06.A BIO Nucleic Acids (PART A)
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Nucleic acids (Description)
A type of macromolecule that stores the genetic code, aides in protein synthesis and stores and releases energy and includes DNA, RNA, and ATP
Nucleic acid (Elements)
Elements that make up this macromolecule include: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and phosphorus
Nucleic acids (Examples)
Examples of this macromolecule include DNA, RNA and ATP
Nucleotide (Description)
A monomer that makes up nucleic acids
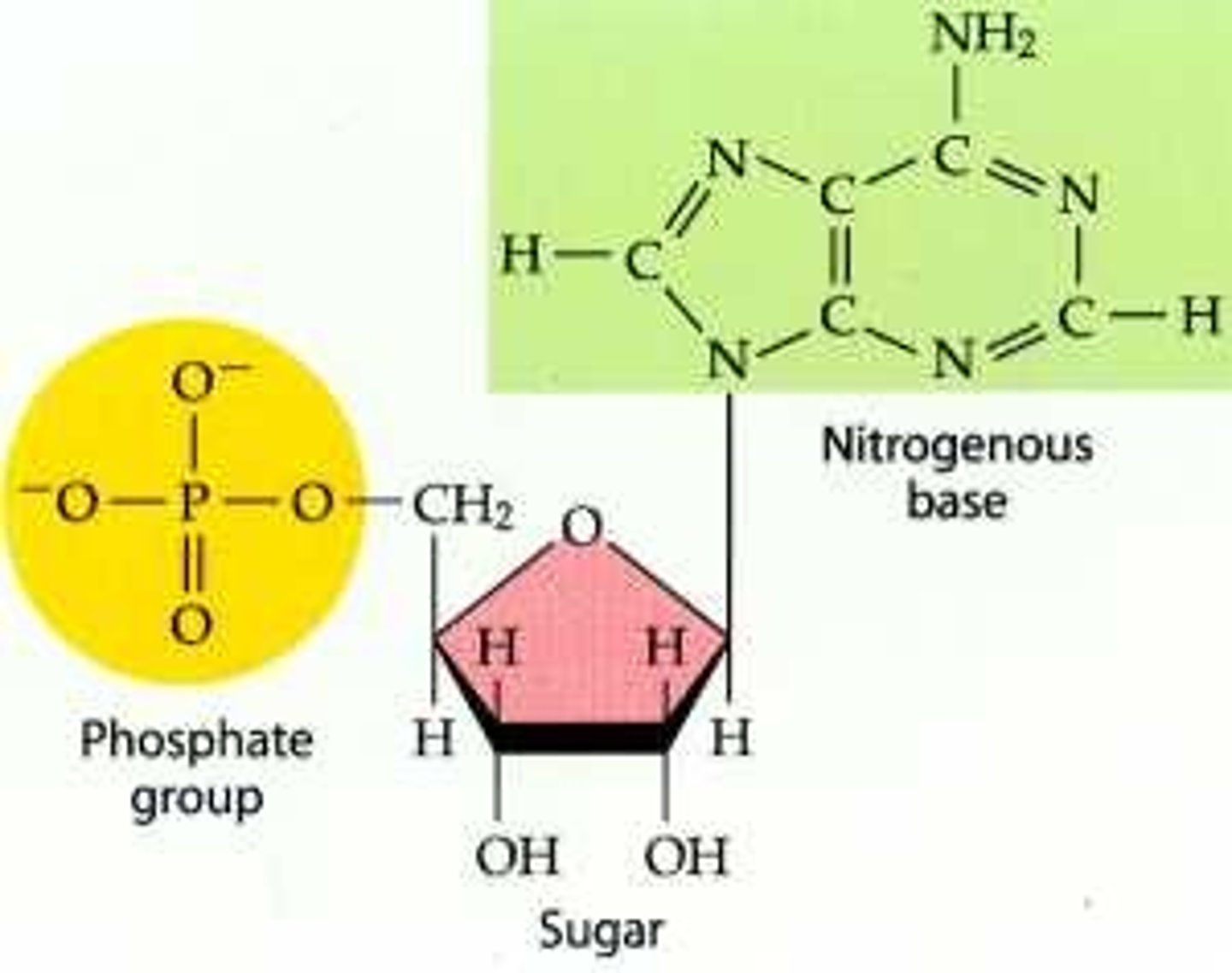
DNA (Function)
A nucleic acid that:
1.) stores genetic info 2) Passes genetic info to offspring and 3) Carries the instructions for making proteins.
RNA (Function)
A nucleic acid that helps to make proteins
ATP (Function)
A type of nucleic acid that is used to store and release energy that is used to do cellular work
DNA (Structure)
Made up of deoxyribose, a phosphate and one of four nitrogen bases, including guanine (G), cytosine (C), adenine (A) and thymine (T)
RNA (Structure)
Made up of ribose, a phosphate and one of four nitrogen bases, including guanine (G), cytosine (C) and adenine (A) and uracil (U)
ATP (Strucuture)
Made up of adenine, ribose and 3 phosphate groups
Nucleotide (Structure)
Made up of a sugar, phosphate and nitrogen base
DNA (# of Strands)
A double stranded nucleic acid
RNA (# of Strands)
A single stranded nucleic acid
ATP (# of Strands)
Modified nucleotide that does NOT form a single or double strand