Exam 2 Psychology IUB
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
What is the definition of personality?
Distinctive and enduring ways of thinking, feeling, and behaving, reflecting consistency across time and situations.
What are the three general goals in personality research?
1. Identification and description of major dimensions of personality. 2. Understanding underlying processes in trait variation. 3. Establishing how well traits predict behavior.
What are the two approaches to identifying basic personality dimensions?
1. Idiographic approach: focuses on traits that uniquely describe individuals. 2. Nomothetic approach: focuses on traits shared among individuals, measured on a continuum.
What is Gordon Allport's contribution to personality theory?
He focused on personality characteristics that make people unique, organizing traits into cardinal, central, and secondary traits.
What are cardinal traits?
Traits that have a pervasive influence on an individual's behavior; not everyone has a cardinal trait.
What are central traits?
Broad traits that influence behavior in many situations.
What are secondary traits?
Traits that influence behavior in very specific circumstances.
What is the psychometric approach in personality research?
Focuses on the measurement of traits using statistical methods, such as factor analysis, to identify trait dimensions.
What is factor analysis?
A statistical method used to investigate inter-correlations among ratings to identify clusters of variables that go together.
What are the three major trait dimensions in Eysenck's theory?
Extraversion, Neuroticism, and Psychoticism.

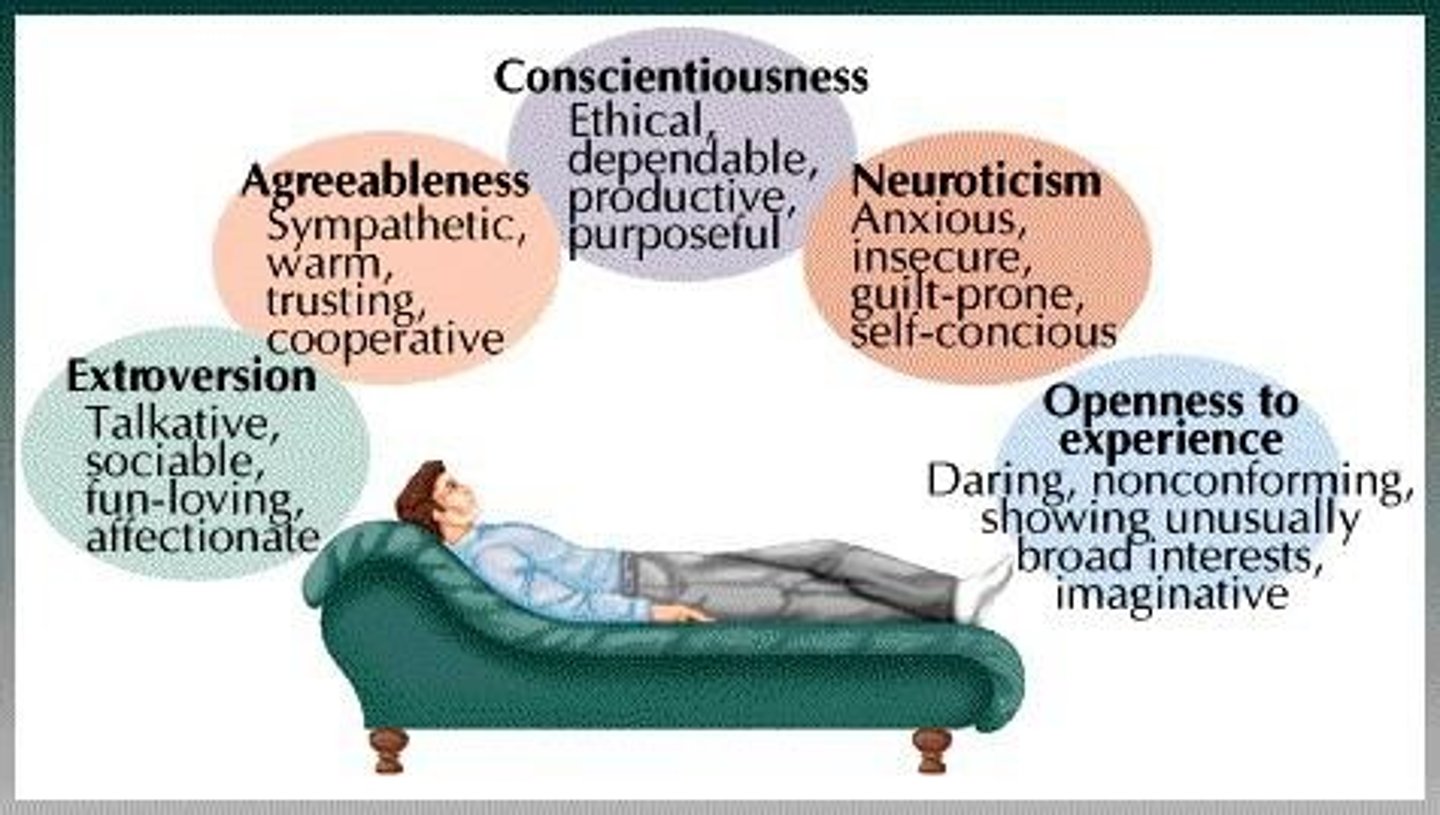
What does the Five Factor Model (Big 5) include?
1. Extraversion 2. Neuroticism 3. Conscientiousness 4. Agreeableness 5. Openness.
What is the significance of reliability and validity in personality measurement?
Reliability refers to the consistency of a measure, while validity assesses whether the model is scientifically tested and accurately reflects personality traits.
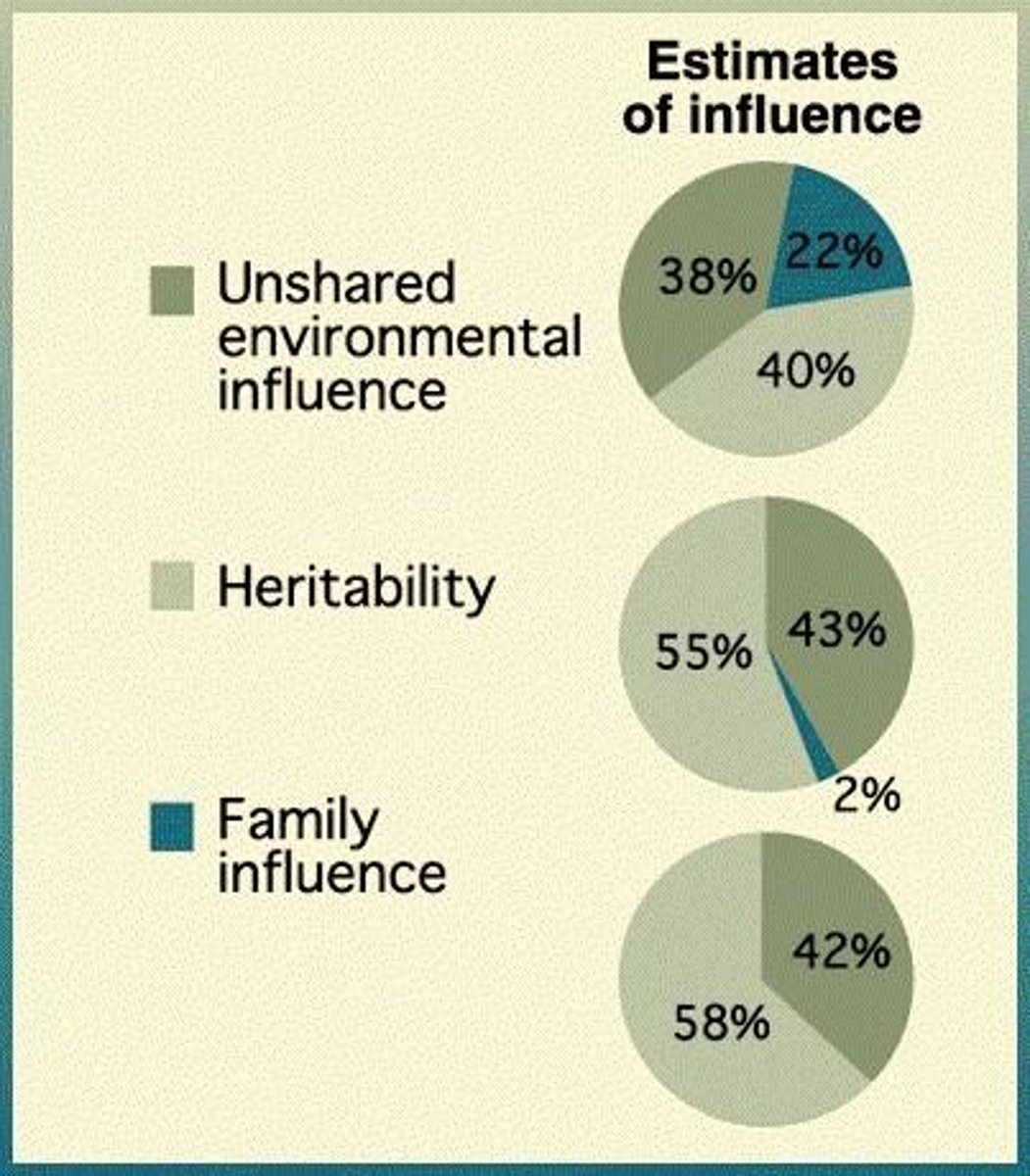
What is the heritability of most personality traits?
The heritability is estimated to be between 0.4 and 0.5, indicating 40-50% genetic influence.
What is the basic equation for personality in behavior genetics?
P = G + E, where P is phenotype, G is genetic influence, and E is environmental influence.
What is the difference between MZ and DZ twins in behavioral genetics?
MZ (monozygotic) twins are identical and share 100% of their genes, while DZ (dizygotic) twins are fraternal and share on average 50% of their genes.
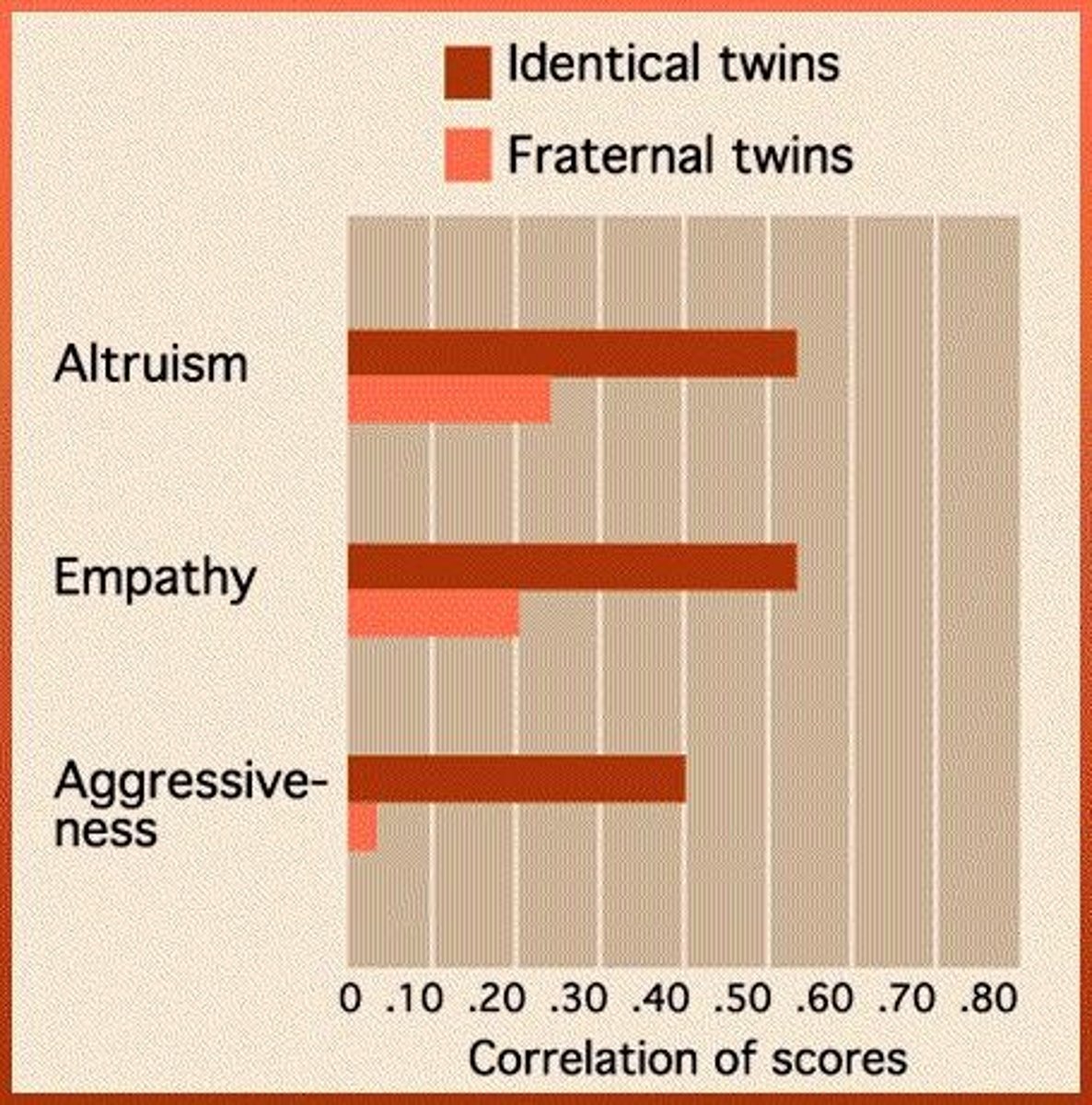
What are shared and non-shared environmental influences?
Shared environment (Es) makes siblings alike, while non-shared environment (En) makes siblings different.
What does the twin study design compare?
It compares the degree of similarity among MZ twins versus DZ twins to estimate genetic and environmental contributions to traits.
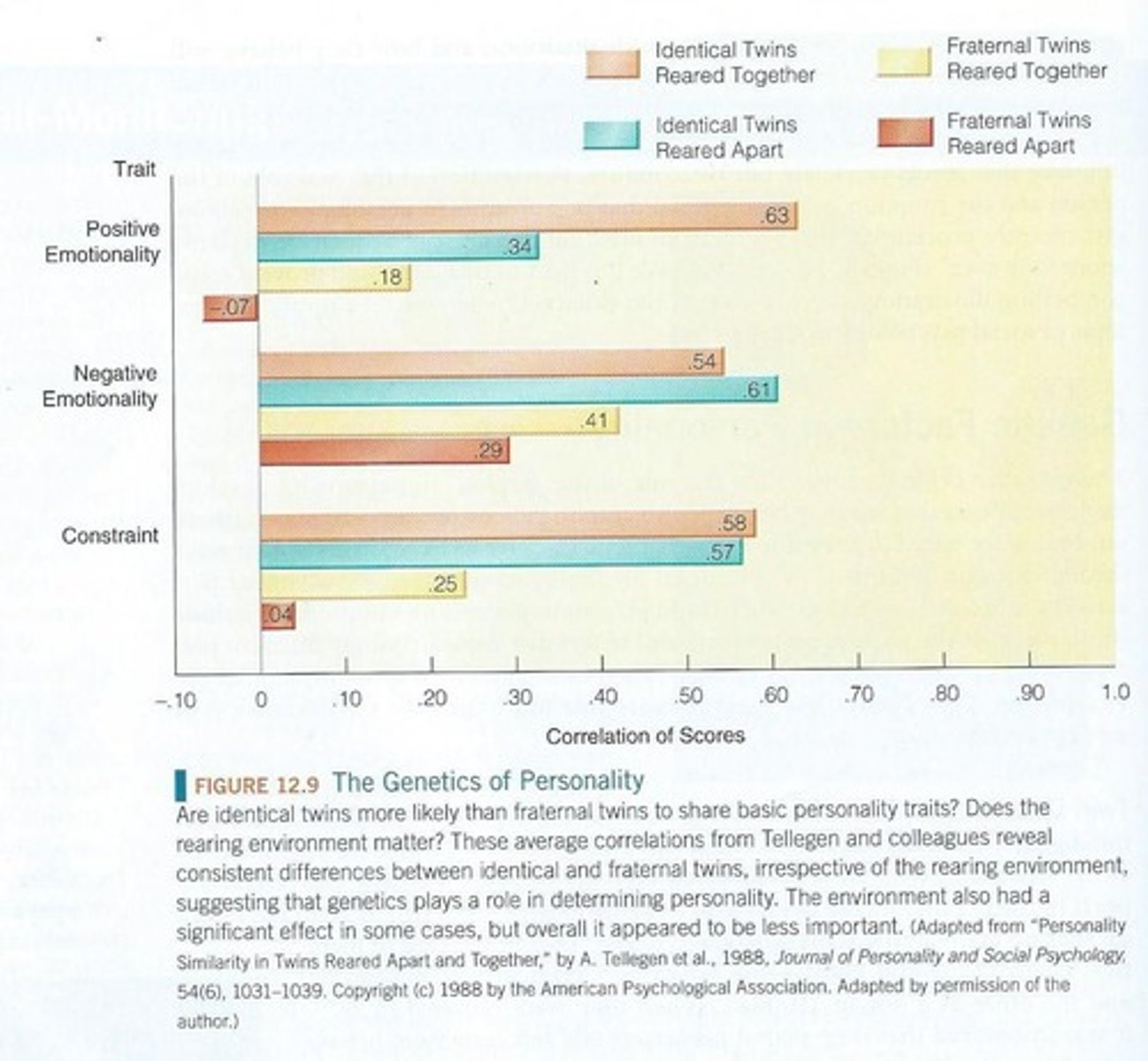
What is the correlation for MZ twins reared together for extraversion?
0.63.
What is the correlation for DZ twins reared together for neuroticism?
0.33.
What is the relationship between personality stability and age?
Personality stability increases after age 30, with declines in neuroticism and increases in conscientiousness observed from teens to 30.
What is positive emotionality in Tellegen's model?
A trait dimension reflecting a tendency towards positive feelings and experiences.
What is negative emotionality in Tellegen's model?
A trait dimension reflecting a tendency towards negative feelings and experiences.
What does constraint refer to in Tellegen's model?
A trait dimension that involves self-control and the ability to regulate impulses.
What are the five dimensions of the Five Factor Model (Big 5)?
Extraversion, Neuroticism, Conscientiousness, Agreeableness, Openness.
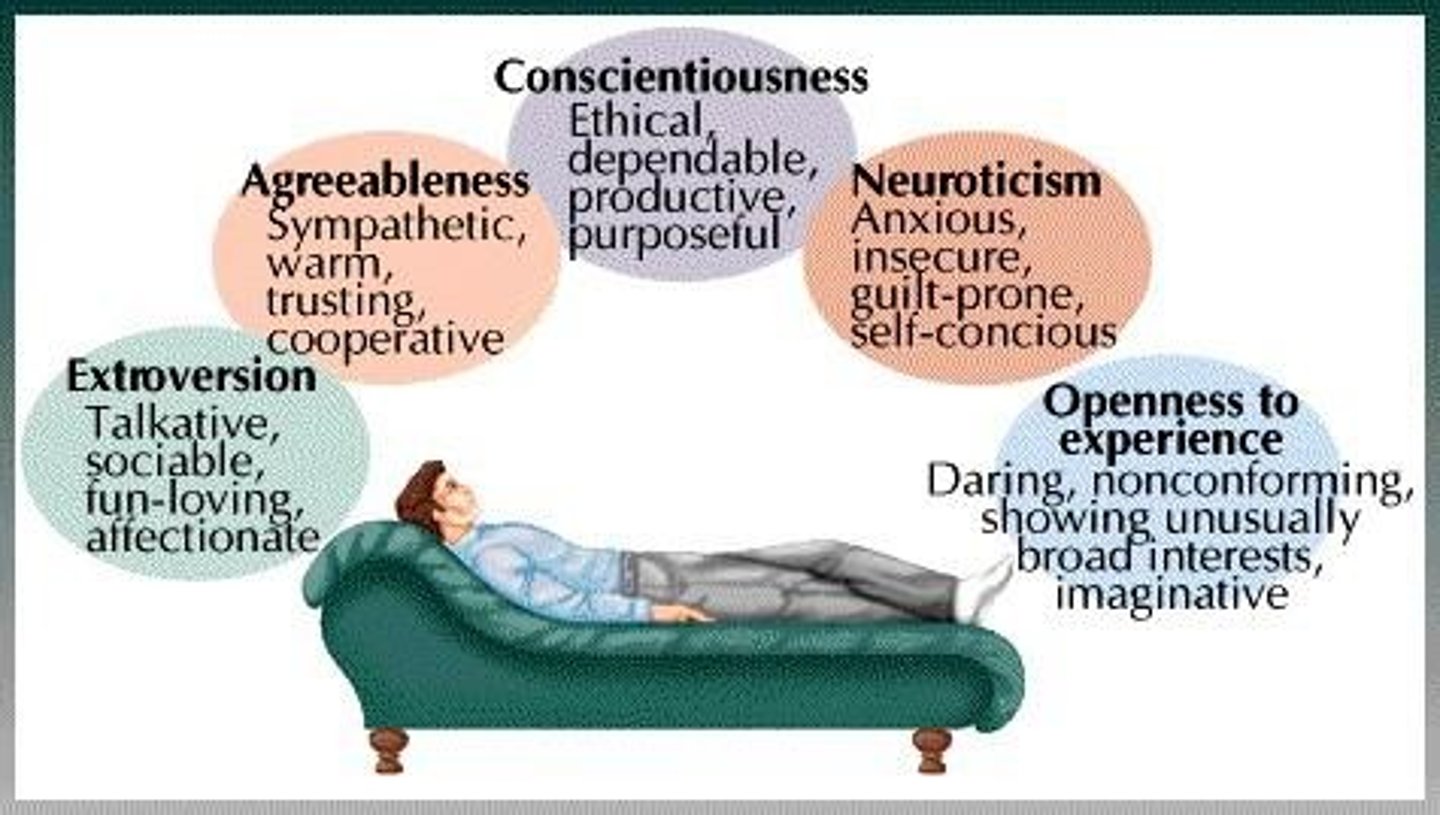
What is the super-trait associated with sociability and assertiveness?
Extraversion.
What physiological processes are linked to Extraversion?
Frontal lobe activity, Amygdala activity, Reticular Activating System, and higher Dopamine activity.
What cognitive process is characterized by a focus on immediate rewards?
Impulsivity.
What are the two types of processes in Carl Jung's theory?
Personal unconscious and collective unconscious.
What is the primary drive identified by Alfred Adler?
Striving for superiority.
What is the main motive according to Karen Horney?
The need for security.
What does Carl Rogers emphasize in his self-theory?
The conflict between one's real self and ideal self.
What are the two types of self-regard according to Carl Rogers?
Conditional positive regard and unconditional positive regard.
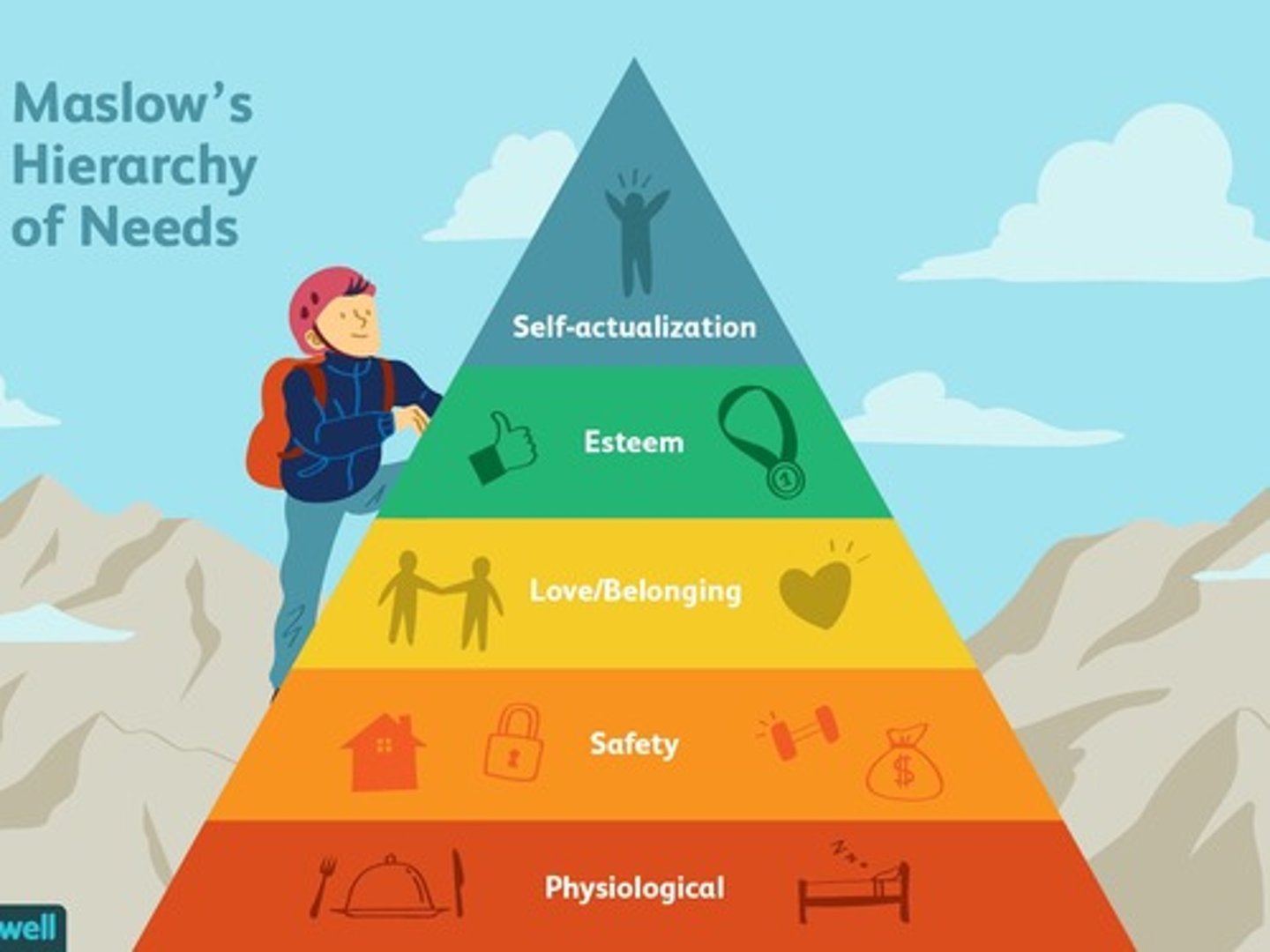
What is the highest need in Maslow's hierarchy of needs?
Self-actualization.
What are the stages of psychosexual development according to Freud?
Oral Stage, Anal Stage, Phallic Stage.
What is the defense mechanism that involves redirecting a drive to a socially acceptable activity?
Sublimation.
What is the defense mechanism characterized by complete forgetting?
Repression.
What is the term for attributing one's own drives or wishes to someone else?
Projection.
What does the term 'reaction formation' refer to in defense mechanisms?
Behaving in a way that is opposite to one's true feelings.
What is the term for returning to an earlier stage of development as a defense mechanism?
Regression.
What is the concept of 'identification' in defense mechanisms?
Becoming like someone else to gain what they have.
What are the characteristics of an oral-dependent personality?
Traits associated with the oral stage of psychosexual development.
What is the Oedipal conflict in Freud's theory?
Guilt and fear regarding competitiveness and intimacy issues.
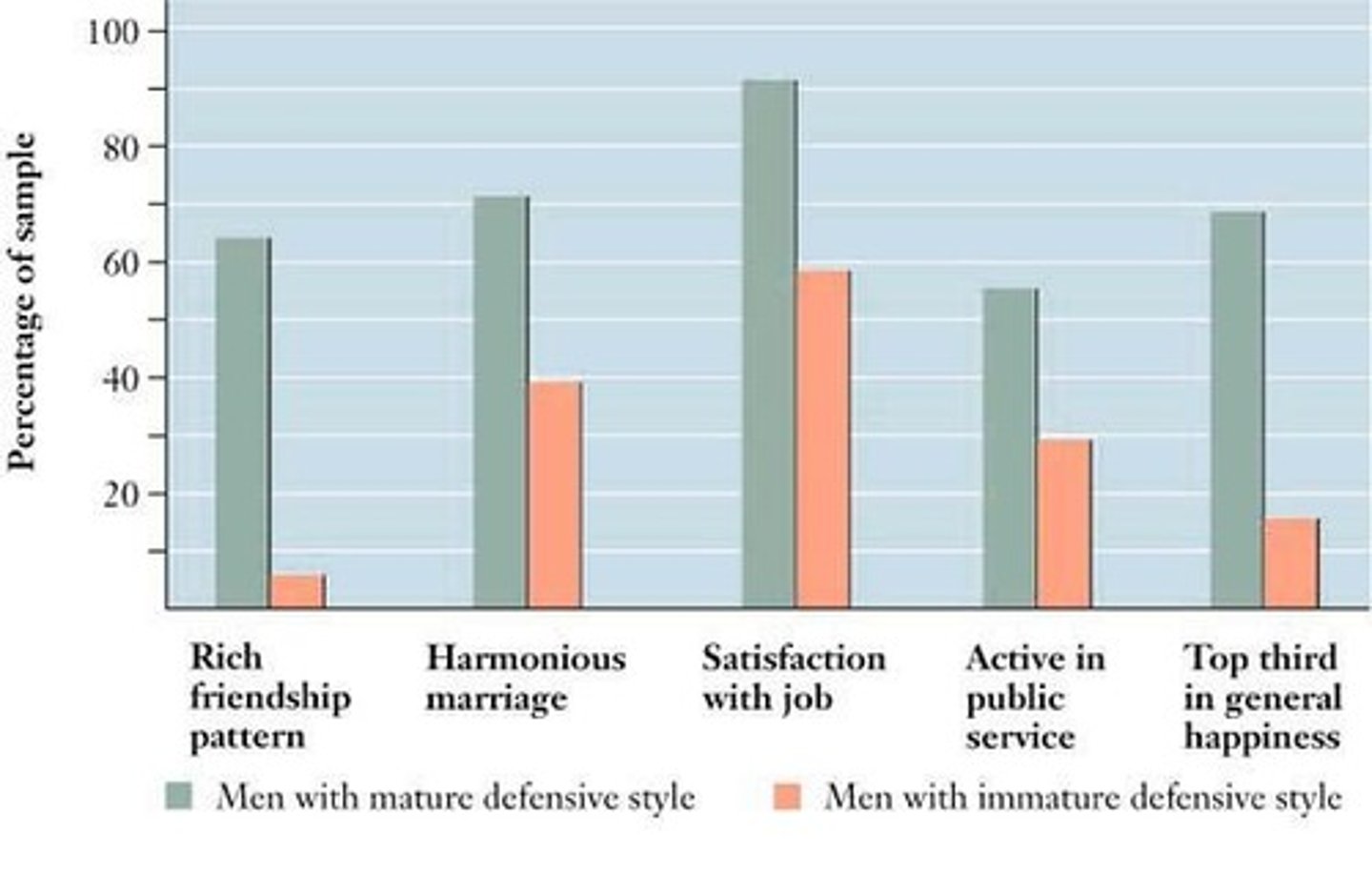
What is the difference between mature and immature defense mechanisms?
Mature defenses include sublimation and humor; immature defenses include projection and regression.
What is the role of the superego in Freud's structure of the psyche?
It acts as the conscience, punishing bad behavior and rewarding good behavior.
What is the motivation of the ego in Freud's theory?
Reality principle.
What does the id represent in Freud's structure of the psyche?
Basic instincts and repressed conflicts, motivated by the pleasure principle.
What are archetypes in Jung's theory?
Universal images that reflect major themes common to all humans.
What are the three coping styles identified by Karen Horney?
Engage others, oppose others, avoid others.
What brain structure is associated with poor impulse control and impaired executive control?
Frontal lobes
What is the effect of increased amygdala activity on personality?
It is associated with anxiety, fearfulness, and shyness.
How do extroverts and introverts differ in terms of physiological arousal?
Extroverts are less aroused and less sensitive to stimulation, while introverts are oversensitive and dislike stimulation.
What neurotransmitter is linked to impulsivity and impulsive aggressiveness?
Low serotonin levels
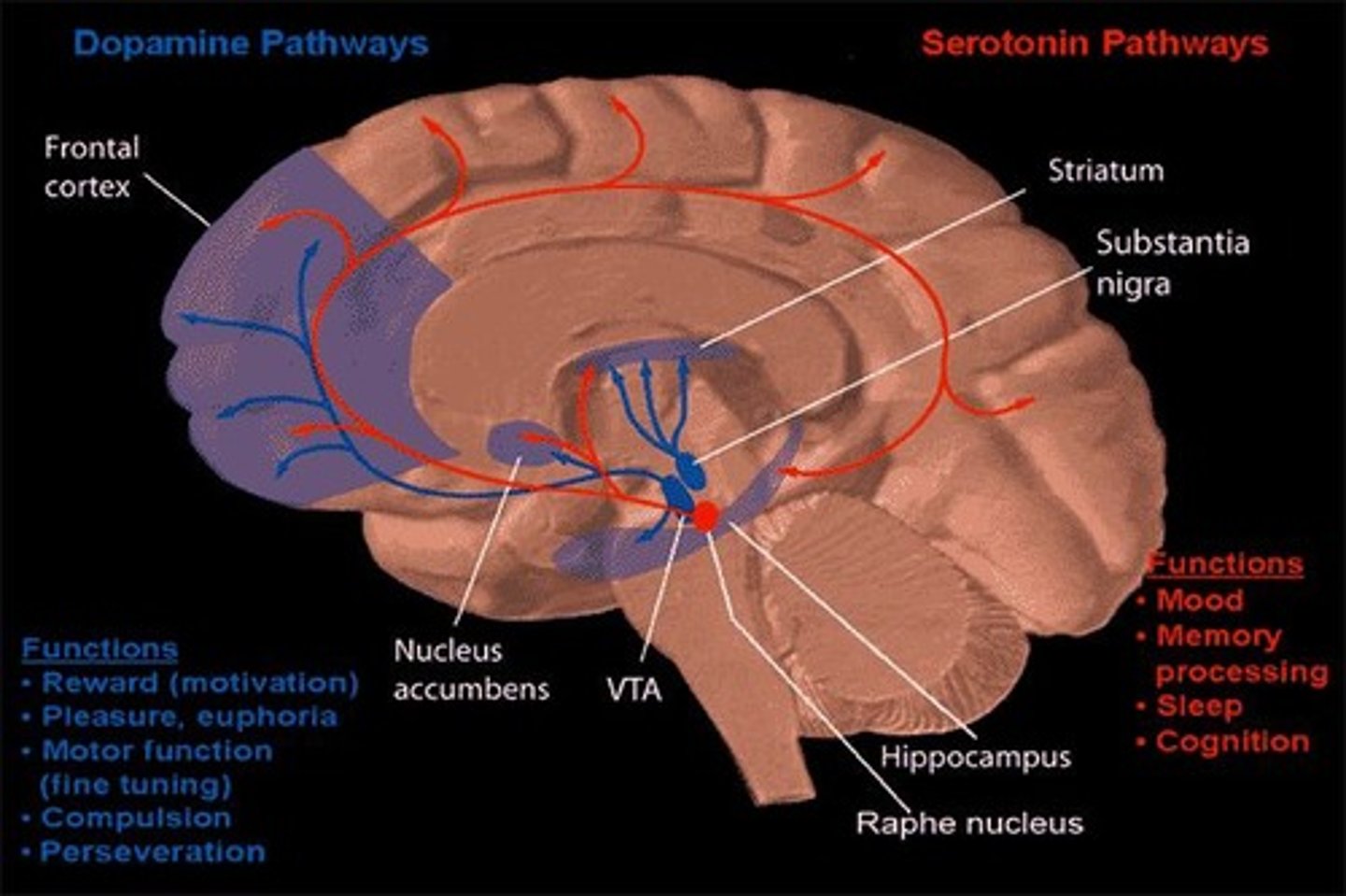
What is the role of dopamine in personality according to behavioral activation?
It is associated with increased sensitivity to potential reward and increased approach behavior.
What does high Behavioral Activation System (BAS) combined with weak Behavioral Inhibition System (BIS) lead to?
Extreme impulsivity
What cognitive bias is associated with impulsivity?
A tendency to focus on immediate events and neglect longer-term consequences.
What is delay discounting in the context of impulsivity?
The tendency to prefer smaller immediate rewards over larger delayed rewards.
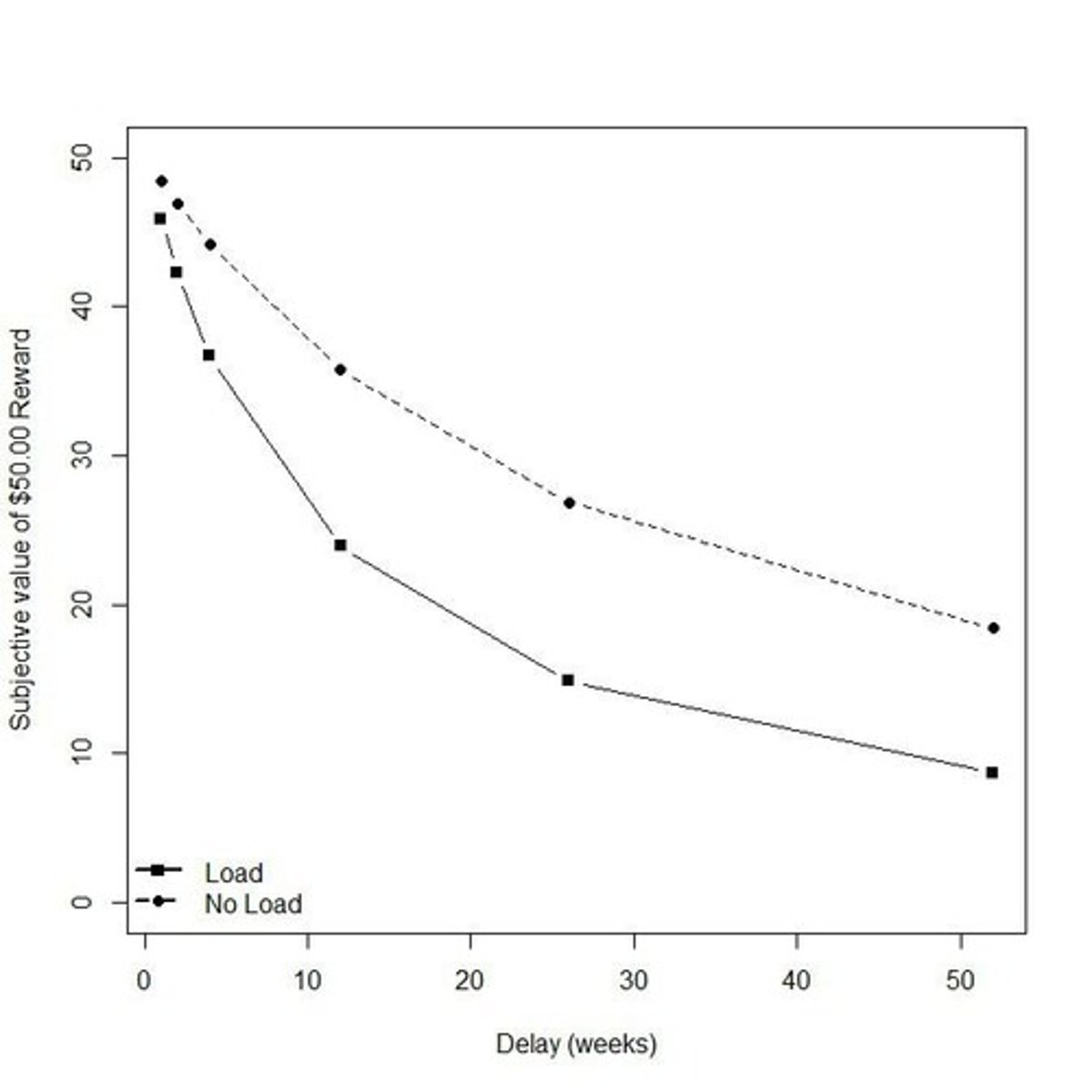
How does harm avoidance relate to risk-taking behavior?
Low harm avoidance is associated with higher risk-taking and less attention to threats.
Who are the main theorists associated with the Social-Cognitive Theory of personality?
Bandura, Rotter, and Mischel
What is the concept of Reciprocal Determinism?
It describes the interaction between person, situation, and behavior.
What are Person Variables in Social-Cognitive Theory?
Cognitive and behavioral styles reflecting individual differences in thoughts and feelings.
What does Locus of Control refer to?
The perception of control over outcomes, which can be internal or external.
What is Self-Efficacy?
Your belief in your ability to perform specific types of behavior.
What is the significance of Delay of Gratification in personality development?
It reflects the ability to delay immediate desires for better long-term outcomes.
What is the basic premise of the Psychodynamic Perspective?
Unconscious forces and conflicts influence motives and behavior.
What are the two basic instincts proposed by Freud?
The life instinct (Eros) and the death instinct (Thanatos).
How do dreams function according to the Psychodynamic Perspective?
They are symbolic wish fulfillments and attempts to resolve conflicts.
What is 'dream work'?
The process by which the ego symbolizes basic wishes and conflicts in dreams.
What are projective tests used for in psychology?
To tap into the unconscious mind and reveal hidden thoughts and feelings.
Name two examples of projective tests.
Rorschach test and Thematic Apperception Test (TAT).
