3.3.1 - revenue
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
define total revenue (TR)
the total value of all sales that a firm incurs
formula for total revenue (TR)
TR = price x quantity
define average revenue (AR)
overall revenue per unit
average revenue (AR) formula
AR = TR/Q
define marginal revenue (MR)
the extra revenue recieved from the sale of an additional unit of output
marginal revenue (MR) formula
MR = change in TR / change in Q
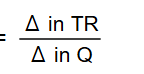
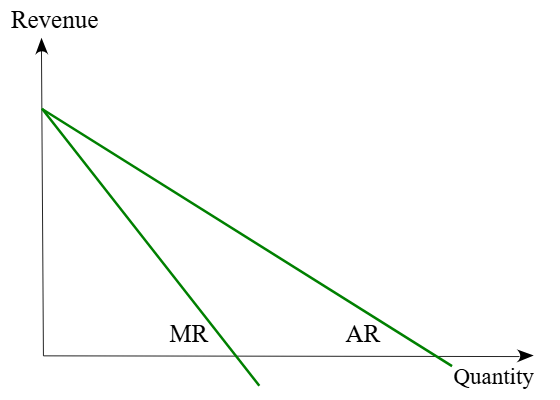
what happens if you want to increase quantity sold
you have to decrease the price for EVERYONE (including the ppl who bought it for higher when your quantity was smaller)
that’s why MR is twice as steep as AR
what is the AR curve
same as price (TR/Q), therefore the same as the demand curve
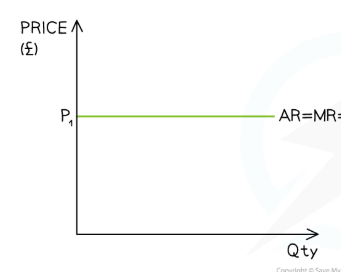
in perfect competition, what do the AR and MR curves look like
all perfectly inelastic
the firm is a price taker
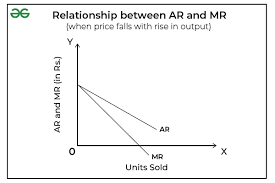
what do the AR and MR curves look like in imperfect competition
downwards sloping
the firm is a price maker
what happens when MR = 0 (to TR, and to PED)
TR is maximised
PED is unitary