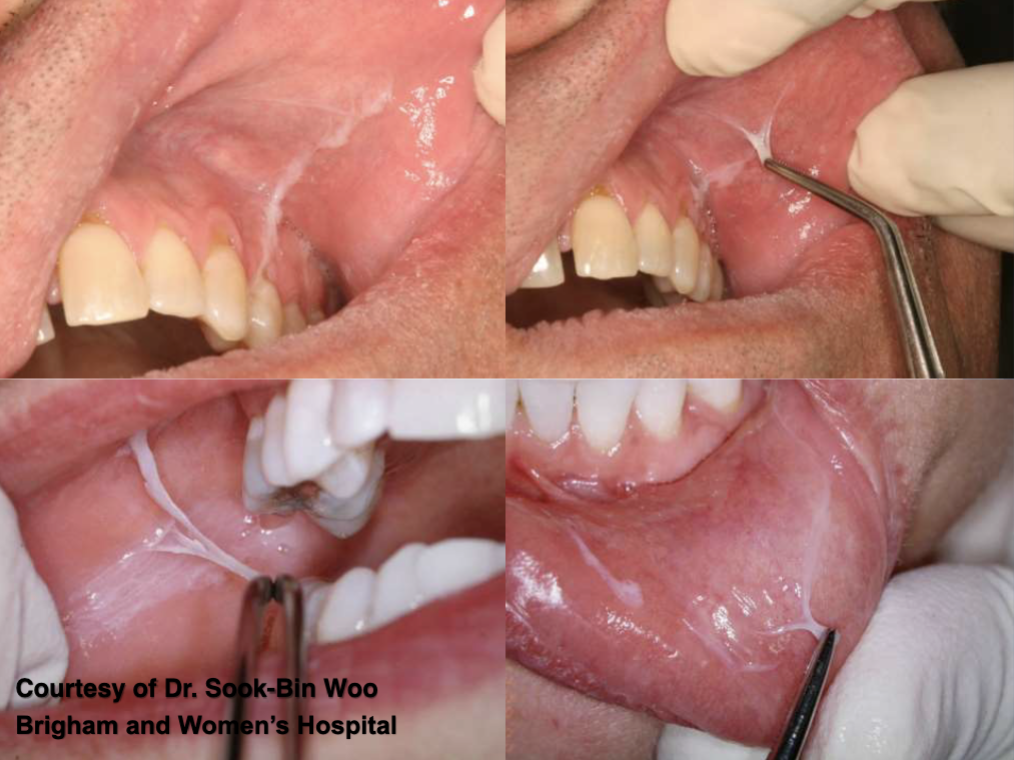
what is this
mouthwash burn
5 causes of iatrogenic medicament chemical injuries
silver nitrate
phenol
endodontic materials
cotton roll “burn”
rubber dam application reduces incidence
2 noninfectious complications of chemo/radiation
mucositis
hemorrhage
3 complications of chemo
mucositis (within days)
bone marrow suppression: thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis
opportunistic infections: herpes simplex, candidiasis
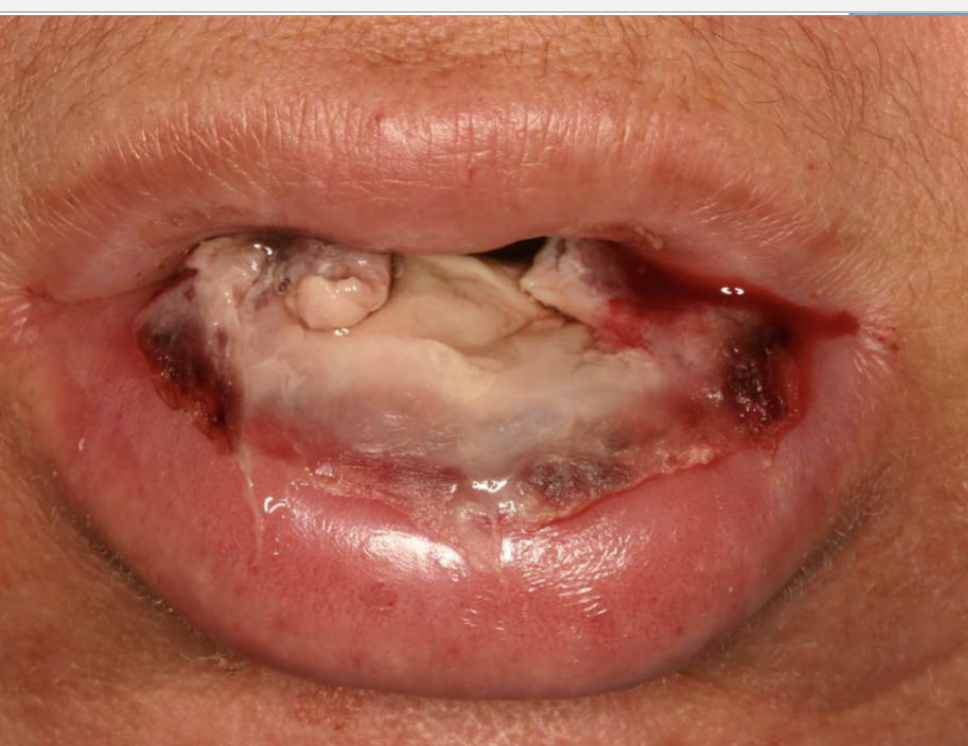
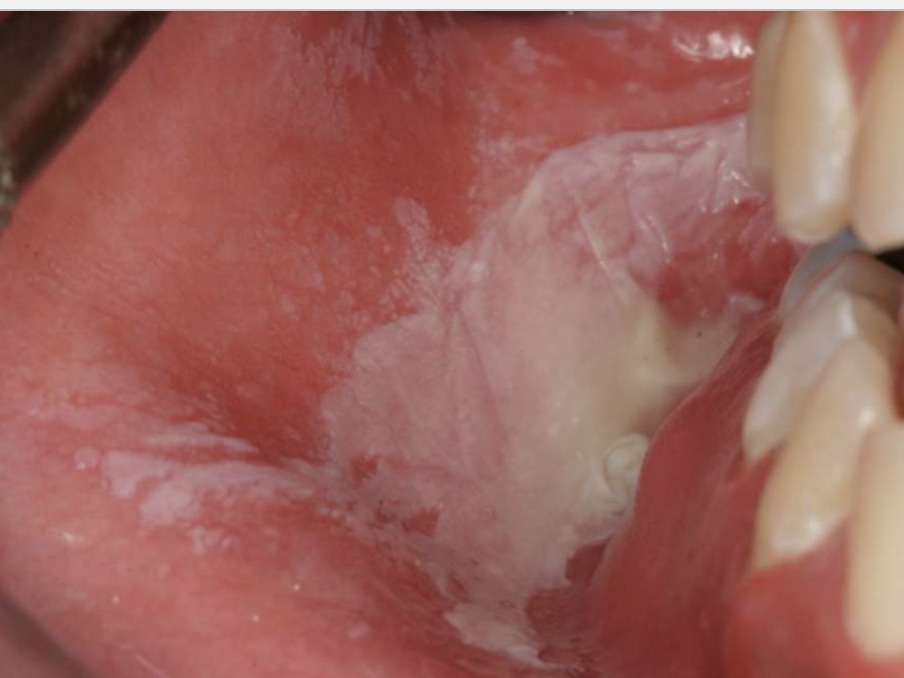
what is this
oral mucositis developed after chemo
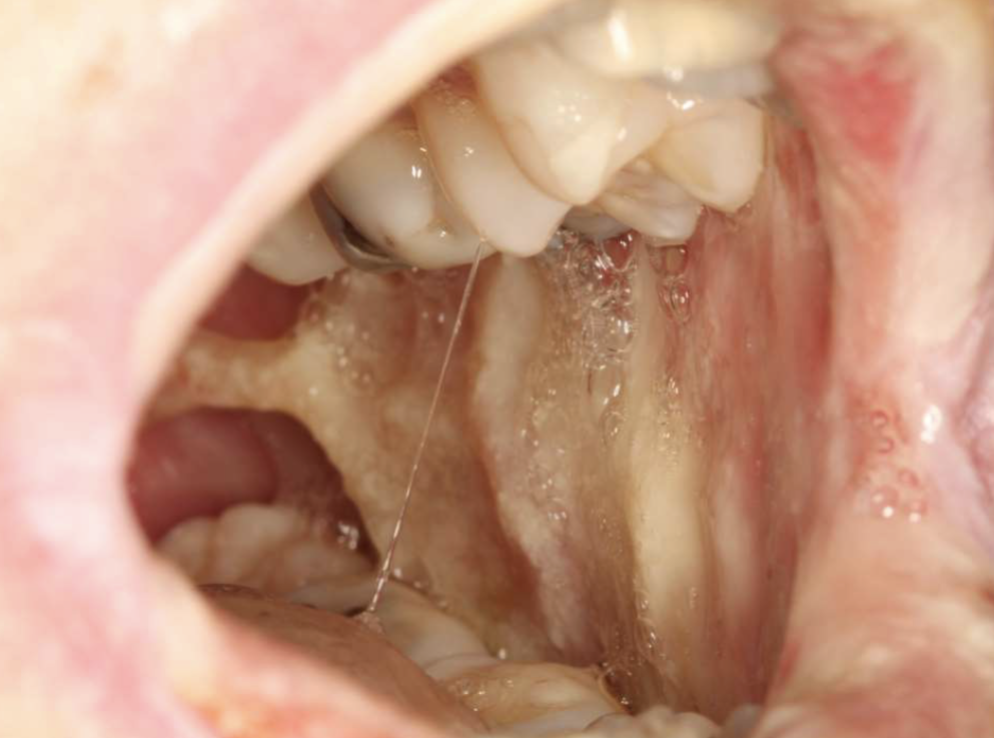
what is this
oral mucositis developed after chemo
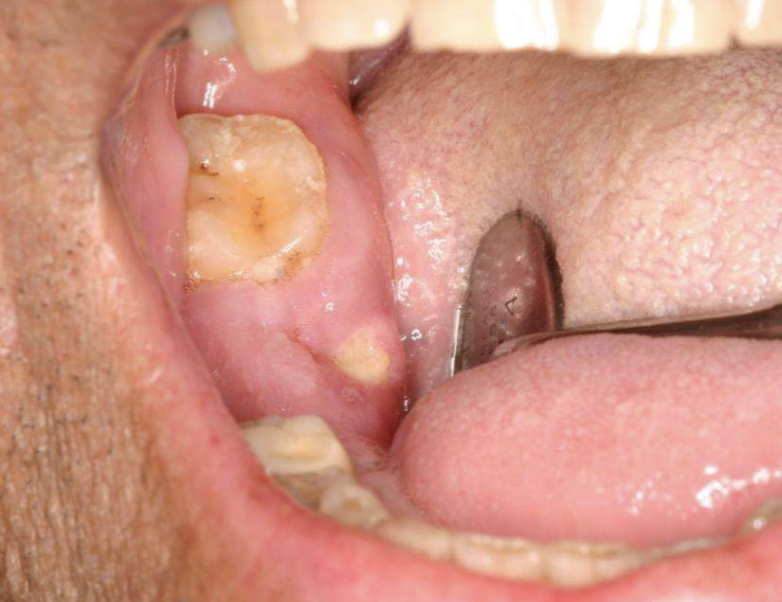
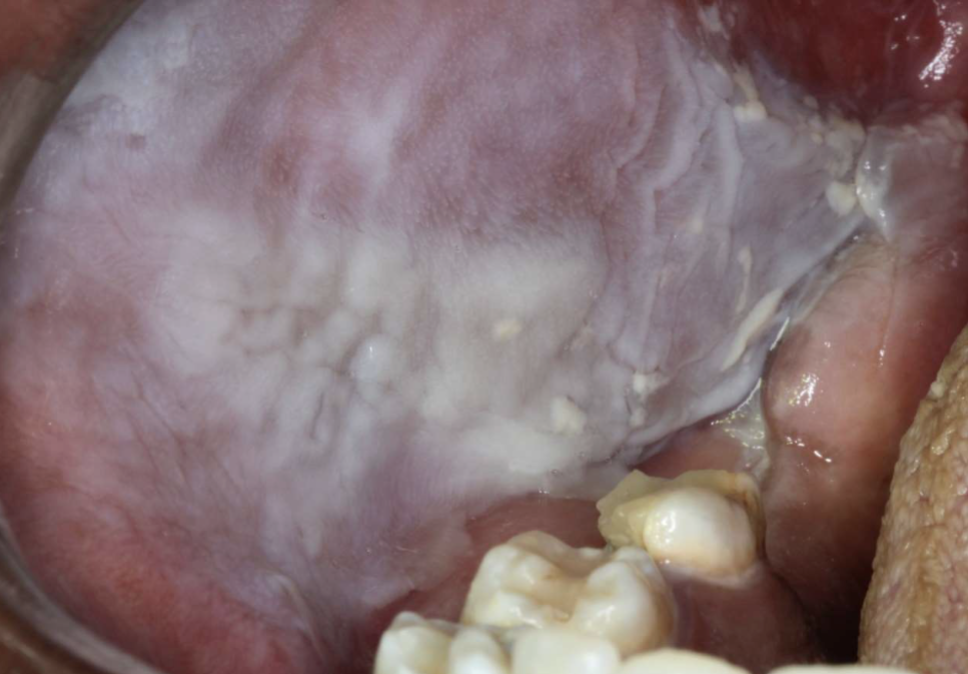
what is this
osteonecrosis of the jaws
6 causes of osteonecrosis of the jaws
meds
radiation
infection
chemicals
trauma
idiopathic
2 med classes that can cause osteonecrosis of the jaws
anti-resorptive agents:
bisphosphonates
denosumab (prolia, xgeva)
anti-angiogenic agents:
monocloncal antibodies (bevacizumab)
tyrosine kinase inhibitors (sunitinib, sorafenib)
3 requirements for diagnosis of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaws (MRONJ)
current/previous tx w/ anti-resorptive or anti-angiogenic agents
no hx of radiation/obvious metastasis of jaws
exposed bone or bone that can be probed through a sinus tract persisting > 8 weeks
9 conditions to rule out when diagnosing medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaws (MRONJ)
Alveolar osteitis
Gingivitis/periodontitis
Sinusitis
Caries
Periapical pathology
Fibro-osseous diseases
Cancer
Condensing osteitis
Temporomandibular disorders
5 pathogeneses of MRONJ
Anti-osteoclastic
Anti-angiogenic
Inflammatory/infectious
Immune dysfunction
Soft tissue toxicity
which type of bisphosphonates are more potent
nitrogen containing
which nitrogen containing bisphosphonates is most potent
zoledronic acid (zemeta) → more likely to cause MRONJ
5 indications for bisphosphonates
Osteoporosis/osteopenia
Multiple myeloma
Metastatic carcinomas to bone
Paget disease
Osteogenesis imperfecta
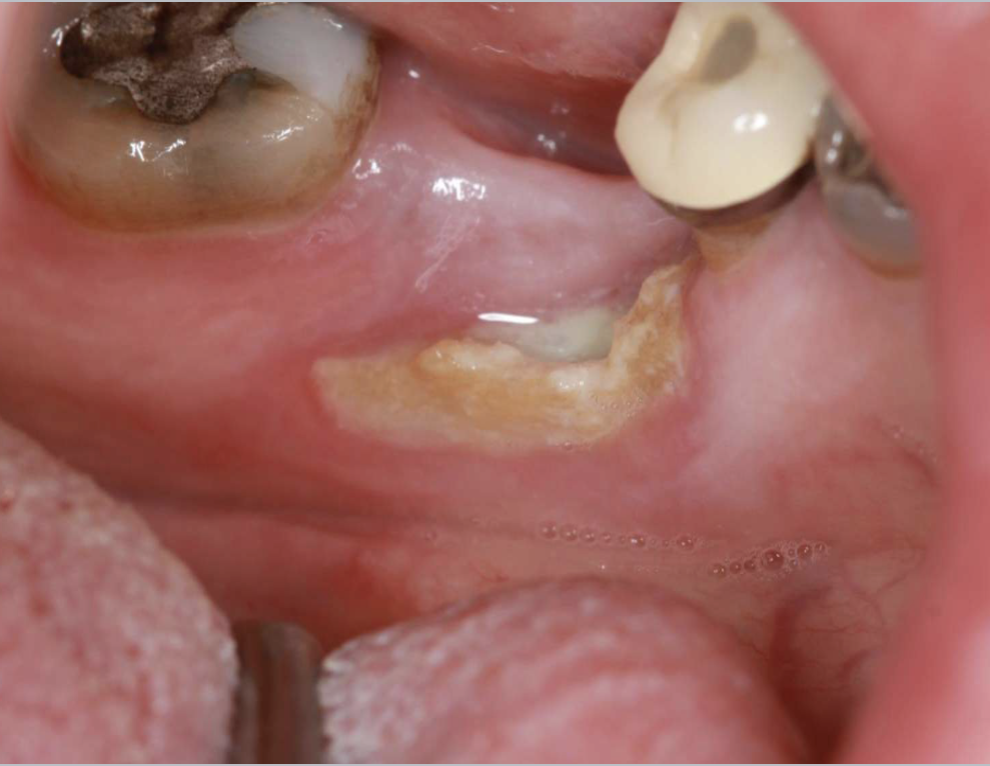
what is this
medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaws (MRONJ)
4 classifications of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaws (MRONJ)
stage 0: non-exposed
stage 1: exposed + asymptomatic
stage 2: exposed + symptomatic
stage 3: extensive
medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaws (MRONJ) affects max or mand more
mand
T/F: MRONJ can show increased radiopacity before presenting w/ clinical evidence of necrosis
true
3 tx options for asymptomatic pts w/ MRONJ
chlorhexidine rinse
smooth rough edges of exposed bone
soft splint
tx option for symptomatic pts w/ MRONJ
antibiotic therapy + chlorhexidine
3 dental considerations for MRONJ
prophylactic dental care
prioritize less invasive procedures
if multiple ext needed, perform by quadrant
3 complications of radiation
thickened saliva via salivary gland hypofunction
mucositis
osteoradionecrosis (radiation-induced osteonecrosis)
2 oral complications of radiation
increased incidence of cervical caries
hypogeusia (reduced taste)
osteoradionecrosis affects max or mand more
mandible
which age of ppl who are more at risk for osteoradionecrosis
60+ years old
3 tx options for radiation induced hyposalivation
pilocarpine/cavimeline
topical fluoride
caphosol
3 tx options for osteoradionecrosis
debridement
antibiotics
prophylactic ext
6 management options for radiation induced mucositis
viscous lidocaine
chlorhexidine
milk of magnesia
kaopectate rinse
palifermin
systemic morphine
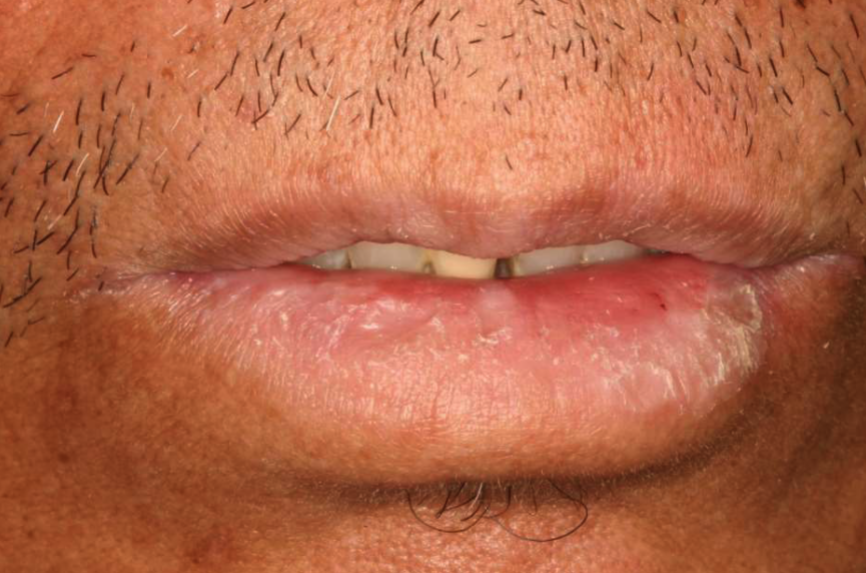
what is this
exfoliative cheilitis: excess production + desquamation of keratin
exfoliative cheilitis affects men or women more
women
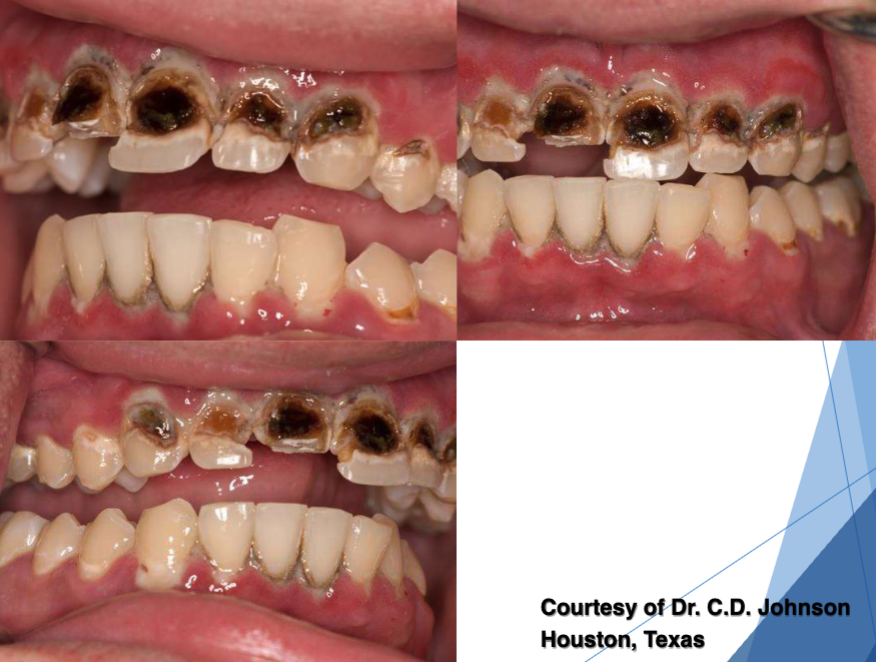
what is this
“Meth Mouth”
3 orofacial complications of meth abuse
xerostomia
bruxism
poor hygiene
7 acute potential complications oral piercings
pain
bleeding
swelling (potential airway obstruction)
infection
lingual nerve damage
speech impairment
allergy
4 chronic potential complications of oral piercings
soft tissue trauma
fractured teeth
hypersalivation
tissue hyperplasia around posts
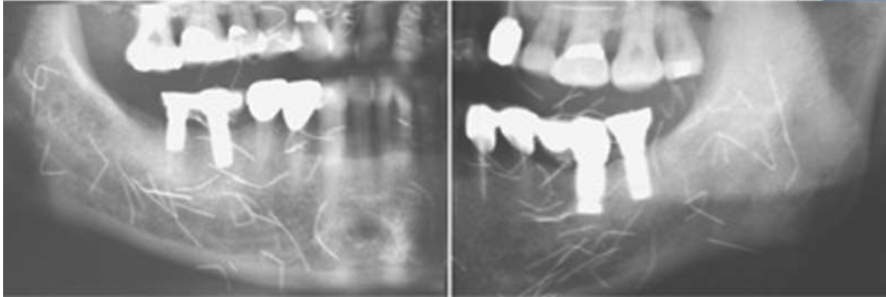
what is this
“Susuk” implantation, common in southeast Asia