Chapter 16 - The Endocrine System
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
what is the endocrine system
coordinates activity of body cells using hormones transported in blood
-response is slower but longer lasting than nervous system
endocrine system controls and integrates:
-reproduction
-growth, development
-electrolyte water and nutrient balance in the blood
-cellular metabolism, energy balance
-mobilization of body defenses
what are the endocrine glands
pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, and pineal glands
hypothalamus is _________ organ
neuroendocrine
amino acid based hormones
amino acid derivatives, peptides, and proteins
steroid hormones
synthesized from cholesterol, gonadal and adrenocortical hormones
effects of hormone on target cells:
-alter plasma permeability / mem potential
-stimulate synthesis of enzymes
-activate or deactive enzymes
-induce sectretory activity
-stimulate mitosis
water-soluble hormones
all amino acid-based hormones except thyroid hormone
-binds to receptors on plasma membrane
-act via G protein second messengers
-cannot enter cell
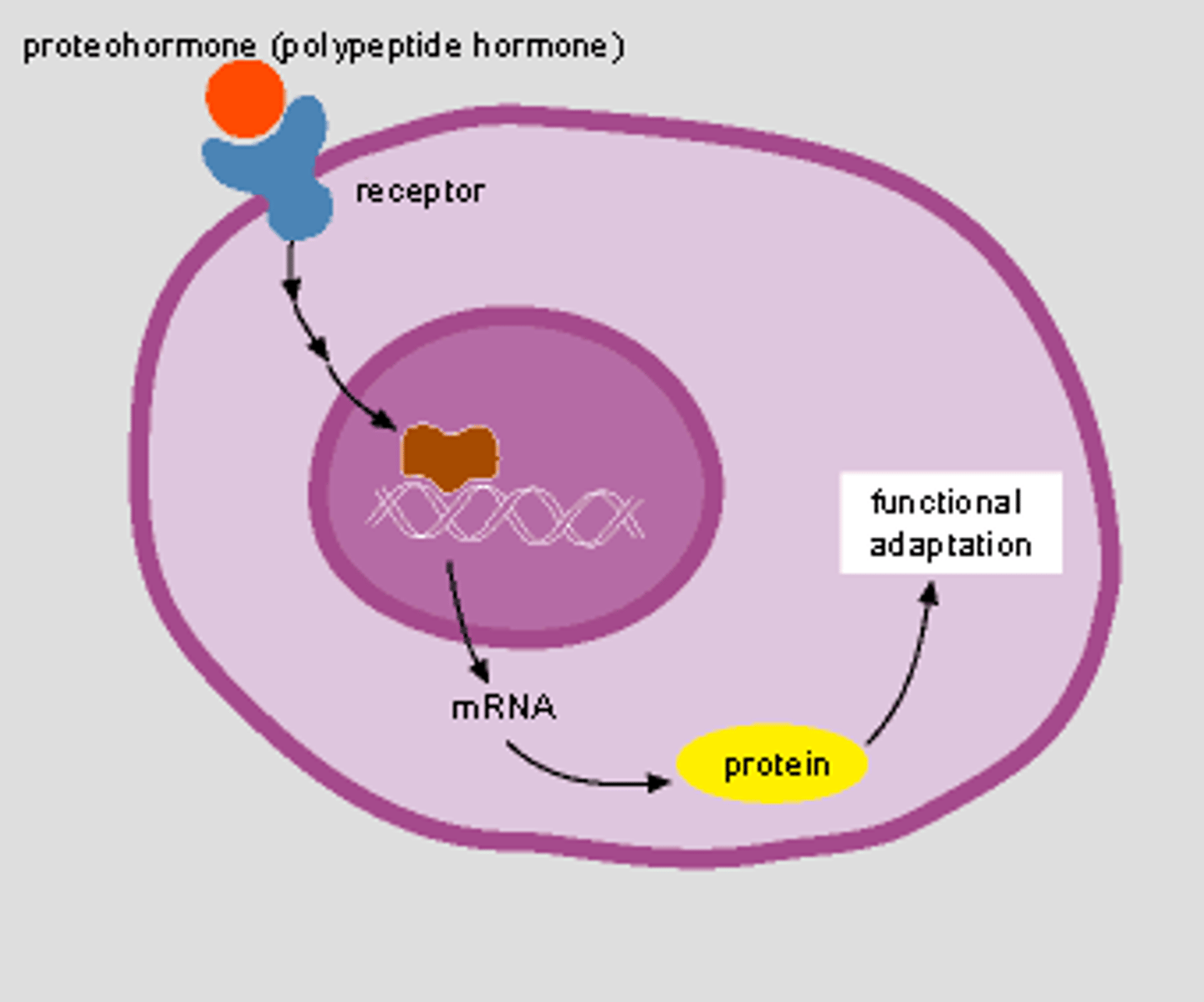
lipid-soluble hormones
steroid and thyroid hormones
-act on intracellular receptors that directly activate genes
-can enter cell
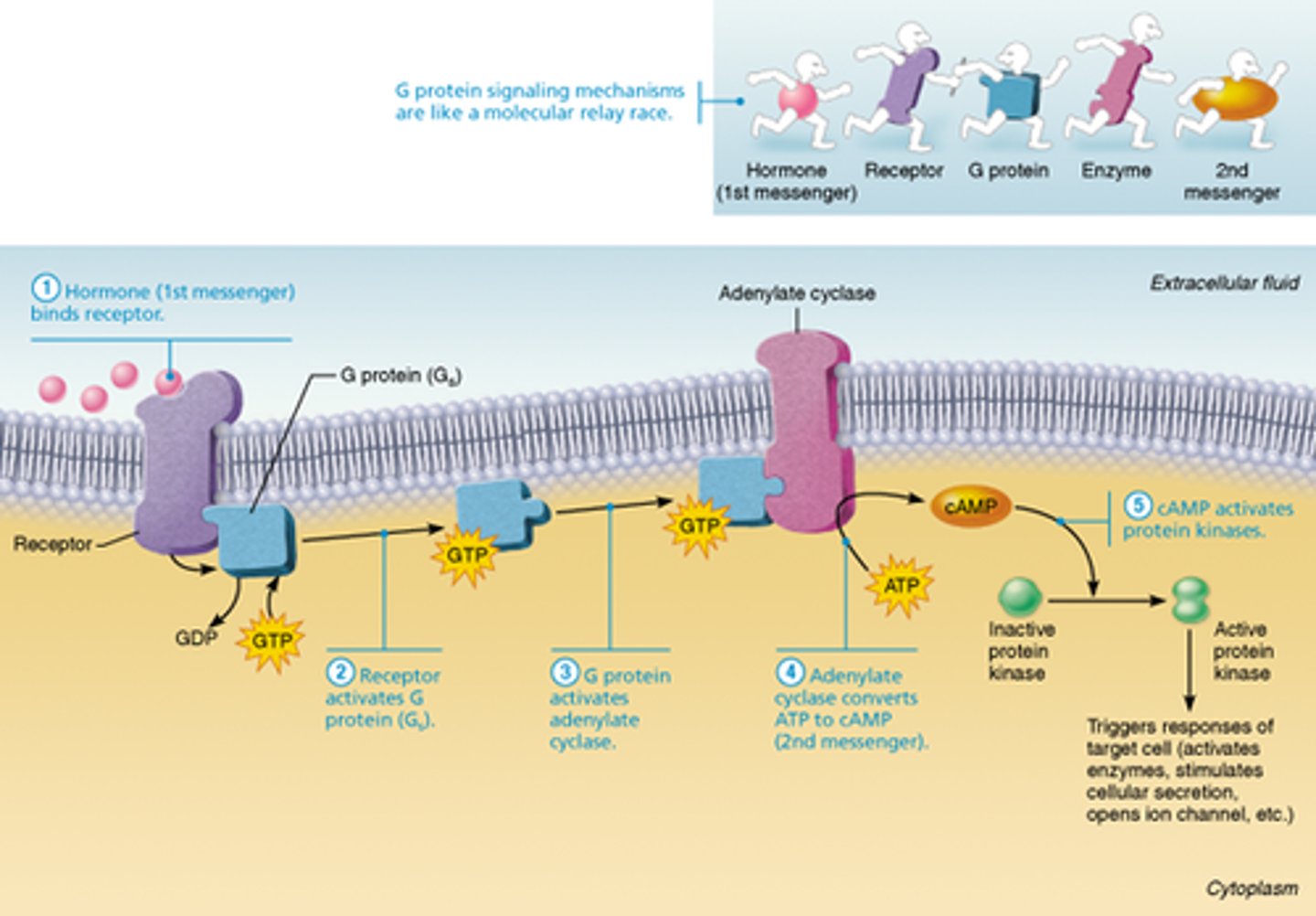
cAMP signaling mechanism (water-soluble hormones)
1. hormone (1st messenger) binds to receptor
2. receptor activates a G protein
3. G protein activates or inhibits effector enzyme adenylate cyclase
4. adenylate cyclase then converts ATP to cAMP (2nd messenger)
5. cAMP activates protein kinases that phosphorylate other proteins
PIP2-calcium signaling mechanism
1. hormone-activated G protein activates a different effector enzyme: phospholipase C
2. activated phospholipase C splits membrane protein, PIP2, into two second messengers:
-diacylglycerol (DAG) activates protein kinases
-inositol trisphosphate (IP3) causes Ca2+ release from intracellular storage sites
3. calcium ions act as another second messenger
-Ca2+ alters enzyme activity and channels, or binds to regulatory protein calmodulin
-calcium-bound calmodulin activates enzymes that amplify cellular response
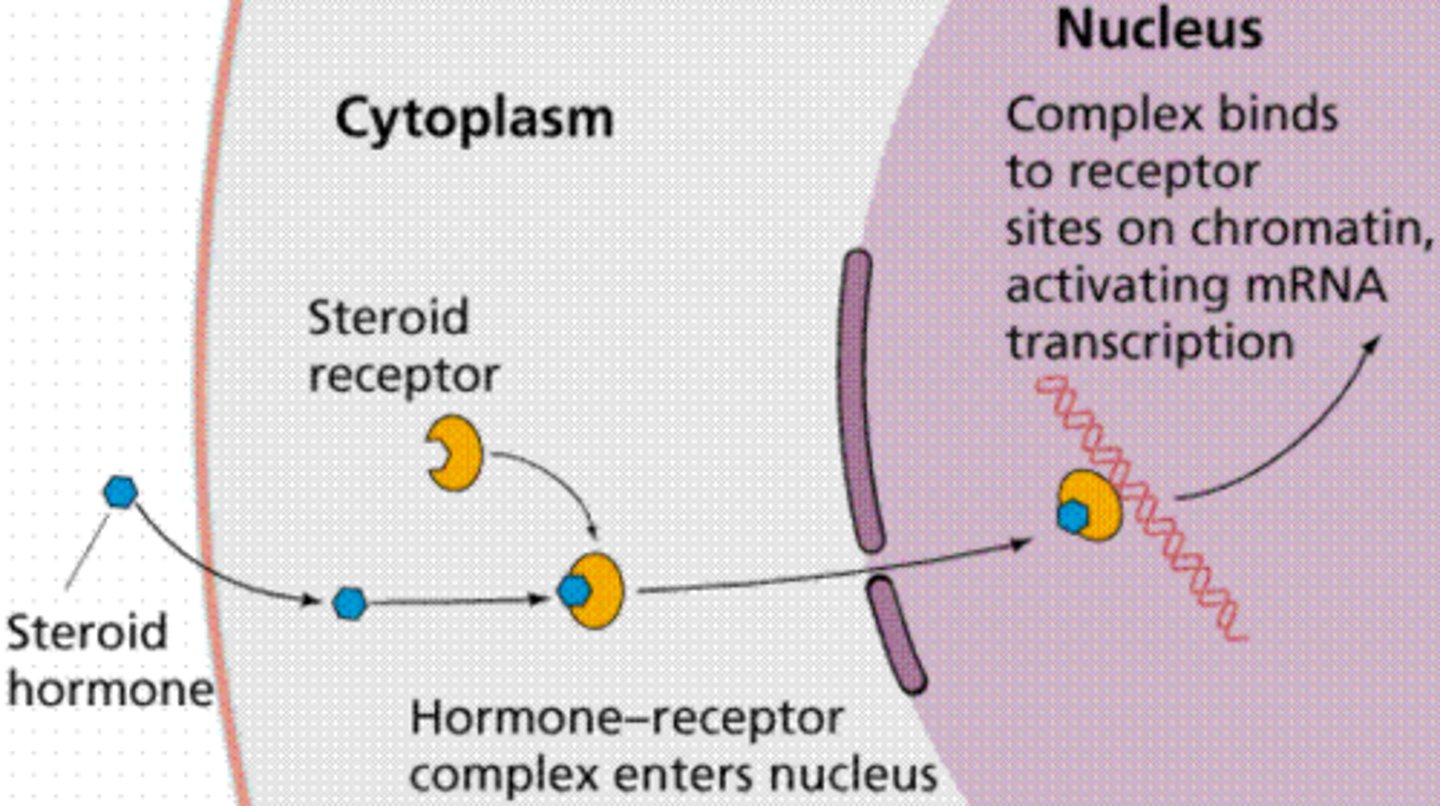
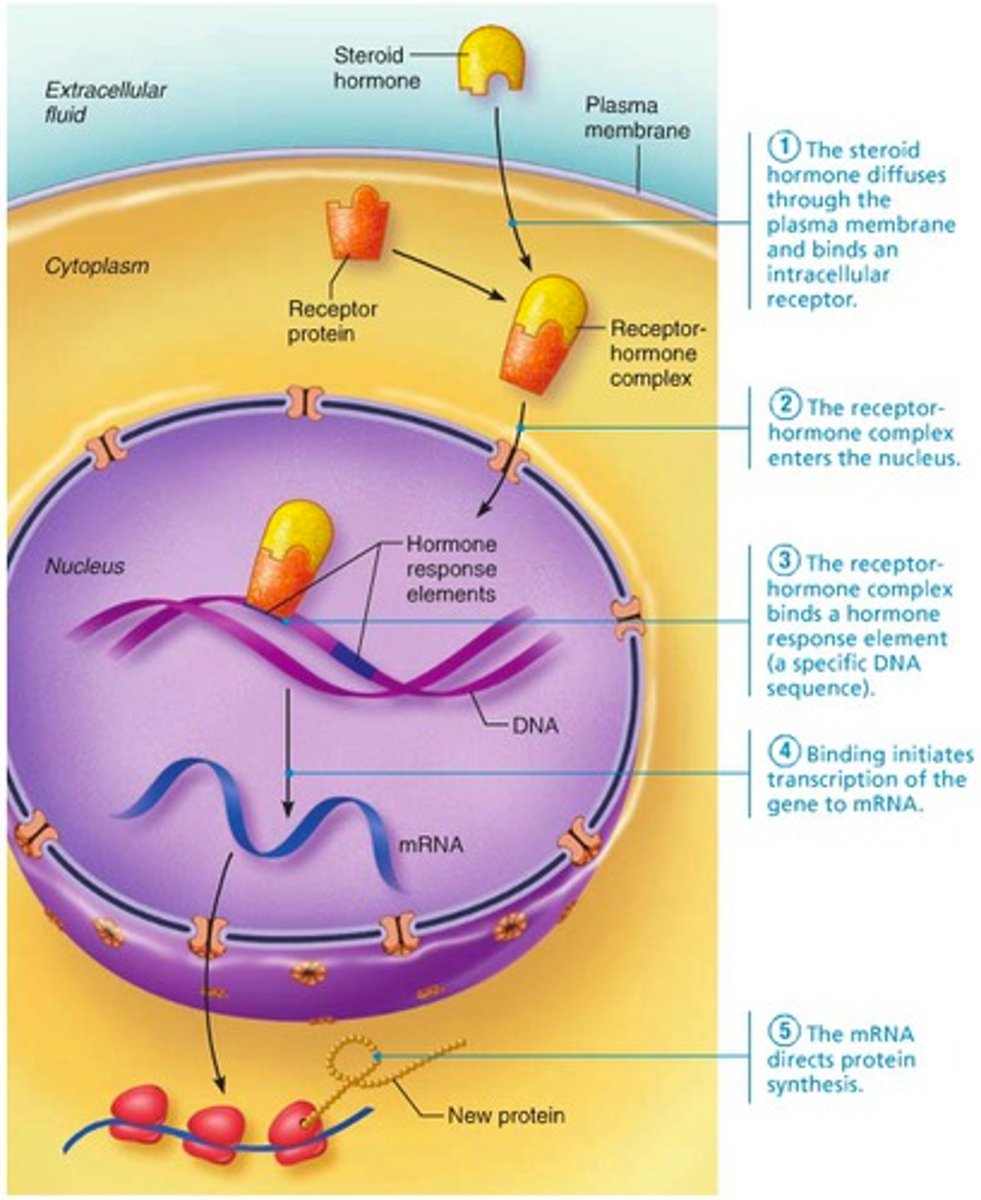
how do lipid soluble hormones work?
diffuse into target cells and bind with intracellular recpeptors
-helps initiate DNA transcription to produce mRNA
-mRNA -> proteins
humoral stimuli
hormone release caused by altered levels of certain critical ions or nutrients
-eg. low Ca2+ in blood, parathyroid gland secrete PTH to increase Ca2+
**environment says...
neural stimuli
nerve fibers stimulate hormone release
-eg. sympathetic fibers stimulate adrenal medulla to secrete NE
**neurons says...
hormonal stimuli
hormones stimulate other endocrine gland to release their hormones
-eg. hormones from hypothalams allows ant. pituitary to secrete hormones that stimulate other endocrine glands
**hormone says...
target cell activation depends on 3 factors:
1. blood levels of the hormone
2. relative number of receptors on or in the target cell
3. affinity (strength) of binding between receptor and hormone
up-regulation
target cells form more receptors in response to low hormone levels
down-regulation
target cells lose receptors in response to high hormone levels
what hormones circulate in blood freely? which don't?
-steroid hormones and thyroid hormone are attached to plasma proteins
-all other hormones circulate without carriers
hormones can be removed from blood by
-degrading enzymes
-kidneys
-liver
concentration of circulating hormones reflects
1. rate of release
2. speed at which it is inactivated and removed from body
half life
time required for level of hormone in blood level to decrease by half
hormones have different response times
-some responses are immediate
-some, especially steroid, can take hours to days
-some are inactive until they enter target cells
permissiveness
one hormone cannot exert its effects without another hormone being present
-eg. reproductive hormones need thyroid hormone to have effect
synergism
more than one hormone produces the same effects on a target cell (amplification)
-eg. glucagon and epinephrine both cause liver to release glucose
antagonism
one or more hormones opposes the action of another hormone (opposite effects)
-eg. insulin and glucagon
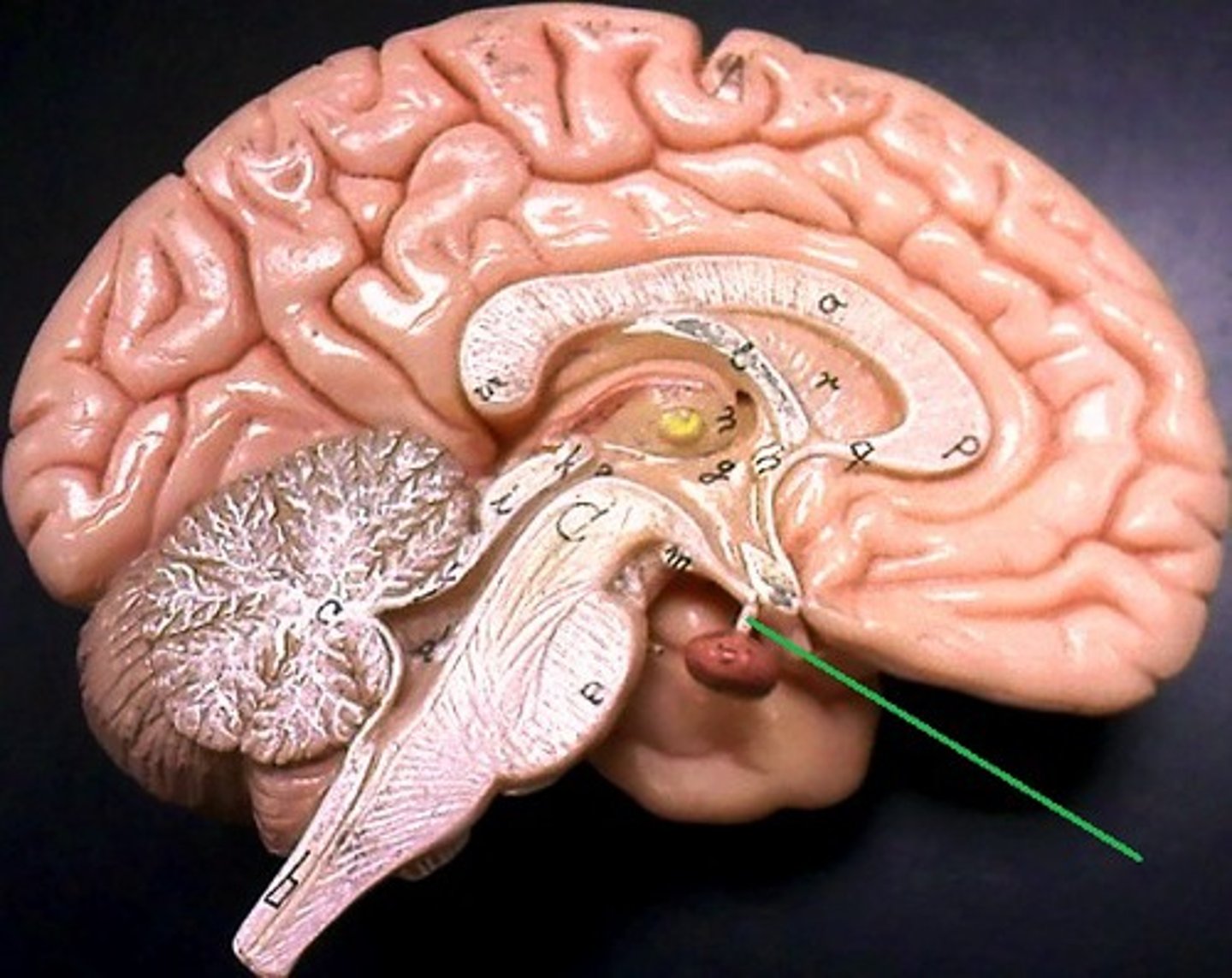
hypothalamus is connected to pituitary gland via stalk called
infundibulum
pituitary secretes at least ## major hormones
eight
2 lobes of the hypothalamus
-posterior pituitary: secretes neurohormones, makes up the neurohypophysis
-anterior pituitary: (adenohypophysis) consists of glandular tissue
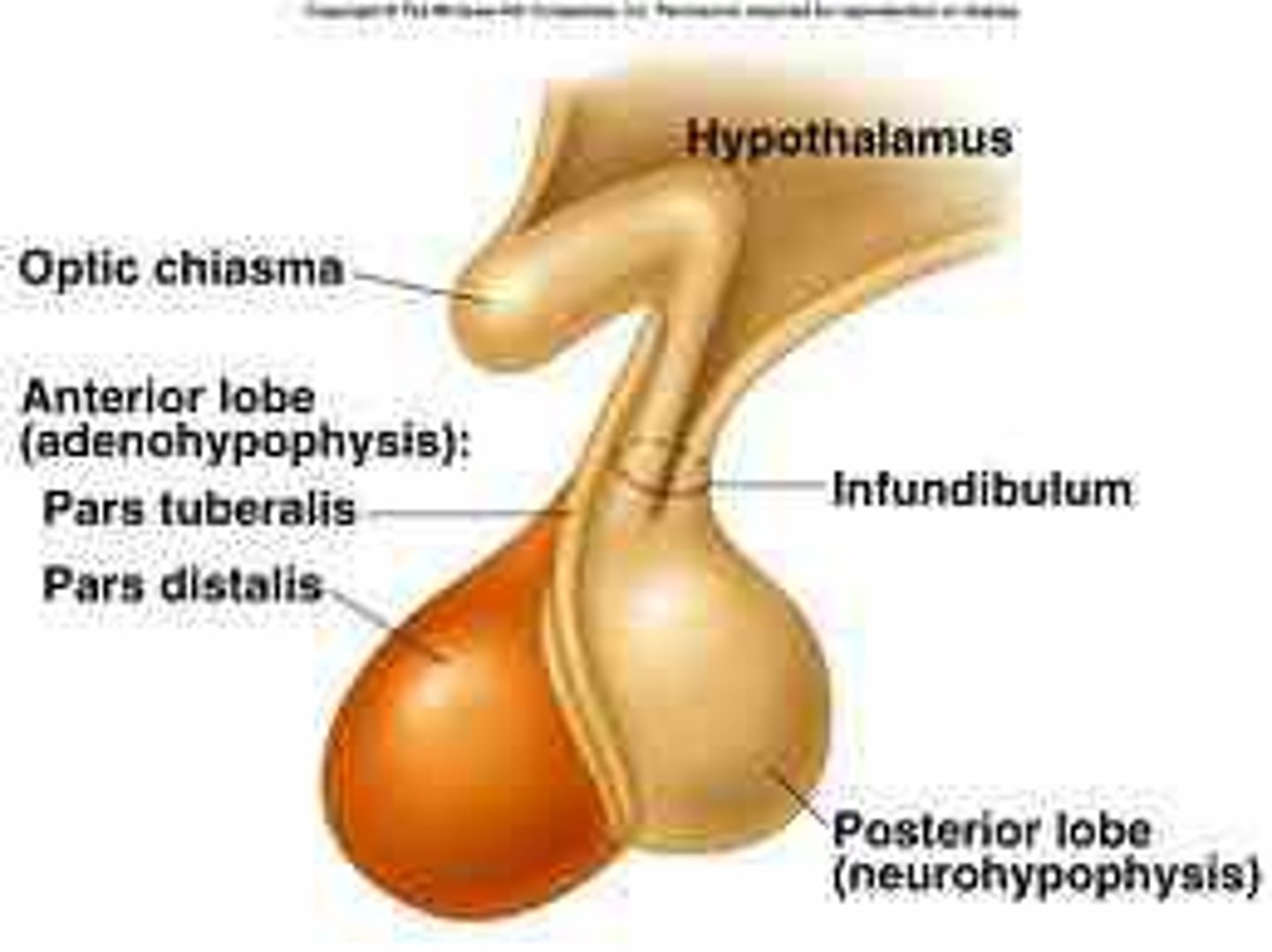
posterior pituitary secretes which neurohormones
oxytocin and ADH (stored in axon terminals and released into blood when neurons fire)
oxytocin
-strong stimulant of uterine contractions for childbirth
-also acts as hormonal trigger for milk ejection
-both positive feedback mechanisms
-acts as neurotrans. in brain (PIP2-calcuim mechanism)
antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
-hypothalamus contains osmoreceptors that monitor solute concentration
-high concentration = posterior pit. release ADH
-tells kidneys to reaborb more water to inhibit or prevent urine formation (prevent water loss by reabsorbing)
anterior pit. and hypothalamic relationships: what does the hypothalamus do?
secretes releasing and inhibiting hormones to anterior pit. to regulate hormone secretion
hypothalamis neurons synthesize releasing and inhibiting hormones. what are they?
GHRH, GHIH, TRH, CRH, GnRH, PIH
hyopophyseal portal system contists of
-primary capillary plexus
-hypophyseal portal veins
-secondary capillary plexus
are the anterior pituitary hormones peptide or steroid?
peptide (amino-acid based / water soluble)
what are the 8 anterior pituitary hormones? which uses cAMP 2nd messenger? which are tropic?
-growth hormone (GH) (does not use cAMP 2nd msg)
-thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) (tropic)
-adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) (tropic)
-follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) (tropic)
-luteinizing hormone (LH) (tropic)
-prolactin (PRL)
hypersecretion of GH
gigantism in children (heights of 8 feet)
acromegaly in adults (overgrowth of hands, feet, face)
hyposecretion of GH
pituitary dwarfism in children (height of only 4 feet)
usually no problems in adults
what does TSH do and how is it released
stimulates normal development and secretory activity of thyroid
-hypothalamus releases thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) which tells anterior pit. to release TSH
what does ACTH do
stimulates adrenal cortex to release cortisol / corticosteroids
what regulates ACTH release
hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing hormone CRH (highest levels in morning)
-fever, hypoglycemia and stressors can alter release of CRH
what are the 2 gonadotropins
follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH)
how is gonadotropin release regulated
-by the gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) during and after puberty
-suppressed by gonadal hormones (feedback)
what does FSH do
stimultes production of gametes (egg or sperm)
what does LH do (males vs females)
promotes production of gonadal hormones
-female: helps mature follicles of egg, triggers ovulation, releases estrogen and progesterone
-male: stimulates production of testosterone
when are LH and FSH present
absent in blood of girls and boys until puberty
what is PRL and how it is released
stimulates milk production in females
-increased estrogen stimulate PRL (cause breast swelling and tenderness during menstral cycle)
-suckling stimulates PRL release and promotes continued milk production
how is PRL regulated
regulation controlled by prolactin-inhibiting hormone (PIH), which is dopamine
-PIH prevents release of PRL until needed
what is the thyroid hormone (TH)
body's major metabolic hormone
-2 forms: T4 (thyroxine ; 2 iodine) and T3 (triiodothyronine ; 3 iodine)
-affects every cell in body
calorigenic effect of TH
increases basal metabolic rate and heat production
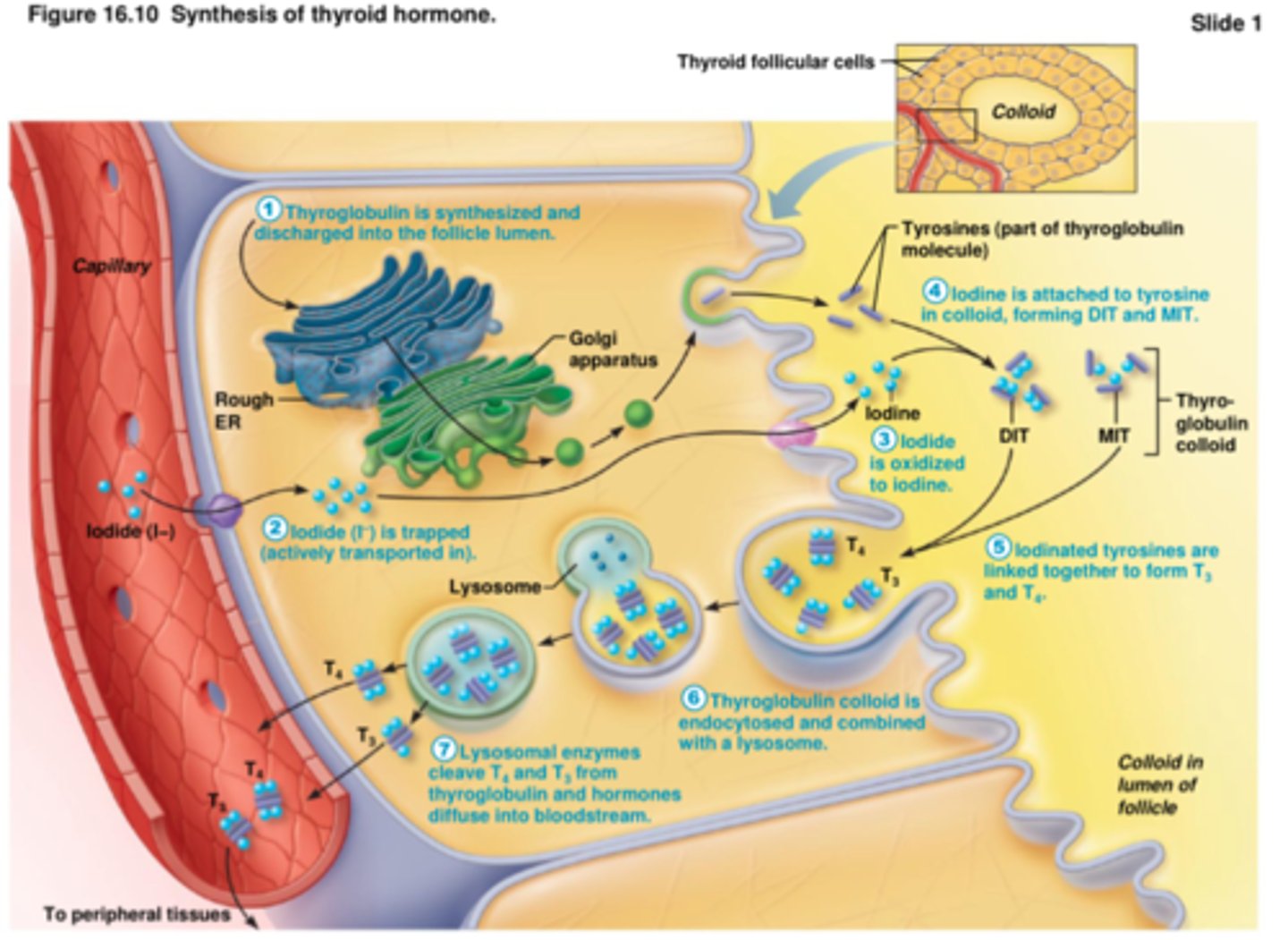
synthesis of thyroid hormone
1. hyroglobulin is synthesized and discharged into the follicle lumen
2. iodides (I-) is trapped (actively transported in)
3. iodide is oxidized to iodine
4. iodine attaches to tyrosine, forming DIT and MIT
5. iodinated tyrosines link together to form T3 and T4
6. thyroglobuli colloid is endocytosed and combined with a lysosome
7. lysosomal enzymes cleave T4 and T3 from thyroglobulin and hormones diffuse into bloodstream
T4 and T3 transported by
thyroxine-binding globulins (TBGs)
T4 vs T3: which is more active
T3 by 10 times
falling TH levels stimulate release of
thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
myxedema
hypothyroidism (hyposecretion of TH in adults)
-low metabolic rate, thick / dry skin, puffy eyes, chilly, constipation, edema, mental sluggishnes, legarthy
goiter
enlargement of the thyroid gland due to lack of iodine
-lack of iodine (hypo), triggers increased TSH secretion, triggering thyroid to synthesize more unuseable thyroglobulin
congenital hypothyroidism
usually caused by poor development of thyroid gland (bc TH is critical for normal skeletal growth and brain development)
-pituitary problems or maternal medication may sometimes affect baby's ability to make TH
-may be asymptomatic or present w weak cry, poor feeding, constipation, jaundice
Graves' disease
hyperthyroidism (hypersecretion of TH)
-antibodies mimic TSH and stimulates TH release
-elevated metabolic rate, sweating, rapid and irregular heartbeats, nervousness, weight loss
-exophthalmos may occur
exophthalmos
bulging eyes
what is calcitonin
produced by parafollicular cells of thyroid gland that lowers blood Ca2+ levels
-antagonistic to PTH
-stimulates Ca2+ uptake and incorporation into bone matrix
what is the parathyroid gland and what does it do
4-8 tiny yellow glands embedded in thyroid
-contain oxyphil, and parathyroid cells that secrete PTH
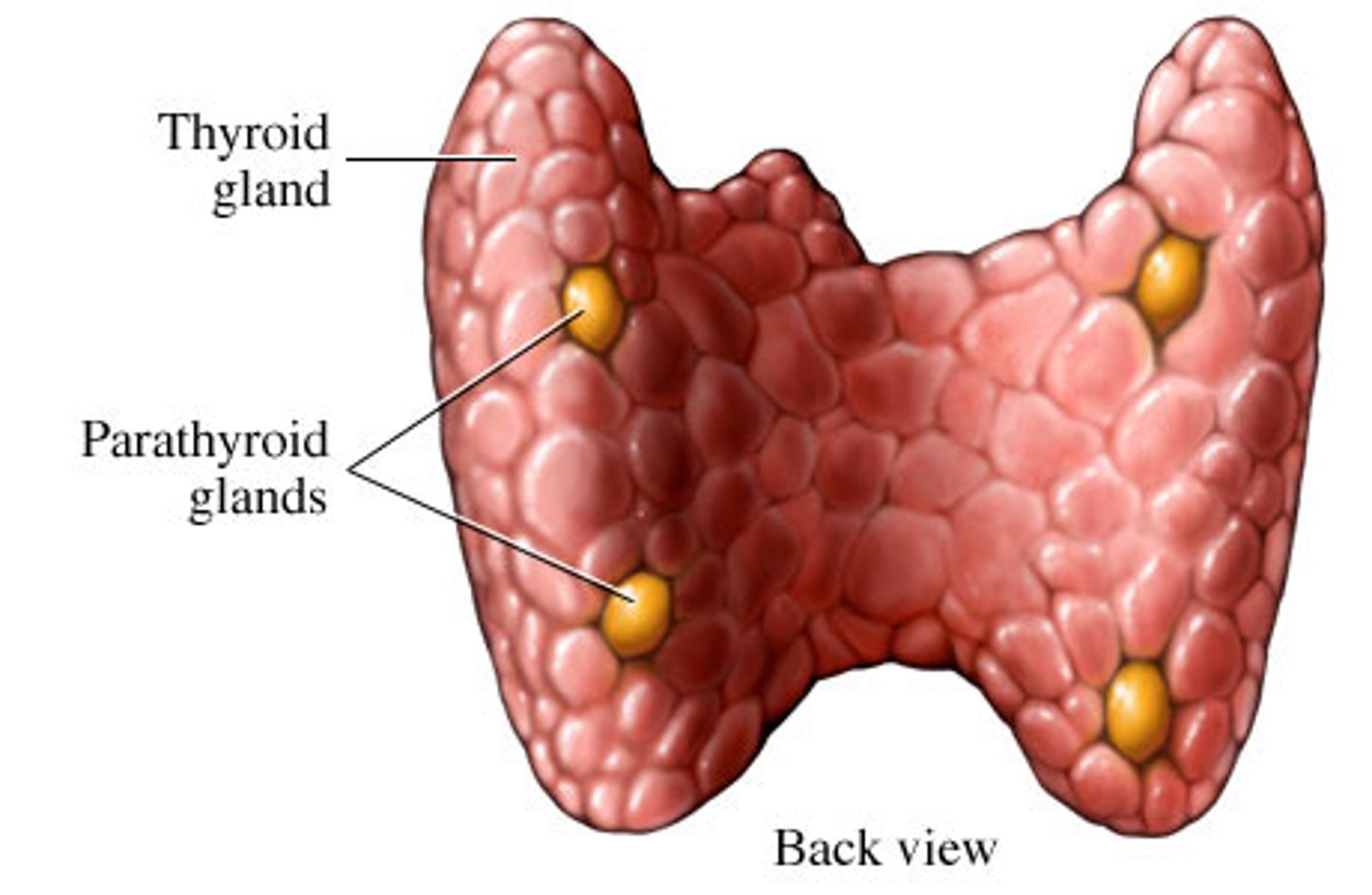
what does PTH do
increases blood Ca2+ levels
-target organs: skeleton, kidneys, intestine
what is the adrenal gland and where is it
paired, pyramid shaped organs on top of kidneys
-aka suprarenal glands
-2 glands in one
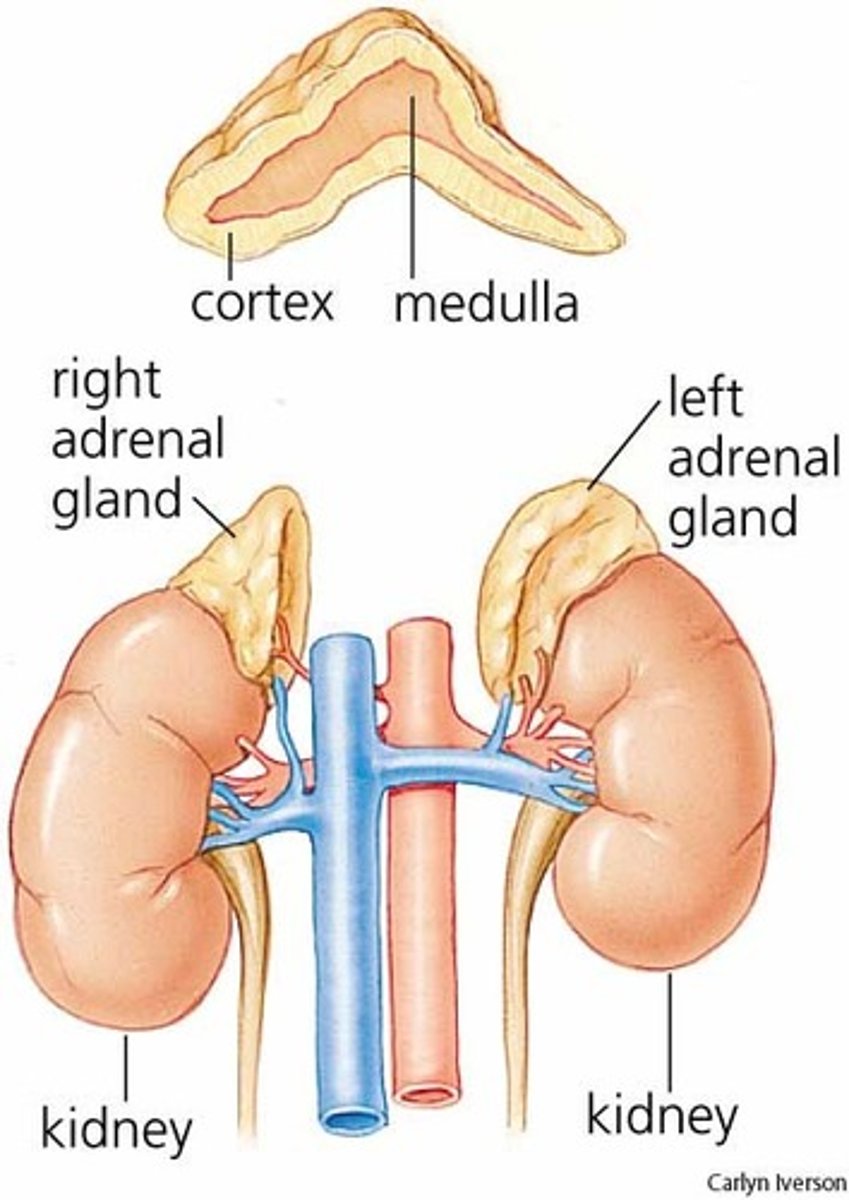
adrenal gland: what are the adrenal cortex and medulla
cortex: synthesize and secrete several different hormones
medulla: part of sympathetic nervous system
what does the adrenal cortex produce
corticosteroids
-not stored in cells
-rate of release depends on rate of synthesis
3 layers of cortical cells produce the different corticosteroids
-zona glomerulosa -> mineralocorticoids
-zona fasciculata -> glucocorticoids
-zona reticularis -> gonadocorticoids
what is aldosterone and what does it do
mineralocorticoid hormone of adrenal cortex
-stimulates Na+ reabsorption by kidneys (increased BP and volume)
-stimulates K+ elimination by kidneys
factors that regulate aldosterone secretion
1. renin-angiotensin-aldosterone mechanism
2. plasma concentration of K+
3. ACTH
what are glucocorticoids of adrenal cortex
keep blood glucose levels relatively constant, influence metabolism, and helps resist stressors
-main one is cortisol
-released in response to CRH/ACTH
-causes increase in blood glucose, fatty acids, amino acids
gluconeogenesis
formation of glucose from fats and proteins
Cushing's syndrome
hypersecretion of cortisol
-depresses cartilage / bone formation amd immune system
-inhibits inflammation
-disrupts neural, crdiovascular, and gastrointestinal function
-seen with "moon" face and "buffalo hump"
-due to tumor on pituitary, lungs, kidney, adrenal cortex
Addison's disease
hyposecretion of cortisol
-decrease in plasma glucose and Na+ levels
-involves deficits in glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids
-weight loss, severe dehyration, hypotension
-seen with bronzing of skin (high ACTH = melain production)
what are gonadocorticoids of adrenal cortex
adrenal sex hormones
-weak androgens (male sex hormones) converted to testosterone, some estrogens
what do gonadotropins do
-onset of puberty and appearance of secondary sex characteristics
-sex drive in women
-source of estrogens in postmenopausal women
medullary chromaffin cells synthesize
catecholamines epinephrine (80%) and norepinephrine (20%)
effects of catecholamines
-vasoconstriction
-increased HR
-increased blood glucose levels
-blood diverted to brain, heart and skeletal muscle
stress in adrenal medulla vs cortex
medulla: short term stress ; involved with NE and epinephrine for fight or flight
cortex: long term stress ; involved with glucocorticoids and some mineralocorticoids
if long term stress response is prolonged...
it can become detrimental, leading to high BP, muscle loss, altered immune function, etc.
what is the pineal gland
small endocrine gland in the brain (3rd ventricle)
-pinealocytes secrete melatonin
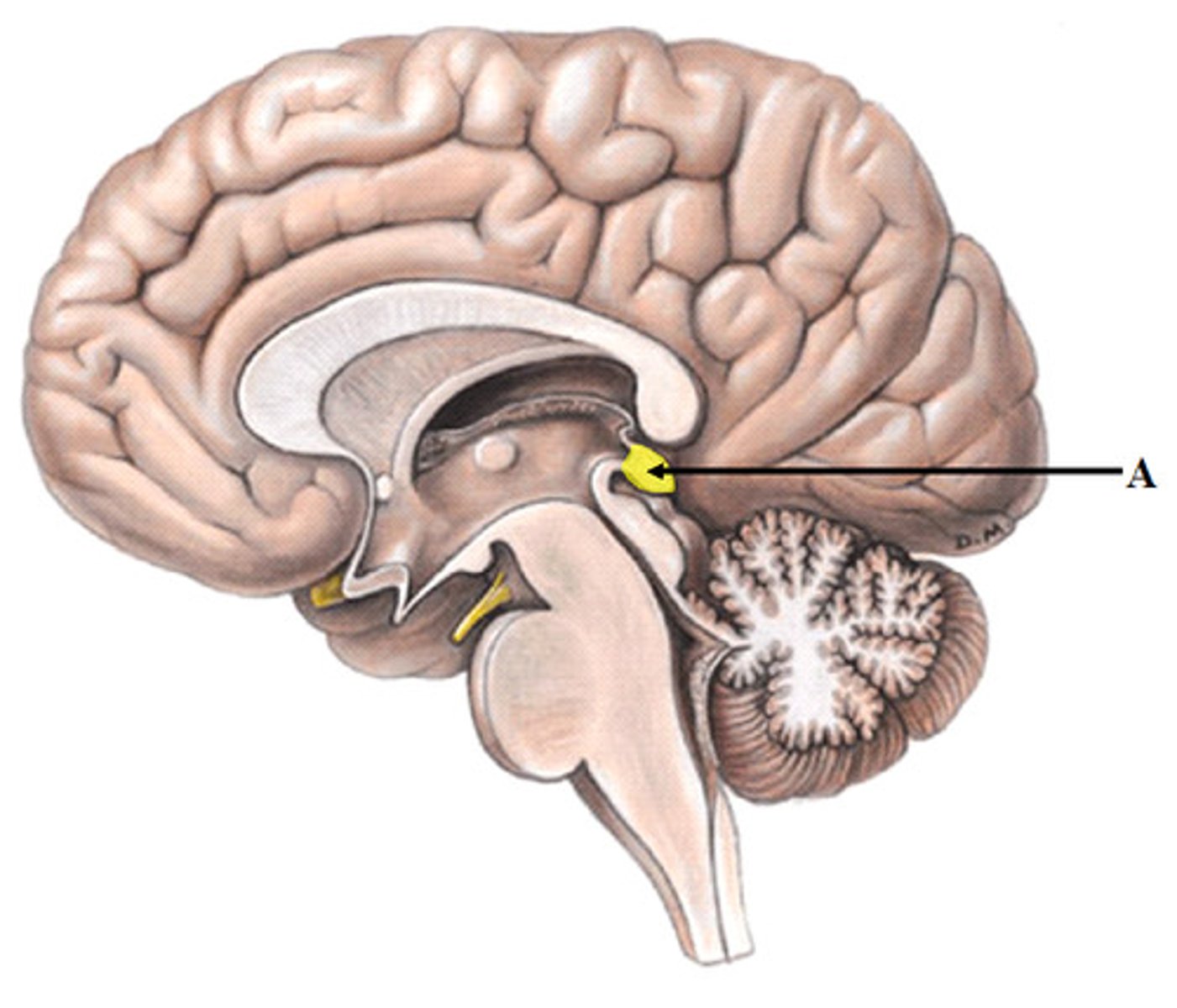
melatonin may affect
-timing of sexual maturation and puberty
-day/night cycles
-physiological processes that show rhythmic variations (body temperature, sleep, appetite)
-production of antioxidant and detoxification molecules in cells
acinar cells (exocrine) in pancreas...
produce enzyme-rich juice for digestion
pancreatic islets (islets of Langerhans) contain endocrine cells. what cells
-alpha cells -> produce glucagon (hyperglycemic hormone)
-beta cells -> produce insulin (hypoglyceminc hormone)
glucagon
triggered by decreased blood glucose levels, rising amino acid levels, sympathetic nervous system
!! increases blood glucose !!
insulin
secreted when blood glucose levels increase
!! decreases blood glucose !!
3 ways insulin lowers blood glucose levels
-enhances membrane transport of glucose into fat and muscle cells
-inhibits breakdown of glycogen to glucose
-inhibits conversion of amino acids or fats to glucose
diabetes mellitus (DM) can be due to...
-hyposecretion of insulin: type 1
-hypoactivity of insulin: type 2
3 cardinal signs of DM
-polyuria—huge urine output
-polydipsia—excessive thirst
-polyphagia—excessive hunger and food consumption
lipidemia
high levels of fatty acids in blood
-occurs when sugars cannot be used as fuel, so in DM, fats are used
ketoacidosis
excessive production of ketones, making the blood acidic
-due to fatty acid metabolism (which forms ketones)
ovaries produce...
estrogen and progesterone
what does estrogen do
-maturation of reproductive organs
-appearance of secondary sexual characteristics
-with progesterone, causes breast development and cyclic changes in uterine mucosa
testes produce....
testosterone
what does testosterone do
-initiates maturation of male reproductive organs
-causes appearance of male secondary sexual characteristics and sex drive
-necessary for normal sperm production
-maintains reproductive organs in functional state
placenta
secretes estrogens, progesterone, and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
adipose tissue release...
-leptin - appetite control; stimulates increased energy expenditure
-resistin - insulin antagonist
-adiponectin - enhances sensitivity to insulin
GI tract: gastrin
stimulates release of HCl
GI tract: ghrelin
stimulates food intake
GI tract: secretin
stimulates liver and pancreas
GI tract: cholecystokinin (CCK)
activates pancreas, gallbladder, hepatopancreatic sphincter