MYCVIR RETROVIRUSES (copy)
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
HIV-1
HIV-2
SIV-1
Lentiviruses (3)
Lentiviruses
Spumaviruses
Oncoviruses
3 groups of retroviruses
HIV-1
Lentivirus that infects humans
HIV-2
Lentivirus that infects humans and primates
Simian immunodeficiency virus-1 (SIV-1)
Lentivirus that infects monkeys
Spumavirus
primates and other animals
Oncoviruses
Human T-cell Lymphotropic virus I
Human T-cell Lymphotropic virus II
Lentus
Latin for “slow” (lengthy/insidious)
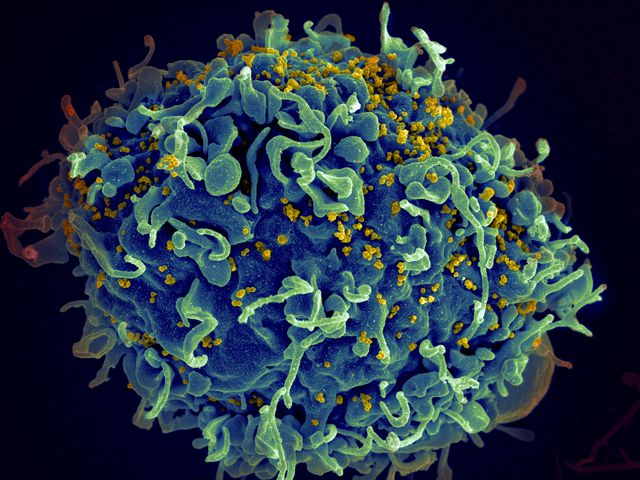
Spherical with a tree-like layered structure
Appearance of HIV-1
pol
env
gag
3 genes HIV-1 shares with other Retroviruses
Possession of control genes and repressor gene
Unique feature of HIV-1
Control genes
rev, tat, vif
What genes?
Repressor gene
nef
What gene?
gp120
gp41
env
p24
gag (3 polypeptides)
CD4 receptor (T-helper cells)
HIV-1 REPLICATION
Binds specifically to what receptor?
Fusion
HIV-1 REPLICATION
HIV-1 penetrates cell by?
Budding
HIV-1 REPLICATION
HIV-1 is released by?
1981
Year AIDS first came to notice
1950
HIV occured as early as what year?
Asymptomatic
Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-related complex (AIDS-related complex)
Full-blown AIDS
3 stages of HIV-1 which leads to AIDS
10-11 years
How many years does it take for asymptomatic stage to become full-blown AIDS?
p24
gp41
gp120
gp160
4 diagnostically important HIV antigens
Blood transfusion
Sexual intercourse
IV drugs
Perianal infection
4 MOT for HIV-1
Promiscuous homosexuals and bisexual men
Prostitutes
Intravenous drug users
Blood recipients
Hemophiliacs
Sexual contacts of these groups
Newborn children born to infected Mothers
Major risk groups of HIV-1
CD4
Monocytes
Macrophages
Regional lymph nodes
Cells of macrophage derivation in the brain
Target cells of HIV-1
Steady decline of CD4 positive T-cells
Immunologic marker for HIV-1
Candidiasis of the respiratory tree
Cryptococcal meningitis
Cryptosporidiosis with persistent diarrhea
Cytomegalovirus infection of organs other than liver, spleen, and lymph nodes
Persistent herpes simplex virus infection
Kaposi’s sarcoma or lymphoma of the brain under 60 years old
Lymphoid interstitial pneumonia and/or pulmonary lymphoid hyperplasia in children under 13 years
Mycobacterium avium, M.kansii or Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
Toxoplasmosis of the brain in patients over 1 month
Presence of any 2 of the following confers HIV-1 infection
ELISA
Most common assay for HIV-1
Immunofluorescence
Western Blotting
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
3 confirmatory tests for HIV-1
Antibody to gag protein
What antibody is detected in ELISA?
Virus Antigen Capture Tests
detect free viral p24 in blood
Lymphocyte cell lines
Isolation for HIV-1
Reverse transcriptase-PCR
– quantitate viral load
– monitor disease progression and response to therapy
– diagnose pediatric HIV-1 infection born to infected HIV-1 positive mothers (false (+) EIA and Western Blotting)
HIV-2
4th human retrovirus isolated from mildly immunosuppressed patients in West Africa
Human T-cell Lymphotropic Virus I (HTLV-I)
1st human retrovirus (Dr. Robert Gallo- US)
Adult T-cell Leukemia Lymphoma (ATLL)
presents as lymphoma of the skin, lymph nodes or both in adults
HAM-TSP
Long motor neurons of spinal cord
Tax protein
P53 tumor suppressor protein
Cell associated
MOT for HTLV-1
Human T-cell Lymphotropic Virus II (HTLV-II)
Isolated in Seattle, USA in patient with “hairy cell” leukemia
< 200 cells
Amount of CD4+ considered to be HIV
Protoonco genes
Genes responsible for proliferation genes
HTLV I and II activate these genes that’s why they’re oncogenic