exam 2 study materials
1/206
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
207 Terms
what is a heme? (ch5)
protein bound prosthetic group
where is heme found? (ch5)
many oxygen transporting proteins, as well as in cytochromes that participate in oxidation reduction
which variable reflects fractional occupancy on a binding graph? (ch5)
Y axis
which variable reflects ligand concentration on a binding graph? (ch5)
X axis
what does a hyperbolic binding curve indicate? (ch5)
saturation of binding sites
what does P + L ⇌ PL represent in protein ligand binding? (ch5)
a reversible binding interaction
what is the primary factor that determines where a ligand binds on a protein? (ch5)
shape complimentary of the binding site
the Bohr effect is best described as… (ch5)
oxygen binding increasing with pH
at which pH does hemoglobin release the most oxygen? (ch5)
7.2
what is the role of carbonic anhydrase in tissues? (ch5)
convert CO2 and water to bicarbonate and acid
the sigmoidal oxygen binding curve of hemoglobin is primarily due to… (ch5)
cooperative binding among subunits
hemoglobin is best suited for oxygen transport because… (ch5)
it transitions between high and low affinity states
myoglobin and the subunits of hemoglobin have… (ch5)
very similar tertiary structures, but different primary structures
an allosteric interaction between a ligand and a protein is one in which… (ch5)
binding of a molecule to a binding site affects binding properties of another site on the protein
which statement is not correct concerning 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate (BPG)? (ch5)
it increases the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen
the amino acid substitution of Val for Glu in hemoglobin S results in aggregation of the protein because of ___ interactions between molecules. (ch5)
hydrophobic
patients with chronic hypoxia (low O2 levels) due to decreased lung function may adapt by increasing their circulating BPG levels. predict which outcome will be true for such a patient. (ch5)
P50 for O2 will be increased
an individual molecular structure within an antigen to which an individual antibody binds is an… (ch5)
epitope
which generalization concerning motor proteins is correct? (ch5)
they convert chemical energy into kinetic energy
the energy that is released by the hydrolysis of ATP by actin is used for… (ch5)
actin filament assembly
the binding site of a protein is complementary to a specific ligand due to which characteristic of the binding site? (ch5)
its size, its shape, its charge, its hydrophobicity
which molecule binds most strongly to heme iron? (ch5)
CO
a significant contribution to the change in hemoglobin affinity for oxygen from pH 7.2 to pH 7.6 is due to a change in protonation state of which amino acid side chain? (ch5)
His
the binding of oxygen to hemoglobin stabilizes the ___ state of the protein due to interactions between ___ residues in the center of the multisubunit complex. (ch5)
R, His
sickle cell anemia is often lethal in childhood, yet the gene for sickle cell hemoglobin persists in the human population. which statement best describes why this is the case? (ch5)
individuals with sickle cell anemia trait are protected from malaria infection, while individuals with normal hemoglobin are not
small molecules attached to larger protein structures that elicit an immune response are referred to as… (ch5)
haptens
the fab regions of an antibody are made of which protein chain? (ch5)
both a light chain and a heavy chain containing variable and constant regions
myosin moves relative to actin filaments by using energy derived from the hydrolysis of what molecule? (ch5)
ATP
nerve impulses control muscle contractions by releasing which ion? (ch5)
Ca2+
individual contractile units in muscle fibers are called… (ch5)
sarcomeres
myosin obtains its high tensile strength due to its composition of… (ch5)
alpha helices supercoiled around each other in a left handed coiled coil
during muscle contraction, the ___ of myofibrils contract and the ___ move closer together due to the movement of myosin thick filaments along actin thin filaments. (ch5)
I bands, Z disks
what role do vitamins like B12 serve in enzyme function? (ch6)
coenzymes
enzyme names often reflect… (ch6)
the reaction they catalyze
what happens to the reaction rate when an enzyme is added? (ch6)
it increases the rate by lowering activation energy
which diagram part represents kinetics in a reaction energy graph? (ch6)
energy of activation
what is the correct sequence of enzyme catalysis? (ch6)
enzyme + substrate → product
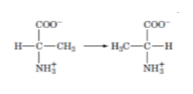
classify the enzymes catalyzing the following reactions according to the 6 classes: (ch6)
isomerase
a good transition state analog… (ch6)
binds to the enzyme more tightly than the substrate
which enzymes are not among the seven internationally accepted classes of enzymes? (ch6)
polymerases
for enzymes in which the slowest (rate-limiting) step is the reaction, ES →k2→ P, Km becomes equivalent to… (ch6)
the dissociation constant Kd for the ES complex
the steady state assumption, as applied to enzyme kinetics implies: (ch6)
the ES complex is formed and broken down at equivalent rates
the concept of induced fit refers to the fact that: (ch6)
substrate binding may induce a conformational change in the enzyme, which then brings catalytic groups into proper orientation
which of the following contains a new stereocenter upon cyclization of glucose? (ch7)
carbon 1
which carbon determines the D or L designation of a sugar? (ch7)
the last stereocenter furthest from the carbonyl
alpha and beta forms of glucose are called? (ch7)
anomers
what is a trios carbohydrate? (ch7)
a carbohydrate with 3 carbon atoms
what kind of projection is used to draw linear forms of sugars? (ch7)
fischer
which of the following is true of sucrose? (ch7)
it contains an acetal linkage
what term describes the sugar derived from animals that includes both alpha and beta D-glucose units? (ch7)
maltose
which component is required to form an acetal from a hemiacetal? (ch7)
another alcohol
what is formed when two monosaccharides form a disaccharide through glycosidic bonding? (ch7)
glycoside
which functional group forms when a hemiacetal reacts with an alcohol? (ch7)
acetal
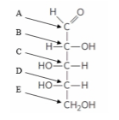
which arrow correctly identifies the atom that will become the anomeric carbon? (ch7)
A
in an ___, the carbonyl group is at the end of the carbon chain, but in an ___, the carbonyl can be at any other position. (ch7)
aldose, ketose
following complete hydrolysis of a sample of glycogen and a sample of cellulose, which is true? (ch7)
both samples consist of a mixture of alpha-D-glucose and beta-D-glucose
during which process are chemical bonds not broken? (ch7)
interconverting between two conformations
to posses optical activity, a compound must be: (ch7)
asymmetric
which pair is anomeric? (ch7)
alpha-D-glucopyranose and beta-D-glucopyranose
when forming a disaccharide maltose from two glucose monosaccharides: (ch7)
water is eliminated and a hemiacetal is converted to an acetal
which compound is not a reducing sugar? (ch7)
sucrose
which of these monosaccharides is not an aldose? (ch7)
fructose
when drawing a haworth perspective formula from a fischer projection, which statement is true regarding anomers? (ch7)
it is alpha if the hydroxyl group on the anomeric carbon is on the opposite side of the ring as the C-6
starch and glycogen are both polymers of? (ch7)
alpha-D-glucose
which is a heteropolysaccharide? (ch7)
glycosaminoglycan
which pair is epimeric? (ch7)
D-glucose and D-mannose
which monosaccharide is not a hexose? (ch7)
ribose
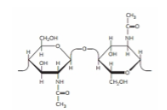
what is the correct linkage designation for the glycosidic bond between the two monosaccharide rings? (ch7)
(beta1-4)
when the linear form of a glucose cyclizes, the product is an… (ch7)
hemiacetal
the reference compound for naming D and L isomers of sugars is: (ch7)
glyceraldehyde
which pair is interconverted in the process of mutarotation? (ch7)
alpha-D-glucopyranose and beta-D-glucopyranose
when two carbohydrates are epimers… (ch7)
they differ only in the configuration around one carbon atom
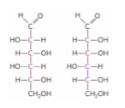
these two monosaccharides can be best described as… (ch7)
epimers
D-glucose is called a reducing sugar because it undergoes an oxidation-reduction reaction at the anomeric carbon. one of the products of this reaction is… (ch7)
D-gluconate
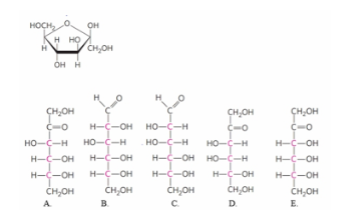
based on the form of the cyclic sugar in a haworth projection, which fischer projection formula could have formed this structure? (ch7)
A
which statement about starch and glycogen is false? (ch7)
both serve primarily as structural elements in cell walls
from the abbreviated name of the compound Gal(beta1-4)Glc, we know that… (ch7)
C-4 of glucose is joined to C-1 of galactose by a glycosidic bond
which of the following is involved in DNA sequencing? (ch8)
complementary base pairing
what makes GC bonds stronger than AT bonds? (ch8)
triple hydrogen bonds
which base pair is not found in DNA? (ch8)
uracil
what is the total height of one complete turn of B-DNA? (ch8)
36A
which technique relies on the principle of nucleotide complementarity? (ch8)
PCR
large Ka means
strong binding
small Kb means
strong binding
for the Hill equation, n = 1 means
no cooperativity
for the Hill equation, n > 1 means
positive cooperativity
for the Hill equation, n < 1 means
negative cooperativity
low pH in the tissues means O2 is released, what state is it in?
T state
high pH in the lungs means O2 is binding, what state is it in?
R state
O2 is released in the
T state
O2 is binding in the
R state
if Keq > 1 then
more products than reactants
Keq < 1 then
less products more reactants
in Michaelis-menten, what influences the rate
the substrate
the michaelis-menten equation is
V0=Vmax[s]/Km+[s]
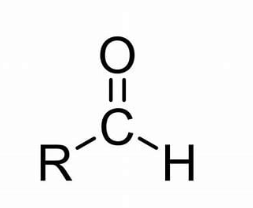
this is an
aldehyde
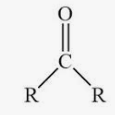
this is a
ketone
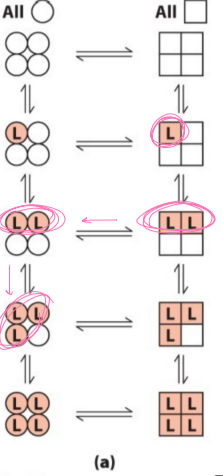
in the concerted enzyme theory diagram…
once a ligand binds, all are changed, all or nothing
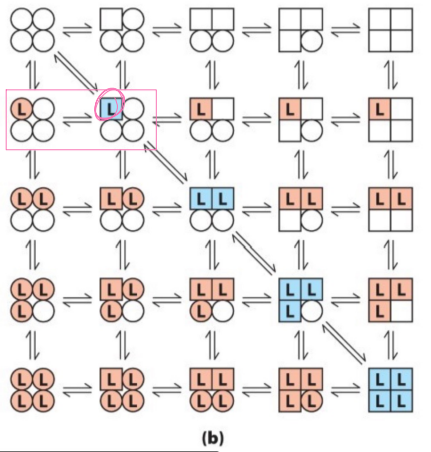
in the sequential enzyme theory diagram…
only affects conformation of the bound ligand, one at a time, based on individual subunit and how it changes
in hemoglobin, which ‘sections’ (alpa 1, beta 2 etc) interact the most?
alpha 1 and beta 1 interact more strongly with each other