bone marrow
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Methods of bone marrow examination
A. Needle Aspiration
1. Trephine Technique ( Turkel Needle)
2. Bone Marrow Biopsy ( Silvermann Needle)
B. Surgical Biopsy ( thick sections of BM and stained with H and E.)
Medulla ossium rubra
(Red Marrow consisting mainly of hematopoietic tissue)
Primitive Hematopoiesis
Derived from the extra- embryonic YOLK SAC;
Consists mainly of nucleated erythroid cells that carry oxygen to the developing embryonic tissues... an early circulatory system
. Probably starts ~ 4 weeks in humans
Where Red marrow is found
d mainly in the Flat bones and in the epiphyseal ends of long bones such as the femur and humerus
medullary cavity, the hollow interior of the middle portion of long bones
Yellow marrow
Bone marrow examination
pathologic analysis of samples of bone marrow obtained by bone marrow aspiration and bone marrow biopsy (often called a trephine biopsy)
Sahla Bone Marrow Needle, iliac crest, with adjustable stop
14 (2.0mm) x 50mm
16 (1.6mm) x 50mm
18 (1.2mm) x 50mm (in child)
Cells of the bone marrow
Erythroid series
Myeloid series
Megakaryocytic series
Monocytic series
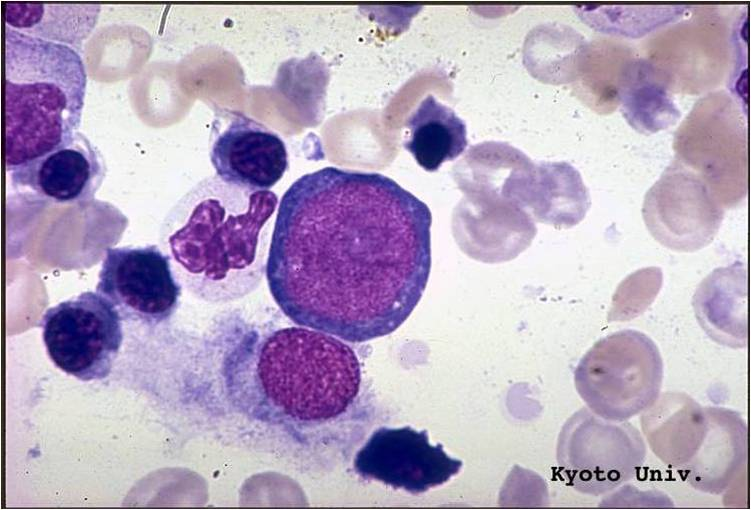
proerythroblast .
Normal proerythroblast in the bone marrow. This is a large cell with a round nucleus and a finely stippled chromatin pattern. Nucleoli are sometimes apparent.
The cytoplasm is moderately to strongly basophilic.
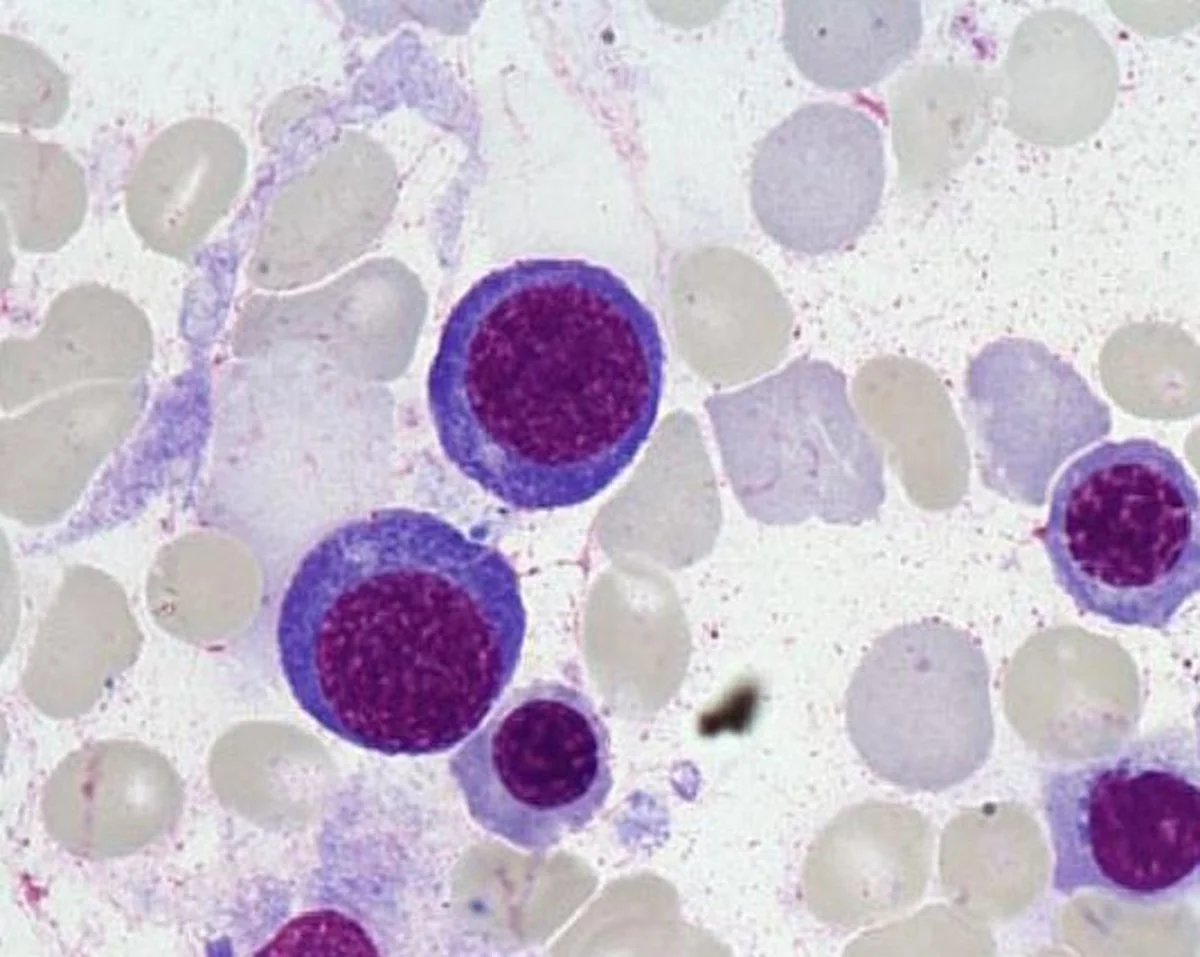
Basophilic erythroblast
Spherical nucleus, nucleoli not visible, basophilic cytoplasm
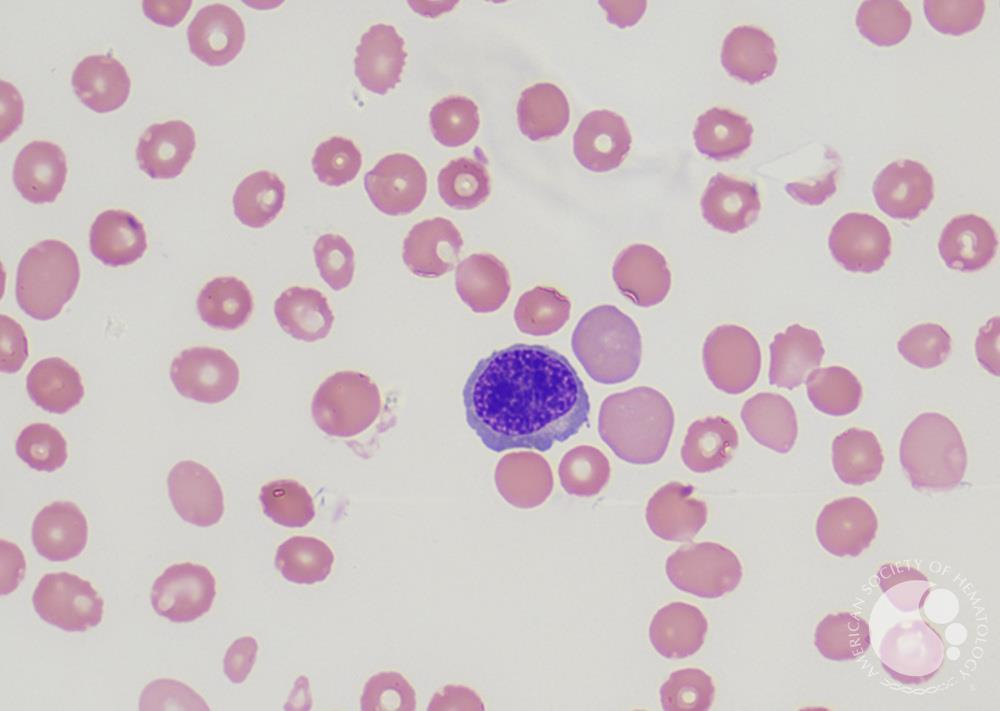
Polychromatophilic erythroblast
smaller nucleus -condensed chromatin, baso- and eosinophilia in the cytoplasm
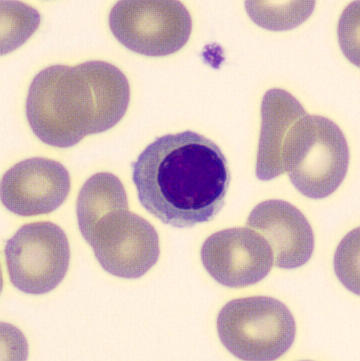
Orthochromatophilic erythroblast
small nucleus with highly condensed chromatin, nucleus extruded, eosinophilic cytoplasm
Myeloid precursors
myeloblast promyelocyte myelocyte metamyelocyte band form mature neutrophil
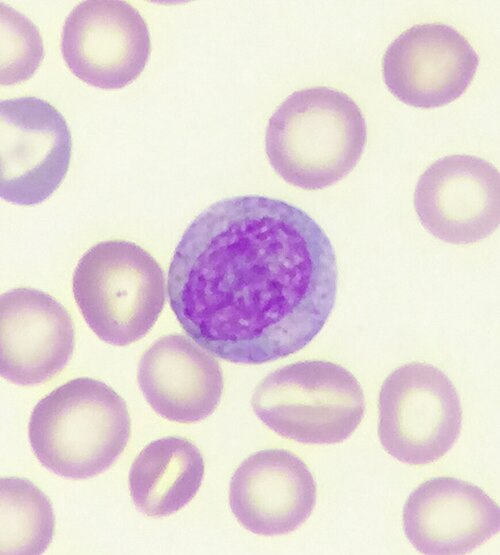
myeloblasts
have no granules but abnormal myeloblasts may have a few granules. Myeloblasts undergo one cell division and mature into promyelocytes.
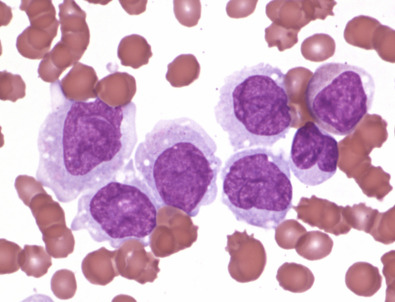
Promyelocytes
have primary or azurophilic granules. They have a Golgi zone a pale area adjacent to the nucleus that is the site of granule production. The chromatin pattern of a promyelocyte shows some condensation or clumping, in contrast to the diffuse chromatin pattern of a myeloblast, but nucleoli are still visible
myeloblast
high nucleocytoplasmic ratio, diffuse chromatin pattern and nucleolus.
promyelocyte
larger and has a lower nucleocytoplasmic ratio and abundant azurophilic granules.
myelocyte
are smaller than promyelocytes and have specific granules that indicate whether they are of neutrophil, eosinophil or basophil lineage. The nucleolus is no longer visible.
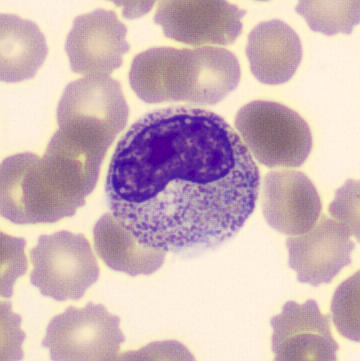
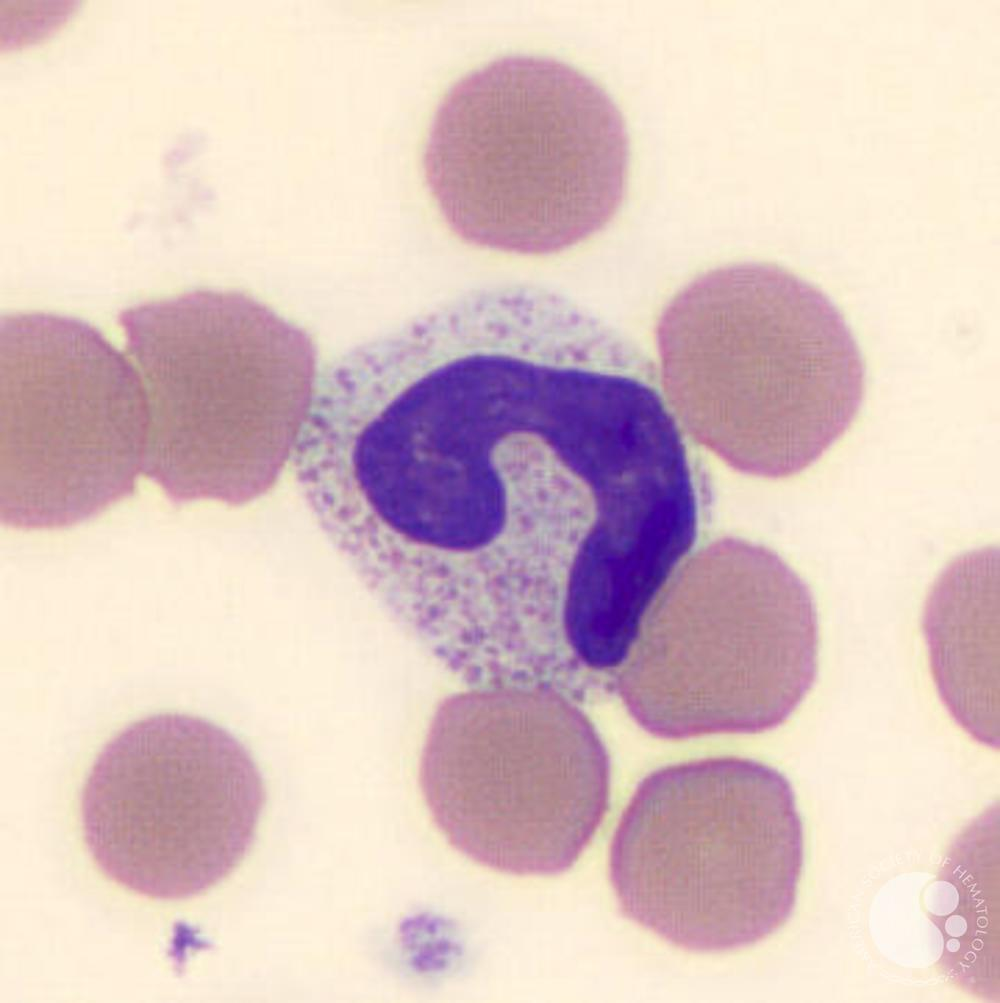
neutrophil metamyelocyte
differs from a myelocyte in having some indentation of the nucleus It differs from a band form in not having any part of its nucleus with two parallel edges
Band or juvenile Neutrophils
There are smaller numbers of cells of neutrophil lineage with non-segmented nuclei. They are referred to as neutrophil band cells or band forms. They are less mature than segmented neutrophils.
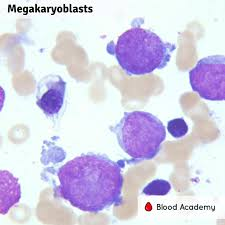
Megakaryoblasts
are the precursors of the megakarycytes. They may show cytoplasmic blebbing.
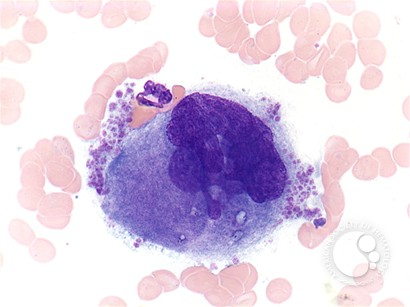
promegakaryocyte
Low power (x10)
Determine cellularity Identify megakaryocytes Look for clumps of abnormal cells Identify macrophages
Higher power (x40, x100)
Identify all stages of maturation of myeloid and erythroid cells. Determine the M:E ratio Perform a differential count Look for areas of BM necrosis. Assess the iron content.
M:E ratio
the ratio of all granulocytic plus monocytic cells (Myeloid) to all erythroblasts (Erythroid). For all bone marrow aspirates examined, the report should specify the M:E ratio and the percentage of lymphocytes and plasma cells. A differential count of at least 200-300 cells should be performed. If there is any borderline abnormality, e.g. in the number of blasts, lymphocytes or plasma cells, a 500 cell differential count should be performed.
BM iron stores
Once all normal and abnormal bone marrow cells have been assessed on a routine stain an iron stain should be examined, using a medium power objective (X 40 or X 50). Storage iron, which stains blue, should be assessed in bone marrow fragments. This image shows normal bone marrow iron.
Jamshidi Type Bone Marrow Biopsy Needle,
8swg (4.0mm) x 10omm
11swg (3.0mm) x 100mm
13swg (2.3mm) x 90mm
14swg (2.0mm) x 90mm (In child)
Aspiration
fast, gives relative quantity if different cell types, gives material to further study
doenst represent all cells
biopsy
gives cell and stroma constitution, represents all cells, explains the dry tap
slow processing
Sites of Puncture in Adults
Sternum and Iliac crest
Sites of Puncture in infants
Tibia and Spinous Processes
Children
Iliac and Spinous ( Vertebral)