Preterm Labor
1/288
Earn XP
Description and Tags
By: Melnie Rose D. Diaz , RN , MN
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
289 Terms
when labor begins before 37 weeks of pregnancy
What is preterm labor?
When the contractions occur in 4 every 20 minutes
How will you know if the patient is in labor?
Above 37 weeks
When can you say that the neonate is viable for extra uterine life?
• cervix is more than 50% effaced.
• >3-4 CM dilated
• rapture of membranes
• SGA ( Small for gestational age )
Criteria for a labor that cannot be halted
between 20 - 37 weeks of gestation
When does labor occur?
We are waiting for the maturity of the lung surfactant
Why do we wait for 37 weeks for delivery?
a complex mixture of lipids and proteins, to reduce the surface tension of the lungs.
what is lung surfactant and its component?
Dilation
opening of the cervix
Effacement
shortening and softening of the cervix
4CM – qualified for admission
7CM – at labor room
10CM – mount pt to OR table
Unless multigravida @ 3cm, dont let her go home
Discuss the what happens to the patient if she is in
4cm
7cm
10cm
1st - by the end of trimester
2nd - Once evry month
3rd - monthly until 9 month then every 2 weeks.
Discuss the frequency of check ups for the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd trimesters.
• cervical length
• Transvaginal Ultrasound
• analysis of the vaginal mucus
• Fetal Fibronectin
How to diagnose preterm labor through
Term Labor
This definition is termed as 40 weeks of pregnancy.
Post term pregnancy
After 40 weeks of gestation
The baby exp. stress inside the uterus; This stress can cause the relaxation of the sphincter muscle that controls the passage of stool.
Compression of umbilical cord
Cord coil
Cord decomposition
Infection
What is the reason for meconium stain
• previous preterm birth
• short interval between pregnancies
• short cervical length
• smoking
• illicit drug use
• perinatal infections
• placental previa
• polyhydramnious
• uterine anomalies
• fetal birth defects
Myriad of Conditions
Yes, the patient is at increased risk of preterm labor in her second pregnancy.
The patient is G2P1, with a history of preterm labor. Is she at risk for preterm labor in her second pregnancy?
Short interpregnancy intervals (IPIs), not long ones, are associated with an increased risk of preterm labor (PTL)
T/F: Long-term interval pregnancies poses high risk for PTL.
2-3 years recovery
Ideal interval for pregnancy to occur again?
Nicotine=Vasoconstriction=plaque=increased BP= perfusion problems
How does smoking can casue PTL
Acreta
Totalis
Types of Placenta Previa
Vaginal Spotting
Pelvic Pressure
Abdominal Tightening
Cramping
Water breaking
Signs of true labor
2nd trimester
In what trimester will you educate about the fetal kick?
10 kicks within 2 hours
What is the normal range of fetal kick count
20-24 weeks
When is the most viable time for fetal kick to occur in weeks
110-160 bpm
Normal FHR?
Fetal fibronectin
A protein produce by trophoblast cells
Preterm contractions are ready to occur
If fetal fibronectin is present in vaginal mucus, it predicts what?
Labor will not occur for at least 14 days
Absence of fetal fibronectin means?
Rest period and Activity level assessment
What is the intervention for activity intolerance
Assess pain levels
Position patient to left side lying position
Paracetamol Analgesics
What is the ideal intervention for Acute pain in patients who has preterm labor
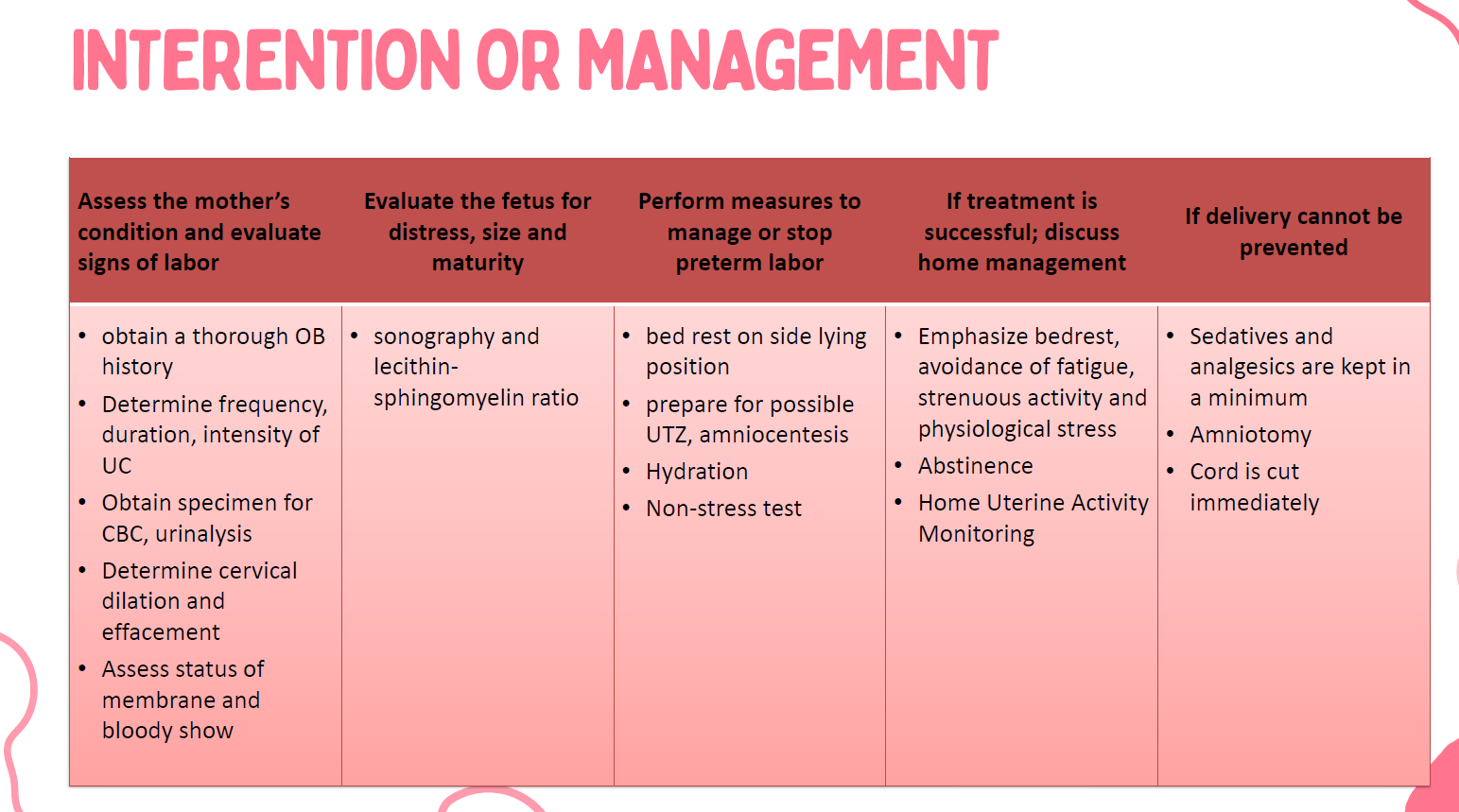
• hospital admission
• bed rest
• CTG / Doppler
• monitor fetal heart tone and
contactions
• IV therapy ( hydration )
• vaginal and cervical cultures
• clean catch urine
Management of preterm labor
No, you cannot directly monitor contractions using a standard Doppler.
Can you monitor contractions using Doppler
Dehydration is eminent and with dehydration, stimulate the pituitary gland to release antidiuretic hormone which may caused to release oxytocin as it increases contractions.
Why is IV therapy important for patients with preterm labor
Tocolytic agents
An agent to halt labor and wait until 37 weeks
Yes, as long as they remain well hydrated and take thier tocolytic agents
Can women at preterm labor be safely cared at home?
Yeast infection
During preganancy what is the risk of an increased in glucose levels?
False: immediately cut the cord and then proceed to resuscitation
T/F in preterm delivery we are still going to wait 3 minutes before cutting the cord
Amniotomy
irrigation of amniotic fluid in the abdomen
CBR w/o BP
Hydration
Tocolytic agents
AVOID activities that could stimulate labor
Beverly Muzuki has started preterm labor and so is put to bed rest. She ask you ‘What else can I do to help prevent having this baby early?”
Empty bladder to relieve uterus pressure
Lie down on your L/R side to promote blood return to uterus
Hydration
Call HP
If uterine contractions occur?
Corticosteroid
What type of medication is used to speed up the lung surfactant development of the fetus
Betamethasone
During the time labor is chemically halted, if the pregnancy is under 34 weeks, a woman is may be given a steroid _____________ to attempt hasten the lung maturity
Tocolytic agents
Used to stop and prevent uterine contractions
magnesium sulfate
Tertabuline
Prostaglandin inhibitor
Nifedipine
Isosuxiprine Hydrochloride
Examples of tocolytic agents
Lowers respiratory distress syndrome
Why is betamethasone preferred?
• should not be usedover 48-72
hours ( can cause death and
heart problems to pregnant
patients )
• not allowed to be given as
outpatient medication
Nursing considerations for Tertabuline
Magnesium sulfate
This medication is used to prevent pre-eclampsia and administered before 32 weeks to prevent cerebral palsy.
Monitor
When administering magnesium sulfate, as a nurse, what should you monitor?
False: Slow IV push it can cause phlebitis/cellulitis
T/F In administering Magnesium Sulfate, it should be a fast IV push to prevent cellulitis (Burning of cells).
Ice packs TSB
What is typically administered concurrently with magnesium sulfate?
Calcium Gluconate
Antidote for magnesium sulfate
Betamethasone
What is the name of the steroid commonly used to hasten fetal lung maturity in pregnancies less than 37 weeks gestation?
24 hrs and last for 7 days
When will betamethasone effect?
2 doses 12 mg, 24 hrs apart
4 doses 6 mg, 12 hrs apart
Dosage for betamethasone
RDS (Respiratory Distress Syndrome)
• Pathologic Apnea
• Infections
• Congenital Heart defects
• Thermoregulation problems
• Feeding Difficulties
• Neurological Disorders
• Anemia
• Jaundice
Risk for premature infants
Respiratory Distress Syndrome
A breathing problem that affects newborns, mostly those who are born early (premature).
Pathologic apnea
Irregular breathing cessation in newborn
Patent Ductus Arteriosus
Example of Congenital Heart defect
72 hours after birth
When does Ductus Arteriosus usually close?
Because of the prematurity of the liver (normal until 2 weeks after birth)
Why is jaundice a risk for premature infants
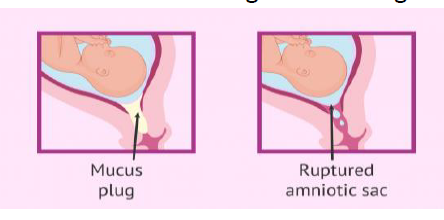
Premature Rupture of Membranes (PROM)
Is the rupture of the chorion and amnion in 1 hour or more before onset of labor.
Chorioamnionitis
PROM is associated with what?
36-40 weeks
PROM usually occurs within _____ weeks of pregnancy
• Leakage of fluid in the vagina which could be a dramatic gush or slow steady trickle
• Constant wetness in the underwear
• Passage of fluid followed by signs and labor
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS of PROM
Preterm labor
Infection
Cord compression
Complications for PROM
• Left side lying position
• Hydrate IVF/ IV therapy
• Hyperperfusion
Fetal distress management
Ferning is evident
Nitrazine test
LABORATORY AND DIAGNOSTIC STUDY FINDINGS
If the fluid is tested with Nitrazine paper, amniotic fluid causes an alkaline reaction on the paper appears BLUE and urine causes an acidic reaction remains YELLOW
If the fluid is tested with Nitrazine paper, amniotic fluid causes an alkaline reaction on the paper appears________ and urine causes an acidic reaction remains ______
✓ Pelvic examination
✓ Nitrazine test
✓ Fern test
Confirm diagnosis of PROM
labor induction should be performed.
If PROM occurred at term, and labor does not begin in 24 hours,
delayed up to a week or more.
If PROM occurred before term, it can be delayed for?
Preterm Rupture of Membranes
You are a Nurse in an OB ward when suddenly, a woman tells you that she experienced a sudden gush of clear fluid from her vagina, followed by continued minimal leakage. She is currently at 35 weeks of pregnancy
Put mother in bed rest
Prevent infection and possible complications
Determine Maternal Fetal status
Provide client and family education
Provide comfort measures such as sacral pressure, back rub, frequent changes in positioning.
• Advise to empty bladder.
• Administer prescribed medications.
• Discourage bearing down
Nursing intervention for PROM
Polyhydramnios
What happens if the amniotic fluid index of the pregnant woman is more than 24 cm, as a nurse, what does this indicate?
Monitor VS OF the mother
FHT every hour
Determine characteristics of vaginal discharge
Uterine contractions
In determining maternal and fetal status of a PROM patient, what should be the following interventions a nurse should do?
Polyhydramnios
This is a disorder in which there is an excessive amniotic fluid formation, more than 2000 ML
500-1000 ml; Color is clear
What is the normal amount of Amniotic fluid?
AF
This is formed by a combination of amniotic membrane and fetal urine
The inability of the fetus to swallow, secondary to tracheoesophageal fistula/stenosis or anencephaly, as evidenced by polyhydramnios
or
Diabetes mellitus
What are the probable cause of polyhydramnios
Multigravida
DM
Maternal Factors for Polyhydramnios
• Fetal Abnormalities
• Anencephaly
• Esophageal Atresia
• Spina Bifida
• Heart Failure
• Congenital Infection
Fetal factors for polyhydramnios
• Unusually rapid enlargement of the uterus
• Difficult to palpate fetal parts because the uterus is tense
• Auscultating FHR is difficult
• Shortness of breath
• Lower extremities varicosities
• Increase weight gain
How will you asses if the patient has Polyhydramnios
• Premature Labor and Delivery
• Abruptio Placentae
• Postpartum Hemorrhage
• Cord Prolapse (cut or strangled cord)
• Malpresentation
Premature Labor and Delivery:
Mechanism: The excessive amniotic fluid can overstretch the uterus, making it more prone to contractions and leading to preterm labor (labor before 37 weeks of gestation). The increased pressure may also contribute to premature rupture of membranes (PROM), which can further increase the risk of preterm birth.
Risks: Premature babies are at increased risk for a variety of health problems due to underdeveloped organs, including respiratory distress syndrome, infections, and neurological issues.
2. Abruptio Placentae:
Mechanism: Abruptio placentae is the premature separation of the placenta from the uterine wall. The increased uterine distension caused by polyhydramnios can put pressure on the placenta and increase the risk of it partially or completely detaching.
Risks: This is a serious complication as it can lead to fetal distress due to lack of oxygen and nutrients, as well as severe maternal bleeding.
3. Postpartum Hemorrhage:
Mechanism: After delivery, the uterus needs to contract strongly to clamp down on blood vessels at the placental site and prevent excessive bleeding. In polyhydramnios, the overstretched uterus may have weakened muscle tone (uterine atony), making it less effective at contracting after birth.
Risks: This can lead to significant blood loss after delivery, requiring medical intervention, including blood transfusions.
4. Cord Prolapse:
Mechanism: Cord prolapse occurs when the umbilical cord slips down through the cervix and into the vagina before the baby during labor or delivery. The excessive fluid in polyhydramnios creates more space, making it easier for the cord to prolapse.
Risks: A prolapsed cord can become compressed between the baby's head and the mother's pelvis, cutting off the baby's oxygen supply. This is a medical emergency requiring immediate intervention. The image mentions "cut or strangled cord," which refers to the compression of the cord, not literally cutting it.
5. Malpresentation:
Mechanism: Malpresentation refers to any fetal position other than the ideal head-down (vertex) presentation for delivery. The extra space in the uterus due to polyhydramnios allows the baby more room to move around, increasing the chance of them settling into a breech (buttocks first) or other non-vertex position.
Risks: Malpresentation can make vaginal delivery more difficult and may necessitate a cesarean section.
Complications for polyhydramnios
Hospitalization is done if symptoms are severe
• Indomethacin therapy
• Amnioreduction
• Amniotomy
• Monitor for premature labor
• Watch closely for hemorrhage after delivery
• assess vital signs
• assess lower extremities edema
• Teach the mother to report any signs of ruptured membranes or uterine contractions
TM for polyhydramnios
ULTRASOUND
Specifically, the amniotic fluid index (AFI) and single deepest pocket (SDP) measurements, obtained through ultrasound, are the key methods used.
What is the best equipment used to assess for polyhydramnios?
Oligohydramnios
You are an OB nurse at the OB ward when suddenly a pregnant patient comes in with the chief complaint that her Amniotic Fluid (AF) volume is around 300 ml and her Amniotic Fluid Index (AFI) is less than 5 cm
5 cm - 24 cm
What is the normal range of AF index?
25-28 weeks
On what gestational age does the anomalies test conducted?
18-20 weeks
On what week of gestation will you be able to know the gender of the baby?
Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR)
a condition where a baby in the womb (fetus) doesn't grow at the expected rate for the gestational age (number of weeks in the pregnancy)
No, not all cases of oligohydramnios involve leakage of amniotic fluid.
Here are some other reasons why oligohydramnios can occur:
Problems with the placenta: The placenta provides the baby with oxygen and nutrients. If it's not functioning properly, it may not produce enough amniotic fluid.
Fetal abnormalities: Certain birth defects, especially those affecting the kidneys or urinary tract, can lead to reduced amniotic fluid production.
Maternal health conditions: Conditions like high blood pressure, diabetes, or dehydration in the mother can also contribute to oligohydramnios.
Post-term pregnancy: As the pregnancy goes past the due date, the amount of amniotic fluid may naturally decrease.
does all cases of oligohydramnios involves leakage?
To detect the presence of trisonomy 21 disorder
Purpose of anomaly test?
CAUSES
• Fetal renal anomalies
• PROM
• Exposure to ACE inhibitors
• IUGR
• Post-term pregnancy
• Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome
What is the caused of oligohydramnios
Uterus small for gestational age
leaking AF
Decreased amount of AF
Sign and symptoms of oligohydramnios
Edema
how does cardiac failure contribute to polyhydramnios?
Cord compression
Fetal hypoxia
Prolonged labor
A patient was admitted for delivery with the complication of Oligohydramnios, as nurse part of the delivery what are the complications you should take note of during delivery?
Answer: D. Fetal heart rate patterns
Rationale: Fetal heart rate patterns are the most sensitive indicator of fetal well-being. In oligohydramnios, the reduced amniotic fluid can lead to cord compression, which can compromise fetal oxygenation. Monitoring the fetal heart rate allows for early detection of distress. While the other options are important, they are not as immediate an indicator of fetal compromise as the fetal heart rate
A client at 36 weeks gestation is diagnosed with oligohydramnios. Which of the following fetal assessments is the PRIORITY for the nurse to monitor?
A. Fetal weight
B. Fetal movement count
C. Amniotic fluid index (AFI)
D. Fetal heart rate patterns
Answer: B. Decrease the risk of umbilical cord compression.
Rationale: Amnioinfusion involves infusing saline into the amniotic cavity. The primary goal in oligohydramnios is to provide cushioning for the umbilical cord, thereby reducing the risk of compression and subsequent fetal hypoxia. While it might have slight effects on the other options, it's not the primary goal.
A client with oligohydramnios is prescribed amnioinfusion during labor. The nurse understands that the primary goal of this procedure is to:
A. Increase the amniotic fluid volume to promote fetal lung maturity.
B. Decrease the risk of umbilical cord compression.
C. Stimulate uterine contractions.
D. Assess fetal lung maturity.
Answer: C. Maternal hypertension
Rationale: Maternal hypertension (high blood pressure) can reduce blood flow to the placenta, which can subsequently lead to decreased amniotic fluid production and result in oligohydramnios. While gestational diabetes can sometimes be associated with polyhydramnios, preterm labor and multiple gestation are not directly linked as risk factors for oligohydramnios.
Which of the following maternal conditions is a known risk factor for oligohydramnios?
A. Gestational diabetes
B. Preterm labor
C. Maternal hypertension
D. Multiple gestation