Comprehensive Sports Injury and Rehabilitation: Muscles, Ligaments, and Foot Anatomy
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Isotonic
Movement through a ROM with a fixed amount of resistance, focused on movement at a joint with muscles shortening and lengthening. Ex. Bicep curl with dumbbell.
Concentric
Muscle shortens against resistance.
Eccentric
Muscles lengthen against resistance.
Isometric
Contraction with no joint movement. Ex. Plank.
Isokinetic
Contraction with fixed speed, equipment needed. Ex. Treadmill.
Muscular endurance
Ability to perform repetitive movements for an extended time.
Static stretching
Isolated, stretched, held for 30 sec (post aerobic activity).
Ballistic stretching
Do not use, specific muscle is isolated, quick stretch—> relaxed—> repeated.
Dynamic stretching
Moving a limb through a ROM.
Muscular power
the ability to exert force quickly. Heavy weight low reps. Ex. Box jump.
Mechanisms of knee injuries
deceleration task with high knee internal extension torque (with or without perturbation) combined with dynamic valgus rotation with the body weight shifted over the injured leg and the plantar surface of the foot fixed flat on the playing surface
Precursors to knee injuries
Change of direction, cutting maneuvers combined with deceleration.
Intrinsic factors
Too many. Ex. Anatomical (BMI, ACL size).
Taping indications
Provide support and stability, immediate first aid, secure a pad or brace, prevent injury, restrict angle of pull, psychological assistance.
Linen tape
Most common tape. Can be expensive
Elastic tape
Used when strong material is desired and for hyperextension injuries.
Hybrid tape
Mix of linen and elastic, used on muscles and joints that need more movement.
Moleskin
Adhesive, used when added strength is needed.
Kinesiology tape
Used to allow ROM, movement of fluids, reduce pain and pressure of underlying tissues.
Rigid tape
Used to improve joint movement by changing alignment or stabilizing a joint.
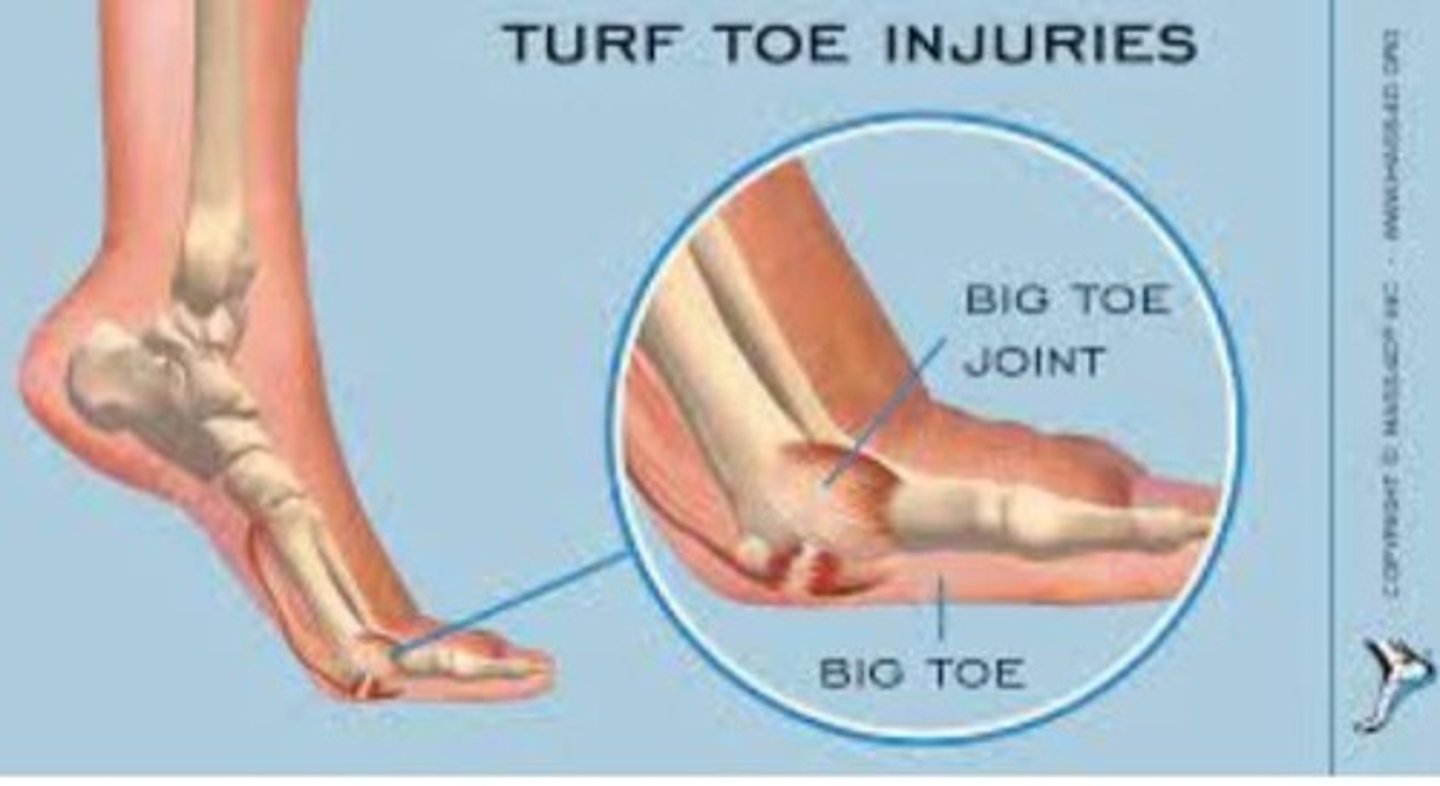
Turf toe
Goal: restrict the extension of the great toe.
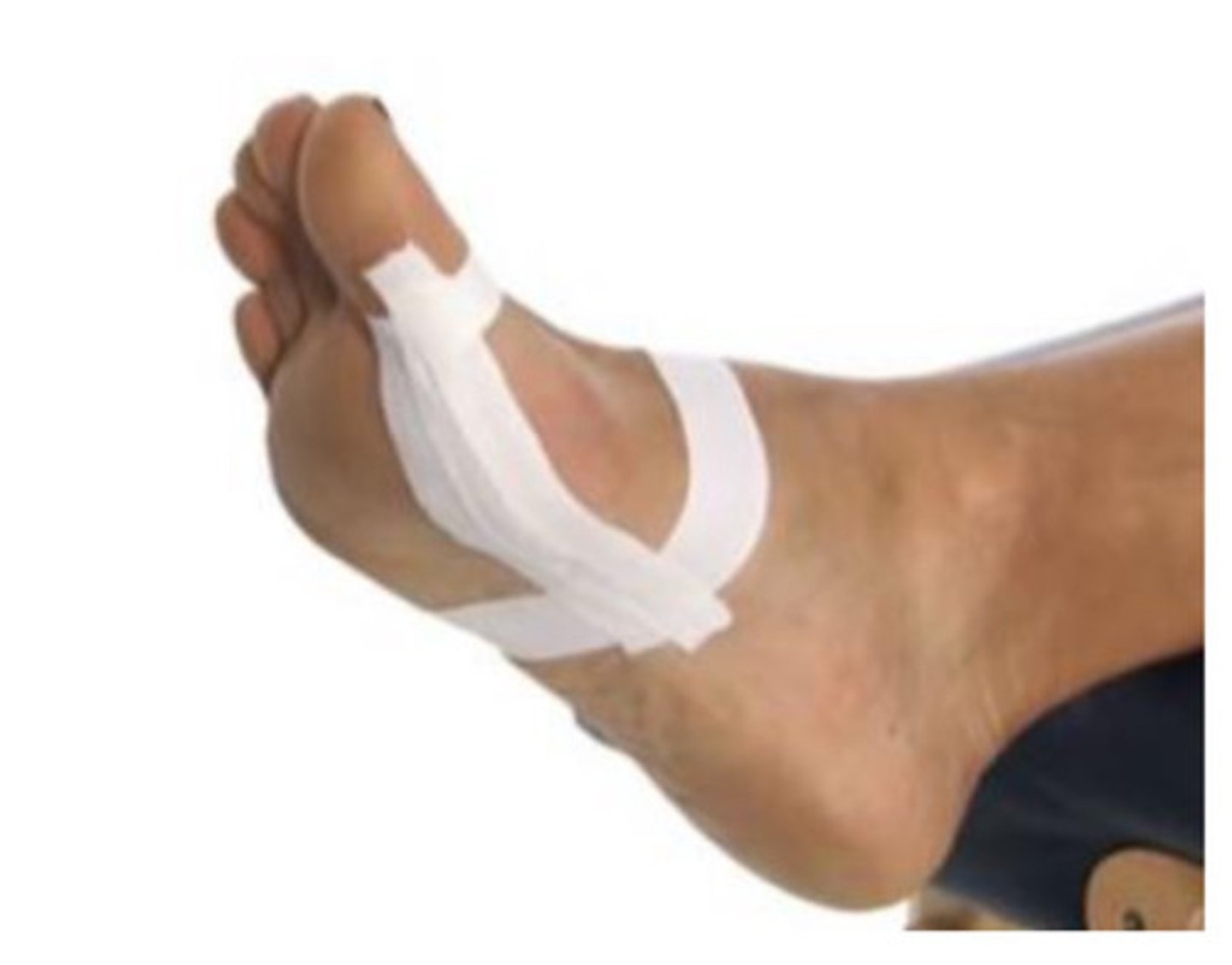
Bunion
Goal: relieve pressure on medial aspect of great toe.
Longitudinal Arch
Goal: keep medial foot from flattening.
Closed basket weave
Goal: support the ankle joint and prevent inversion.
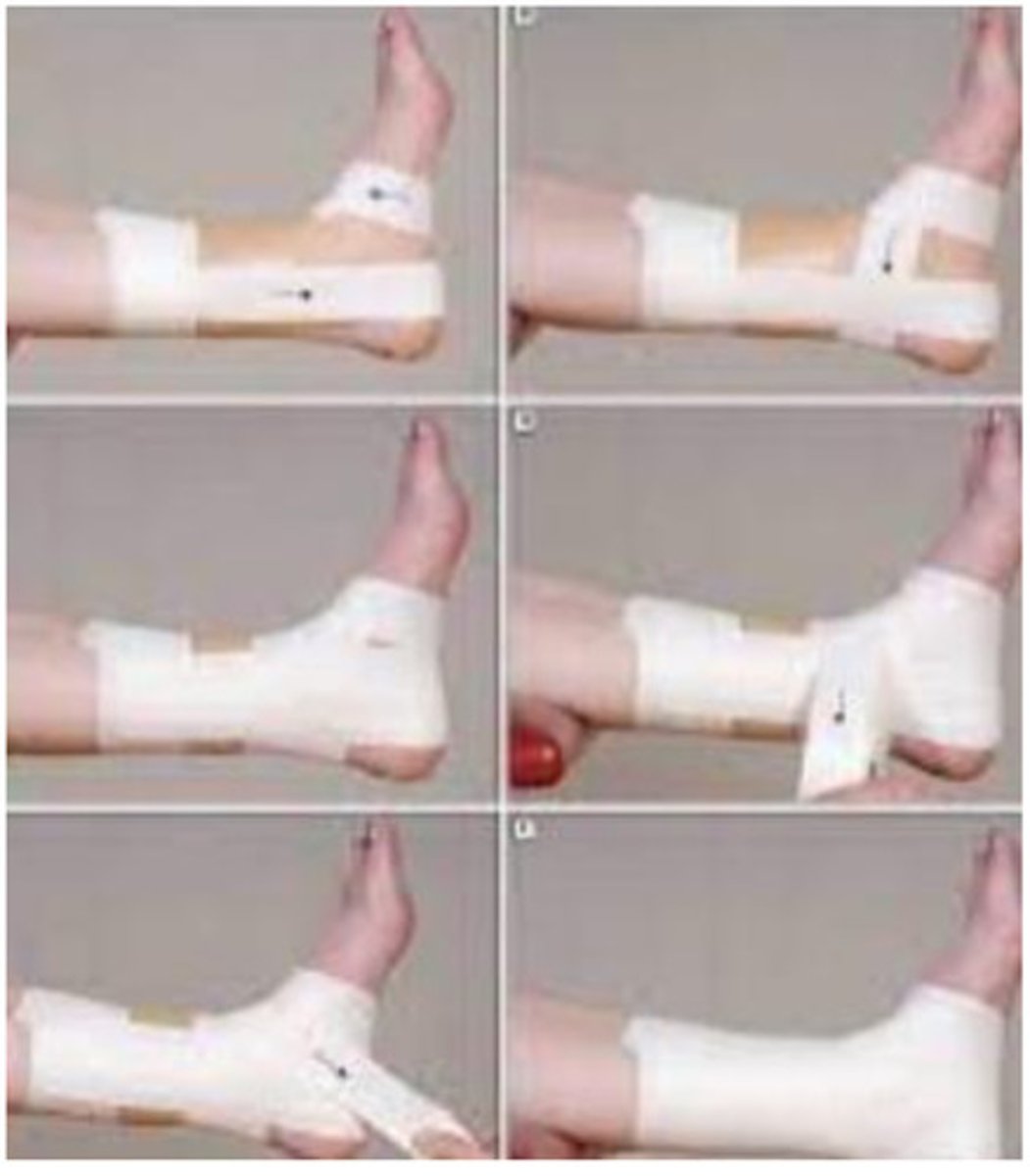
Achilles Tendon
Goal: restrict the amount of dorsiflexion at the ankle.
Elastic wrapping techniques
helpful for applying compression and support to an area, best for musculoskeletal sprains and strains, come in different sizes based on area
Open basket weave
Goal: prevent swelling in acute ankle sprains, not to be used during activity.
NOCSAE
National operating committee on standards for athletic equipment. Football, baseball, softball helmets.
CSA
Canadian Standards Association. Eye guards and ice hockey helmets.
achilles tendon rupture
• complete rupture of achilles tendon (commonly at 2-3 inc from calcaneus)
• Achilles tendon is the thickets tendon in the body
• sx: feeling of getting shot of kicked in the back of the leg, hearing a pop, pain unable to walk, swelling, deformity
• TX: splint, ice, crutches, refer to physician, surgical repair 4-6 month recovery
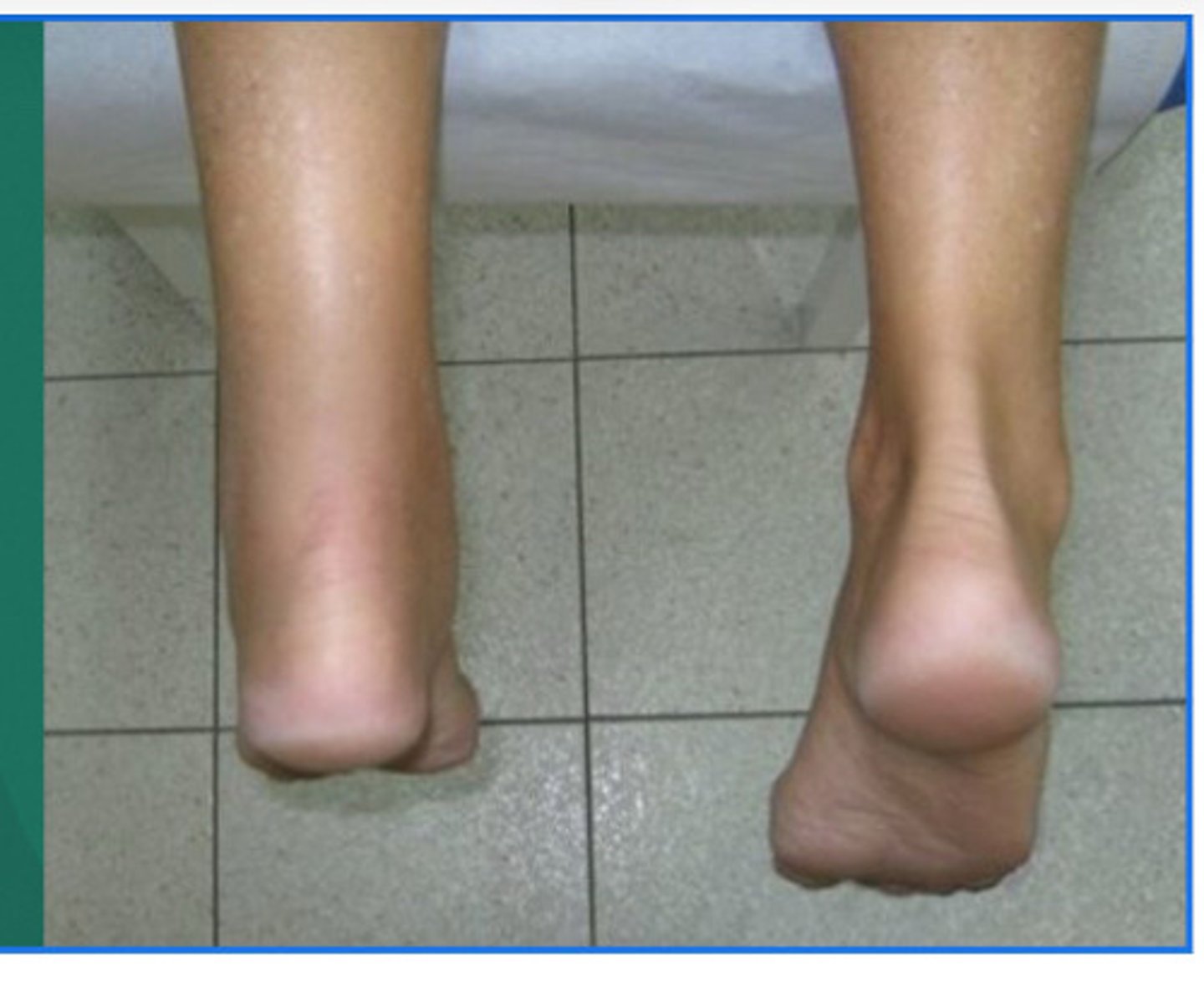
MOI for Achilles tendon rupture
Forced dorsiflexion, direct blow to the tendon, forceful contraction of the Gastroc, older population.
Great Toe Sprain (Turf toe)
Helps kick a ball, push off phase balance.
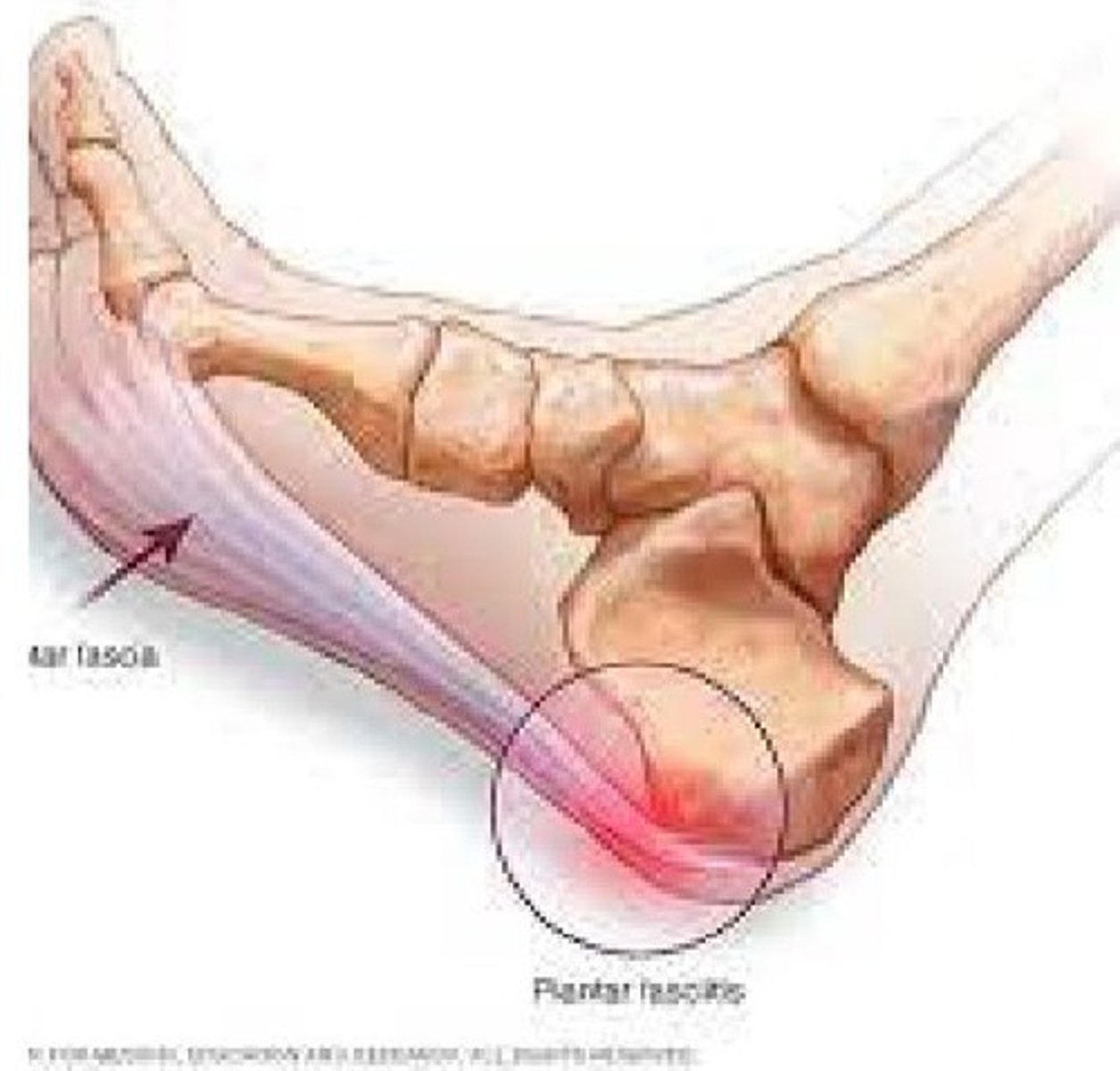
Plantar Fasciitis
Tough layer on the bottom of the foot becomes inflamed.
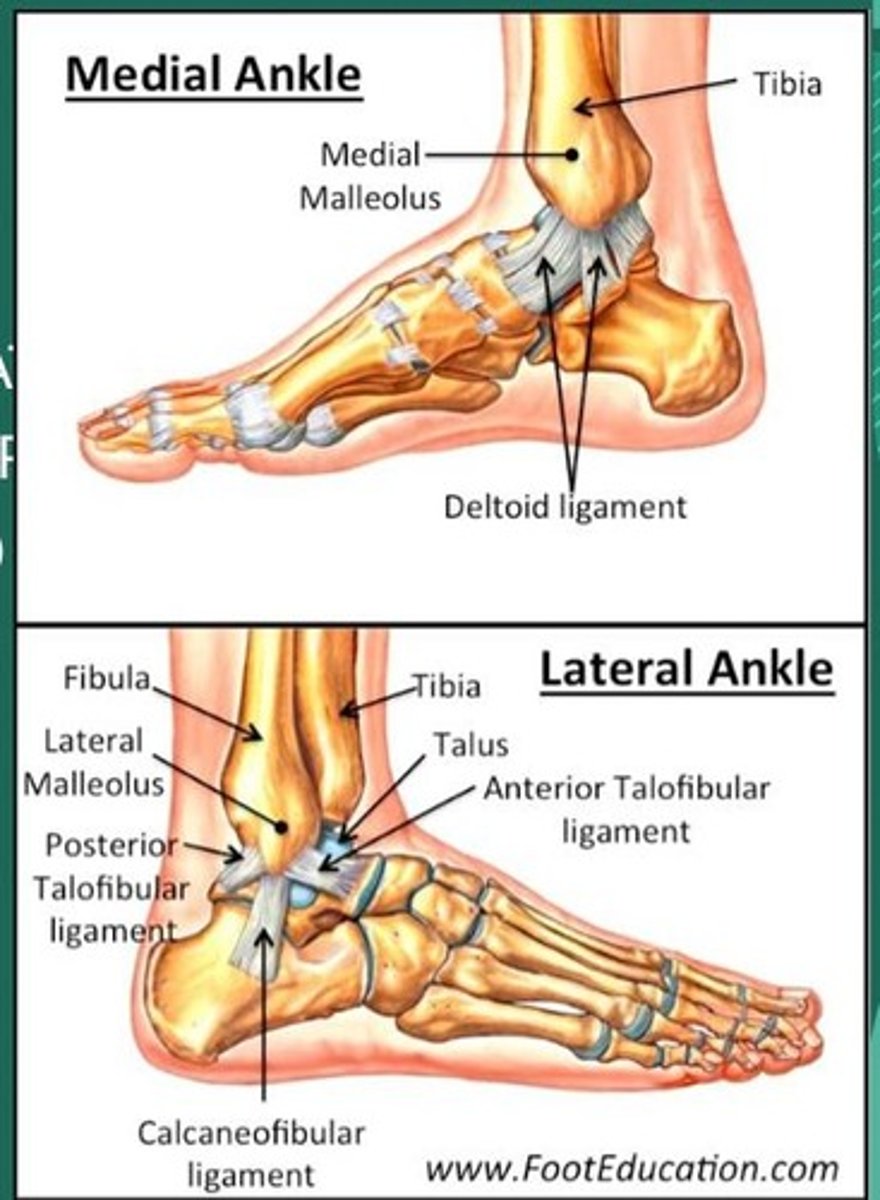
Lateral and medial ankle sprains
85% of ankle sprains are caused by excessive inversion, others are caused by excessive eversion.
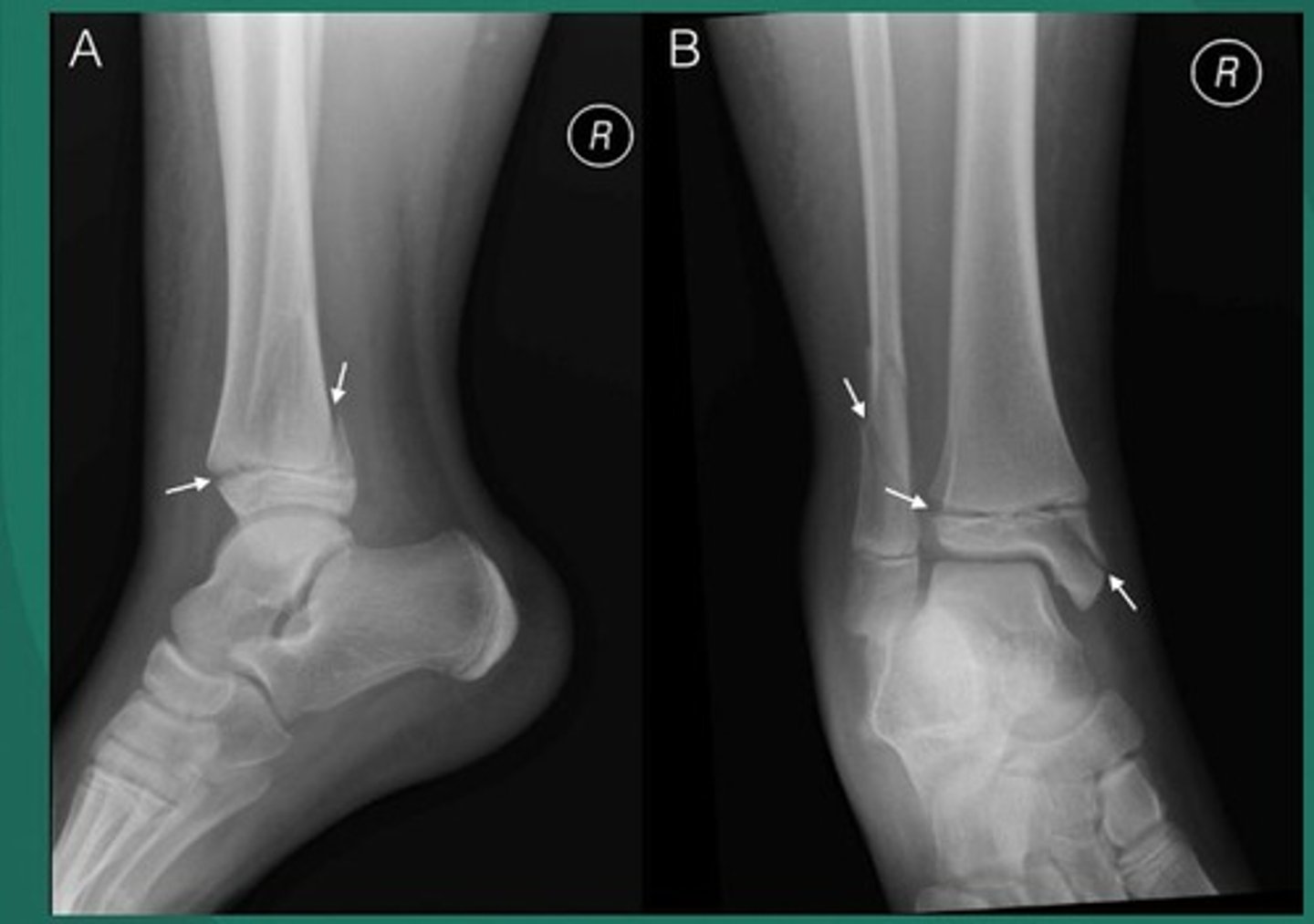
Syndesmosis sprain
High ankle sprain.
Toe abnormalities
Hammertoes, Hallux valgus (bunion), Ingrown toenail.
Anterior compartment syndrome
Muscles of the anterior aspect of the tibia are compressed by swelling.
Types of fractures
Jones fracture, epiphyseal fracture, stress fracture.
Medial tibial stress syndrome
Overuse/chronic injury, medial muscle fibers become torn and irritated.
Achilles tendinitis
Overuse, repetitive movements causes Achilles tendon to break down and become inflamed.
Quad or hamstring strain
Groin strain
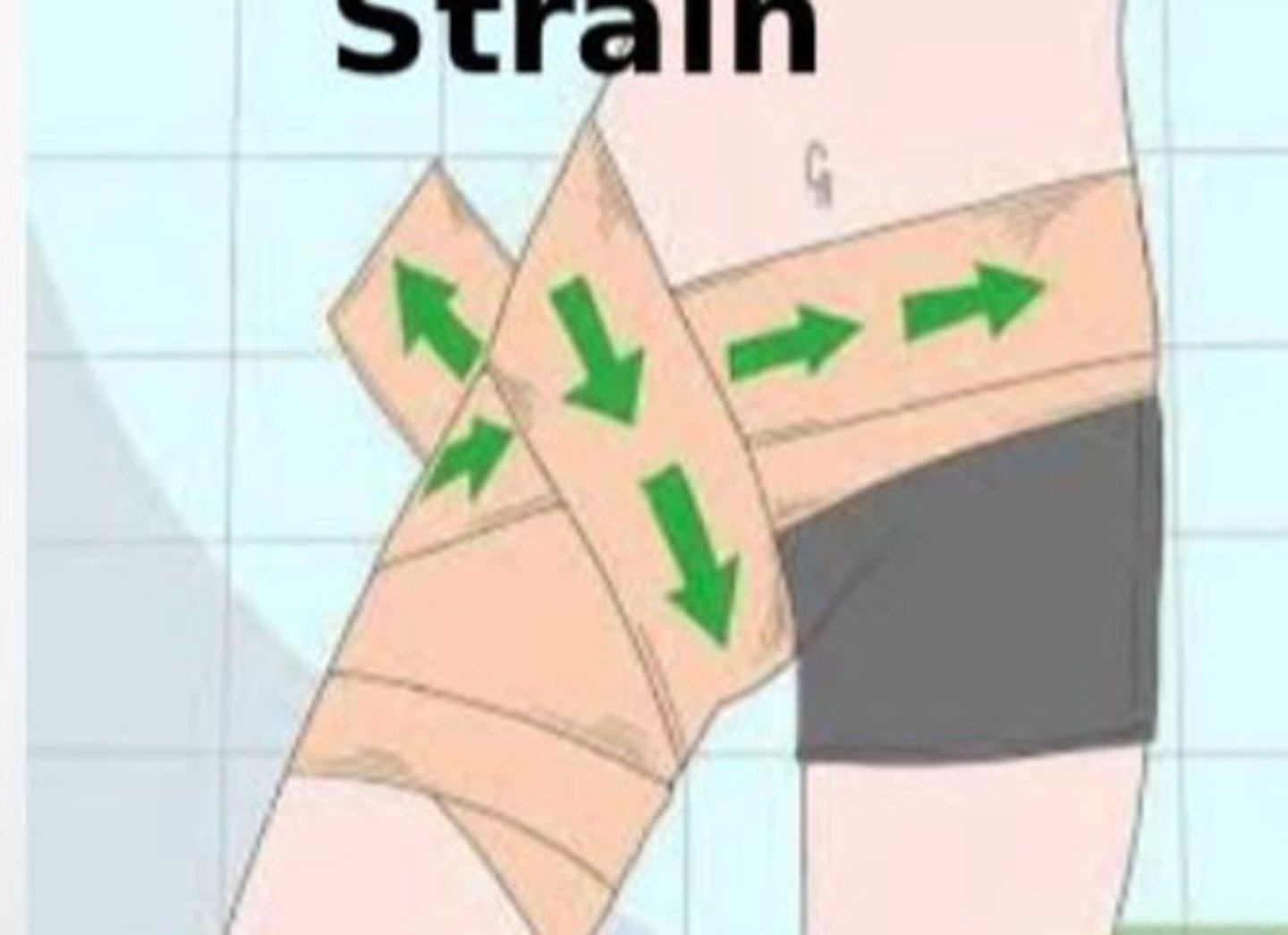
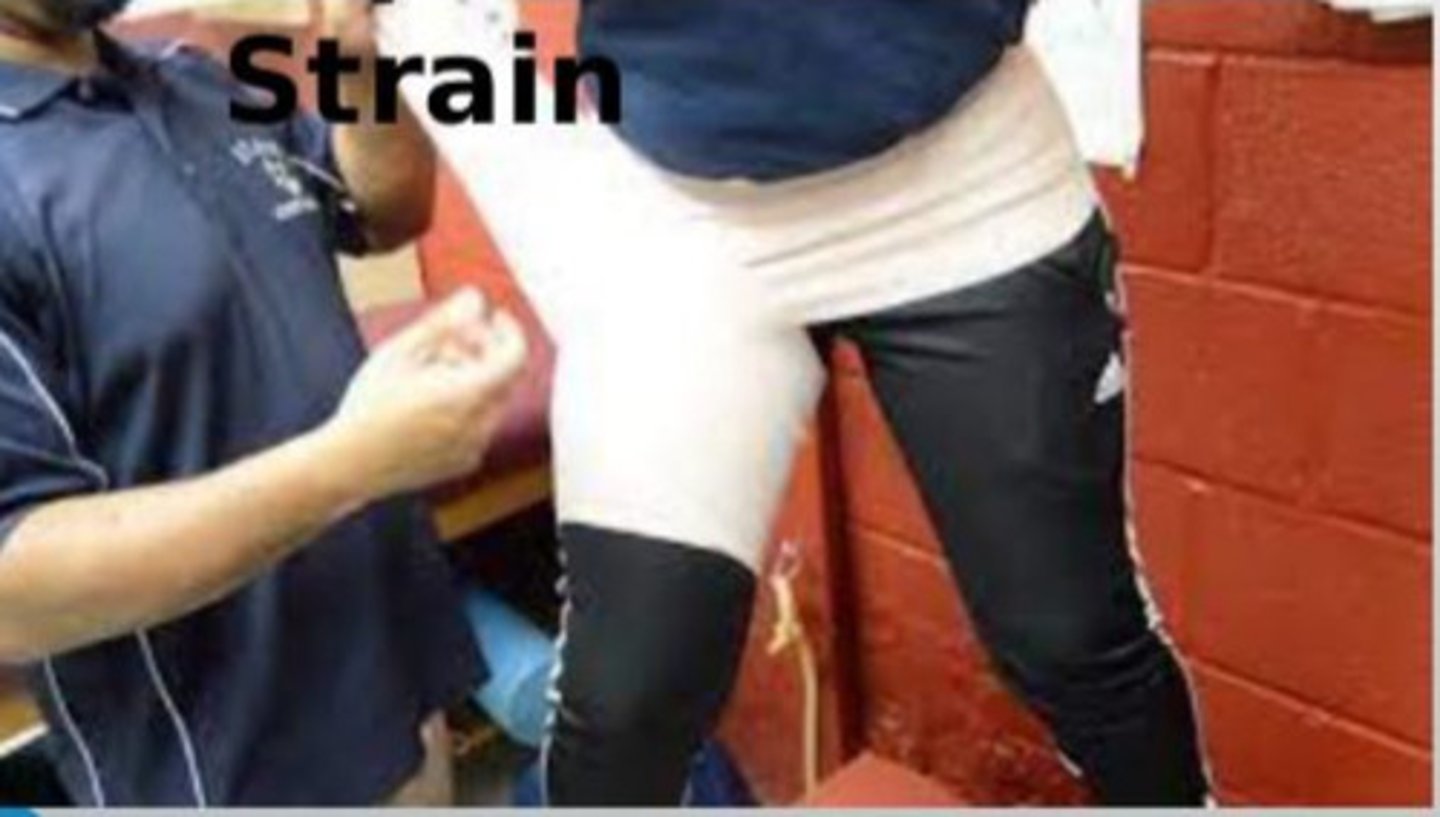
Hip flexor strain

Shoulder dislocation
