Lecture 5- monetary policy and the Phillips curve
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Diagram showing structure of the Short-run- Model
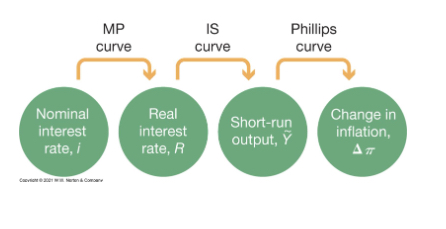
Who sets the bank rate and what is it
The bank of England sets the Bank rate
And it is a nominal intrest rate that BoE charges banks to borrow funds
What must match the central bank lendinf rate
Commercial banks borrowing from each other daily at the overnight rate
cannot charge a higher rate
Everyone would use the central bank
Banks cannot charge a lower rate
Everyone would borrow at the lower rate and lend back to the central bank at a a higher rate(arbitrage)
The lender would run out of resource quickly
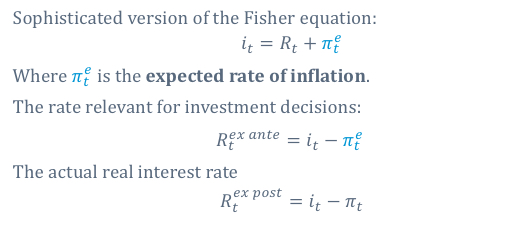
What is the fisher equation

What are the sticky equation assumptions

What does sticky inflation allow central banks to do

What is the sophisticated version of the fisher equation
What is the MP and the IS curve

Show the MP curve in the IS-MP diagram
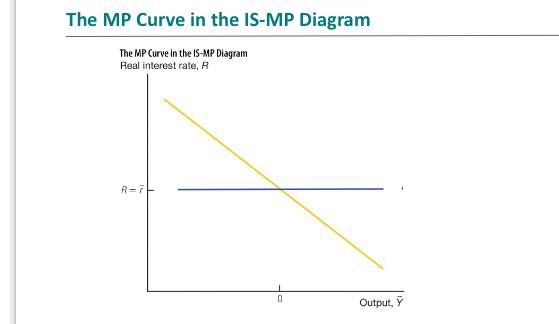
When is the economy at its potential

What happens if the central bank raises the interest rate

What happens if the intrest rate is raised in the IS/MP diagram
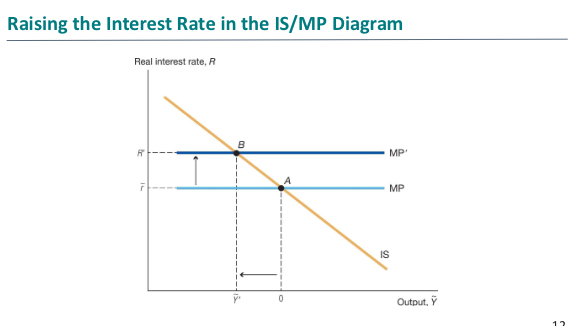
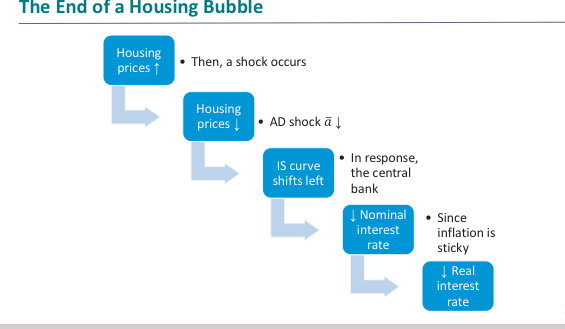
Diagram showing the ends of a housing bubble
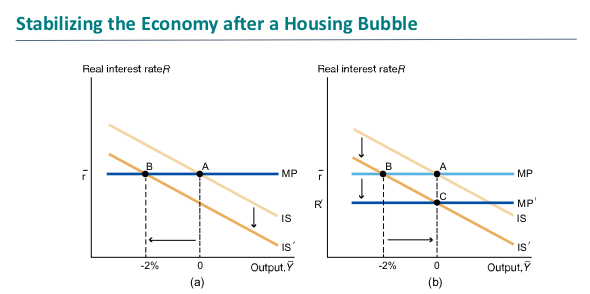
Graph showing the economy after a housing bubble
For economic actors what are the most important rates
central banks controls the overnight interest rate
Most important is the market intrest rates
Why is the market intrest rate different
-cost of commercial banks
-default risk
Duration of loans varies from 1 to 30 years
Example question
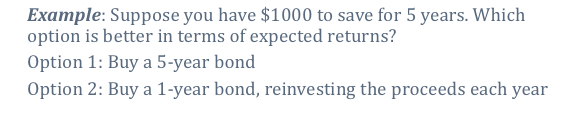
Answer words
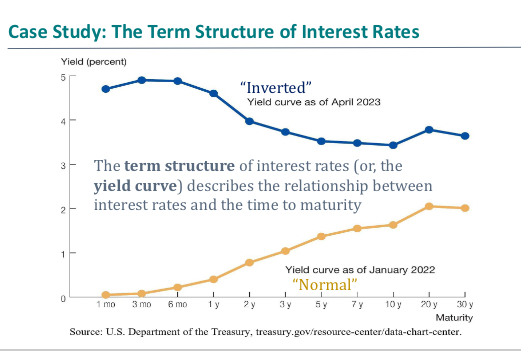
Annualised intrest rates on investments of differential lengths should yeild the same returns
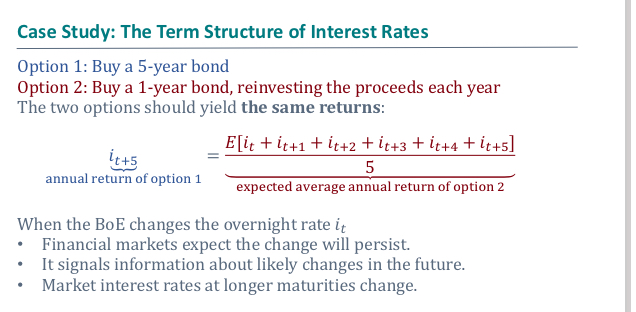
What is the term structure of interest rates and graph
What is the inflation rate
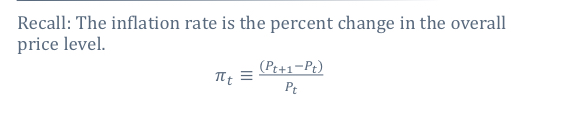
What do firms set their prices based on

What is the Phillips curve equation with expected inflation and demand conditions
Then assuming adaptive expectations
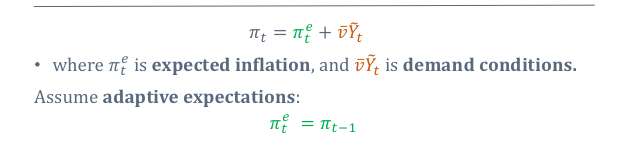
What do firms do according to this
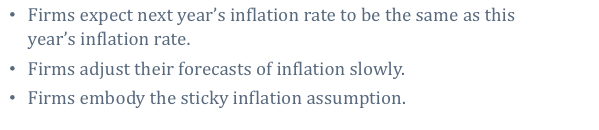
Using this equation define change in inflation and therefore express the Philips curve as
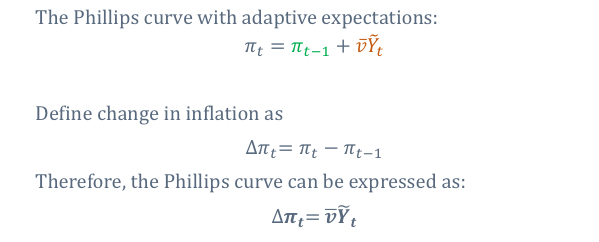
What is the Philips curve equation graph
What does the Philips curve equation look like when you add shocks o dash to the Philips curve
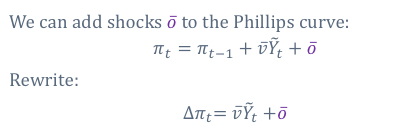
What does inflation depend on
Expectations of inflation
Demand conditions
Shocks to inflation
What is the effect of a change in the Phillips curve After an oil price shock
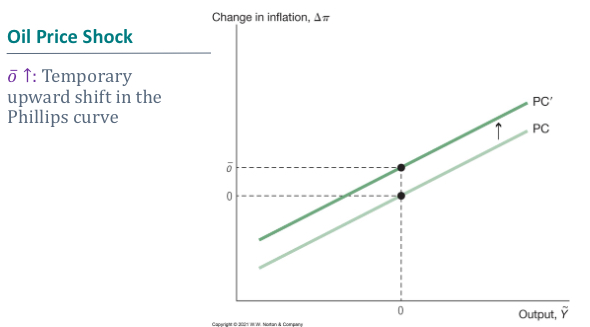
What is cost push inflation driven by

What is demand push inflation driven by
Changes in short-run output
Due to shocks to aggregate demand( C,I,G,EX-IM)
Recap table
Quantity theory of money equation
Short run model
Mp curve
Iscurve
Phillips curve
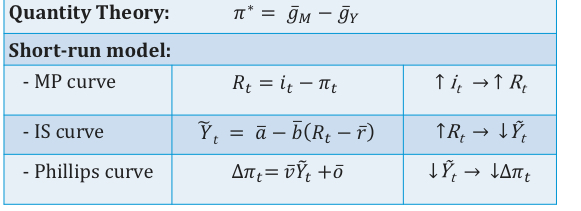

Which is correct

History of inflation in the US table
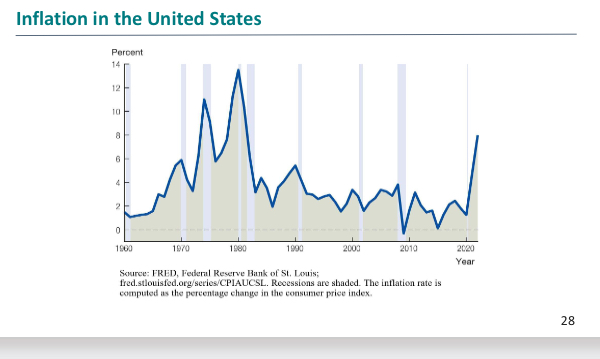
What does reducing the evil of inflation in the long run require and why
Tight monetary policy

Is curve showing tightening monetary policy
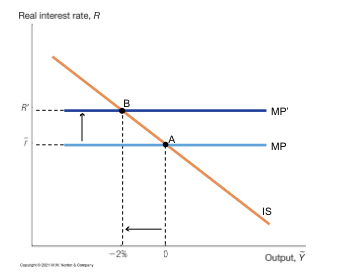
Phillips curve showing a recession and falling inflation
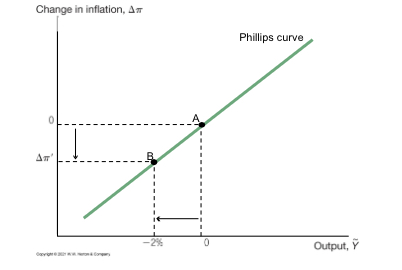
Overall what is volcker disinflation

Real intrest output and inflation rate graph showing disinflation over time
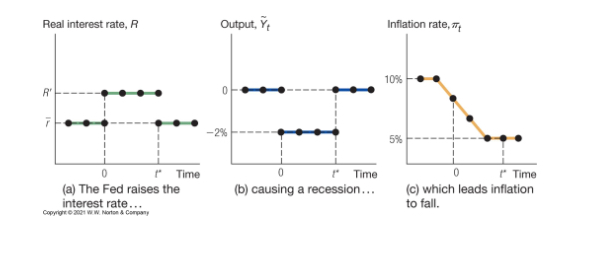
What was the great inflation of the 1970s and what was the three reasons

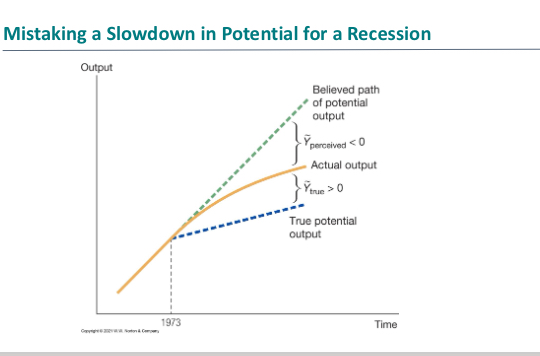
Graph showing mistaking a slowdown in potential for a recession
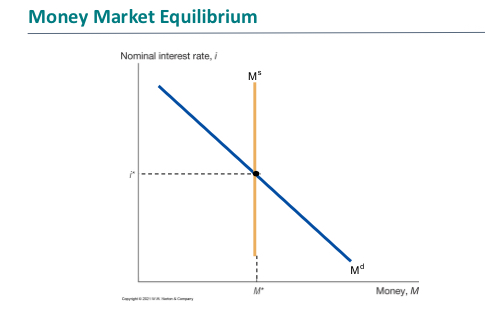
What is the money supply controlled by
Controlled by the central bank
vertical line at the desired level of money supply
What is money demand
Households can either hold money (cash) or buy bonds that pay a nominal intrest rate i
Money demand decreases in i
What is the nominal rate of money demand and what does the curve look like
Is the opportunity cost of holding money
Is downward sloping
What does the money market equilibrium look like
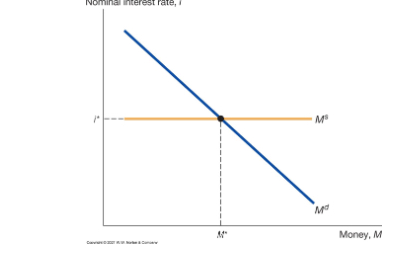
How does the central bank control the nominal interest rate
By supplying the money that is demanded at that rate
What does the central banks controls the money supply through
To increase the money supply
To decrease the money supply
Open-market operations

Why I t instead of Mt

Targeting the nominal intrest rates graph
What is the Philips curve with rational expectations equation
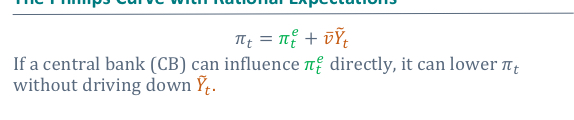
What is a soft landing one high inflation
