Biology II Lesson 3: Kidney Regulation Part I
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
What does RAAS stand for? What is its role?
RAAS stands for Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System. Its role is to maintain blood pressure and volume.
The juxtaglomerular cells are a key player in the RAAS system. They are smooth muscle cells located in the capillaries of the kidney. In certain conditions, these cells will be stimulated to release:
(A) Angiotensin
(B) ADH
(C) Aldosterone
(D) Renin
(D) Renin
In certain conditions, these cells will be stimulated to release renin.
Which of the following are triggers for renin release?
I. High blood pressure
II. Sympathetic nerve cell activation
III. Macula densa cells sensing high Na+ levels
(A) I and III only
(B) II only
(C) II and III only
(D) I, II, and III
(B) II only
Renin release is triggered by:
- LOW blood pressure
- sympathetic nerve cell activation
- Macula densa cells sensing LOW Na+ levels
Notice that all of these signal to the body that there is low blood pressure. The purpose of the RAAS is to maintain blood pressure and volume; thus, it needs to know when blood pressure is too low.
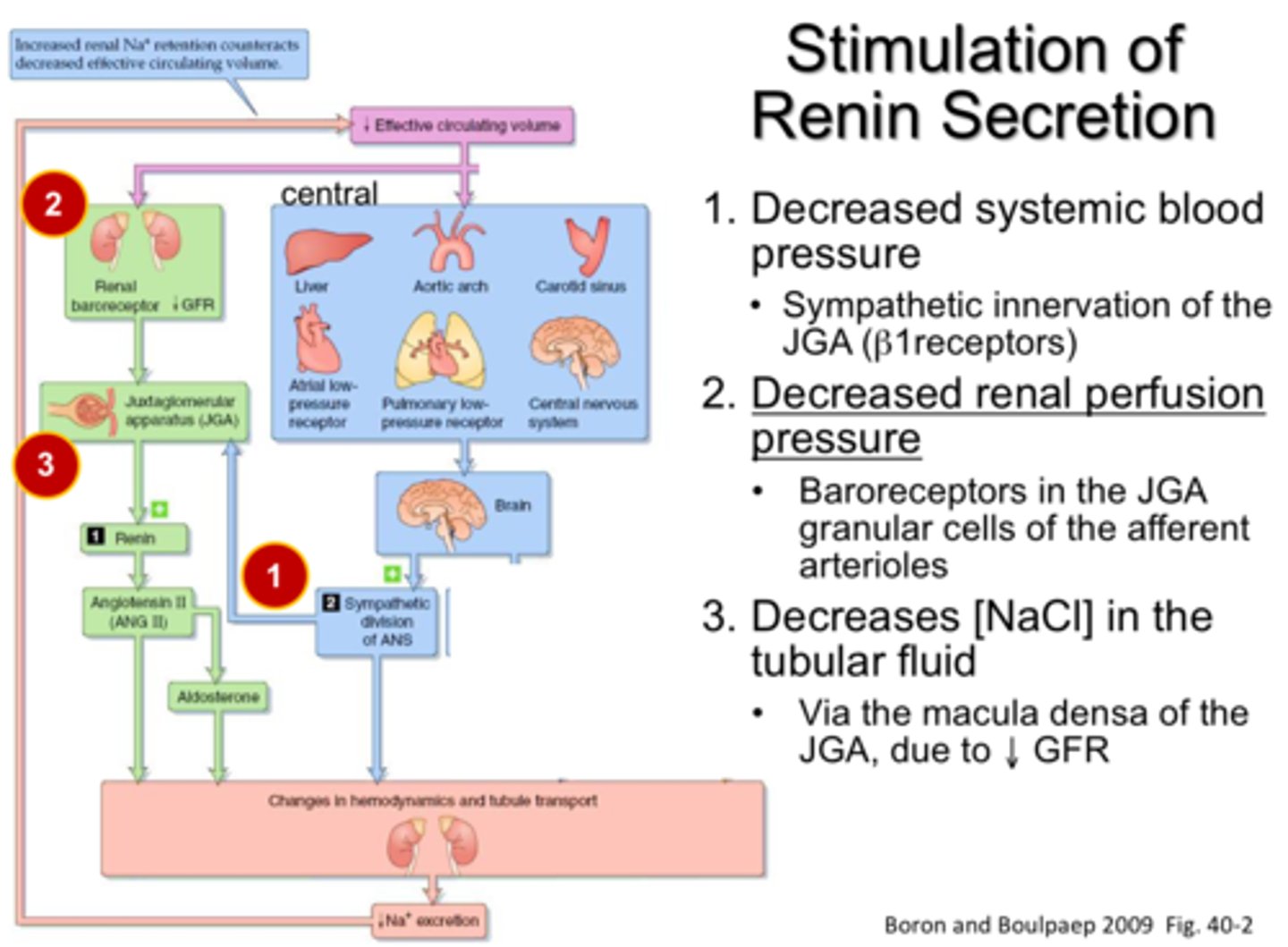
What do Macula densa cells release in response to low levels of sodium to trigger the release of renin in juxtaglomerular cells?
(A) Prostaglandin
(B) ADH
(C) Aldosterone
(D) Angiotensinogen
(A) Prostaglandin
Macula densa cells release prostaglandin (a paracrine hormone) to trigger the release of renin.
CRB True or false? If a person is eating lots of proteins, then they will likely secrete Ammonia or Urea in the kidneys.
True. If a person is eating lots of proteins, then they will likely secrete Ammonia or Urea in the kidneys.
CRB In which part of the kidneys would you expect to see the secretion of Ammonia and Urea to occur?
(A) PCT
(B) Loop of Henle
(C) DCT
(D) Collecting Duct
(A) PCT
In the Proximal Convoluted Tubule, Ammonia and Urea will be secreted.
The juxtaglomerular apparatus is composed of which of the following structures:
I. Macula Densa Cells
II. Juxtaglomerular Cells
III. Mesangial Cells
(A) I and III only
(B) II only
(C) II and III only
(D) I, II, and III
(D) I, II, and III
The Juxtaglomerular apparatus is composed of macula densa cells, juxtaglomerular cells, and the mesangial cells.
Compare the location of the macula densa cells, the juxtaglomerular cells, and the mesangial cells.
The macula densa cells line the distal convoluted tubule, which is where they are sensing the low Na+ levels.
The juxtaglomerular cells line the vessel walls of the afferent arteriole, glomerulus, and efferent arteriole.
The mesangial cells line the macula densa cells, juxtaglomerular cells, and the glomerular capillaries.
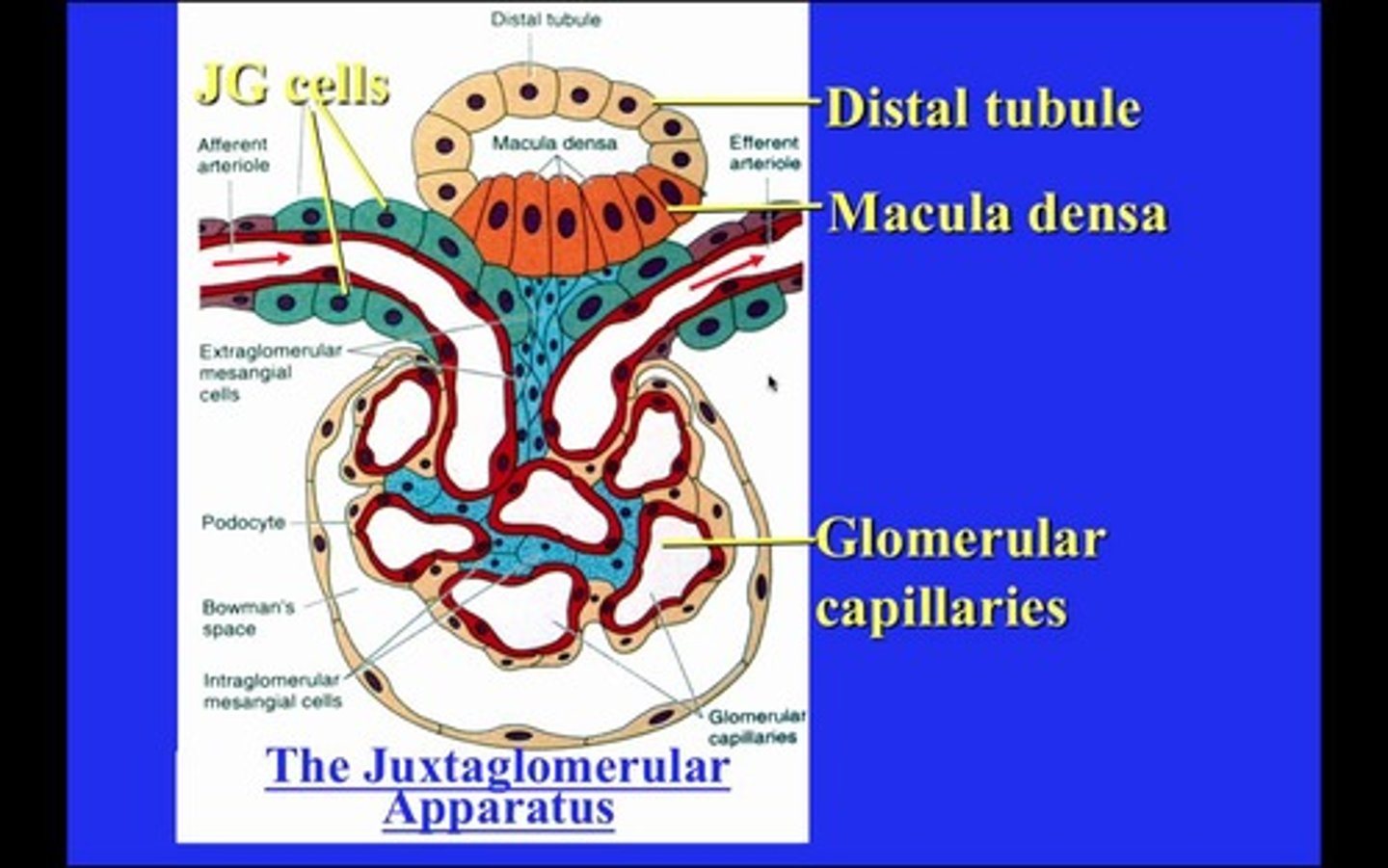
Why does a low level of Na+ in the distal convoluted tubule indicate that there is low blood pressure in the body?
If blood pressure is low, less blood will get filtered into bowman's capsule, resulting in lower amounts of sodium in the nephron.
Angiotensinogen is produced in the:
(A) Gall Bladder
(B) Kidney
(C) Liver
(D) Small intestine
(C) Liver
Angiotensinogen is produced in the liver.
What triggers angiotensinogen to convert into its active form of angiotensin I? What triggers angiotensin I to convert into its VERY active form of angiotensin II?
Angiotensinogen is to converted into its active form of angiotensin I when renin encounters it in the bloodstream and cleaves off a huge chunk of it (442 out of its 452 amino acids!).
Angiotensin I will then get converted into Angiotensin II via the cleavage of two more amino acids by the Angiotensin Converting Enzymes (ACEs) that line the endothelial cells of capillary walls.
Angiotensin Converting Enzymes (ACEs) primarily line the endothelial cells in the capillaries of which major organ?
(A) kidney
(B) lungs
(C) heart
(D) spleen
(B) lungs
Angiotensin I gets converted into Angiotensin II by endothelial cells lining the capillary walls found primarily within the lungs.
CRB Which of the following classes of drugs will decrease blood pressure by affecting the kidneys?
I. Statins
II. ACE Inhibitors
III. Proton Pump Inhibitors
(A) II only
(B) I and II only
(C) I and III only
(D) I, II and III
(A) II only
ACE Inhibitors decrease blood pressure by affecting the kidneys.
Statins are known for being lipid-lowering medications.
Proton Pump Inhibitors are often meant to decrease stomach acid production to decrease heartburn.
What effect will angiotensin II have on each of the following organs?
(1) Smooth Muscle
(2) Kidney Cells
(3) Pituitary Gland
(4) Adrenal Gland
(1) Smooth Muscle - Enhance vasoconstriction, increasing resistance and blood pressure.
(2) Kidney Cells - Increase water reabsorption, increasing the blood volume.
(3) Pituitary Gland - Increase ADH secretion.
(4) Adrenal Gland - Increase aldosterone secretion.
CRB Which of the following are known to inhibit ADH secretion?
I. Caffeine
II. Vanilla
III. Alcohol
(A) I only
(B) I and II only
(C) I and III only
(D) II and III only
(C) I and III only
Caffeine and Alcohol are known to inhibit ADH secretion.
What does ADH stand for and what is its role?
ADH stands for Antidiuretic Hormone. Its role is to maintain blood pressure and volume.
CRB Antidiuretic Hormone, or ADH, also has another common name. Which of the following is the common name for ADH?
(A) Vasodilation
(B) Vasopressin
(C) Renoretention
(D) Vasoretention
(B) Vasopressin
Vasopressin is another name for ADH.
What effect will ADH have on each of the following organs?
(1) Smooth Muscle
(2) Kidney Cells
(1) Smooth Muscle - Enhance vasoconstriction, increasing resistance and blood pressure.
(2) Kidney Cells - Increase water reabsorption, increasing the blood volume.
Notice that these are the same effects as angiotensin II at these locations.
What effect will aldosterone have on each of the following organs?
(1) Smooth Muscle
(2) Kidney Cells
What effect will aldosterone have on each of the following organs?
(1) Smooth Muscle - None.
(2) Kidney Cells - Increase water reabsorption, increasing the blood volume.
CRB Which of the following would you expect to increase water retention in the kidneys?
I. Vasopressin
II. Aldosterone
III. ADH
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) I and III only
(D) I, II and III
(D) I , II and III
Vasopressin/ADH and Aldosterone will all increase water retention in the kidneys.
CRB Which type of hormones are Aldosterone and ADH, respectively?
(A) Steroid, Steroid
(B) Steroid, Peptide
(C) Peptide, Steroid
(D) Peptide, Peptide
(B) Steroid, Peptide
Aldosterone is a steroid hormone, whereas ADH is a peptide hormone.
Via what mechanism does it increase the reabsorption of water and on what part of the nephron does it act?
- ADH
- Aldosterone
- Angiotensin II
ADH will increase the number of water channels in the distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct, directly increasing the reabsorption of water.
Aldosterone will increase the reabsorption of Na+ in the distal convoluted tubule and the collecting duct, which will pull water with it as it increases the osmotic pressure in the peritubular capillaries.
Angiotensin II acts on the same location with the same mechanism as aldosterone.
CRB True or false? Solutes that enter the Interstitium, the Connective Tissue lining the tubules, will end up in the Distal Convoluted Tubule.
False. Solutes that enter the Interstitium, the Connective Tissue lining the tubules, will end up in the bloodstream.
What specific effect does aldosterone exert on the basolateral surface versus the apical surface of the cells lining the nephron?
Aldosterone will increase the activity of the Na+/K+ pump that lines the basolateral surface, resulting in more Na+ entering the peritubular capillaries and more K+ entering the cells that line the nephron.
Aldosterone also increases the number of K+ channels and Na+ channels in the apical surface, allowing more K+ to enter the nephron for excretion and more Na+ to enter the cell for reabsorption.
CRB Between Aldosterone and ADH, which of the major water-conserving hormones would you expect to affect blood osmolarity the most?
Antidiuretic Hormone can affect water levels without affecting the solute levels, meaning it can have a larger effect on blood osmolarity.
Aldosterone would alter both solute (Na+) and water concentrations.
Where is the adrenal gland located as compared to the kidney.
The adrenal gland is located just above the kidney.
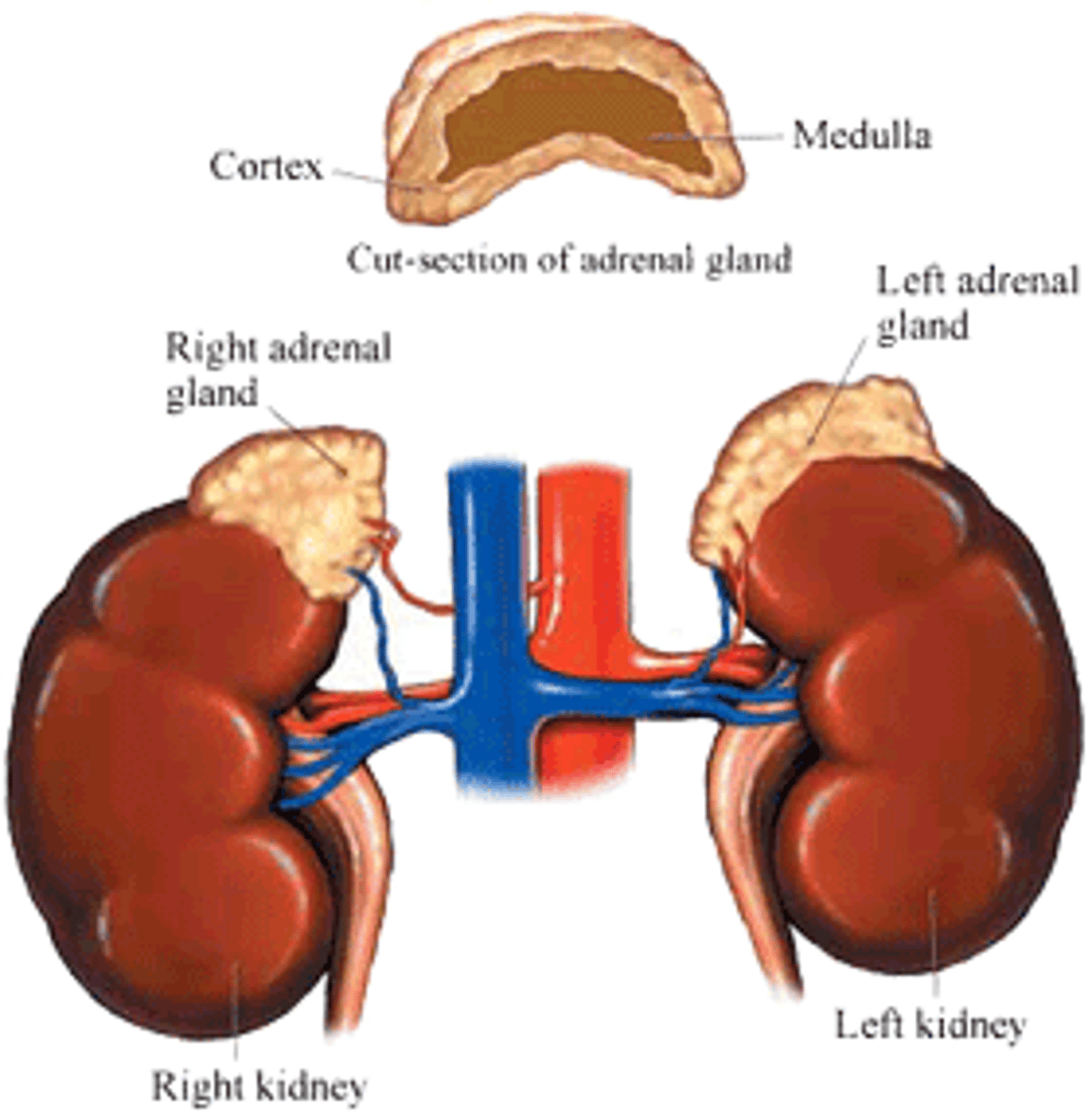
Aldosterone is produced and released from the adrenal medulla or the adrenal cortex?
Aldosterone is produced and released from the adrenal cortex.
Which of the following can be thought of as a precursor to aldosterone?
(A) Cholesterol
(B) ADH
(C) Cortisol
(D) Testosterone
(A) Cholesterol
Upon receiving appropriate triggers, cholesterol is converted into aldosterone.
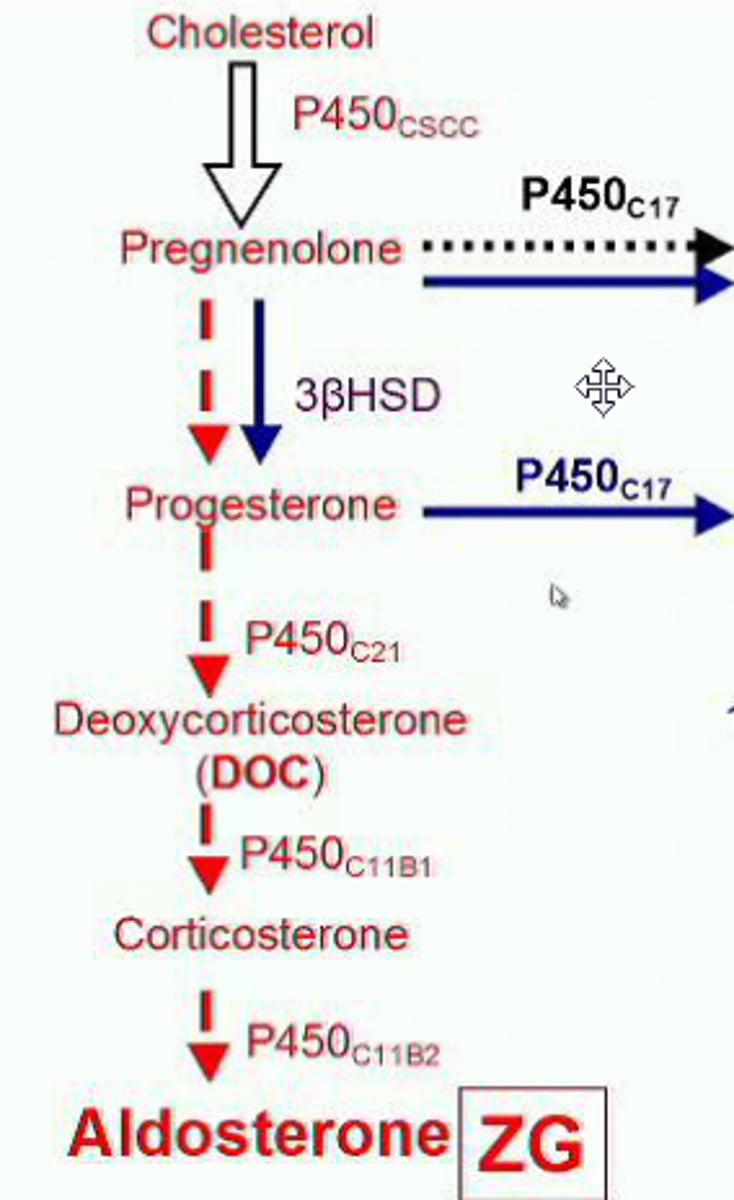
Which of the following directly causes the release of aldosterone from the adrenal cortex?
I. Increase in potassium
II. Decrease in blood pressure
III. Increase in Angiotensin II
(A) I and II Only
(B) I and III Only
(C) II and III Only
(D) I, II, and III
(B) I and III Only
Increases in potassium and angiotensin II levels directly trigger the production and release of aldosterone from the adrenal cortex.
A decrease in blood pressure will not DIRECTLY cause the release of aldosterone. It does so indirectly via angiotensin II.