Pulp Therapy in the Primary Dentition
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
what is different from GA and LA
LA can still feel pressure senses etc but GA means reflexes and all nerves are shut off
means it is dangerous
why do we not extract primary teeth
loss of space - malocclusion
mastication
speech
aesthetics
avoidance of GA
what is accessory root canals
common in furcation
why we need to vitality test as bacteria can cause pulpal death
are little channels across the root and into the PDL
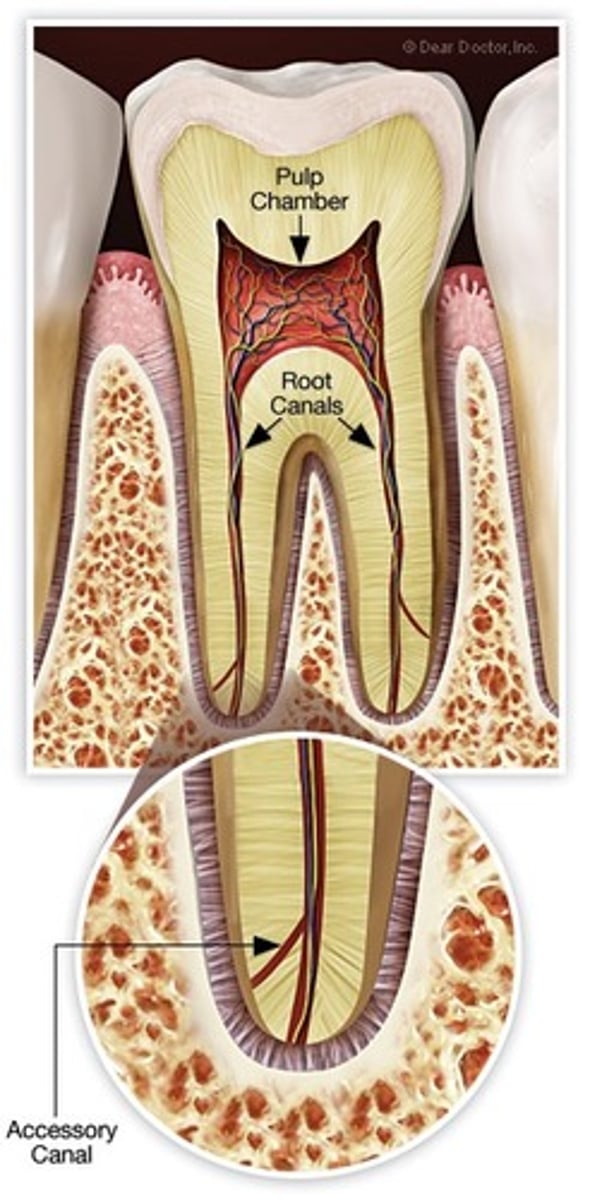
what is the difference in pulp chamber in primary and secondary root
Increased number if accessory canals foramina and prosperity of pulpal floors
Primary root canals are more ribbon like
Fine, filamentous pulp system and difficult to debride
root canals do not open at the apex of the root in primary teeth
when do we do a pulpotomy
irreversible pulpitis without abscess infection
what caujses irreversible pulptitis
caries
trauma
wear
What is carious exposure
pulp chamber is exposed to the oral cavity and bacteria air etc due to decay
what is a pulp polyp
caries is so bad there is only a shell of tooth around pulp tissue that is very swollen
this is overgrown due to bacteria etc and is broken with excavator
what pulp therapy do we do on vital teeth
pulp capping
pulpotomy
desensitising pulp therapy
when do we extract instead of pulp therapy
tooth is unrstorebale long term
pt uncooperative
medically compromised eg bleeding disorder
ortho extractions
what is a pulpotomy
Removal of the coronal portion of an exposed vital pulp
when would be not do a pulpotomy
abcess
no bleeding - tooth is dead
too much bleeding - indicates radicular inflammation
what medicaments are used
formocresol
ferric sulphate
gluteraldehyde
calcium hydroxide
what is formocresol and how does it work
tricesol - antiseptic
formalin - tissue fixative
binds bacterial and pulp proteins together so they dont decompose
is bacteriacidial and devitalising
tissue is fixed and inert to bacterial enzymes
why do we not use formocresol
mutagenic and carcinogenic properties found in animal studies
absorbed quick and goes into kidneys and liver etc
can leach into apical foramen and bad cos tooth germ is behind
devitalises 80-90% radicular pulp
what is ferric sulphate and how does it work
haemostatic - stops bleeding into pulp chamber
15% ferric sulphate in the lulp for 15 seconds
what is gluteraldehyde
aqueous solution 2-4%
powerful fixative discovered to have toxic effects
innfecetive compared to formocresol
linked to asthma
what is calcium hydroxide
allows dentine bridge of tertiary dentine to form due to irritant which cuts off inaffected radicular pulp from diseased coronal portion
encourages new dentine formation and creates a barrier from bacterial invasion
what is the clinical technique for pulpotomy
LA always necessary
isolate with DAM
outline form to access caries
caries removal and ensure margins are clear
remove caries from the cavity overlying pulpal roof so u can see horns
remove entire roof of pulp chamber but not the floor
remove contents of diseased pulp with excavator or slow speed bur
irrigate with saline and then pressure
apply medicament and restore with calcium hydroxide pulp base - medicament is what stops the bleeding
add zinc oxide eugenol into cavity
then SSC
what is always necessary for a pulpotomy
LA cos the tooth is vital
if there is excess bleeding what do we do
means there is possible inflammed radicular pulp;
do desensitising pulp therapy
pulpectomy
extract
what is desensitising pulpotomy
reduce pulpal inflammation and/or symptoms in order to facilitate extraction or pulpectomy
indicates carious exposure but no signs or symptoms of loss of vitality
also indicates hyperaemic or hyperalgasic pulp
how do we do desensitising pulpotomy
open access to chamber
dont use medicament, put on ledermix - mix of abx and steroid on exposed site
then restore with a well sealed temp restoration and review 7-10 days