PTSD
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
What is Post Traumatic Stress Disorder?
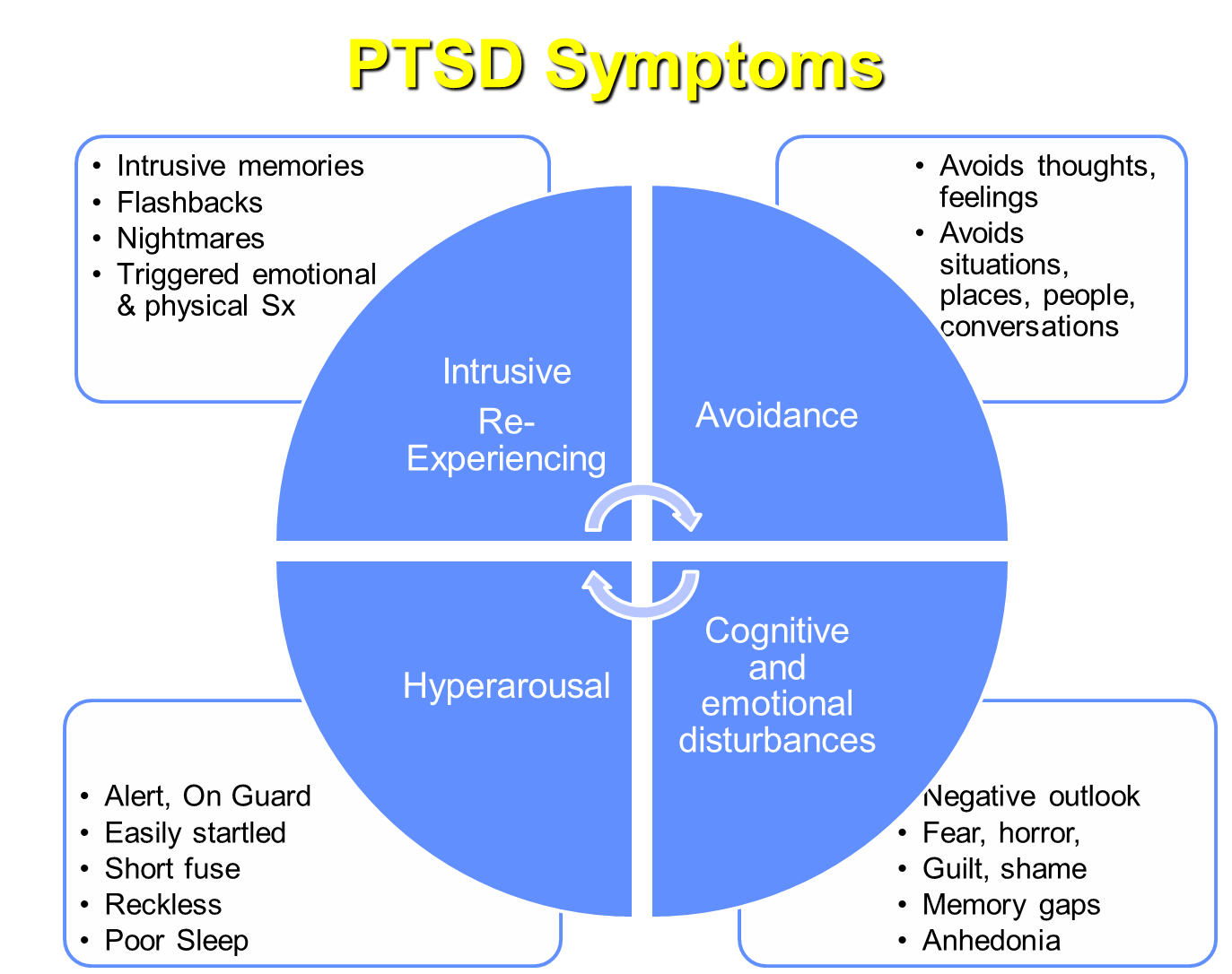
Following exposure to trauma such as serious injury or sexual violence, whether that’s experiencing, witnessing, or learning about it resulting in stress symptoms. These symptoms must last for longer than one month and cause significant distress/impairment
1) Intrusion
→ recurrent involuntary memories about the event with intense psychological distress when reminded about the event
2) Avoidance
→ avoidance of distressing memories, leading to them avoiding anything that might remind them about it
3) Negative Alterations in Cognition and Mood
→ inability to recall things about the event as well as guilt and shame
4) Hyperarousal
→ agitated and easily startled
→ poor sleep
May also be dissociative if there is substantial symptoms of depersonalization
What is the dysregulated fear response that results in PTSD?
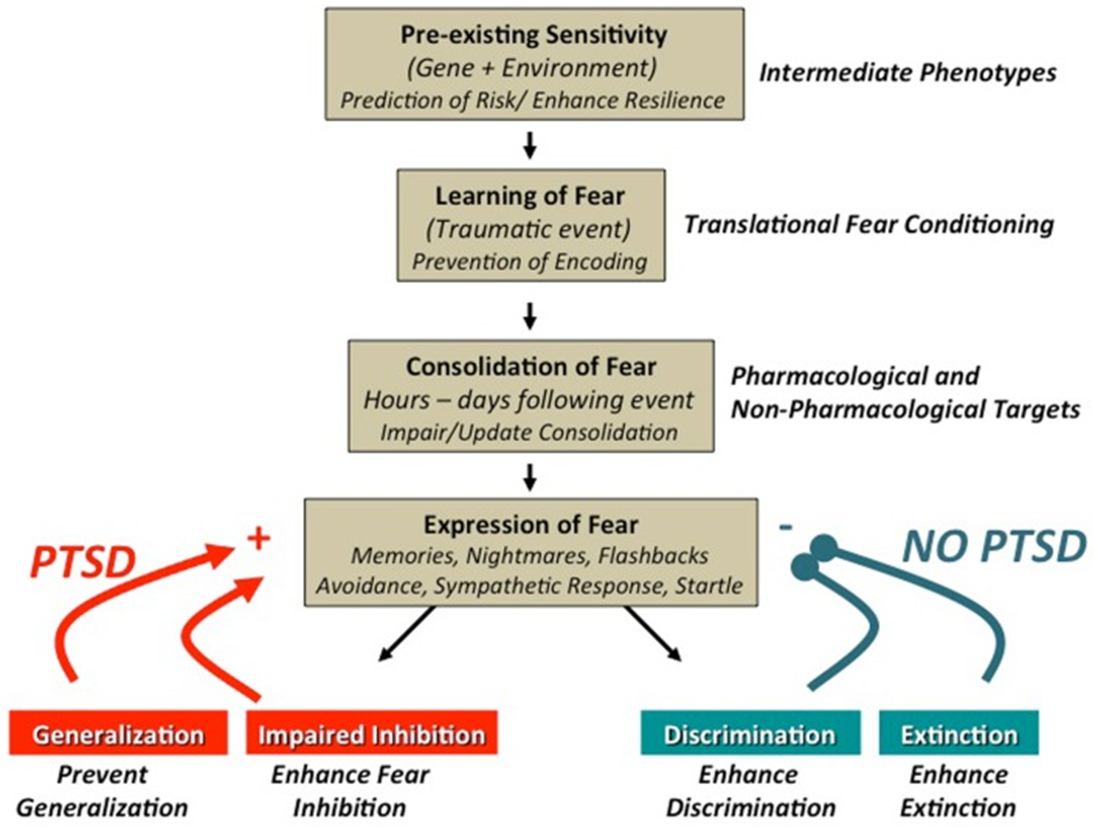
During PTSD you have an initial explosion of fear, fight, or flight in our amygdala and encoding into our hippocampus
1) Patients with PTSD will consistently re-expose themselves to the trigger that caused the initial trauma resulting in enhancement and impaired discrimination due to extinction
→ patients will impaired discrimination or being able to tell the difference between a danger cue and a safe cue
→ patients will have enhanced fear conditioning where the fear response is exaggerated
What are the different portions of the brain responsible for regulation of stress?
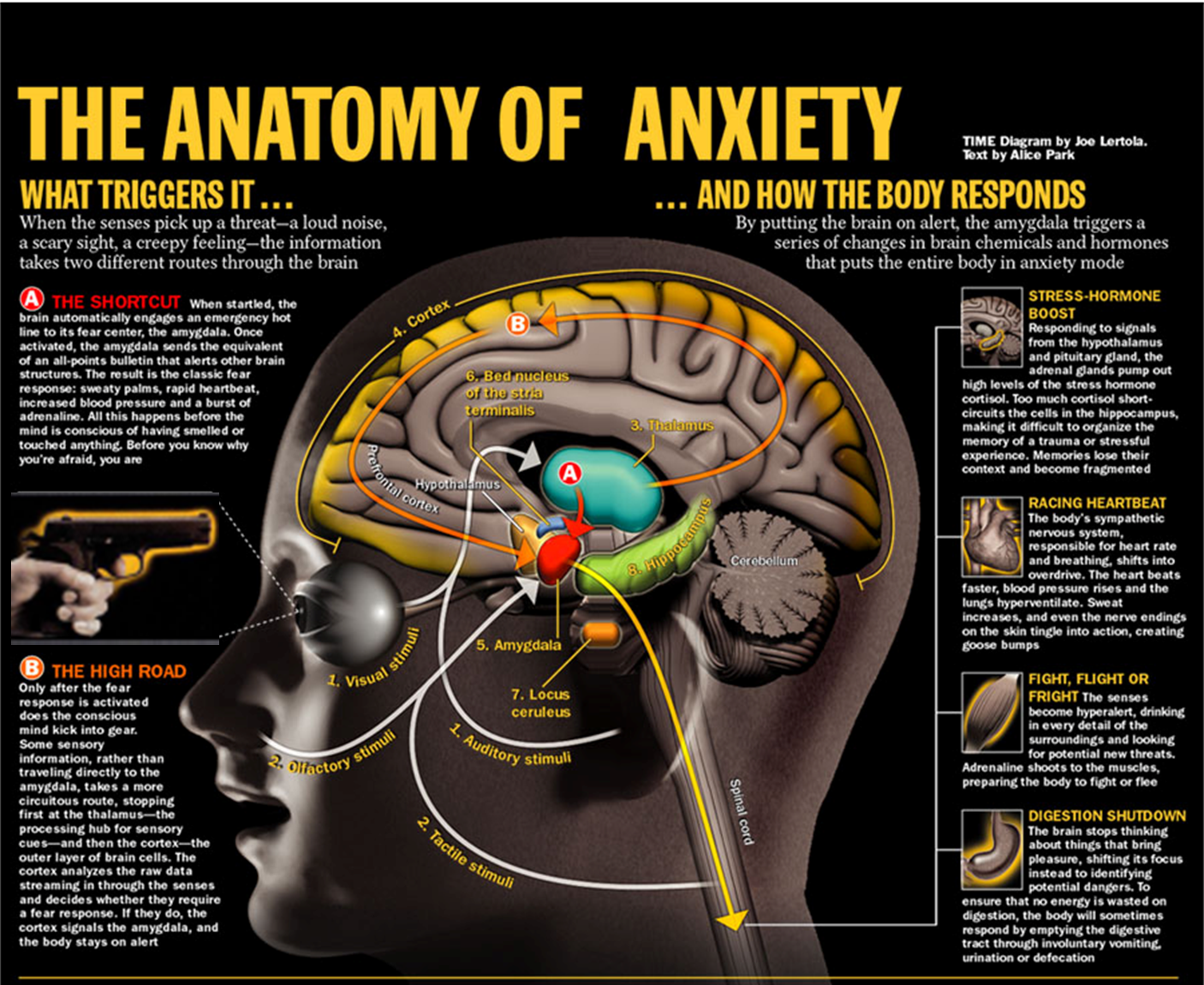
When you are exposed to some stressful stimuli
1) Auditory and Visual Stimulus
→ processed first by the thalamus and then shunted to the amygdala and cortex
2) Olfactory and Tactile Stimulus
→ goes directly to the amygdala
3) Cortex is responsible for giving meaning to our sensations while the Prefrontal Cortex allows us to turn off anxiety
4) Amygdala is our emotional core and alarm center and is responsible for triggering our fear response
→ the Amygdala will send signals to the bed nucleus of stria terminalis which perpetuates the fear response leading to long term fear
→ Locus Coeruleus also receives signals from the amygdala and initiates the anxiety response
→ Hormones from this fear response are regulated by the hypothalamus and pituitary
5) Memories will then be stored in the Hippocampus
What is the treatment plan for a patient with PTSD?
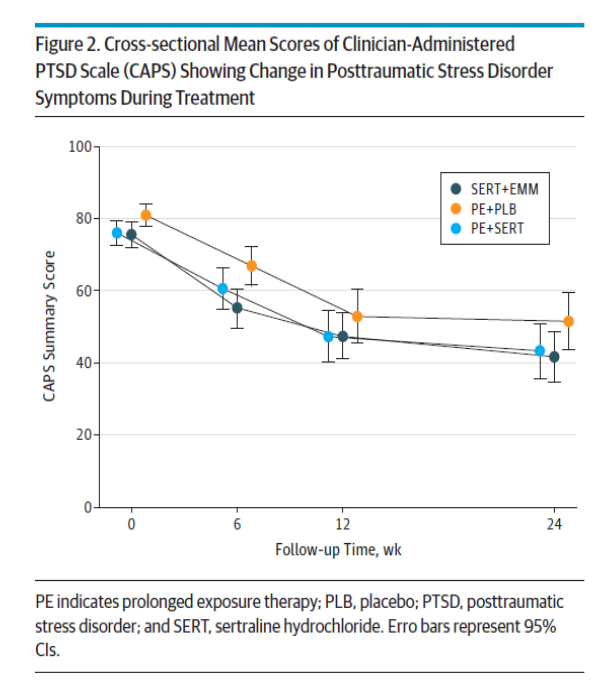
Patients are often provided trauma-focused evidence based psychotherapies as a first line treatment but medications and life-style changes are also used
→ includes prolonged exposure therapy, cognitive processing therapy, and eye movement desensitization and reprocessing
1) SSRI-Medications such Sertraline and Paroxetine are also used and are the only FDA approved drugs for usage
→ the SNRI venlafaxine while not FDA approved is promising
2) Patients who received their preferred treatment and got treatment earlier often saw the most benefit
Which drugs are used to treat sleep and nightmares in patients with PTSD?
Prazosin - nightmare therapy as a alpha-1 adrenergic antagonist
Trazodone - PTSD related insomnia
Why are benzodiazepines not used for PTSD?
Benzos are not recommended for usage in PTSD as they do not prevent the outcomes of PTSD
→ has potential for harm