BIOL 117 Exam #3 (Stephanie Young)
1/194
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
195 Terms
epithelial tissue
forms a protective layer on the outside of the body and forms the lining of many organs
connective tissue
provides support for other tissue and can also help keep tissues together
muscle tissue
involved in movement
nervous tissue
communicates information via electrochemical signals from one part of the body to another
You bring a new pet fish home from the pet store and need to let it adjust to the new environment in the fish tank. You are allowing the fish to ______ to the new environment
acclimate
Adaptations are genotypic and long-term, while acclimations are phenotypic and short term.
True
Toucans are homeotherms. Based on this information ALONE, you could correctly predict that toucans…
keep a constant body temperature even though their environment temperature changes
If an animal can be described as both an endotherm and a homeotherm, then this animal…
can produce its own heat and keep a constant body pressure
The most direct ancestors of land plants were most likely
green algae
Which of the following characteristics are found in ALL land plants?
presence of nucleus in cells, participate in alternation of generations, cell wall made or cellulose, and spores
In plants, gametes are ____ and produced using ____
Haploid/mitosis
In plants, sporophytes produce _____ and grow from?
Spores / Gametes
Which of the following group of plants have sporophyte dominant life cycles?
gymnosperms, vascular seedless plants, and angiosperms
Which groups of land plants require water in order for sperm to fertilize the egg?
vascular and nonvascular seedless plants
Which set contains the most closely related terms?
Megasporangium, megaspore, egg, and ovule
Angiosperms are the most successful terrestrial plants. Which of the following features is unique to them and helps account for their success?
Fruits enclosing seeds
In which plant tissue does the majority of photosynthesis occur?
ground tissue
Which structure is correctly paired with its tissue system?
tracheid, vascular tissue
epidermis
gas exchange or absorption of water
phloem
transports sugar
collenchyma
provides structural support
xylem
transports water up a plant
Which of the following is derived from ground tissue system?
pith
zone of cellular division
cells of the apical meristem and primary meristem devide
zone of cellular elongation
cells increase their length, pushing the root downward
root cap
protect the apical meristem as the root lengthens and sense gravity
zone of cellular maturation
cells develop into the cells that make up the three tissue systems
Which of the following lists the portion of a mature 60 ft tree that contains the oldest tissues?
the trunk at soil level
Which statement best characterizes secondary growth in plants?
It results from cell divisions in the vascular and cork cambia.
Where are the youngest wood and the youngest bark in a tree trunk?
Youngest wood is toward the outside, near the vascular cambium; youngest bark is the inner part, next to the vascular cambium
The vascular cambium of a tree produces both secondary xylem and secondary phloem
True
Birds secrete uric acid as their nitrogenous waste because uric acid ____.
requires little water for nitrogenous waste disposal, this conserving water and reducing body mass
Ammonia is likely to be the primary nitrogenous waste in living conditions that include _____.
lots of freshwater flowing across the gills of a fish
Which group of animals most likely excretes the largest volume of urine relative to their body size?
freshwater fish
Which of the following statements is true regarding marine/saltwater fish?
The tend to lose water to their environment.
In our kidneys, blood is initially filtered through the
renal corpuscle
How does the osmolarity of kidney tissues change as you move from the cortex to the medulla?
It increases
this ascending limb
passive transport of salts
descending limb
passive transport of water
proximal tubule
reabsorbs electrolytes, nutrients, and water
Biologists recently have been able to produce mice that lack functioning genes for aquaporins. How does their urine compare to that od individuals with normal aquaporins?
higher volume and lower osmolarity
All animals rely on diffusion for the exchange of gasses with their various environments.
true
Consider the various structures animals have for exchanging gasses. In order to maximize the diffusion for gasses from one area to anther, you would want _______.
Large surface area, large difference in partial pressures between the two areas, and a thin barrier of diffusion
Organisms with which of the following respiratory organs use countercurrent exchange to maximize gas exchange?
Organisms with gills
Oxygen will diffuse form blood to tissues faster in response to which of the following conditions?
A decrease in the partial pressure of oxygen in the tissue
Which of the following is the destination for blood traveling through the pulmonary artery?
the lungs
Order the blood flow within a 4 chambered heart
Oxygen deficient blood flows from the right atrium to the right ventricle
Oxygen deficient blood flows through the pulmonary artery
Oxygen rich blood flows into the left atrium through the pulmonary vein
Oxygen rich blood passes an atroventricular valve
Oxygen rich blood moves through the left ventricle through the aorta
Why is cooperative binding important?
It makes hemoglobin sensitive to small changes in oxygen demand, or Po2 (partial pressures of oxygen) of tissues
The fetus developing inside a mother has hemoglobin with a higher affinity for oxygen that the mother
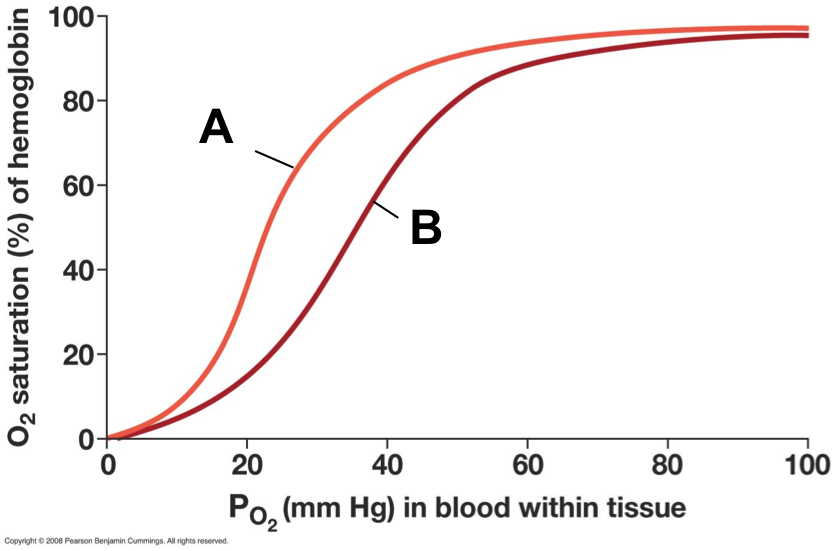
Which curve represents the fetus?
A
A mutation within a DNA sequence occurs. This mutation changes the amino acid that will later be translated. What is the least probably outcome of this mutation?
The change in the amino acid sequence will change the function of the protein for the better (advantageous mutation).
Which of the following is an example of how the morphological species concept might be used to classify organisms?
Two fossils from two extinct jungle cats are categorized as the same species based on the similar shape of the jawbone.
Primary endosymbiosis
nearly eukaryotic cell engulfs an early prokaryotic cell that had the ability to generate its own energy through either oxygen reduction or photosynthesis
Secondary Endosymbiosis
an early eukaryotic cell engulfs another early eukaryotic cell that had the ability to generate its own energy through photosynthesis
Heterokaryotic cells in fungi are considered to be diploid
false
Which of the following classification of animals can be described as radial symmetric animals with true tissues and specialized stinging cells known as nematocysts?
Cnidaria
Which of the following classification of animals most specifically describes an animal that is a bilateral protostome, is a coelomate, and has a body plan that consists of a head, thorax, abdomen, three pairs of legs and two pairs of wings?
Insecta
Which of the following classification of animals can be described as bilateral deuterostomes with true tissues and a coelom, but that lacks cephalization?
Echinodermata
pair rule genes
cells organized in to individual segments
effector genes
triggers apoptosis
master regulator genes
establishes anterior and posterior ends of a developing organism
homeotic genes
responsible for the correct placement of appendages/structures
according to Rick’s law, diffusion will increase when the surface area available for gas exchange decreases
False
Countercurrent exchange across the surface of gills results from an oxygen concentration gradient between the blood of the animal and the surrounding waters
true
Which of the following is a characteristic of cross current exchange?
oxygenated water and non-oxygenated blood flow in opposite directions across gill tissue in fish
Maximizes diffusion
Is utilized by aquatic organisms to obtain oxygen
Allows for a continuous concentration gradient to form
Capillaries
composed of thin endothelial cells that leak fluid
arteries
blood pressure is highest in these vessels
Veins
Utilize one-way valves to move blood back toward the heart
Arteries
move blood away from the heart
At the end of a capillary found closest to an arteriole, we would expect which of the following to be true of osmotic pressure in relation to one another?
High blood pressure and low osmotic pressure
Which is not a characteristic of osmoregulation in marine (salt-water) fish?
Lose bodily electrolytes through diffusion
Euryhaline animals cannot tolerate large fluctuations in the osmolarity of their environment
false
Considering the three types of nitrogenous wastes produced in animals, which of the following statements is true?
Uric acid is mostly insoluble in water
The majority of the water that is filtered from the blood in the kidney is regained by the body at the region of the look of hence is known as ____.
descending limb
The renal cortex of a human kidney has a higher salt content than the renal medulla.
False
The site of waste exchange between blood within capillaries and the kidney is the
renal corpuscle
Land plants are considered to be monoplyetic with a common ancestor in green algae
true
the characteristic of having the ability to photosynthesize would be found in land plants, but not in green algae
false
Saprophytes are diploid organisms
True
Gametes are created through ____.
Mitosis
gametophytes are plants that grow from ____ and produce ____.
Spores / Gametes
Non-vascular seedless plants
dominant gametophyte and dependent sporophyte
vascular seedless plants
dominant sporophyte and independent gametophyte
vascular seed plants
dominant sporophyte and dependent gametophyte
In the life cycle of an angiosperm, what is the male gametophyte?
the pollen grain
Which of the following [plant cells secrete the cuticle?
Epidermal cells
Meristems contain tissues that will later become fully functioning plant tissues. Which type of embryonic plant tissue will later become vascular tissue?
Procambium
What kind of tissue gives the appearance of growth rings in woody plants?
secondary xylem
loose connective tissue
functions as a type of padding for internal organswhic
which of the following types of muscle tissues are involuntary?
Cardiac and smooth
What type of connective tissue has a solid extracellular matrix that allows for stiff, yet flexible structural support?
cartilage
Which of the following is not a characteristic shared by all plants?
cells that contain cell walls made of chitin
The characteristic of having the ability to photosynthesize would be found in land plants, but not in green algae
false
Gametophytes are plants that grow from ___ and produce___.
spores / gametes
gametes are created through
mitosis
Sporophytes are diploid organisms
true
Animal cells that secrete more hormones have more what
rough er
cells that act in the immune response have more what
more lysosomes
flattened structures
folds of tissue increase surface area
projections (villi)
finger-like projections of surface
highly branched structures
very small tubules from one large tubule