Multi-store Model of Memory + STM + LTM
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Who propsed the Multi-store model
What process extends duration of the STM + tranfers it to LTM
2 types
What is the process of recalling info from the LTM
What happens
When is info transferred from SR to STM
Atkinson & Shiffrin (1968)
Rehearsal
- Maintainance Rehearsal
- Elaborative Rehearsal
Retrieval
Transferred to STM
When we pay attention to it
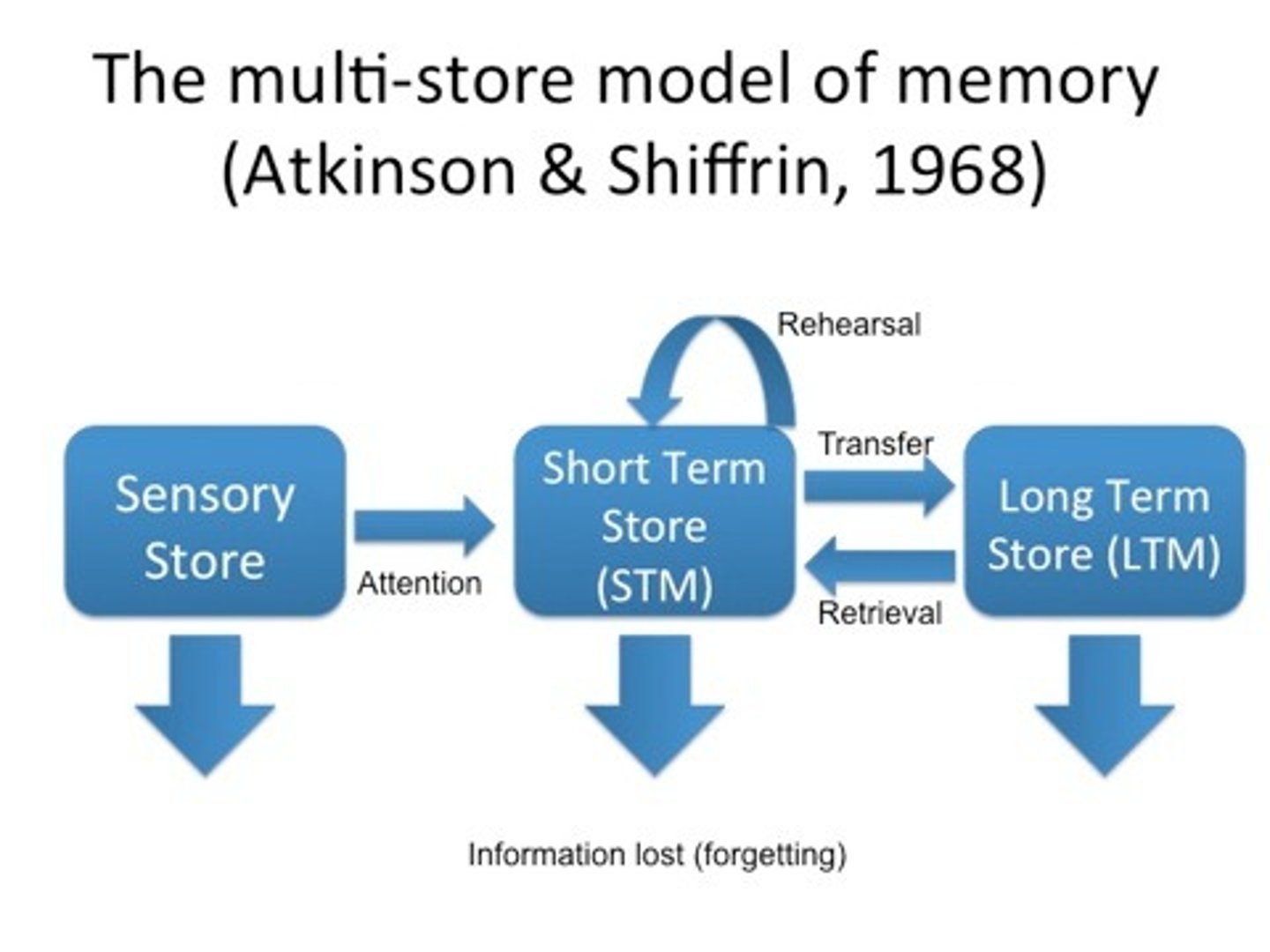
What are the 3 key features of memory
Coding
Storage
Retrieval
3 types of coding
Visual
Acoustic
Semantic
What are the 3 stores of memory
Sensory register
Short-term memory
Long-term memory
What info is held in the sensory register
How much stores does it have
When does the info pass into the STM
Capacity
Duration
All stimuli from environment passes into or is held in it
5 stores, 1 for each sense
Information only passes into STM if paid attention to
Very high capacity
Info is held for a Split Second
How is info coded in the sensory register
What are the 5 stores in the SR
Depending on the sense involved eg Iconic memory for visual information
Haptic memory - Touch
Echoic memory - Audio
Iconic memory - Visual
Olfactory memory - Smell
Gustatory memory - Taste
Scientific criteria strength of MSM
- Meets scientific criteria
- Has been developed using the scientific process of theory construction
- Predictions of the model have been tested by gathering empirical evidence
- For example Baddeleys recall study which supported the idea of separate memory stores of STM and LTM
- Therefore having scientific credibility led to increased research in this area in the past, leading to our modern understanding of memory systems
Contradictory research on the Multi-store model
What did they find
How does this contradict the MSMs idea that rehearsal is the only way to get info from the STM to LTM
Craik and Tulving (1975)
- 3 groups Participants were read out 60 words
- 1 group was made to process the words Visually by focusing on the appearance ,
- 1 group made to process the word Acoustically by focusing on the sound of the word
- 1 group made to process the word Semantically by focusing on the meaning
- Participants were then asked to free recall as much as they could remember
Found:
Group who processed the word Semantically had Best recall
Group who processed word Visually had Worst recall
Shows that attaching meaning to something helps move info from STM to LTM
Reduces Reliabilty of the MSM
What is coding
How the memory is stored
When does info from the SR to the STM
When payed attention to
How is LTM memory coded
How is info in the LTM recalled
Capacity
Duration
Who researched this
Mainly semantically (based on meaning)
Retrieval
Info from LTM is accessed and transferred to the STM
Unlimited
Up to a life time
Bahrick (1974)
How is info in the STM mainly coded
Who researched this
Mainly Acoustically
Baddeley (1966)
How long is info stored in the STM
Capacity
How can the capacity be increased
How is it mainly coded
Around 18 seconds
Limited to 5+/-2 (Jacobs)
"Chunking" - grouping pieces of info
Mainly Acoustically
Who conducted research into the duration of STM?
Peterson & Peterson (1959)
Read nonsense trigrams to participants and got them to recall after different amounts of time had passed
Found 5% were able to recall after 18 seconds
Suggests capaicty is 20 - 30 seconds
What study found the capacity of the STM?
What was found
Jacobs (1887)
Administered a digit span test to participants
Participants always remembered between 5 and 9 for letters and numbers
When does information for STM pass to the LTM
Two types of rehearsal
When it is rehearsed
Maintenance rehearsal - Repeating info
Elaborative rehearsal - Connecting new info to existing info
How can the capacity of the STM be assessed
How does it assess capacity
Digit Span test
Jacobs (1887)
Amount of digits recalled by an individual is their digit span
What research was conducted on Coding of the STM and LTM
Baddeley (1966)
Tested the recall of 4 groups of participants different lists of words
Found that similar sounding (acoustic) words get mixed up when using the STM
Similar meaning words get mixed up when using the LTM
Shows a distinction in how info is coded in each store
Who established how memory in the STM is coded
Conrad (1964)
Asked participants to recall a sequence of letters
Found participants were more likely to similar sounding letters than similar looking letters
Suggests the STM is coded mainly Acoustically
Who made suggestions on how the capacity of the STM can be increased
What did he find
Miller (1956)
Reveiwed research into the STM
Noticed people recall 5 words as easy as 5 letters
Meaning the STM can store 5+/-2 chunks of info, increasing its capacity
Research on the duration of the LTM
Bahrick (1975)
Obtained yearbook of 392 Americans aged 17-74
Tested participant recall by
1. Recall from photos of classmates
2. Free recall of names of classmates
- Found participants within 15 years of graduation were 90% accurate in photo recognition and 60% in free name recall
- Participants After 48 years of graduation were 70% accurate in photo recognition and 30% in name recall
Suggests LTM can last up to a lifetime
What research was conducted on the STMs Duration
What did they suggest the duration was
Peterson & Peterson (1959)
STM duration is between 20 and 30 seconds
Read nonsense trigrams to particpants
Prevented rehearsal by making them count in 3s backwards
Got them to recall after different periods of time
Found that 5% of participants recalled accurately after 5 seconds.
Suggests duration is between 20 and 30 seconds
Limitation of Conrad and Jacobs studies
- Task is artificial
- Tasks such as recalling a list of numbers has little relevance to everyday life.
- Real life tasks are more complex and include remembering many different types of information as well as dealing with all the extra stimuli from the environment that may be taken into the STM and distract us, taking up the limited space
- Therefore cannot be generalise these findings to real life short term memory tasks.
- This reduces the ecological validity of the research
Strength of Jacobs research into STM
- Easy to replicate
- Because they use standardised procedures and controlled conditions and collect objective and empirical data
- They can also be used to directly test hypothesis an theories such as the Multi store model and so meet the criteria for psychology as a science
- This leads to scientific credibility of the research in this area, leading to more research funding in this area
- Therefore allowing our knowledge to progress
Strength of Peterson and Petersons study
- Controlled lab experiment
- Allows extraneous variables to be minimised
- Allows for greater internal validity as the DV can be isolated and tested properly