Need to Know
1/238
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
239 Terms
Macroevolution
evolution at a scale larger than speciation above the species level depicted in a tree-like diagram
Phylogeny
the hypothesized evolutionary relationships of a group of species, represented as a phylogenetic tree
ALL organisms are related by
descent from a common ancestor.
There is a bifurcating (branching) pattern to evolution
as in speciation events where a single lineage splits into two or more distinct lineages.
Change in characteristics occurs
in lineages over time
Evolution is not a
progressive ladder it is a rooted, branching tree
A taxonomic unit at any level is called a
taxon
What are the 8 levels of classification in order of biggest to smallest
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
Humans and apes
share a common ancestor
Linnaeus came up with
a hierarchical classification system that goes from the most inclusive taxa to the least inclusive/most specific taxa
There are three Domains (that was not known until 70’s)
Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya

What is this part of a phylogenic tree known as
Sister Taxa

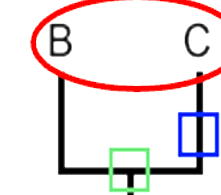
What does the blue box represent
The unique ancestor of C
What does the green box represent
The common ancestor of B and C
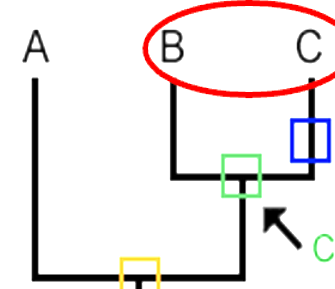
What does the yellow box represent
The common ancestor of A, B, and C
Each species or unit being mapped on the phylogeny is a
taxon
Sister groups or sister taxa share
their most common ancestor
Each lineage has
ancestors that are unique to that line
Each phylogeny has/represents a
time line
The branches of a tree can be
rotated or swiveled around branch points without changing relationships
In phylogeny square or V trees
equal the same thing just different representations
Basal Taxon (Outgroup)
refers to a lineage that diverges early in the history of a group and lies on a branch that is close to the common ancestor of the group.
A clade or a monophyletic group is
a grouping that includes a common ancestor and all the descendents (living and extinct) of that ancestor
Clades can be nested in
larger clades
The oldest taxa is
the basal taxon that diverged first from the common ancestor. (Closest to the root of the tree)
Paraphyletic Group/Clade
a grouping that includes a common ancestor but not all of its descendants.
Polyphyletic Group/Clade
Grouping of species with different common ancestors
To infer phylogenies, systematists gather information about
structures, protein/DNA sequences… of living organisms and fossils
Organisms with more similarities are likely to be
more closely related than organisms with different structures or sequences
Homologies are
phenotypic and genetic similarities due to shared ancestry
Homologous Structures
Anatomical features in different species that share a common ancestry, reflecting evolutionary relationships.
Analogous Structures
Anatomical features in different species that serve similar functions but do not share a common ancestry, resulting from convergent evolution.
Contrast between Homologous and Analogous Structures
The contrast between homologous and analogous structures lies in their origins; homologous structures arise from a common ancestor and reflect evolutionary relationships, while analogous structures evolve independently to perform similar functions without sharing a common ancestry.
Convergent Evolution
The process by which unrelated species evolve similar traits or adaptations in response to similar environmental challenges, leading to analogous structures.
A phylogenetic tree represents a
hypothesis about evolutionary relationships
Phylogenetic trees show
patterns of descent, not phenotypic similarity
Phylogenetic trees do not always indicate
when species evolved or how much change occurred in a lineage
Do NOT assume that
a taxon evolved from the taxon next to it – sister taxa share a common ancestor, which was neither one of the descendent taxa
Divergent Evolution
the process in which two or more related species become more dissimilar over time, often due to different environments or selective pressures.
Homologous Structures are created by
Divergent Evolution
Vestigial Structures
A feature in an organism that is a historical remnant of a structure that served a function in the ancestor of the organism
Analogous structures are created by
Convergent Evolution
Shared Ancestral Character
A character that originated in an ancestor of the clade and are not useful for deducing relationships withing the clade (i.e. Backbone)
Shared Derived Trait
An evolutionary novelty unique to a particular clade which are useful in determining relationships/ building phylogenies (i.e. Legs)
An outgroup is used to
Distinguish between shared ancestral and derived characters
A trait can be both
Ancestral and Derived
We use a character matrix to
construct the simplest phylogeny with the fewest evolutionary steps (principle of parsimony)
Traits shared by many were
derived early and those shared by few evolved later
A derived trait is one that
Differs from its form in the ancestor of a lineage
The amniotes —reptiles, birds, and mammals—are distinguished from amphibians by their
Water-sealing amniotic membranes that protects the embryo from drying out
Phylogeny
is the evolutionary history of a species or a group of species
Why Study Phylogeny?
Classification: depict accurate patterns of relatedness for
organizing the diversity of life on Earth
• Forensics: assess DNA evidence in court cases to inform
situations, e.g. where someone has committed a crime or
where the father of a child is unknown.
• Identifying the origin of pathogens: to learn more about a
new pathogen outbreak and which species it is related to
• Conservation: to inform conservation policy about species
to prevent them from becoming extinct.
• Bioinformatics & computing: Computer algorithms involved
in analyzing molecular data and finding optimal
phylogenetic trees. Merging of Computer Science & Biology
binomial nomenclature
a system for naming species using two Latin names, the genus and species.
The discipline of systematics
Classifies organisms and determines their evolutionary relationships, and represented in a phylogeny
Linnaean taxonomy and systematics can
differ from each other
Anatomical homologies are sometimes
not visible in adult organisms, only in the embryonic state
Horizontal Gene Transfer
The movement of genes from one genome to another
Vertical Gene Transfer
The movement of genes from parent to offspring
Horizontal Gene Transfer occurs by
exchange of transposable elements and plasmids, viral infection, and fusion of organisms
Disparities between gene trees can be explained by
Horizontal Gene Transfer
Horizontal Gene Transfer has played a key role in
The evolution of both prokaryotes and eukaryotes
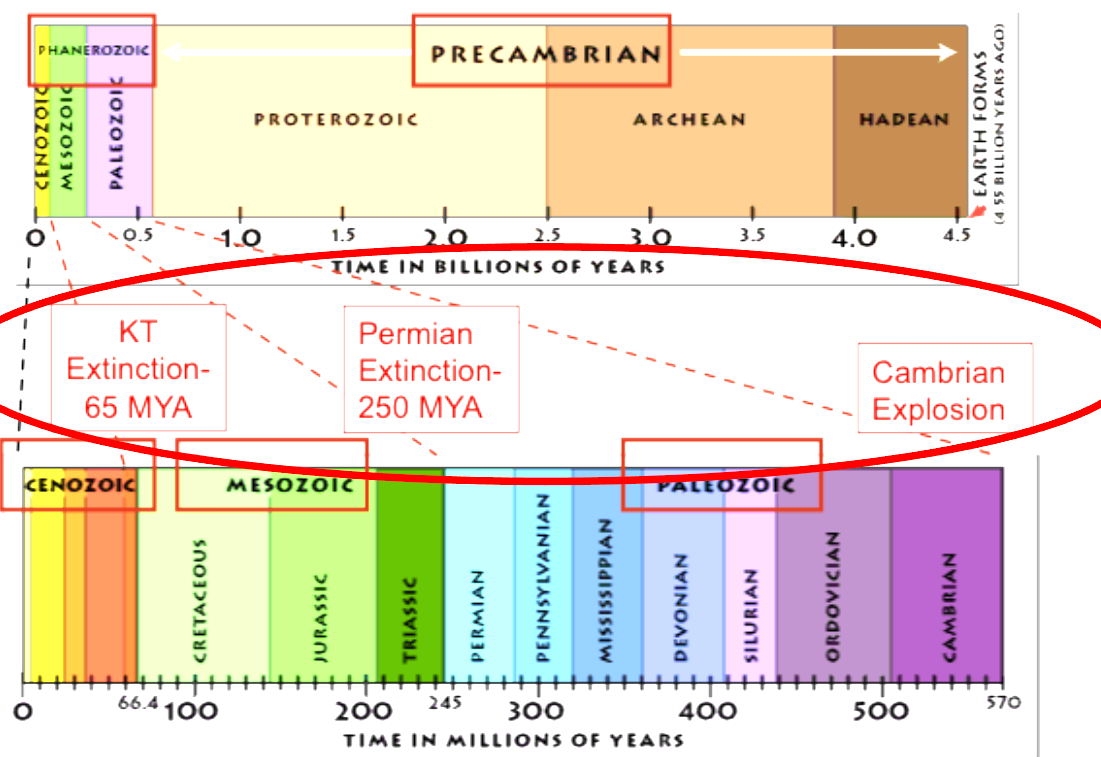
Which way do you read a geologic record table
Right to Left
Cambrian Explosion
A significant event in Earth's history marked by a rapid diversification of life forms in the fossil record, occurring approximately 541 million years ago. (Oldest of the three events)
Permian Extinction
The mass extinction event that occurred around 252 million years ago, leading to the loss of approximately 90% of marine species and 70% of terrestrial vertebrates, marking the end of the Paleozoic Era. (Second oldest of the three events)
KT Extinction
The mass extinction event that occurred around 66 million years ago, resulting in the extinction of approximately 75% of species, including the dinosaurs, marking the end of the Mesozoic Era. (Youngest of the three events)
What are the four steps of the Hypothesis if the formation of simple cells (Abiogenesis)
The four steps of the hypothesis for the formation of simple cells include the synthesis of organic molecules, the formation of polymers, the development of self-replicating molecules, and the encapsulation of these molecules within membranes to form protocells.
RNA was most likely the
first genetic material
The tree of life is not
a branching tree it’s more of a tangled web
Lateral gene transfe
is sideways between different lineages
Antibiotic resistance is due to
horizontal gene transfer and you can pick up resistant strains in hospitals
Any bacteria or virus that has infected you can
change your genome
8% of the human genome came from
viral infection
Inserting corrected genes into humans
CRISPER
We have gone through
5 ME and we are living through the 6th ME now
Precambrian Eon
1-Life originated (expand soon) (precursors of prokaryotes by 3.5 bya)
2-Prokarytotes gave rise to oxygen revolution 2.7 bya
3-1st eukaryotic cell came into existence 1.8 bya
Paleozoic era
Old Life
Mesozoic era
Mid Life
Cenozoic
Current Life
Organic molecules may have formed in certain types of
clay minerals (the clay facilitated reactions in helping materials stick together)
Miller and Urey and others generated
generated amino acids and RNA bases using heat and electrical spark (modeling volcanic heat and lightning) under early Earth conditions in the lab
What do you need for a protocell?
Fats and water (lipid drop) You form a compartment if you mix lipids with water
Life began the moment that
genetic molecules began to replicate and evolve by natural selection
Life began in a
self-catalyzing RNA world
The existence of ribozymes
(RNA that can serve as an enzyme) (before proteins existed) may have been the first genetic material
By natural selection, cells with DNA
had to have formed as DNA is a more long-term stable molecule
The first organisms were
single celled prokaryotes (Earths sole inhabitants for 1.5 Billion Years)
Stromatolites
The oldest fossils (3.5 Billion Years Ago)
Most atmospheric Oxygen (O2) is of
Biological Origin
The O2 revolution marks a change in Earth’s atmosphere due to
Photosynthetic prokaryotes (Not Plants)
Banded Iron Formations are
evidence in change in atmosphere
The endosymbiont theory proses that
Mitochondria and plastids (Chloroplasts) were formally small prokaryotes living within larger host cells as prey or internal parasite
What caused the second increase of oxygen
Plants
Oxygen is very reactive (TOXIC)
It can even damage our cells and DNA by creating unstable free radicals, antioxidants protect us (Oxygen may be why aging might be inevitable)
In the oxygen revolution there was
selection for primarily aerobic bacteria and cell respiration
Way more energy is produced through
aerobic respiration compared to anaerobic respiration.
What came first Mitochondria or Chloroplast
Mitochondria
All eukaryotic cells have
Mitochondria but not chloroplasts
Which eukaryotes have plastids
Plants and algae
Three steps of Serial Endosymbiosis
Large cell establishes membranes and inner compartments (invagination of membrane making a double membranous nucleus)
Larger cell then engulfs a small prokaryote (aerobic bacterium, photosynthetic bacterium)
Those prokaryotes then become organelles withing the larger cell leading to the formation of mitochondria and chloroplast
Why is serial endosymbiosis a theory
There is a lot of evidence for this: Scientists have demonstrated endosymbiosis in the lab and both organelles have their own circular DNA that looks like bacterial DNA. The inner membrane of organelles looks like those of bacteria. They divide like bacteria. They even have ribosomes that look like bacterial ribosomes (as well as sensitivity to antibiotics)