Clustering Analysis
5.0(3)Studied by 64 people
Card Sorting
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:29 PM on 11/7/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
1
New cards
Cluster Analysis (or Clustering)
Is the task of grouping a set of objects
2
New cards
What is the name for groups that have objects that are more similar to each other than those in other groups?
Cluster
3
New cards
Each cluster is a collection of __________.
data objects
4
New cards
What is clustering also known as?
Segmentation
5
New cards
Objects in a group will be similar or _________ to one another and different from the objects in other groups.
homogeneous
6
New cards
What happens to intra-cluster distances when clustering groups?
They are minimized
7
New cards
What happens to inter-cluster distances when clustering groups?
They are maximized
8
New cards
Different methods to calculate distance.
Euclidean, Manhattan, Chebyshev
9
New cards
Manhattan distance formula
|x1-x2| +|y1-y2|
10
New cards
Euclidean distance formula
sqrt((x1-x2)^2 +(y1-y2)^2)
11
New cards
What is the name of the method used to handle calculating distance with multiple data points
K-means clustering method
12
New cards
What does k-means mean?
Average distance between clusters
13
New cards
K-Means Algorithm
1.Select K points as the initial centroids
2.repeat
3. Form K clusters by assigning all points to the closest centroid
4.Recompute the centroid of each cluster
5. Until the centroids don't change
2.repeat
3. Form K clusters by assigning all points to the closest centroid
4.Recompute the centroid of each cluster
5. Until the centroids don't change
14
New cards
What is Manhattan distance?
A distance metric between two points in a N dimensional vector space
15
New cards
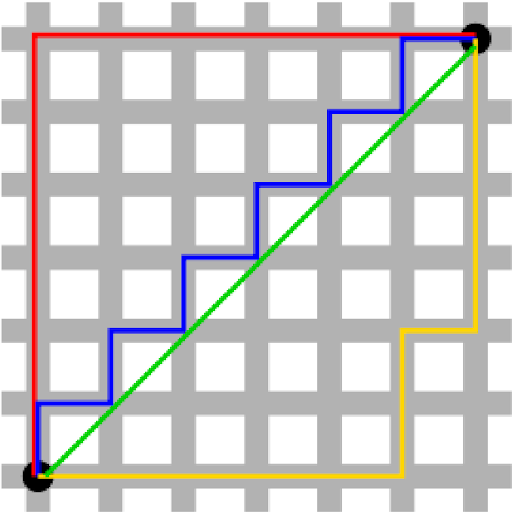
Which line represents Manhattan distance?
the blue line
16
New cards
What is manhattan distance often used to calculate the distance of?
integrated circuits where wires only run parallel to the X or Y axis
17
New cards
Manhattan distance is also called_______.
Minkowski's L1 distance
18
New cards
What is Euclidean distance?
The straight line distance between two points.
19
New cards
What formula does euclidean distance take from?
Pythagorean theorem
20
New cards
What type of approach is the k-means clustering method?
Partitional clustering approach
21
New cards
What must be specified in k-means clustering?
Number of clusters(k)
22
New cards
What methods can be used to select k?
Subject-matter knowledge, convenience, constraints, arbitrarily
23
New cards
Hierarchical clustering
Produces a set of nested clusters organized as a hierarchical tree
24
New cards
What can hierarchical clustering be visualized as?
Dendrogram
25
New cards
Dendrogram
A tree-like diagram that records the sequences of merges or splits
26
New cards
What are the strengths of hierarchical clustering?
No assumptions on the number of clusters(any number of clusters can be obtained by cutting the dendrogram at the proper level), they correspond to meaningful taxonomies
27
New cards
What are the two main types of hierarchical clustering?
Agglomerative and Divise
28
New cards
Agglomerative
(bottom up method) starts with the points as individual clusters and each step, merge the closest pair of clusters until only one cluster left
29
New cards
Divisive
(top bottom method) start with one, all-inclusive cluster and at each step, split a cluster until each cluster contains a point.
30
New cards
Examples of Clustering.
Document clustering, marketing, city-planning
31
New cards
What type of learning is clustering?
Unsupervised
32
New cards
Association Rule Mining
Given a set of transactions, find rules that will predict occurrence of an item based on the occurrences of other items in the transaction.
33
New cards
What is the goal of association rule mining?
Finding regularities in data
34
New cards
Example of association rule mining
Target product recommendation
35
New cards
What is the goal of market basket analysis?
To determine the strength of all the association rules among a set of items.
36
New cards
What question does the application of market basket analysis answers?
Which items are likely to be purchased together?
37
New cards
Support
({X,Y} or X-> Y): how often X and Y go together. # of records containing X and Y divided by total # of records.
38
New cards
Confidence
(X -> Y): how often Y go together with X. # of records containing X and Y divided by # of records containing X