ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 1 – Introduction to the Human Body (Vocabulary Flashcards)
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering key terms from Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Gross anatomy
The study of large body structures visible without magnification (macroscopic anatomy).
Microscopic anatomy
The study of structures that can be observed only with a microscope or magnification; includes cytology and histology.
Cytology
The study of cells.
Histology
The study of tissues.
Regional anatomy
The study of interrelationships of all structures within a specific body region.
Systemic anatomy
The study of the structures that make up a discrete body system (organs working together).
Interrelationship
How different anatomical structures relate and work together within a region or system.
Homeostasis
Maintenance of relatively stable internal conditions despite environmental changes.
Physiology
The scientific study of the chemistry and physics of the structures of the body and how they work together to sustain life.
Form dictates function (Related)
The principle that the structure of an object or organism determines its function.
Anatomy vs physiology
Anatomy concerns structure; physiology concerns function and mechanisms of how structures work.
Structural organization
The arrangement of the body’s parts from small to large (chemical to organismal).
Chemical level
1) The lowest level of organization, involving atoms and molecules.
Cellular level
2) Level of organization focusing on cells as basic units of life.
Tissue level
3) Level of organization where groups of similar cells perform a common function.
Organ level
4) Level where two or more tissue types form a distinct structure with specific functions.
Organ system level
5) Level where groups of organs work together for major body functions.
Organismal level
6) Highest level of organization: the whole living human.
Subatomic particles
Fundamental particles smaller than atoms (e.g., quarks, electrons).
Atoms
Basic units of matter that combine to form molecules.
Molecules
Two or more atoms bonded together; building blocks of cells and structures.
Organelles
Functional structures within cells, such as mitochondria and ribosomes.
Cells
The smallest independently functioning units of life; basic units of tissues and organs.
Tissue
A group of similar cells performing a specific function.
Organ
A structurally distinct unit composed of two or more tissue types performing one or more physiological functions.
Organ system
A group of organs that work together to perform major functions for the body.
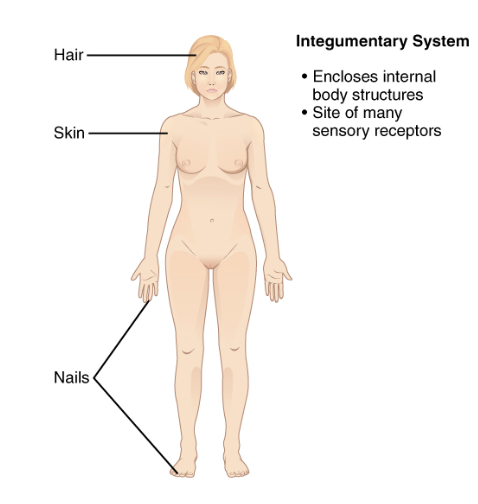
Integumentary system
Skin and associated structures; protects, regulates temperature, and serves sensory roles.
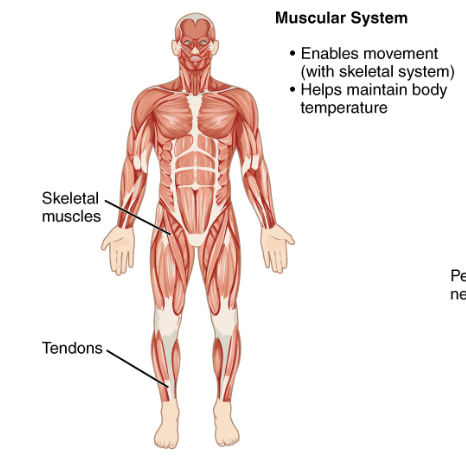
Muscular system
Muscles and tendons; enables movement and posture.
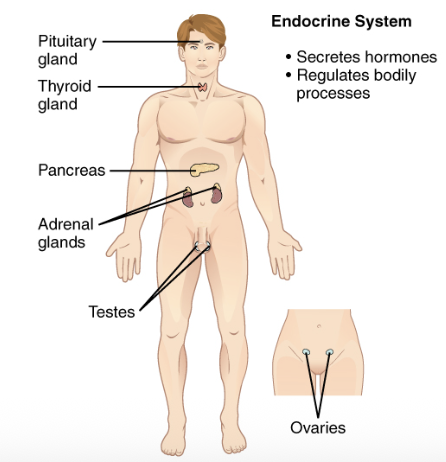
Endocrine system
Glands that secrete hormones regulating body processes.
Skeletal system
Bones, joints, and connective tissues that support and protect the body and enable movement.
Nervous system
Network of neurons and supportive cells controlling rapid responses to stimuli.
Cardiovascular system
Heart and blood vessels; transfers nutrients, gases, and wastes.
Lymphatic system
Supports immune function and fluid balance by returning fluids and filtering pathogens.
Digestive system
Organs that break down food, absorb nutrients, and eliminate waste.
Respiratory system
Air passageways and lungs responsible for gas exchange.
Urinary system
Kidneys and associated structures that remove waste and regulate water/electrolytes.
Reproductive system
Organs involved in producing offspring; differ between sexes but share developmental features.
Organization (compartmentalization)
Body’s trillions of cells arranged within internal compartments to protect and separate processes.
Metabolism
All chemical reactions in the body; energy transformation and use.
Anabolism
Metabolic reactions that build larger, more complex molecules from smaller ones.
Catabolism
Metabolic reactions that break down larger molecules into smaller ones, releasing energy.
Responsiveness
Ability to sense and respond to internal and external changes.
Movement
Motion of body parts, organs, and cells; not just limb movement but cellular processes as well.
Development
All changes in life from birth to death, including growth, differentiation, and repair.
Differentiation
Specialization of cells to perform particular tasks.
Growth
Increase in body size via cell number, size, and extracellular material.
Reproduction
Formation of new organisms from parent organisms.
Oxygen
Essential gas for cellular respiration; ~20% of air supports energy production (ATP). (Requirement for Human Life)
Nutrients
Substances in food necessary for survival; include water, energy-yielding (Carbs & lipids) and body-building nutrients (Proteins/amino acids), and micronutrients (Vitamin & minerals). (Requirement for Human Life)
Water
Critical nutrient essential for life processes.
Temperature (narrow range)
Body reactions occur best within a limited temperature range around 37°C (98.6°F). (Requirement for Human Life)
Atmospheric pressure (narrow range)
Pressure of the atmosphere must stay within a limited range for optimal body function. (Requirement for Human Life)
Enzymes
Biological catalysts whose activity is temperature-dependent; helps metabolic reactions proceed.
Negative feedback
A control mechanism that reduces or cancels the original Stimulus to restore homeostasis.
Positive feedback
A control mechanism that enhances the original stimulus, often in cascades, beneficial for short-term events.
Control mechanism components
Receptor (sensor), control center, and effector that regulate body variables.
Receptor
Sensor that detects changes in the internal or external environment.
Control center
Interprets input from receptors and determines required response. (Brain)
Effector
Structure that executes the response as directed by the control center.
Anatomical position
Standard body posture: standing upright, feet together, palms forward, arms at sides.
Regional terms
Terms naming body areas (e.g., brachium=arm, antebrachium=forearm, femur=thigh, crus=leg).
Directional terms
Terms describing relative location: anterior, posterior, superior, inferior, lateral, medial, proximal, distal, superficial, deep.
Body sections & planes
Planes (sagittal, midsagittal, parasagittal, frontal/coronal, transverse) used to divide the body or organs for study.
Dorsal vs ventral cavities
Posterior (dorsal) and anterior (ventral) body cavities that house organs.
Cranial cavity
Part of the dorsal cavity housing the brain.
Spinal (vertebral) cavity
Part of the dorsal cavity enclosing the spinal cord.
Thoracic cavity
Ventral cavity containing heart and lungs; separated from the abdominal cavity by the diaphragm.
Abdominopelvic cavity
Ventral cavity subdivided into abdominal and pelvic cavities.
Pleura
Serous membranes around the lungs (pleural cavities).
Pericardium
Serous membranes around the heart (pericardial cavity).
Peritoneum
Serous membranes lining the abdominal cavity and covering abdominal organs.
Parietal vs visceral serous membranes
Parietal lines cavity walls; visceral covers organs; the space between holds serous fluid.
Abdominal regions and quadrants
Nine regions and four quadrants used to locate organs within the peritoneal cavity.
Homeostatic imbalance
Disruption of homeostasis increasing disease risk and aging-related changes.