Unit 3.5 Circulation & Gas Exchange
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/115
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:34 PM on 12/13/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
1
New cards
Circulation & Gas Exchange
1. **Circulatory Systems**
* Gastrovascular Cavities
* Open and Closed Circulatory Systems
* Organization in Vertebrates
a. Single Circulation
b. Double circulation
c. Evolutionary variation in double circulation
2. **Coordinated Cycles**
* Mammalian Circulation
* Mammalian Heart
* Heart’s Rhythmic Beat
3. **Blood Vessels**
* Blood Vessel Structure & Function
* Blood Flow Velocity
* Blood Pressure
* Capillary Function
* Fluid Return by Lymphatic System
4. **Blood**
* Blood Composition and Function
* Cardiovascular Disease
5. **Gas Exchange**
* Partial Pressure Gradients
* Respiratory Media
* Respiratory Surfaces
a. Gills (Aquatic Animals)
b. Tracheal Systems (Insects)
c. Lungs
6. **Breathing and Ventilation**
* Breathing in Amphibians
* Breathing in Birds
* Breathing in Mammals
* Breathing Control in Humans
7. **Adaptations for Gas Exchange**
* Coordination of Circulation and Gas Exchange
* Respiratory Pigments
* Respiratory Adaptations in Mammals
2
New cards
**oxygen, dioxide, diffusion,** uni, square
**Circulatory Systems**
* In exchange of materials, both required resources (ex. nutrients and **____**) and waste products (ex. **carbon _____**) must cross the plasma membrane to enter / exit the cell
* Small molecules move by **_____**
* Random thermal movement
* Difference in **concentration gradient**
causes net movement
* ___cellular organisms: exchange materials
with environment directly via diffusion
* Direct exchange **not possible** for
multicellular organisms
* Diffusion is slow: Time for a substance to diffuse is proportional to the ____ of the distance
* In exchange of materials, both required resources (ex. nutrients and **____**) and waste products (ex. **carbon _____**) must cross the plasma membrane to enter / exit the cell
* Small molecules move by **_____**
* Random thermal movement
* Difference in **concentration gradient**
causes net movement
* ___cellular organisms: exchange materials
with environment directly via diffusion
* Direct exchange **not possible** for
multicellular organisms
* Diffusion is slow: Time for a substance to diffuse is proportional to the ____ of the distance
3
New cards
direct, between, short
**Circulatory Systems**
* Two basic adaptations for efficient exchange in animals:
1. **Simple body plan**
* invertebrates, cnidarians, flatworms
* Body shape places many or all cells in ____ contact with the environment for direct exchange
2. **Circulatory system**
* systems move fluid ______ each cell’s immediate surroundings and the body tissue
* exchange with the environment and exchange with body tissues occur over ___ distances
* Two basic adaptations for efficient exchange in animals:
1. **Simple body plan**
* invertebrates, cnidarians, flatworms
* Body shape places many or all cells in ____ contact with the environment for direct exchange
2. **Circulatory system**
* systems move fluid ______ each cell’s immediate surroundings and the body tissue
* exchange with the environment and exchange with body tissues occur over ___ distances
4
New cards
Circulatory Systems
* Gastrovascular Cavities
* Open and Closed Circulatory Systems
* Organization in Vertebrates
a. Single Circulation
b. Double circulation
c. Evolutionary variation in double circulation
* Open and Closed Circulatory Systems
* Organization in Vertebrates
a. Single Circulation
b. Double circulation
c. Evolutionary variation in double circulation
5
New cards
Hydras, cnidarians, Planarians
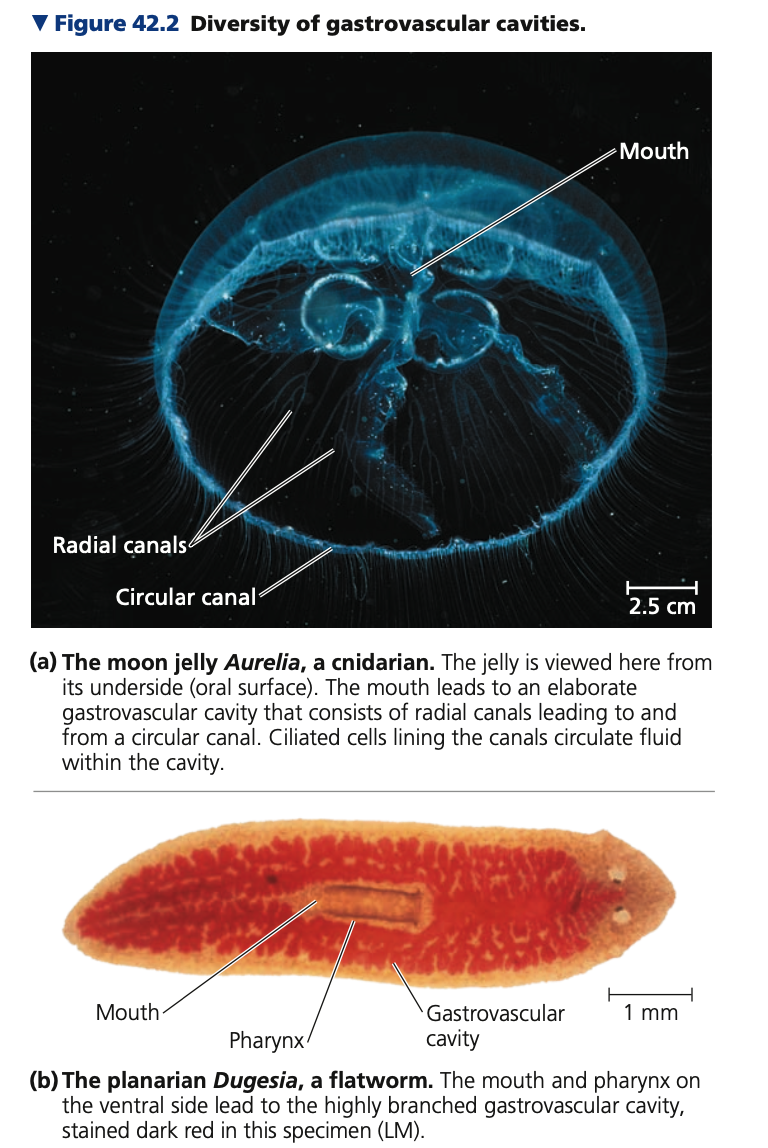
**Gastrovascular Cavities**
* Animals with **no distinct circulatory system**
* Their body shapes maximize contact between cells and environment
1. **______**
* thin branches of the gastrovascular cavity extend into tentacles
2. **Jellies and _____**
* more elaborate branching pattern
3. **______ and flatworms**
* Gastrovascular cavity + flat body = increased surface area, decreased diffusion distance -> efficient exchange
* Animals with **no distinct circulatory system**
* Their body shapes maximize contact between cells and environment
1. **______**
* thin branches of the gastrovascular cavity extend into tentacles
2. **Jellies and _____**
* more elaborate branching pattern
3. **______ and flatworms**
* Gastrovascular cavity + flat body = increased surface area, decreased diffusion distance -> efficient exchange
6
New cards
water, 2
**Gastrovascular Cavities**
* Functions in distribution of nutrients and digestion
* Opening at 1 end connects cavity to ____
* Fluid bathes inner and outer tissue layers to facilitate gas exchange and cellular waste
* Only cells that line the cavity have direct contact to nutrients released by digestion
* Body wall is only __ cells thick so nutrients only have to diffuse a short distance
* Functions in distribution of nutrients and digestion
* Opening at 1 end connects cavity to ____
* Fluid bathes inner and outer tissue layers to facilitate gas exchange and cellular waste
* Only cells that line the cavity have direct contact to nutrients released by digestion
* Body wall is only __ cells thick so nutrients only have to diffuse a short distance
7
New cards
2, **interstitial, hydrostatic**
**Open and Closed Circulatory Systems**
* 3 basic components
1. **Heart**
* Muscular pump that powers circulation
2. **Circulatory fluid**
3. **Interconnecting vessels**
\
* connects the aqueous environment of the body cells to the organs that exchange gases, absorb nutrients, and dispose of wastes
* In mammals, oxygen only diffuses across __ layers of cells in the lungs to reach blood
* the circulatory system carries oxygen rich blood around through vessels
* during circulation, oxygen diffuses to
**______ fluid** (fluid that bathes
cells)
* The **heart** powers **circulation** by using
metabolic energy to elevate the circulatory fluid’s **______ pressure** (pressure exerted on surrounding vessels)
* 3 basic components
1. **Heart**
* Muscular pump that powers circulation
2. **Circulatory fluid**
3. **Interconnecting vessels**
\
* connects the aqueous environment of the body cells to the organs that exchange gases, absorb nutrients, and dispose of wastes
* In mammals, oxygen only diffuses across __ layers of cells in the lungs to reach blood
* the circulatory system carries oxygen rich blood around through vessels
* during circulation, oxygen diffuses to
**______ fluid** (fluid that bathes
cells)
* The **heart** powers **circulation** by using
metabolic energy to elevate the circulatory fluid’s **______ pressure** (pressure exerted on surrounding vessels)
8
New cards
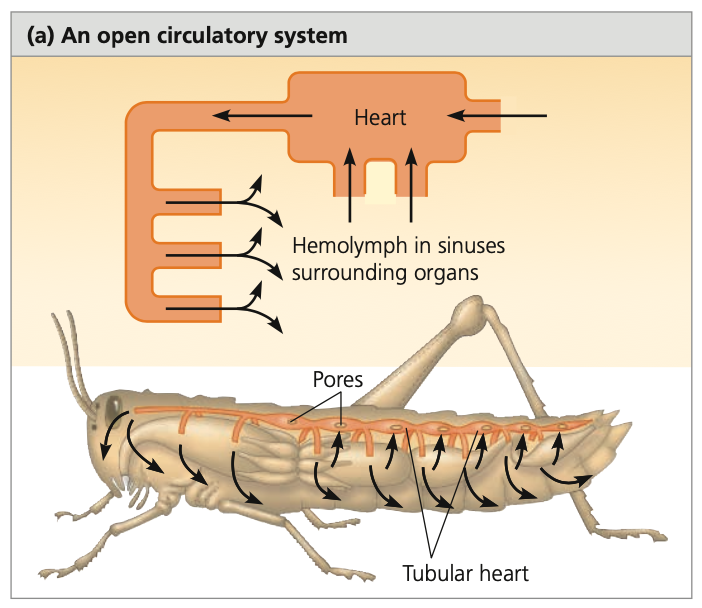
**hemolymph,** Arthropods, molluscs, pump, sinuses, pores, Lower
**Open Circulatory System**
* Circulatory fluid = interstitial fluid = ______
* ____ (ex. grasshoppers) and ______
* Larger crustaceans (ex. Lobsters and crabs)
* Have more extensive system of vessels and accessory _____
* Circulation:
* Heart contracts to pump hemolymph through vessels into interconnected _____ spaces surrounding organs)
* Inside the sinuses, hemolymph and body cells exchange materials
* Heart relaxes to draw back hemolymph through ____
* Pores have valves that close during contraction
* Body movements squeeze sinuses to assist in circulation
* Advantages:
* _____ hydrostatic pressure = less energy needed for the system
* n spiders, they use the hydrostatic pressure to extend their legs
* Circulatory fluid = interstitial fluid = ______
* ____ (ex. grasshoppers) and ______
* Larger crustaceans (ex. Lobsters and crabs)
* Have more extensive system of vessels and accessory _____
* Circulation:
* Heart contracts to pump hemolymph through vessels into interconnected _____ spaces surrounding organs)
* Inside the sinuses, hemolymph and body cells exchange materials
* Heart relaxes to draw back hemolymph through ____
* Pores have valves that close during contraction
* Body movements squeeze sinuses to assist in circulation
* Advantages:
* _____ hydrostatic pressure = less energy needed for the system
* n spiders, they use the hydrostatic pressure to extend their legs
9
New cards
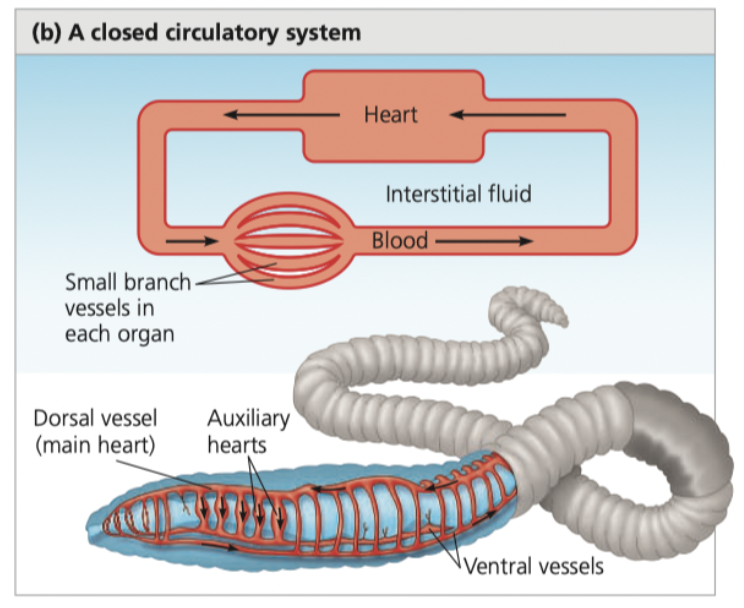
**blood,** interstitial, cells, annelids, cephalopods, vertebrates, High
**Closed Circulatory System**
* Circulatory fluid (confined to vessels) = **_____,** different to interstitial fluid
* heart/s pump blood into larger vessels that branch into smaller ones, which infiltrate tissues and organs
* Chemical exchange
* Between blood and ______ fluid
* Between interstitial fluid and body ____
* _____ (earthworms), ____ (squids and octopuses), and all _____
* Advantages:
* ___ blood pressure = effective delivery of oxygen and nutrients in
* Circulatory fluid (confined to vessels) = **_____,** different to interstitial fluid
* heart/s pump blood into larger vessels that branch into smaller ones, which infiltrate tissues and organs
* Chemical exchange
* Between blood and ______ fluid
* Between interstitial fluid and body ____
* _____ (earthworms), ____ (squids and octopuses), and all _____
* Advantages:
* ___ blood pressure = effective delivery of oxygen and nutrients in
10
New cards
Organization in vertebrates
a. Single Circulation
b. Double circulation
c. Evolutionary variation in double circulation
b. Double circulation
c. Evolutionary variation in double circulation
11
New cards
Cardiovascular system
➔ The system of heart and blood vessels in vertebrates \\n
◆ total length of blood vessels in an average human adult is **2X Earth’s circumference at the equator**
◆ total length of blood vessels in an average human adult is **2X Earth’s circumference at the equator**
12
New cards
2
* hearts of all vertebrates contain __ **or more muscular chambers**
1. **Atria (singular: atrium)**
* chambers that receive blood entering
the heart
2. **Ventricles**
* chambers responsible for pumping blood out of the heart
1. **Atria (singular: atrium)**
* chambers that receive blood entering
the heart
2. **Ventricles**
* chambers responsible for pumping blood out of the heart
13
New cards
Blood vessels
1. Arteries
2. Veins
3. Capillaries
14
New cards
Arteries
* carry blood from the heart toward
capillaries, to organs throughout the
body
* Branch out into **arterioles**
capillaries, to organs throughout the
body
* Branch out into **arterioles**
15
New cards
Arterioles
* Small blood vessels that connect **arteries** to **capillaries**
16
New cards
Capillaries
* Microscopic vessels with thin, porous walls
* Form networks called **capillary beds,** which infiltrate tissues, passing within a few cell diameters of every cell in the body
* Large surface area: main site of the exchange of gases / chemicals via diffusion
* Form networks called **capillary beds,** which infiltrate tissues, passing within a few cell diameters of every cell in the body
* Large surface area: main site of the exchange of gases / chemicals via diffusion
17
New cards
Venules
* Small blood vessels at the
downstream end of **capillaries** connecting to **veins**
downstream end of **capillaries** connecting to **veins**
18
New cards
Veins
* Carry back blood to the heart from capillaries
19
New cards
direction, portal
**Cardiovascular system**
* Important note: veins and arteries are **NOT distinguished** by the blood’s **oxygen content**
* Veins and arteries are distinguished by the ______ in which they carry blood
* Exception: _____ veins -> carry blood between pairs of capillary beds
* Ex: Hepatic portal vein -> blood from capillary beds in the digestive system to capillary beds in the liver.
* Important note: veins and arteries are **NOT distinguished** by the blood’s **oxygen content**
* Veins and arteries are distinguished by the ______ in which they carry blood
* Exception: _____ veins -> carry blood between pairs of capillary beds
* Ex: Hepatic portal vein -> blood from capillary beds in the digestive system to capillary beds in the liver.
20
New cards
Sharks, bony, 2, gills, vessel
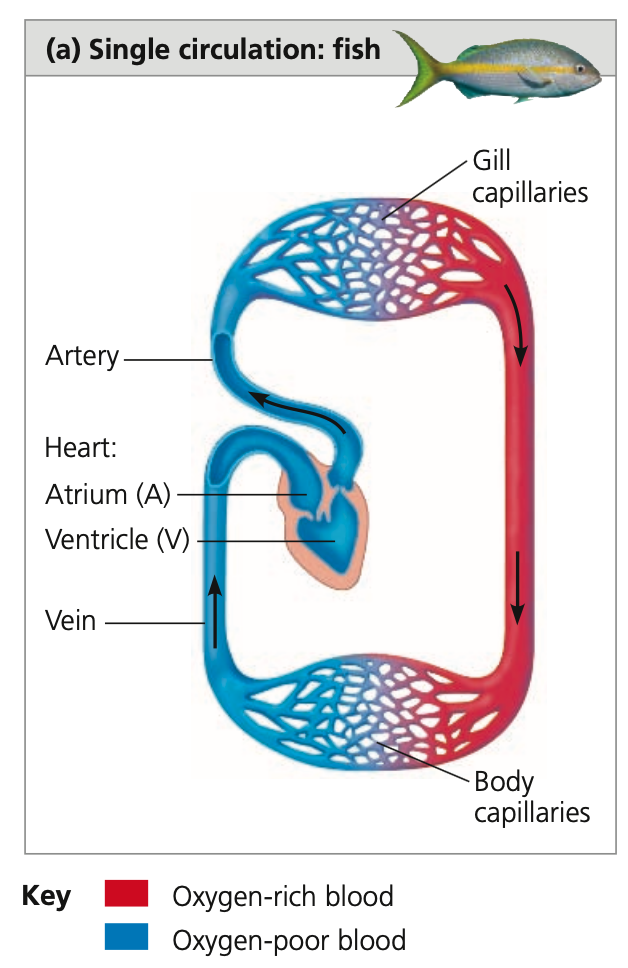
**Single Circulation**
* blood travels through the body and returns to its starting point **in a single circuit (loop)**
* __, rays, and ___ fishes
* **__** chambers: atrium and ventricle
* Atrium collects blood entering the heart
* Blood moves to ventricle, which contracts to pump blood into a capillary bed in the ___
* Net diffusion: oxygen enters blood, carbon dioxide leaves blood
* As blood leaves the gills, capillaries converge into a ____ that carries oxygen-rich blood to capillary beds throughout the body
* Following the gas exchange in capillary beds, blood enters veins to return to heart
* blood travels through the body and returns to its starting point **in a single circuit (loop)**
* __, rays, and ___ fishes
* **__** chambers: atrium and ventricle
* Atrium collects blood entering the heart
* Blood moves to ventricle, which contracts to pump blood into a capillary bed in the ___
* Net diffusion: oxygen enters blood, carbon dioxide leaves blood
* As blood leaves the gills, capillaries converge into a ____ that carries oxygen-rich blood to capillary beds throughout the body
* Following the gas exchange in capillary beds, blood enters veins to return to heart
21
New cards
2, **repressurizes,** pressure
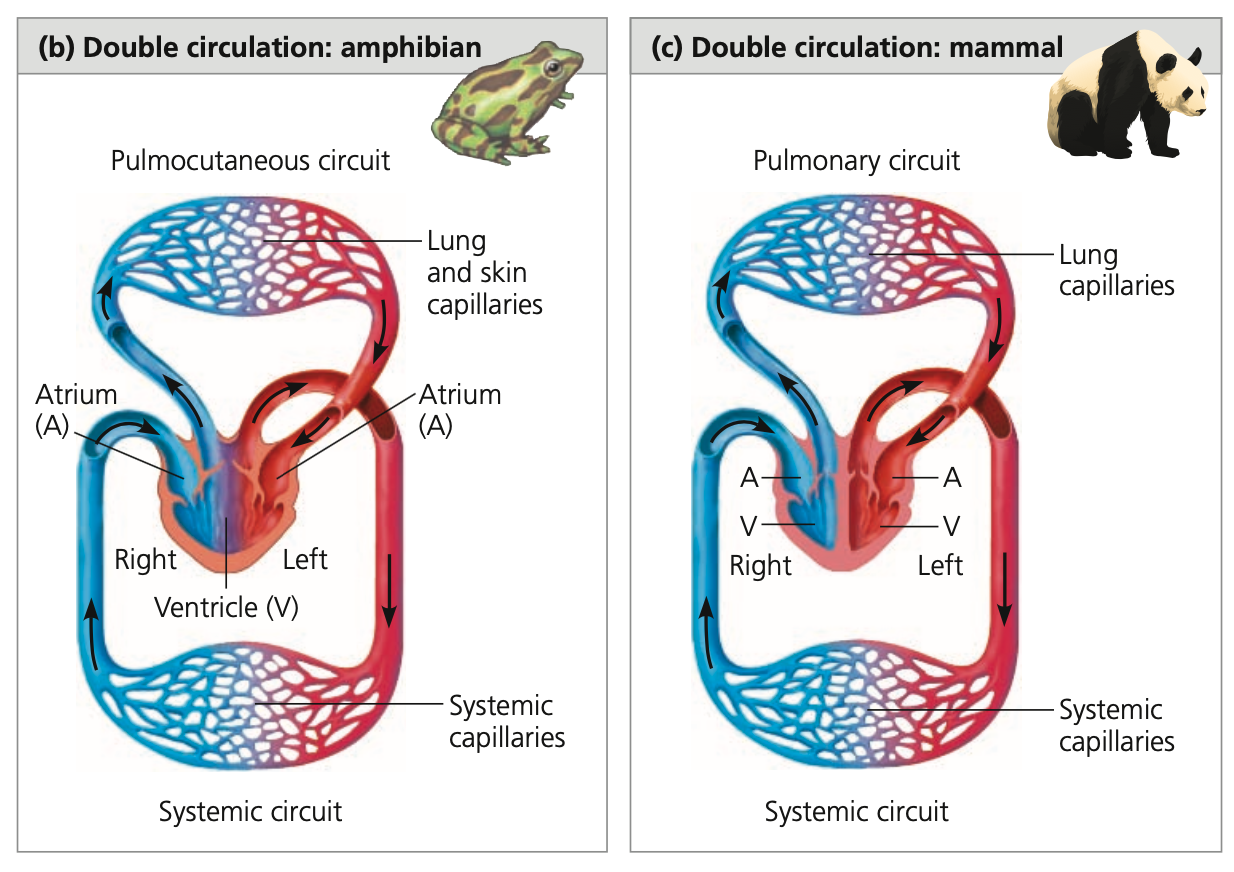
**Double Circulation**
* An arrangement wherein there are **_ circuits** of blood flow
* Pumps of the two circuits combine into the heart, simplifying coordination of the pumping cycles
* Amphibians, reptiles, and mammals
* Provides a vigorous flow of blood to the organs because the heart ______ the blood after it passes through the capillary beds of the lungs or skin
* Single circulation has reduced blood ______ in comparison because of direct gas exchangein
1. **Gas exchange circuit**
2. **Systemic circuit**
* An arrangement wherein there are **_ circuits** of blood flow
* Pumps of the two circuits combine into the heart, simplifying coordination of the pumping cycles
* Amphibians, reptiles, and mammals
* Provides a vigorous flow of blood to the organs because the heart ______ the blood after it passes through the capillary beds of the lungs or skin
* Single circulation has reduced blood ______ in comparison because of direct gas exchangein
1. **Gas exchange circuit**
2. **Systemic circuit**
22
New cards
right, poor, beds, Pulmonary, lungs, Pulmocutaneous, skin
**Gas exchange circuit**
* ____ side of the heart pumps oxygen ____ blood to the capillary ____ of the gas exchange tissues
* Net movement: oxygen in and carbon dioxide out
1. **______ circuit**
* In most vertebrates, reptiles, and mammals
* gas exchange takes place in the ____
2. **________ circuit**
* in amphibians
* because gas exchange takes place in capillaries in the lungs and ___
* ____ side of the heart pumps oxygen ____ blood to the capillary ____ of the gas exchange tissues
* Net movement: oxygen in and carbon dioxide out
1. **______ circuit**
* In most vertebrates, reptiles, and mammals
* gas exchange takes place in the ____
2. **________ circuit**
* in amphibians
* because gas exchange takes place in capillaries in the lungs and ___
23
New cards
left, rich, higher
**Systemic circuit**
* ____ side of the heart pumping oxygen-___blood from the gas exchange tissues to capillary beds in organs and tissues throughout the body
* Following the gas exchange, oxygen-poor blood returns to the right-side of heart, completing the circuit
* Often much _____ blood pressure than gas exchange circuit
* ____ side of the heart pumping oxygen-___blood from the gas exchange tissues to capillary beds in organs and tissues throughout the body
* Following the gas exchange, oxygen-poor blood returns to the right-side of heart, completing the circuit
* Often much _____ blood pressure than gas exchange circuit
24
New cards
intermittent
**Evolutionary variation in double circulation**
* some vertebrates with double circulation are _______ breathers
* amphibians and many reptiles fill their lungs with air periodically
* Long periods with no gas exchange, or rely on a different gas exchange tissue (ex. skin)
* some vertebrates with double circulation are _______ breathers
* amphibians and many reptiles fill their lungs with air periodically
* Long periods with no gas exchange, or rely on a different gas exchange tissue (ex. skin)
25
New cards
3, systemic, pulmocutaneous, incomplete, septum,
**Evolutionary variation in double circulation**
* **Frogs and other amphibians have a heart with __ chambers—two atria and one ventricle**
* Ridge with the ventricle
* Diverts most (about 90%) of
the oxygen-rich blood from the left atrium into the ______ circuit
* Diverts most of the oxygen-poor blood from the right atrium into the ______ circuit
* When underwater, the ______ division of the ventricle shuts off most blood flow to the lungs
* Blood flow continues to the skin, the sole site of gas exchange when submerged
* **In the 3-chambered heart of turtles, snakes, and lizards**
* incomplete _____ partially divides the single ventricle into right and left chambers
* 2 aortas (major arteries) lead to systemic circulation
* Similar to amphibians, controls relative amount of blood flow to lungs and body
* **Frogs and other amphibians have a heart with __ chambers—two atria and one ventricle**
* Ridge with the ventricle
* Diverts most (about 90%) of
the oxygen-rich blood from the left atrium into the ______ circuit
* Diverts most of the oxygen-poor blood from the right atrium into the ______ circuit
* When underwater, the ______ division of the ventricle shuts off most blood flow to the lungs
* Blood flow continues to the skin, the sole site of gas exchange when submerged
* **In the 3-chambered heart of turtles, snakes, and lizards**
* incomplete _____ partially divides the single ventricle into right and left chambers
* 2 aortas (major arteries) lead to systemic circulation
* Similar to amphibians, controls relative amount of blood flow to lungs and body
26
New cards
4, continuous, Endotherm, independently, convergent
**Evolutionary variation in double circulation**
* **_-chambered hearts of alligators and other crocodilians**
* Complete septum divides ventricles pulmonary and systemic circuits connect where the arteries exit the heart
* Connection allows arterial valves shunt blood flow away from lungs temporarily (when underwater)
* **In birds and mammals**
* Unlike others, has ______ breathing
* cannot vary blood flow to the lungs without varying blood flow throughout the body in parallel
* _______, meaning they use more energy than ectotherms (10x)
* So they need to deliver 10x amount of oxygen and fuel in their circulatory systems
* Adaptation -> separate and _______ powered systemic and pulmonary circuits and by large hearts
* In birds and mammals reflects ______ evolution
* **_-chambered hearts of alligators and other crocodilians**
* Complete septum divides ventricles pulmonary and systemic circuits connect where the arteries exit the heart
* Connection allows arterial valves shunt blood flow away from lungs temporarily (when underwater)
* **In birds and mammals**
* Unlike others, has ______ breathing
* cannot vary blood flow to the lungs without varying blood flow throughout the body in parallel
* _______, meaning they use more energy than ectotherms (10x)
* So they need to deliver 10x amount of oxygen and fuel in their circulatory systems
* Adaptation -> separate and _______ powered systemic and pulmonary circuits and by large hearts
* In birds and mammals reflects ______ evolution
27
New cards
Coordinated Cycles
* Mammalian Circulation
* Mammalian Heart
* Heart’s Rhythmic Beat
* Mammalian Heart
* Heart’s Rhythmic Beat
28
New cards
Right, arteries, beds, veins, atrium, ventricle, aorta, coronary, diffusion, venules, superior, inferior, atrium
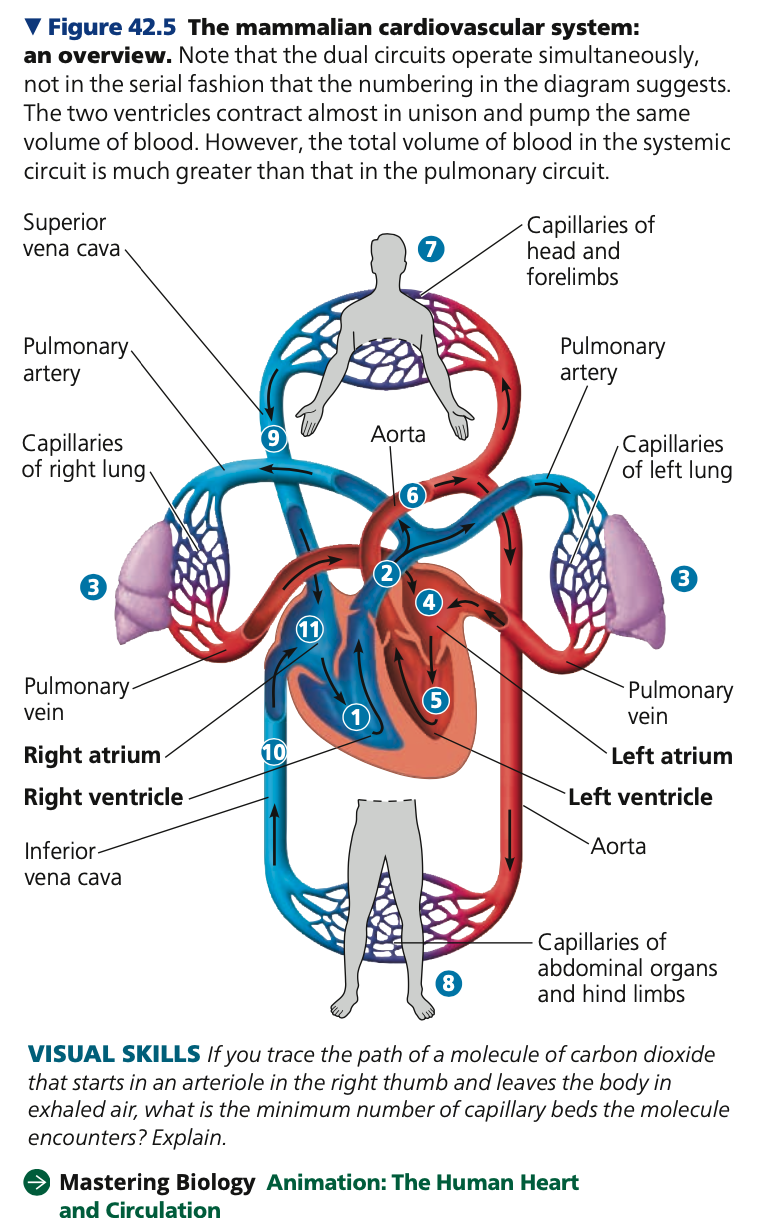
**Mammalian Circulation**
1. **____ ventricle** contracts and pumps
oxygen-poor blood -> **pulmonary _____** ->
lungs
2. Blood flows into **capillary ___** in both lungs,
loading oxygen and unloading carbon
dioxide
3. Oxygen-rich blood returns from the lungs ->
**pulmonary** -> **left ____** -> **left _____** -> body tissues through the systemic circuit
4. Blood leaves via **____** -> arteries throughout the body
1. Aorta branches into **_____ arteries** which supply blood to the heart muscle itself
2. Aorta branches into capillary beds in the head and arms (forelimbs)
3. Aorta descends into abdomen -> arteries -> capillary beds in the abdominal organs and legs (hindlimbs)
5. Within the capillary beds, throughout the body, **net _____**: oxygen from blood to the tissues, carbon dioxide (produced by cellular respiration) into blood.
6. Capillaries rejoin, forming **_____** -> lead to **veins**
1. Oxygen-poor blood -> head, neck, limbs channel into **_____ vena cava**
2. Oxygen-poor blood -> trunk and hindlimbs into **____ vena cava**
7. **Venae cavae** -> **right ____** -> **right ventricle**
1. **____ ventricle** contracts and pumps
oxygen-poor blood -> **pulmonary _____** ->
lungs
2. Blood flows into **capillary ___** in both lungs,
loading oxygen and unloading carbon
dioxide
3. Oxygen-rich blood returns from the lungs ->
**pulmonary** -> **left ____** -> **left _____** -> body tissues through the systemic circuit
4. Blood leaves via **____** -> arteries throughout the body
1. Aorta branches into **_____ arteries** which supply blood to the heart muscle itself
2. Aorta branches into capillary beds in the head and arms (forelimbs)
3. Aorta descends into abdomen -> arteries -> capillary beds in the abdominal organs and legs (hindlimbs)
5. Within the capillary beds, throughout the body, **net _____**: oxygen from blood to the tissues, carbon dioxide (produced by cellular respiration) into blood.
6. Capillaries rejoin, forming **_____** -> lead to **veins**
1. Oxygen-poor blood -> head, neck, limbs channel into **_____ vena cava**
2. Oxygen-poor blood -> trunk and hindlimbs into **____ vena cava**
7. **Venae cavae** -> **right ____** -> **right ventricle**
29
New cards
sternum, thin, thick, force, volume
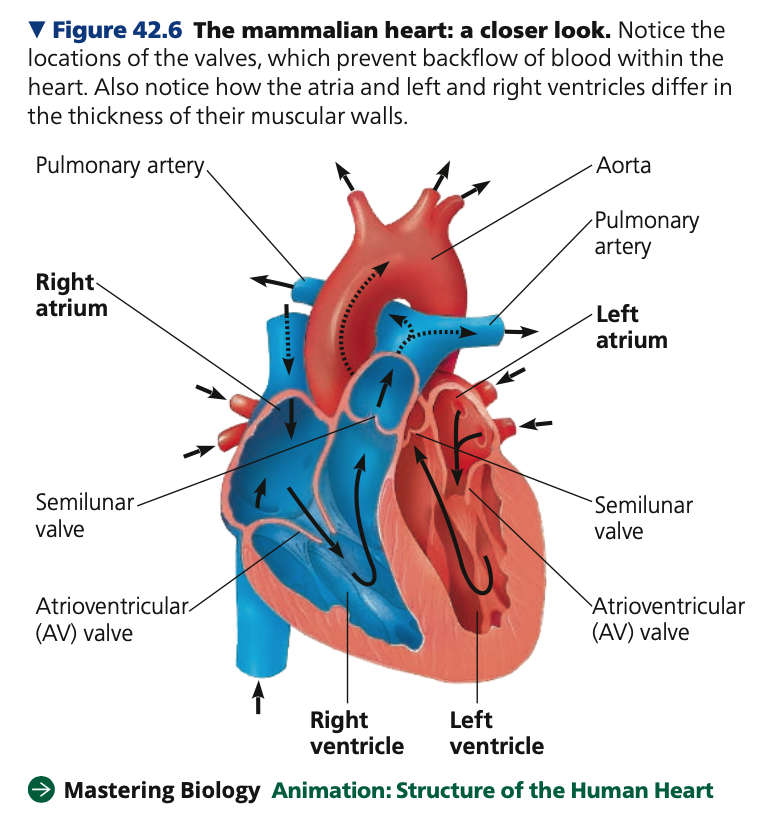
**Mammalian Heart**
* size of a clenched fist and consists mostly of cardiac muscle
* Located behind the _____ (breastbone)
1. **2 atria**
* Blood collection ___-walled upper chambers
* receiving blood returning from lungs and tissues
* Much of the blood that enters the atria flows into the ventricles while all four heart chambers are relaxed
* The remainder is transported by the atria contracting right before the ventricles contract
2. **2 ventricles**
* Blood collection, ____-walled lower chambers
* Pumps blood away throughout the body via systemic circulation
* Left ventricle > right ventricle in terms of ____ during contraction
* Left ventricle = right ventricle in terms of ______ of blood pumped when contracted
* size of a clenched fist and consists mostly of cardiac muscle
* Located behind the _____ (breastbone)
1. **2 atria**
* Blood collection ___-walled upper chambers
* receiving blood returning from lungs and tissues
* Much of the blood that enters the atria flows into the ventricles while all four heart chambers are relaxed
* The remainder is transported by the atria contracting right before the ventricles contract
2. **2 ventricles**
* Blood collection, ____-walled lower chambers
* Pumps blood away throughout the body via systemic circulation
* Left ventricle > right ventricle in terms of ____ during contraction
* Left ventricle = right ventricle in terms of ______ of blood pumped when contracted
30
New cards
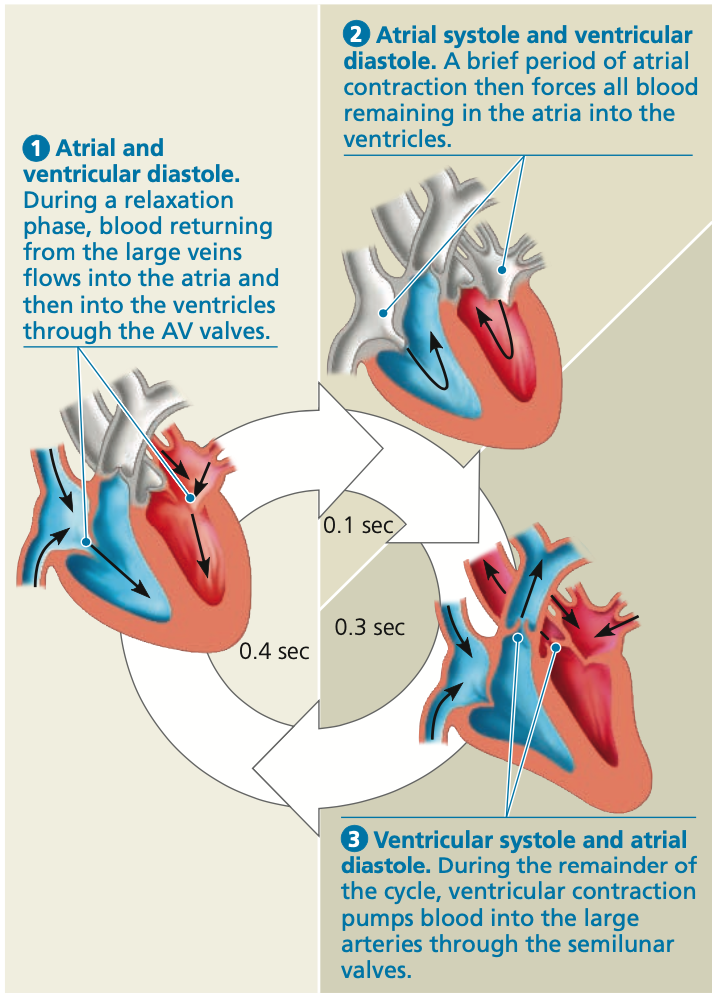
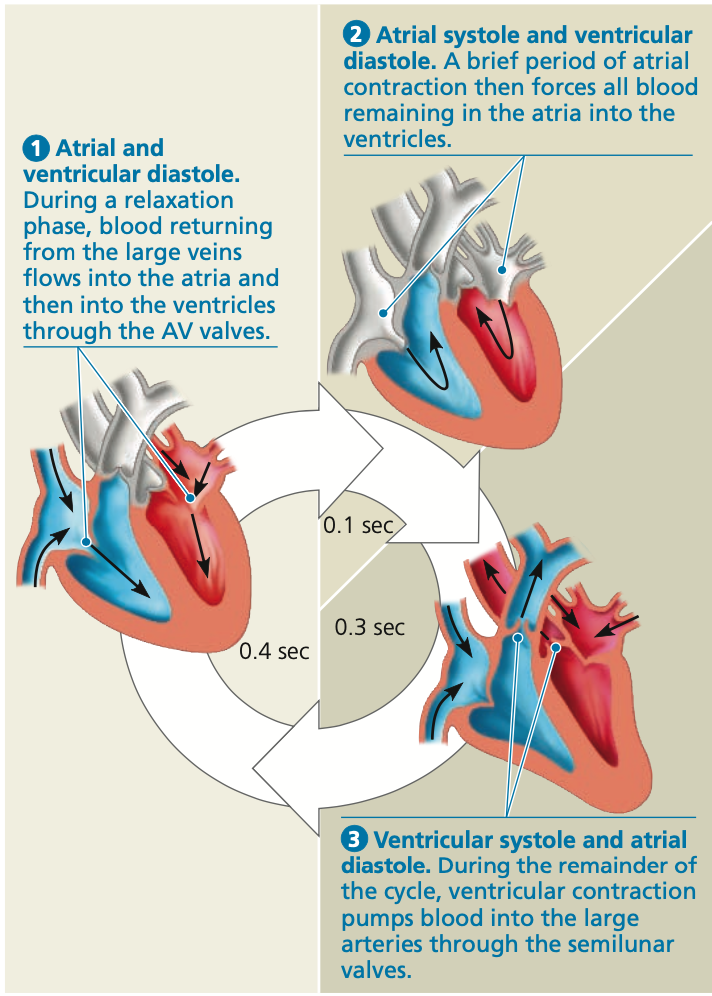
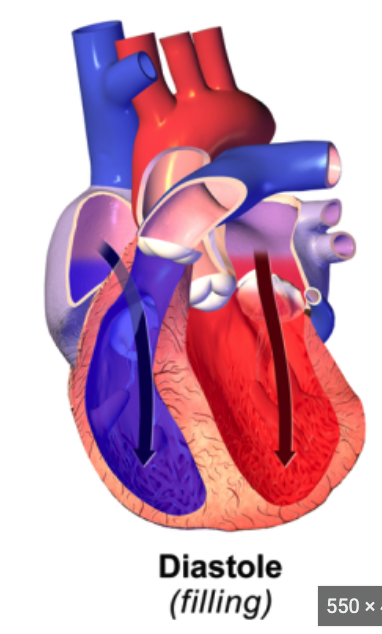
Cardiac cycle
* complete sequence of pumping and filling of blood
31
New cards
Systole
* **contraction** phase of the cycle
32
New cards
Diastole
* **Relaxation** phase of the cycle
33
New cards
volume, exercise
**Cardiac output**
* _____ of blood each ventricle pumps per minute
* **Heart rate x stroke volume**
* In humans: 5L/min
* Product (72 bpm x 70 mL)
* Equal to the total amount of blood in the body
* increased oxygen demand during _____ = increase in cardiac output (up to 5x)
* Affected by 2 factors:
1. Heart rate
2. Stroe volum
* _____ of blood each ventricle pumps per minute
* **Heart rate x stroke volume**
* In humans: 5L/min
* Product (72 bpm x 70 mL)
* Equal to the total amount of blood in the body
* increased oxygen demand during _____ = increase in cardiac output (up to 5x)
* Affected by 2 factors:
1. Heart rate
2. Stroe volum
34
New cards
Heart rate
* rate of **contraction** (number of beats per minute)
* Typical resting heart rate in humans: **72 bpm** (beats per minute)
* Typical resting heart rate in humans: **72 bpm** (beats per minute)
35
New cards
Stroke volume
* **amount** of blood pumped by a ventricle in a single contraction
* Average stroke volume in humans: **70 mL**
* Average stroke volume in humans: **70 mL**
36
New cards
**connective**
**Valves**
* Flaps of **_______ tissue** that prevents **backflow** of blood
* Ensures blood moves in the same direction
* Open when pushed from one side, closed when pushed from the other
1. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid, mitral/bicuspid)
2. Semilunar valves (pulmonary, aortic)
* Flaps of **_______ tissue** that prevents **backflow** of blood
* Ensures blood moves in the same direction
* Open when pushed from one side, closed when pushed from the other
1. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid, mitral/bicuspid)
2. Semilunar valves (pulmonary, aortic)
37
New cards
fibers, **closes,** Right, left
1. **Atrioventricular valves**
* Between each atrium and ventricle
* anchored by strong _____ that prevent them from turning inside out during ventricular systole
* The pressure from ventricles **contracting ____** the valves, preventing backflow into atria
**a. Tricuspid valve**
■ ____ AV
**b. Mitral (Bicuspid) valve**
■ ____ AV
38
New cards
**exits,** artery, aorta, **opens**
2. **Semilunar valves**
* At the **___** of the heart
**a. Pulmonary semilunar valve**
■ where the pulmonary ____ leaves the right ventricle
**b. Aortic semilunar valve** \n ■ where the ____ leaves the left ventricle
* The pressure from ventricles **contracting ____** the valves
* The ventricles relaxing -> built up blood pressure in the pulmonary artery and aorta -> closes the valve
39
New cards
Lub, dup
**Mammalian Heart**
* “lub-dup, lub-dup, lub-dup” -> sound of the heart during a stethoscope that reflects the
* ___ - recoil of blood against the closed AV valves
* ___ - vibrations caused by closing of the semilunar valves
* “lub-dup, lub-dup, lub-dup” -> sound of the heart during a stethoscope that reflects the
* ___ - recoil of blood against the closed AV valves
* ___ - vibrations caused by closing of the semilunar valves
40
New cards
Heart murmur
* Abnormal sound produced when blood squirts back through a defective valve
* May be congenital or from an infection
* But not always caused by a defect and does not always need surgery
* When severe, may need a mechanical replacement valve
* May be congenital or from an infection
* But not always caused by a defect and does not always need surgery
* When severe, may need a mechanical replacement valve
41
New cards
autorhythmic
**Heart’s Rhythmic Beat**
* Heartbeat originates in the heart itself for vertebrates
* some cardiac muscle cells are ______ = can contract and relax repeatedly without any signal from the nervous system
* Heartbeat originates in the heart itself for vertebrates
* some cardiac muscle cells are ______ = can contract and relax repeatedly without any signal from the nervous system
42
New cards
**right, pacemaker,** electrical, gap, fluids
**Sinonatrial (SA) node**
* Cluster of autorhythmic cells found in the wall of the **___ atrium**
* The heart’s **______;** sets the **rate** and **timing** at which all cardiac muscle cells contract
* Some arthropods have pacemakers in the nervous system
* produces ______ impulses like nerve cells
* Cardiac muscle cells are electrically coupled through ___ junctions
* Impulses spread within heart tissue, generating currents that can be measured when they reach the skin via body ___
* Cluster of autorhythmic cells found in the wall of the **___ atrium**
* The heart’s **______;** sets the **rate** and **timing** at which all cardiac muscle cells contract
* Some arthropods have pacemakers in the nervous system
* produces ______ impulses like nerve cells
* Cardiac muscle cells are electrically coupled through ___ junctions
* Impulses spread within heart tissue, generating currents that can be measured when they reach the skin via body ___
43
New cards
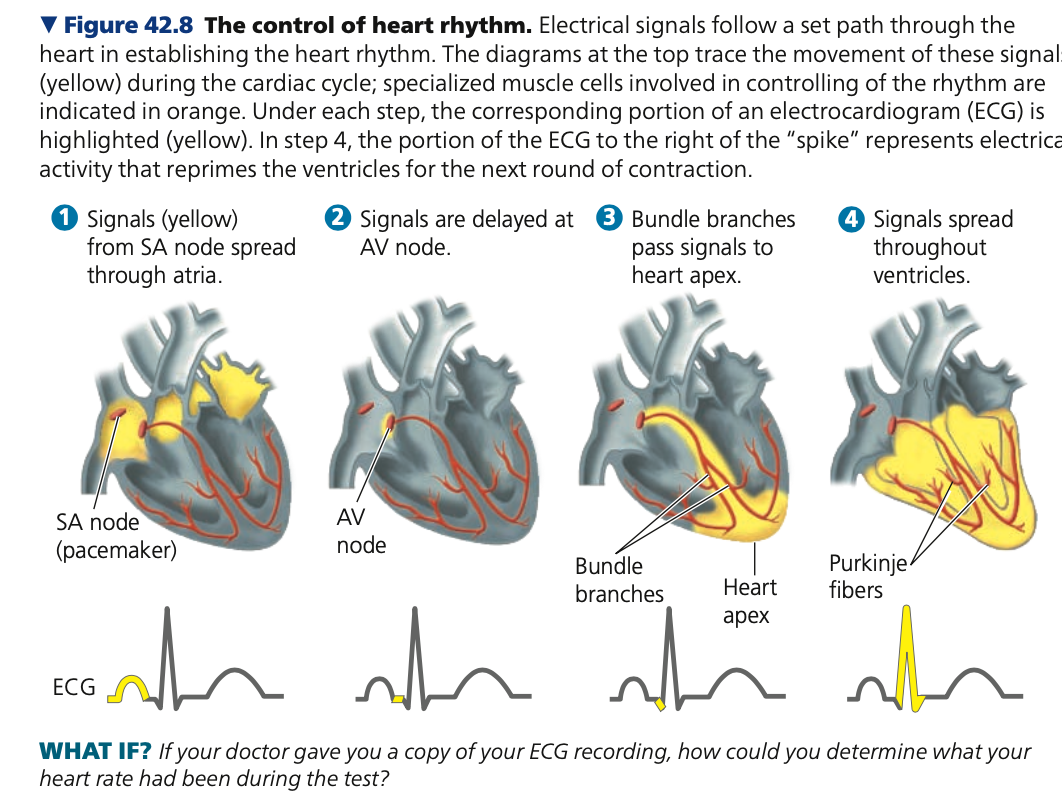
electrodes, cycle, atrioventricular
**Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG)**
* ______ placed on the skin record the currents to measure electrical activity of the heart
* graph of current against time has a shape that represents the stages in the cardiac ____
* Impulses from SA node spread through the walls of the atria, causing contraction
* Impulses reach other autorhythmic cells in the atria, which form a relay point called the _______ node (AV)
* ______ placed on the skin record the currents to measure electrical activity of the heart
* graph of current against time has a shape that represents the stages in the cardiac ____
* Impulses from SA node spread through the walls of the atria, causing contraction
* Impulses reach other autorhythmic cells in the atria, which form a relay point called the _______ node (AV)
44
New cards
connects, delays, apex, Purkinje
**Atrioventricular node**
* electrically ______ the heart's atria and ventricles
* ____ signal between atria and ventricles, allowing the atria to empty completely (before the ventricle contracts and fills)
* After the delay, signals are conducted to the heart and throughout ventricular walls by specialized structures called bundle branches and ______ fibers
* electrically ______ the heart's atria and ventricles
* ____ signal between atria and ventricles, allowing the atria to empty completely (before the ventricle contracts and fills)
* After the delay, signals are conducted to the heart and throughout ventricular walls by specialized structures called bundle branches and ______ fibers
45
New cards
**Physiological,** sympathetic, parasympathetic, **Hormones,** temperature
**Heart’s Rhythmic Beat**
* **_______ cues** alter heart tempo by regulating the pacemaker function of the SA node
* Sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the nervous system are responsible
* more active: _______ division speeds up the pacemaker, increasing heart rate to meet higher oxygen demand
* less active: the _______ division slows down pacemaker, decreases heart rate, conserving energy
* **_____** also affect the pacemaker
* Ex: Epinephrine and norepinephrine speeds it up
* Increased ______ speeds up pacemaker, higher heart rate
* **_______ cues** alter heart tempo by regulating the pacemaker function of the SA node
* Sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the nervous system are responsible
* more active: _______ division speeds up the pacemaker, increasing heart rate to meet higher oxygen demand
* less active: the _______ division slows down pacemaker, decreases heart rate, conserving energy
* **_____** also affect the pacemaker
* Ex: Epinephrine and norepinephrine speeds it up
* Increased ______ speeds up pacemaker, higher heart rate
46
New cards
Blood Vessels
* Blood Vessel Structure & Function
* Blood Flow Velocity
* Blood Pressure
a. Changes during cardiac cycle
b. Regulation of blood pressure
c. Blood pressure & gravity
* Capillary Function
* Fluid Return by Lymphatic System
* Blood Flow Velocity
* Blood Pressure
a. Changes during cardiac cycle
b. Regulation of blood pressure
c. Blood pressure & gravity
* Capillary Function
* Fluid Return by Lymphatic System
47
New cards
Blood Vessel Structure & Function
1. Capillaries
2. Arteries & veins
48
New cards
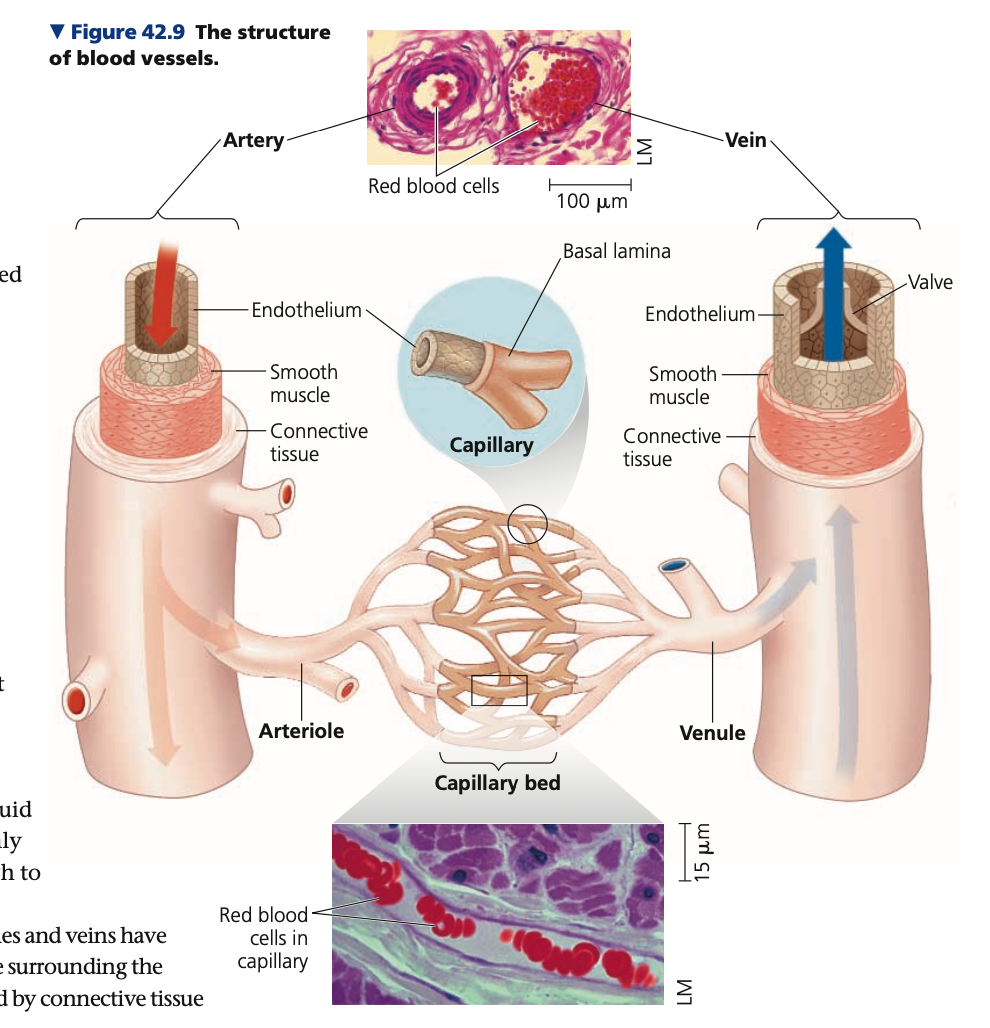
single, **lumen,** resistance
**Endothelium**
* A __ layer of flat epithelium line the central _____ (cavity) of all blood cells
* minimizes ______ to fluid flow
* Surrounded by tissue layers that differ depending on the type of blood tissue
* A __ layer of flat epithelium line the central _____ (cavity) of all blood cells
* minimizes ______ to fluid flow
* Surrounded by tissue layers that differ depending on the type of blood tissue
49
New cards
RBC, lamina, interstitial
1. Capillaries
* Smallest blood vessels
* Diameter only slightly greater than a ___
* Very thin walls consisting of an endothelium and basal _____ (one surrounding extracellular layer)
* Only site for exchange of substances between blood and ______ fluid because of very thin walls
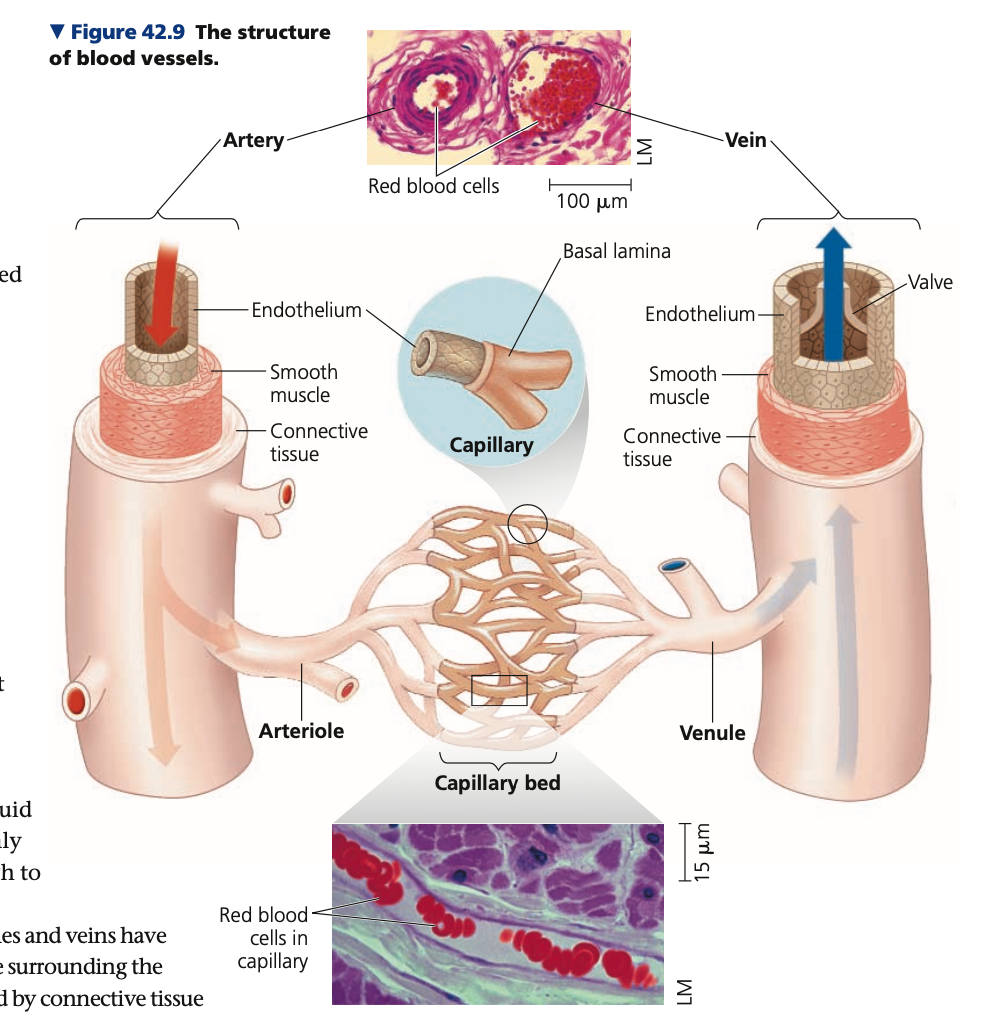
50
New cards
2, connective, elastic, collagen, smooth, elastic, pressure, 1/3, unidirectional
2. **Arteries & veins**
* __ layers surround the endothelium (outer and inner)
* Outer - ____ tissues, ___ fibers (to allow stretch and recoil) and ______ ( for strength)
* Inner - ___ muscle and more ___ fibers
* **Arterial walls are thick, strong, elastic**
* To accommodate high blood
______ (BP) and recoil
* nervous system signals and hormones act on smooth muscle in arteries and arterioles -> dilation or constriction to regulate blood flow
* **Vein walls are about __ as thick as an artery since lower BP to accommodate**
* Unlike arteries, have valves to maintain a ______ flow of blood despite low BP
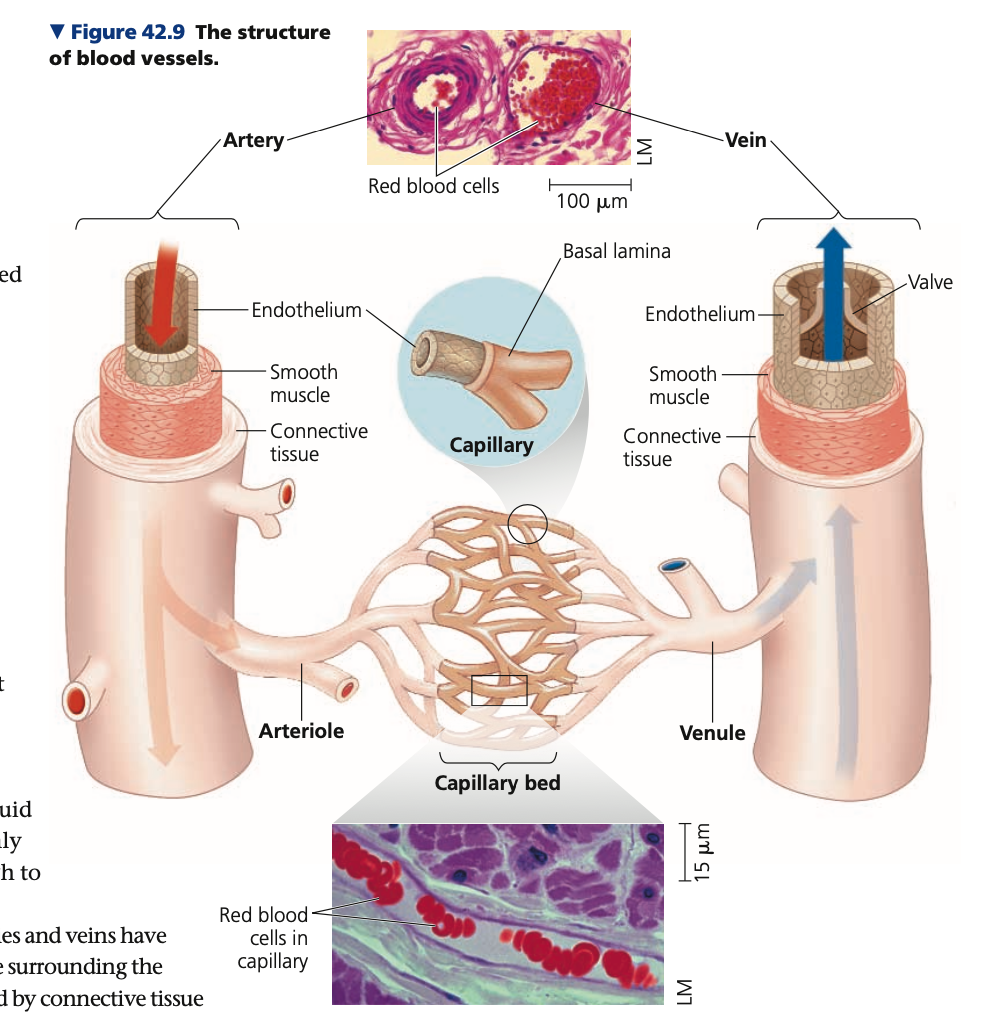
51
New cards
slows, cross-sectional, venules
**Blood Flow Velocity**
* blood ____ as it moves from arteries to arterioles to the much narrower capillaries
* Because the total cross-sectional area of capillaries > arteries and other parts of the circulatory system
* 500x more slowly in the capillaries (aorta- 48cm/sec, capillaries- 0.1cm/sec)
* Increase in ________ area -> decrease in velocity
* Blood speeds up moving from capillaries to _____ and veins because total cross-sectional area decreases
* blood ____ as it moves from arteries to arterioles to the much narrower capillaries
* Because the total cross-sectional area of capillaries > arteries and other parts of the circulatory system
* 500x more slowly in the capillaries (aorta- 48cm/sec, capillaries- 0.1cm/sec)
* Increase in ________ area -> decrease in velocity
* Blood speeds up moving from capillaries to _____ and veins because total cross-sectional area decreases
52
New cards
lengthwise, sideways, **recoil,** resistance
**Blood Pressure**
* Like all fluids, blood moves from areas of **high to low pressure**
* Heart ventricle contracts, generating blood pressure, exerting a force in all directions
* part of the force directed **_______** in an artery causes the blood to flow away from the heart (the site of highest pressure)
* Part of the force directed _______ stretches the wall of artery
* Ventricle contracts -> elastic arterial walls **____**, maintaining BP and blood flow
* Once blood enters tinier vessels (arterioles and capillaries), the small diameters generate substantial ______ to flow
* Like all fluids, blood moves from areas of **high to low pressure**
* Heart ventricle contracts, generating blood pressure, exerting a force in all directions
* part of the force directed **_______** in an artery causes the blood to flow away from the heart (the site of highest pressure)
* Part of the force directed _______ stretches the wall of artery
* Ventricle contracts -> elastic arterial walls **____**, maintaining BP and blood flow
* Once blood enters tinier vessels (arterioles and capillaries), the small diameters generate substantial ______ to flow
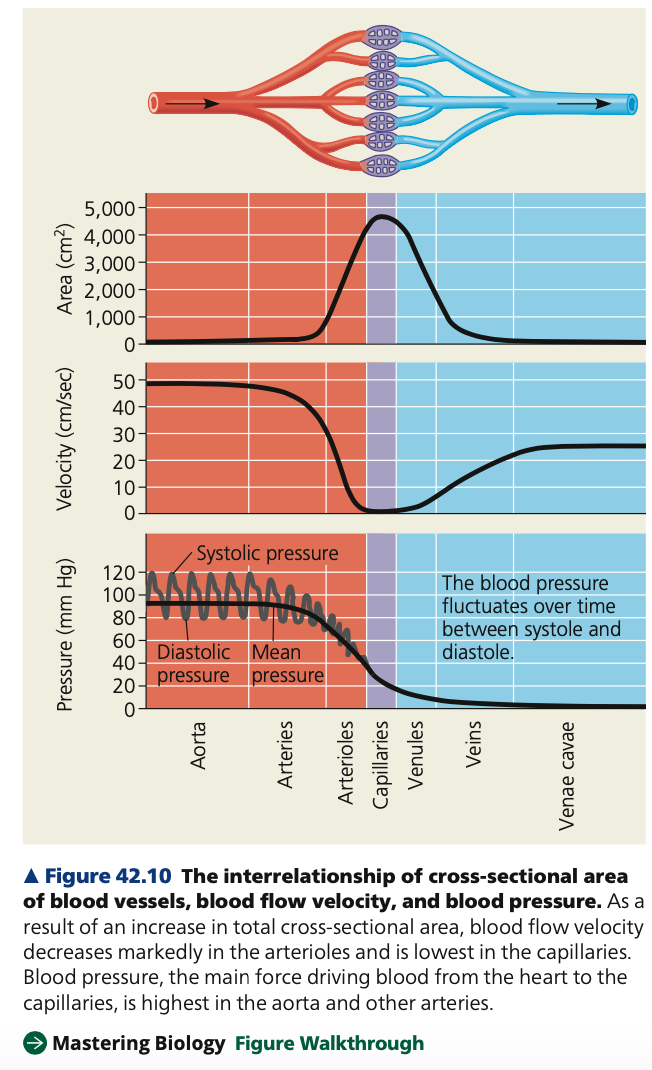
53
New cards
Blood pressure
a. Changes during cardiac cycle
b. Regulation of blood pressure
c. Blood pressure & gravity
b. Regulation of blood pressure
c. Blood pressure & gravity
54
New cards
Changes during cardiac cycle
1. Systolic pressure
2. Diastolic pressure
55
New cards
**highest,** arterial, faster
**Systolic pressure**
* arterial BP at its **______**, when the heart contracts during ventricular systole
* Each contraction spikes BP and stretches ______ walls, cause them to bulge, which is the pulse we feel
* Felt on the inner wrist
* Pressure surge partly due to narrow openings of arterioles impeding exit of blood from arteries
* Blood enters ____ than it can leave, so vessels stretch wider due to increased BP
* arterial BP at its **______**, when the heart contracts during ventricular systole
* Each contraction spikes BP and stretches ______ walls, cause them to bulge, which is the pulse we feel
* Felt on the inner wrist
* Pressure surge partly due to narrow openings of arterioles impeding exit of blood from arteries
* Blood enters ____ than it can leave, so vessels stretch wider due to increased BP
56
New cards
**Lower,** arteries, contracts
**Diastolic pressure**
* **____** but substantial pressure when
the ventricles **relax** during **diastole**;
* elastic walls of _____ snap back
* Before enough blood flows into arterioles to completely relieve arterial pressure, heart _____ again
* Keeps arteries pressurized continuously to maintain blood flow
* **____** but substantial pressure when
the ventricles **relax** during **diastole**;
* elastic walls of _____ snap back
* Before enough blood flows into arterioles to completely relieve arterial pressure, heart _____ again
* Keeps arteries pressurized continuously to maintain blood flow
57
New cards
Regulation of blood pressure
* Homeostatic mechanisms **alter the diameter of arterioles** to regulate arterial blood pressure
1. Vasodilation
2. Vasoconstriction
1. Vasodilation
2. Vasoconstriction
58
New cards
Vasoconstriction
* smooth muscles in arteries contract -> arterioles narrow
59
New cards
Vasodilation
* smooth muscles in arteries relax -> arterioles widen, lowering arterial B
60
New cards
vasodilation, increases
**Regulation of blood pressure**
* These two processes are often coupled to changes in cardiac output that also affect BP
* To meet adequate blood flow and changing demands of the body
* Heavy exercise -> _______ in working muscles to meet higher oxygen demand
* The cardiac output ______ at the same time so BP doesnt drop while still supporting increased blood flow
* These two processes are often coupled to changes in cardiac output that also affect BP
* To meet adequate blood flow and changing demands of the body
* Heavy exercise -> _______ in working muscles to meet higher oxygen demand
* The cardiac output ______ at the same time so BP doesnt drop while still supporting increased blood flow
61
New cards
artery, 120, 70
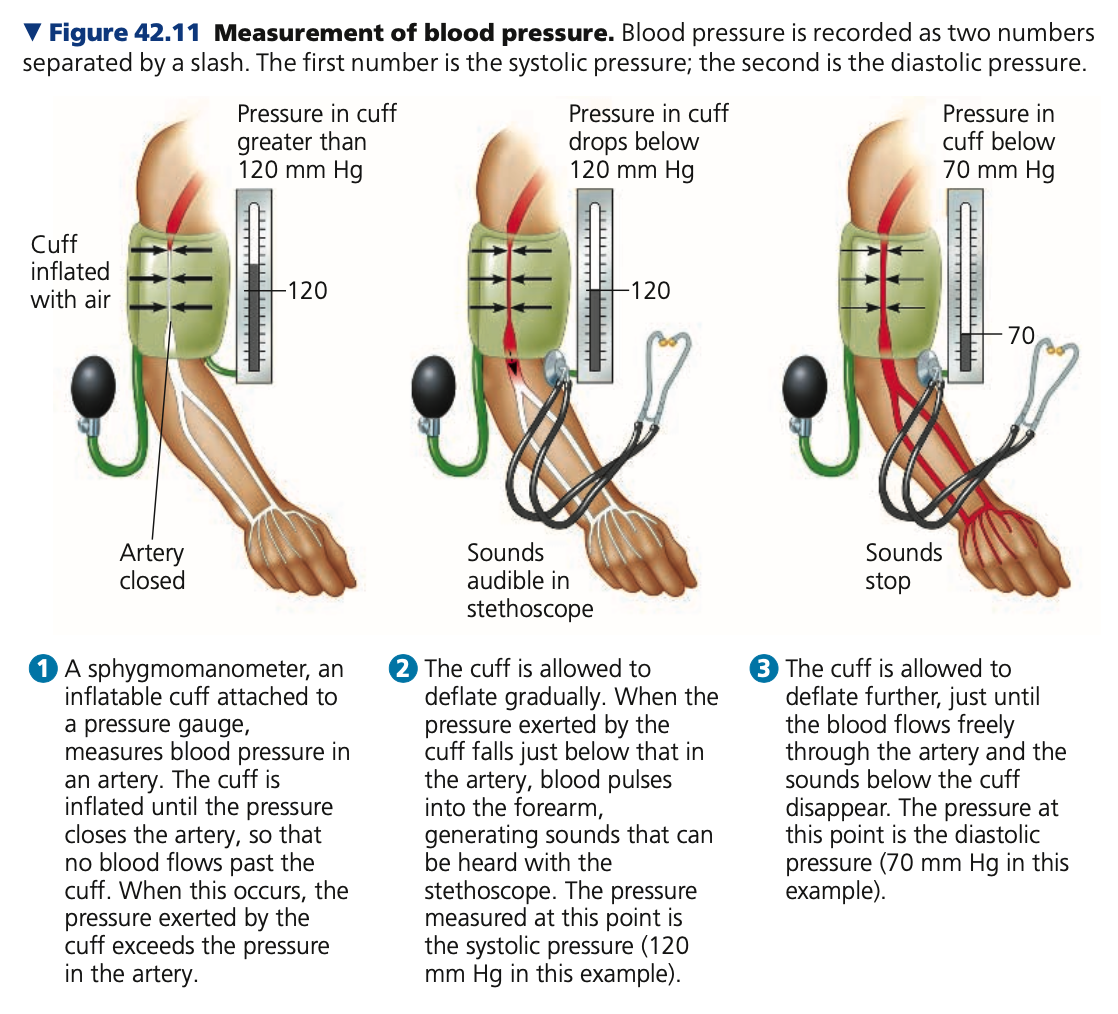
**Blood pressure & gravity**
* BP is generally measured for an _____ in the arm at the same height as the heart
* For a healthy 20 year old human at rest, the arterial BP is:
* ___ mm Hg (mercury) at systole
* __ mm Hg at diastole
* Expressed as 120/70 (systole/diastole)
* BP is generally measured for an _____ in the arm at the same height as the heart
* For a healthy 20 year old human at rest, the arterial BP is:
* ___ mm Hg (mercury) at systole
* __ mm Hg at diastole
* Expressed as 120/70 (systole/diastole)
62
New cards
less, **Fainting,** level, high, reduce
**Blood pressure & gravity**
* Gravity greatly affects BP: when standing, your head is higher (0.53 m higher) than your chest so the BP in your brain is ___ than near the heart by \~27 mm Hg
* **______ response**
* Nervous system detects that
the **BP in your brain** is below the level needed to provide adequate blood flow
* Casues **collapse** so that the head is at the ____ of the heart, to increase blood flow in the brain
* Animals with long necks: need ___ BP to overcome gravity
* Giraffe - need 250 mm Hg systolic pressure at the heart to get blood to its head (when standing straight)
* When lowering head, to drink, one-way valves, sinuses, and feedback mechanisms _____ cardiac output to lower BP in the head to prevent brain damage
* Dinosaurs with 10m long necks need \~760 mmHg systolic pressure at the heart when head is fully raised
* Data suggests that they did not have a heart strong enough to generate this BP
* Instead, they fed closer to the groun
* Gravity greatly affects BP: when standing, your head is higher (0.53 m higher) than your chest so the BP in your brain is ___ than near the heart by \~27 mm Hg
* **______ response**
* Nervous system detects that
the **BP in your brain** is below the level needed to provide adequate blood flow
* Casues **collapse** so that the head is at the ____ of the heart, to increase blood flow in the brain
* Animals with long necks: need ___ BP to overcome gravity
* Giraffe - need 250 mm Hg systolic pressure at the heart to get blood to its head (when standing straight)
* When lowering head, to drink, one-way valves, sinuses, and feedback mechanisms _____ cardiac output to lower BP in the head to prevent brain damage
* Dinosaurs with 10m long necks need \~760 mmHg systolic pressure at the heart when head is fully raised
* Data suggests that they did not have a heart strong enough to generate this BP
* Instead, they fed closer to the groun
63
New cards
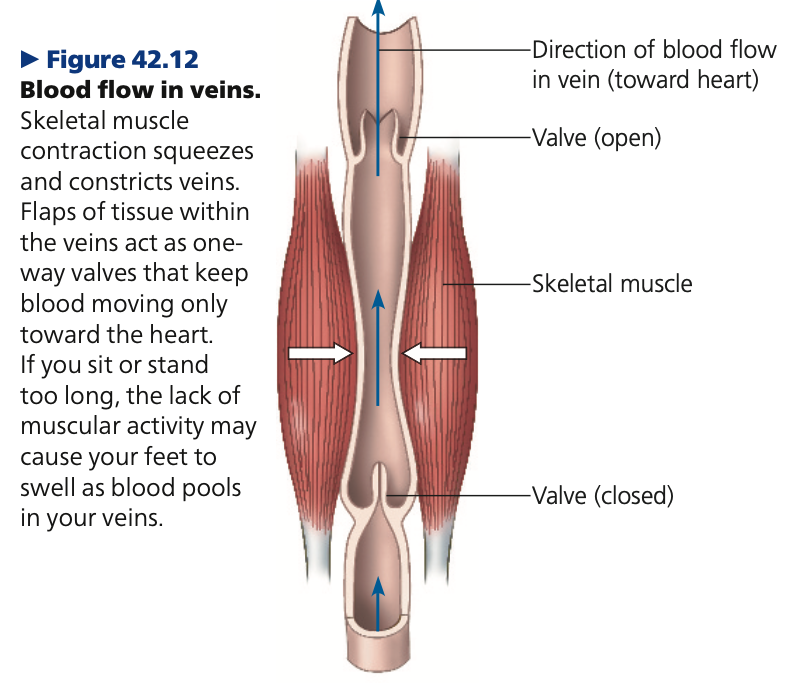
veins, legs, rhythmic, skeletal, moderate
**Blood pressure & gravity**
* Gravity affects blood flow in __*,*__ ___ especially **in the ___**
* Gravity draws blood downward to your feet, impeding its return to the heart
* Have valves to maintain the unidirectional flow of return to heart, since BP in veins is relatively low
* _______ contractions of smooth muscles also help in movement
* contraction of ______ muscles (like during exercise) also assist this flow
* In some instances, athletes can suffer heart failure if they abruptly stop exercise
* Leg skeletal muscles stop contracting and relaxing -> less blood return to the heart -> inadequate blood flow that can cause heart damage
* athletes encouraged to follow hard exercise with _____ activity to cool down heart rate to resting level
* Gravity affects blood flow in __*,*__ ___ especially **in the ___**
* Gravity draws blood downward to your feet, impeding its return to the heart
* Have valves to maintain the unidirectional flow of return to heart, since BP in veins is relatively low
* _______ contractions of smooth muscles also help in movement
* contraction of ______ muscles (like during exercise) also assist this flow
* In some instances, athletes can suffer heart failure if they abruptly stop exercise
* Leg skeletal muscles stop contracting and relaxing -> less blood return to the heart -> inadequate blood flow that can cause heart damage
* athletes encouraged to follow hard exercise with _____ activity to cool down heart rate to resting level
64
New cards
meal, exercise, **smooth,** arterioles, **precapillary**
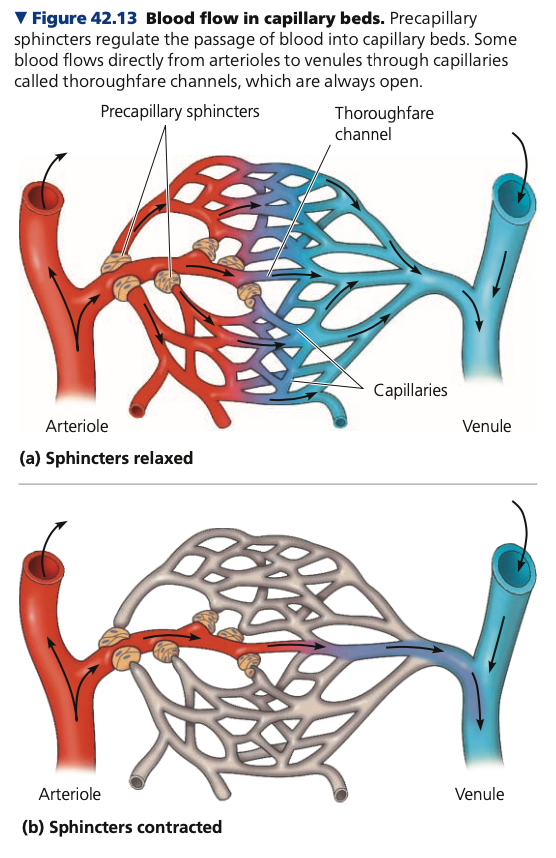
**Capillary Function**
* blood is always flowing through only **5–10%** of the body’s capillaries
* Capillaries in the brain, heart, kidneys, and liver usually remain at capacity
* At other sites, blood supply varies over time as blood goes from one destination to another
* Ex. after a ____, blood supply increases to digestive tract
* Ex. during _____, blood is diverted from digsetive tract to skeletal muscles
* Capillaries **lack _____ muscle,** so they alter blood flow through other mechanisms
* constriction or dilation of the ______ that supply capillary beds
* **______ sphincters** - rings of smooth muscle located at the entrance to capillary beds
* Open and close to regulate passage of blood
* blood is always flowing through only **5–10%** of the body’s capillaries
* Capillaries in the brain, heart, kidneys, and liver usually remain at capacity
* At other sites, blood supply varies over time as blood goes from one destination to another
* Ex. after a ____, blood supply increases to digestive tract
* Ex. during _____, blood is diverted from digsetive tract to skeletal muscles
* Capillaries **lack _____ muscle,** so they alter blood flow through other mechanisms
* constriction or dilation of the ______ that supply capillary beds
* **______ sphincters** - rings of smooth muscle located at the entrance to capillary beds
* Open and close to regulate passage of blood
65
New cards
nerve, hormones, local, histamines, dilation, vesicles, pores
**Capillary Function**
* These blood flow altering mechanisms are regulated by signals: __ impulses, ___, and ___ chemicals
* Ex. _____ released by cells at a wound site causes vaso_____ -> increase blood flow, more WBC to fight invading microorganisms
* Across the thin walls of capillaries, substances exchange between blood and interstitial fluid
* Macromolecules carried across endothelium in _____ that form on 1 side via endocytosis, and release contents on the other side by exocytosis
* Small molecules just diffuse across the endothelial cells or through ____ in the capillary wall
* Pores also provide transport for small solutes (sugars, salt, urea), and for bulk flow of fluid into tissues driven by capillary BP
* These blood flow altering mechanisms are regulated by signals: __ impulses, ___, and ___ chemicals
* Ex. _____ released by cells at a wound site causes vaso_____ -> increase blood flow, more WBC to fight invading microorganisms
* Across the thin walls of capillaries, substances exchange between blood and interstitial fluid
* Macromolecules carried across endothelium in _____ that form on 1 side via endocytosis, and release contents on the other side by exocytosis
* Small molecules just diffuse across the endothelial cells or through ____ in the capillary wall
* Pores also provide transport for small solutes (sugars, salt, urea), and for bulk flow of fluid into tissues driven by capillary BP
66
New cards
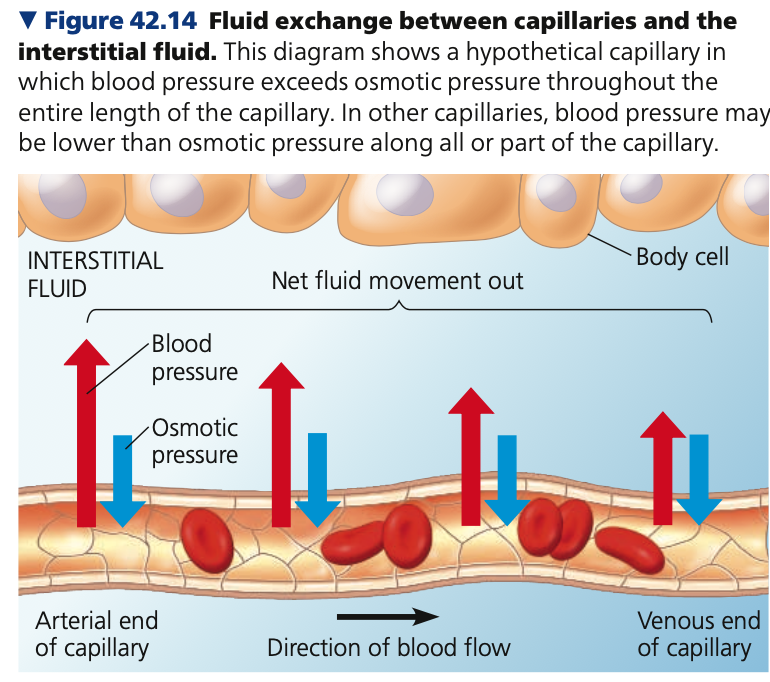
BP, proteins, **osmotic ,** interstitial
**Capillary Function**
* 2 opposing forces control movement of fluid exchanged between capillaries and surrounding tissues
1. Blood pressure
2. Blood osmotic pressure
* __ drives **fluid out** of capillaries
* Blood ______ pulls fluid back
* Too large to pass through endothelium and stay in the capillaries
* Responsible for much of the **blood’s _____ pressure**
* Difference in between blood and ______ fluid opposes fluid movement out
* Between the opposing forces, BP is greater -> **net loss of fluid** to interstitial fluid
* 2 opposing forces control movement of fluid exchanged between capillaries and surrounding tissues
1. Blood pressure
2. Blood osmotic pressure
* __ drives **fluid out** of capillaries
* Blood ______ pulls fluid back
* Too large to pass through endothelium and stay in the capillaries
* Responsible for much of the **blood’s _____ pressure**
* Difference in between blood and ______ fluid opposes fluid movement out
* Between the opposing forces, BP is greater -> **net loss of fluid** to interstitial fluid
67
New cards
diffusion, **veins, lipids, valves,** contractions, Skeletal
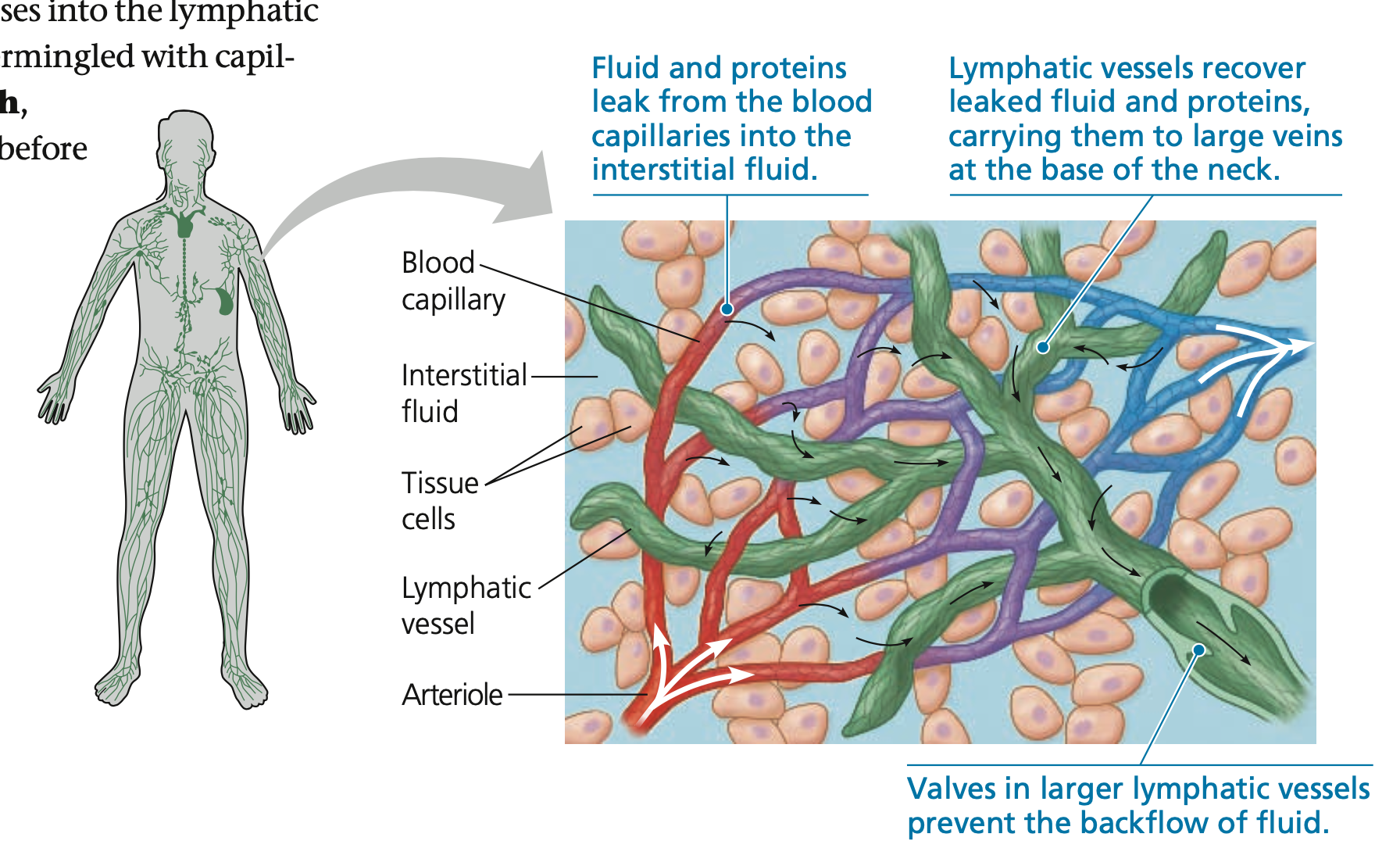
**Fluid Return by Lymphatic System**
* adult human body loses **~4–8 L of fluid** from capillaries to the surrounding tissues
* Also a bit of leakage of blood proteins
* **Lymphatic system** recovers and returns lost fluid, through ______ vessels intermingled with capillaries
* **Lymph,** the recovered fluid; circulates the lymphatic system before draining into large **____ at the neck**
* Cardiovascular and lymphatic system joins to complete **recovery of lymph** and **transfer of _____** from small intestine to blood
* Movement of lymph in lymph vessels relies on mechanisms similar to that of the vein
* Lymph vessels also have **____** to prevent backflow
* Rhythmic ______ also help draw in fluid
* _____ contractions also assist in movement of lymph
* adult human body loses **~4–8 L of fluid** from capillaries to the surrounding tissues
* Also a bit of leakage of blood proteins
* **Lymphatic system** recovers and returns lost fluid, through ______ vessels intermingled with capillaries
* **Lymph,** the recovered fluid; circulates the lymphatic system before draining into large **____ at the neck**
* Cardiovascular and lymphatic system joins to complete **recovery of lymph** and **transfer of _____** from small intestine to blood
* Movement of lymph in lymph vessels relies on mechanisms similar to that of the vein
* Lymph vessels also have **____** to prevent backflow
* Rhythmic ______ also help draw in fluid
* _____ contractions also assist in movement of lymph
68
New cards
**Edema,** elephantiasis
**Fluid Return by Lymphatic System**
* **_____** is the **accumulation of fluid** in affected tissues caused by disruptions in movement of lymph
* Ex. a species of parasitic worms that lodge in lymph vessels, blocking movement and causing _______, condition marked by extreme swelling usually in limbs
* **_____** is the **accumulation of fluid** in affected tissues caused by disruptions in movement of lymph
* Ex. a species of parasitic worms that lodge in lymph vessels, blocking movement and causing _______, condition marked by extreme swelling usually in limbs
69
New cards
**filtering,** WBC, cancer, Asthma
**Lymph nodes**
* Small, **lymph-______ organs** along a lymph vessel
* Role in body defense
* Inside each has a honeycomb of connective tissues with spaces full of ___s
* During an infection, WBC multiplies and nodes become swollen
* Lymph nodes may also trap circulating ____ cells
* Doctors check for swollen lymph nodes when one feels sick; these may also reveal spread of cancer
* Lymphatic system plays a role in harmful immune responses ex. ______, so it is an active area of research
* Small, **lymph-______ organs** along a lymph vessel
* Role in body defense
* Inside each has a honeycomb of connective tissues with spaces full of ___s
* During an infection, WBC multiplies and nodes become swollen
* Lymph nodes may also trap circulating ____ cells
* Doctors check for swollen lymph nodes when one feels sick; these may also reveal spread of cancer
* Lymphatic system plays a role in harmful immune responses ex. ______, so it is an active area of research
70
New cards
Blood
* Blood Composition and Function
a. Plasma
b. Cellular elements
c. Stem cells
d. Blood clotting
* Cardiovascular Disease
a. Atherosclerosis
b. Heart attack
c. Stroke
d. Risk factors & treatments
a. Plasma
b. Cellular elements
c. Stem cells
d. Blood clotting
* Cardiovascular Disease
a. Atherosclerosis
b. Heart attack
c. Stroke
d. Risk factors & treatments
71
New cards
continuous, **blood**
**Blood**
* In open circulatory systems, the circulatory fluid is ______ and has the same composition as with the interstitial fluid
* In closed circulatory systems, the circulatory fluid is **____,** which is specialized
* Exchange
* Transport
* Defense
* In open circulatory systems, the circulatory fluid is ______ and has the same composition as with the interstitial fluid
* In closed circulatory systems, the circulatory fluid is **____,** which is specialized
* Exchange
* Transport
* Defense
72
New cards
Blood Composition and Function
a. Plasma
b. Cellular elements
c. Stem cells
d. Blood clotting
b. Cellular elements
c. Stem cells
d. Blood clotting
73
New cards
**plasma**
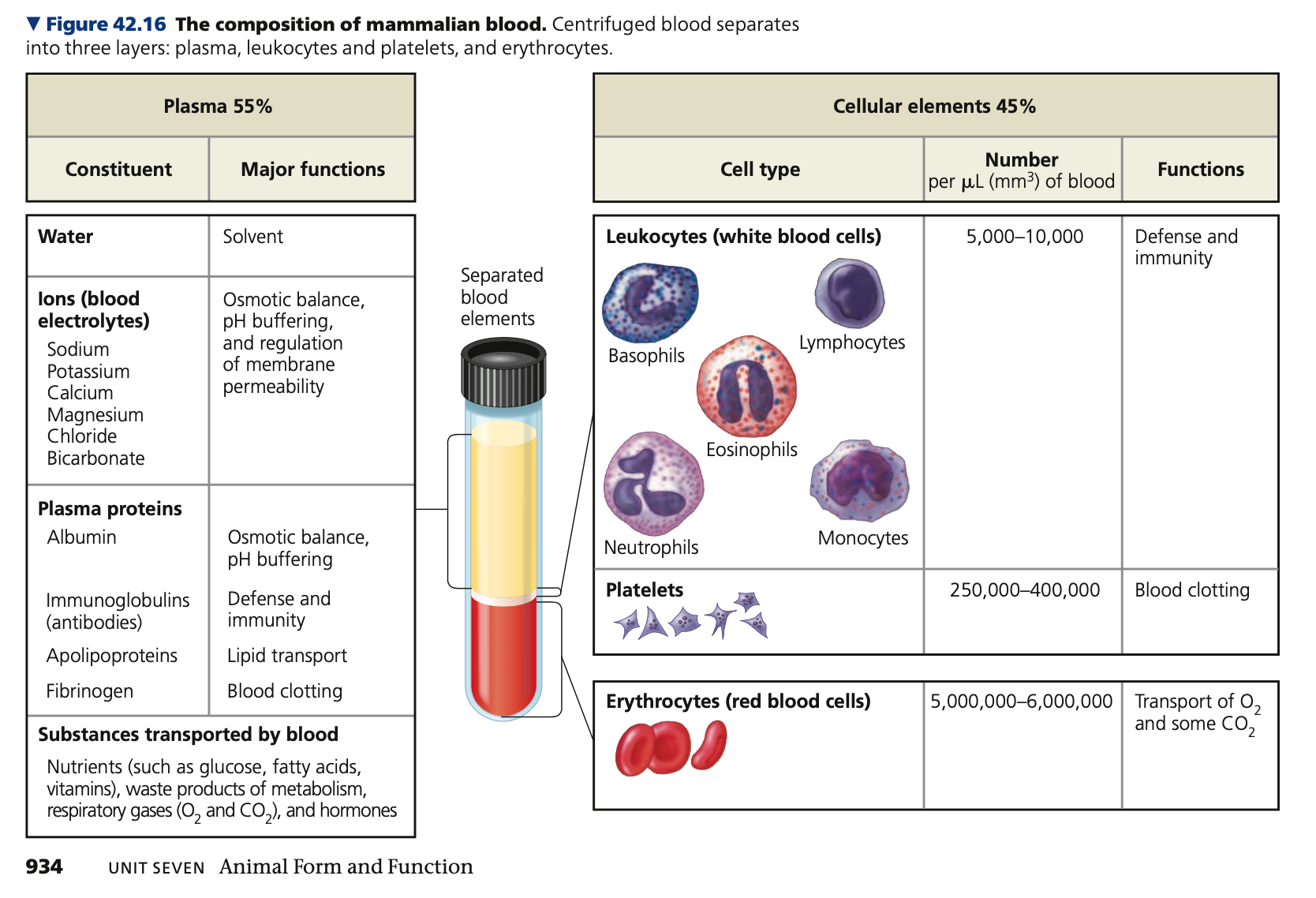
**Blood Composition and Function**
* Vertebrate blood is a connective tissue consisting of cells suspended in a liquid matrix called **_____**
* Cellular elements - \~45% of the blood volume, and the remainder is plasma
* Vertebrate blood is a connective tissue consisting of cells suspended in a liquid matrix called **_____**
* Cellular elements - \~45% of the blood volume, and the remainder is plasma
74
New cards
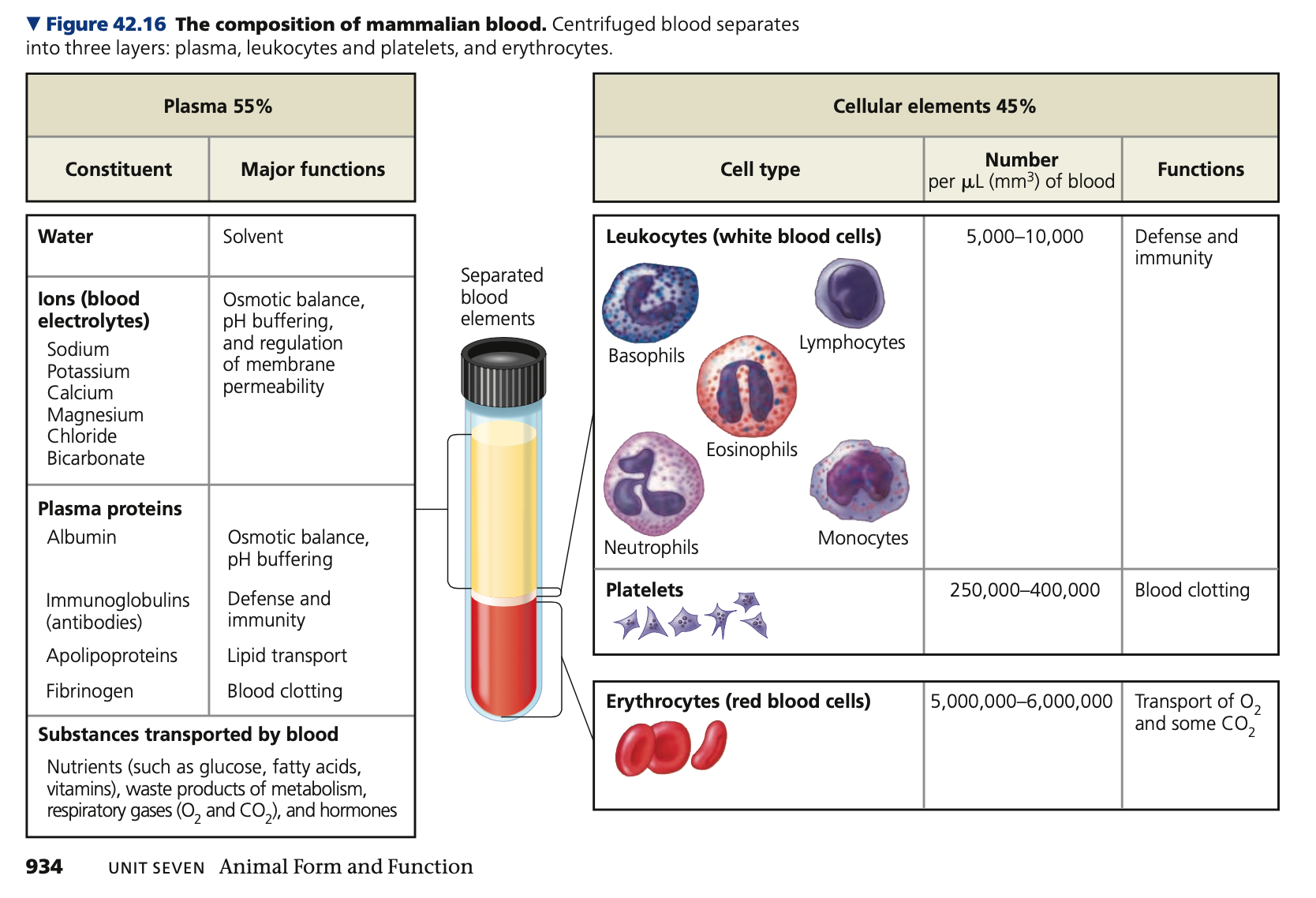
Buffer, electrolytes, albumins, Immunoglobins, apolipoproteins, fibrinogens
**Plasma**
* Ions and proteins dissolved in the plasma that function in osmotic, regulation, transport and defense
1. **Inorganic salts (dissolved ions)**
* _____ the blood
* Maintain osmotic balance
* Concentration of ions in plasma directly affects composition of interstitial fluid
* Ions have a vital role in muscle and nerve activity
* Plasma ______ must remain within narrow concentration ranges to serve all these functions
\
2. **Plasma proteins**
* Ex. ______
* Acts as buffers against PH changes
* Maintain osmotic balance between blood and interstitial fluid
* Ex. _________
* Antibodies that combat viruses and foreign agents
* Ex. __________
* transport lipids that are
insoluble in water and only travel in blood when bound to proteins
* Ex. ______
* Act as clotting factors that plug leaks when blood vessels are injured
* Ions and proteins dissolved in the plasma that function in osmotic, regulation, transport and defense
1. **Inorganic salts (dissolved ions)**
* _____ the blood
* Maintain osmotic balance
* Concentration of ions in plasma directly affects composition of interstitial fluid
* Ions have a vital role in muscle and nerve activity
* Plasma ______ must remain within narrow concentration ranges to serve all these functions
\
2. **Plasma proteins**
* Ex. ______
* Acts as buffers against PH changes
* Maintain osmotic balance between blood and interstitial fluid
* Ex. _________
* Antibodies that combat viruses and foreign agents
* Ex. __________
* transport lipids that are
insoluble in water and only travel in blood when bound to proteins
* Ex. ______
* Act as clotting factors that plug leaks when blood vessels are injured
75
New cards
**Serum,** protein, Capillary
**Plasma**
* **_____** refers to blood plasma from which clotting factors have been removed
* also contains nutrients, metabolic wastes, respiratory gases, and hormones
* has a much higher _____ concentration than interstitial fluid, although the two fluids are otherwise similar
* ______ walls are not very permeable to proteins
* **_____** refers to blood plasma from which clotting factors have been removed
* also contains nutrients, metabolic wastes, respiratory gases, and hormones
* has a much higher _____ concentration than interstitial fluid, although the two fluids are otherwise similar
* ______ walls are not very permeable to proteins
76
New cards
**erythrocytes,** hemoglobin, **leukocytes,** phagocytizing
**Cellular elements**
1. **Red blood cells (_______)**
* Transport oxygen throughout the body
* Most numerous blood cells
* Contain ______
* Iron-containing protein that transports oxygen
\
2. **White blood cells (______)**
* Function in defense
* Five major types:
* Monocytes
* Neutrophils
* Basophils
* Eosinophils
* Lymphocytes
* Function in defense by _______ bacteria and debris or by producing antibodies
* Found both in and outside of circulatory system
\
3. **Platelets**
* Fragments of cell involved in **blood clotting**
1. **Red blood cells (_______)**
* Transport oxygen throughout the body
* Most numerous blood cells
* Contain ______
* Iron-containing protein that transports oxygen
\
2. **White blood cells (______)**
* Function in defense
* Five major types:
* Monocytes
* Neutrophils
* Basophils
* Eosinophils
* Lymphocytes
* Function in defense by _______ bacteria and debris or by producing antibodies
* Found both in and outside of circulatory system
\
3. **Platelets**
* Fragments of cell involved in **blood clotting**
77
New cards
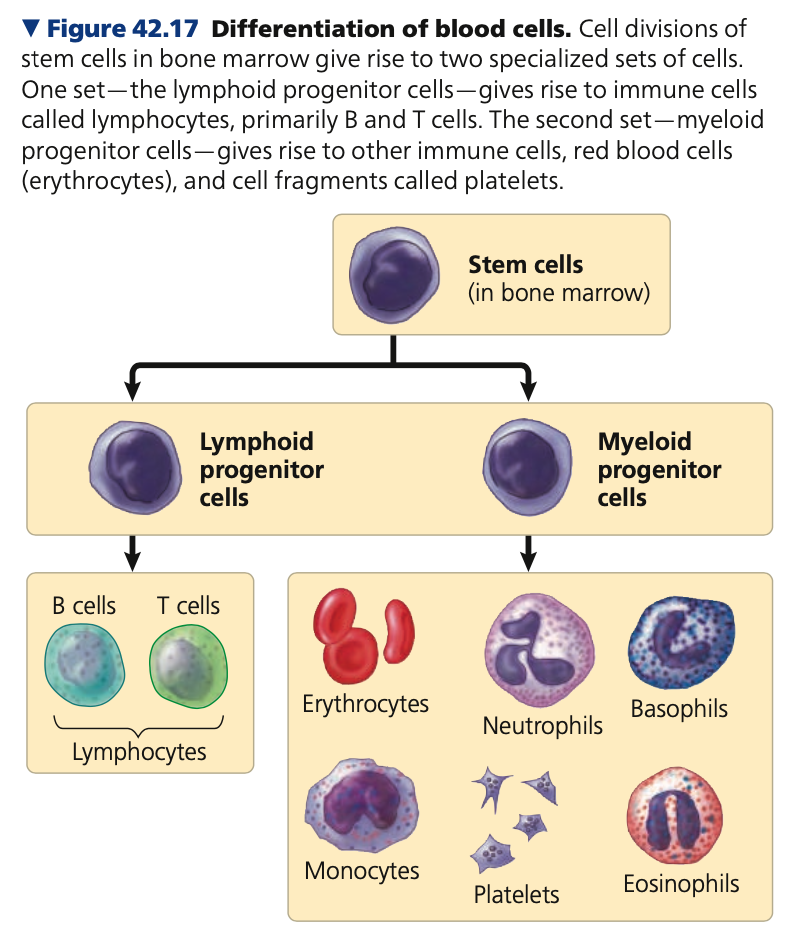
**erythropoietin**
**Stem cells**
* Cellular elements of blood wear out and are replaced constantly throughout a person’s life
* Erythrocytes , leukocytes, and platelets all develop from a common source of stem cells
* In the red marrow of bones
* Hormone **_______** (EPO) stimulates erythrocyte production when oxygen delivery is low
* Cellular elements of blood wear out and are replaced constantly throughout a person’s life
* Erythrocytes , leukocytes, and platelets all develop from a common source of stem cells
* In the red marrow of bones
* Hormone **_______** (EPO) stimulates erythrocyte production when oxygen delivery is low
78
New cards
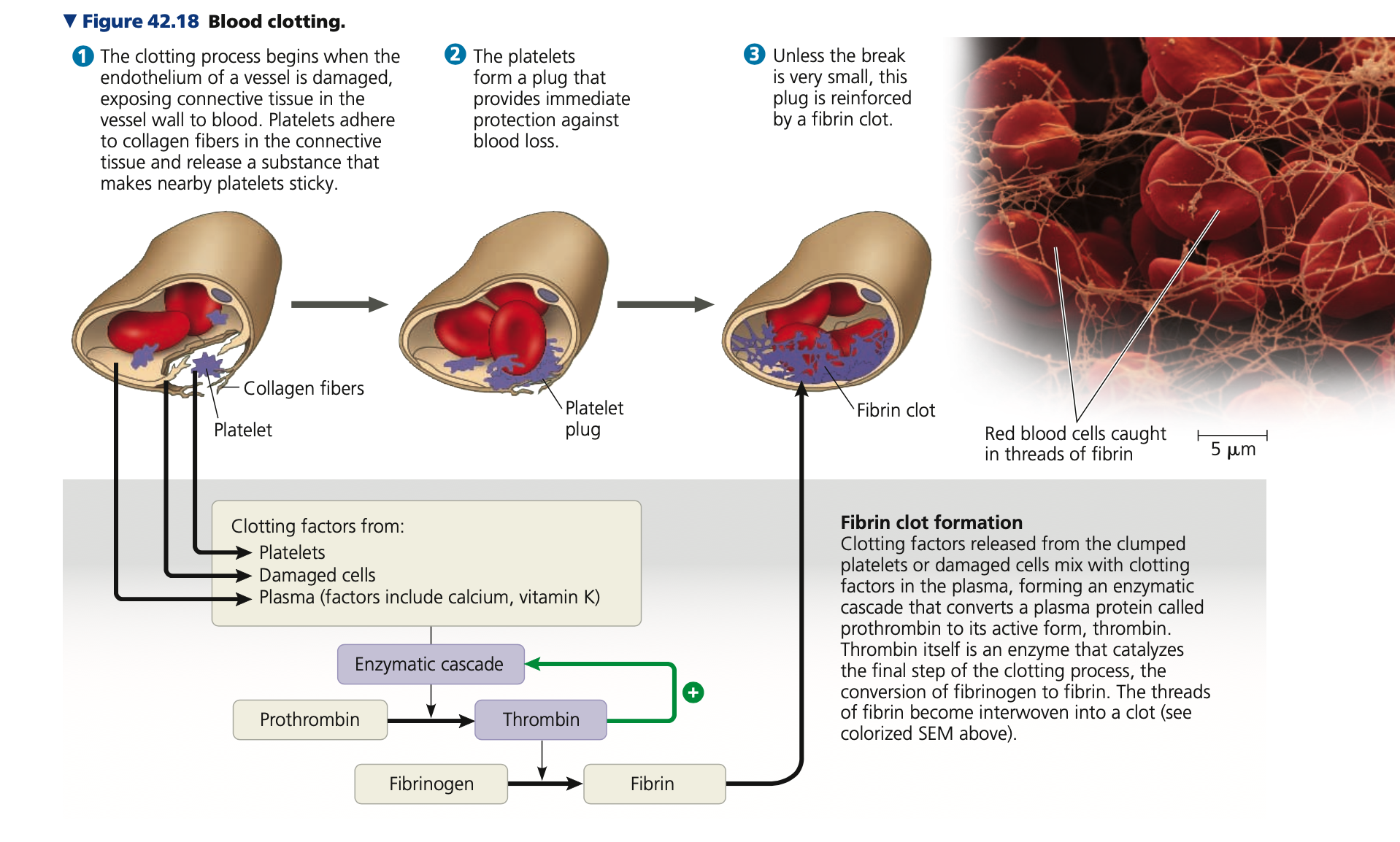
fibrinogen, fibrin, **thrombus**
**Blood clotting**
* Platelets function in blood clotting
* When the endothelium of a blood vessel is damaged, clotting mechanism begins
* Cascade of complex reactions converts ______ to fibrin, forming a clot
* A blood clot formed within a blood vessel is
called a ______
* Can block blood flow
* Platelets function in blood clotting
* When the endothelium of a blood vessel is damaged, clotting mechanism begins
* Cascade of complex reactions converts ______ to fibrin, forming a clot
* A blood clot formed within a blood vessel is
called a ______
* Can block blood flow
79
New cards
Cardiovascular Disease
a. Atherosclerosis
b. Heart attack
c. Stroke
d. Risk factors & treatments
b. Heart attack
c. Stroke
d. Risk factors & treatments
80
New cards
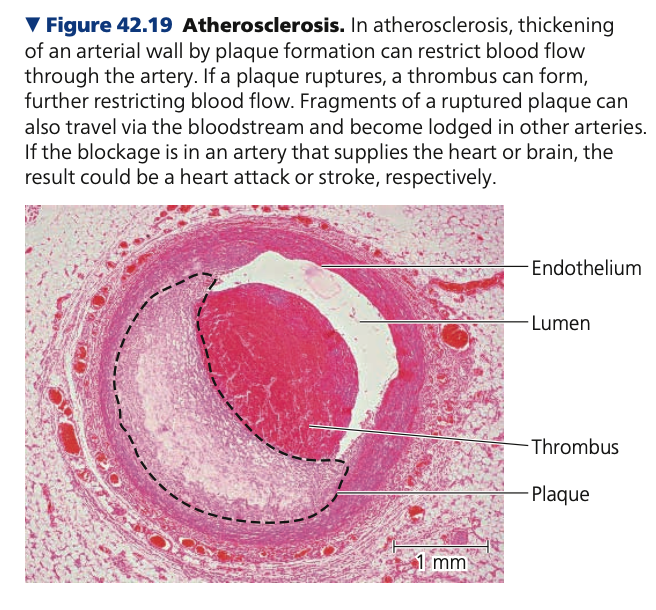
fatty, cholesterol, plaque, Angina, coronary
**Atherosclerosis**
* Hardening of the arteries caused by the accumulation of ___ deposits
* Damage or infection can roughen the lining and lead to inflammation.
* Leukocytes are attracted to the damaged lining and begin to take up lipids, including ______.
* A fatty deposit called a ____ develops in the inner wall of the arteries, causing the wall to become thick and stiff.
* Threat of heart attack or stroke becomes much greater, but there may be warnings of this impending threat
* Example: _____ pectoris
* Occasional chest pains caused by a partially blocked ______ artery
* Signal that part of the heart is not receiving enough blood, especially when the heart under physical or emotional stress
* Hardening of the arteries caused by the accumulation of ___ deposits
* Damage or infection can roughen the lining and lead to inflammation.
* Leukocytes are attracted to the damaged lining and begin to take up lipids, including ______.
* A fatty deposit called a ____ develops in the inner wall of the arteries, causing the wall to become thick and stiff.
* Threat of heart attack or stroke becomes much greater, but there may be warnings of this impending threat
* Example: _____ pectoris
* Occasional chest pains caused by a partially blocked ______ artery
* Signal that part of the heart is not receiving enough blood, especially when the heart under physical or emotional stress
81
New cards
infarction, blockage, small, resuscitation
**Heart Attack**
* Also called a myocardial ______
* Damage or death of cardiac muscle tissue resulting from the ______ of one or more coronary arteries
* The coronary arteries are _____ in diameter and vulnerable to obstruction
* Such blockage can destroy cardiac muscle quickly because the beating heart cannot survive without oxygen.
* Even if the heart stops breathing, the victim may survive if a heartbeat is restored by cardiopulmonary ______ (CPR) within a few minutes of the attack
* Also called a myocardial ______
* Damage or death of cardiac muscle tissue resulting from the ______ of one or more coronary arteries
* The coronary arteries are _____ in diameter and vulnerable to obstruction
* Such blockage can destroy cardiac muscle quickly because the beating heart cannot survive without oxygen.
* Even if the heart stops breathing, the victim may survive if a heartbeat is restored by cardiopulmonary ______ (CPR) within a few minutes of the attack
82
New cards
**nervous, thrombus,** plaques
**Stroke**
* Death of **______ tissue** in the **brain** due to a lack of oxygen
* The effects of a stroke and the individual’s chance of survival depend on the extent and location of the damaged brain tissue.
* Heart attacks and strokes frequently result from a **_____** that clogs a coronary artery or an artery in the brain.
* A key step in thrombus formation is the rupture of _____ by an inflammatory response.
* The thrombus may originate at the site of the blockage, or it may develop elsewhere and be transported until it becomes lodged in an artery too narrow for it to pass.
* Death of **______ tissue** in the **brain** due to a lack of oxygen
* The effects of a stroke and the individual’s chance of survival depend on the extent and location of the damaged brain tissue.
* Heart attacks and strokes frequently result from a **_____** that clogs a coronary artery or an artery in the brain.
* A key step in thrombus formation is the rupture of _____ by an inflammatory response.
* The thrombus may originate at the site of the blockage, or it may develop elsewhere and be transported until it becomes lodged in an artery too narrow for it to pass.
83
New cards
Cholesterol
Major contributor to atherosclerosis.
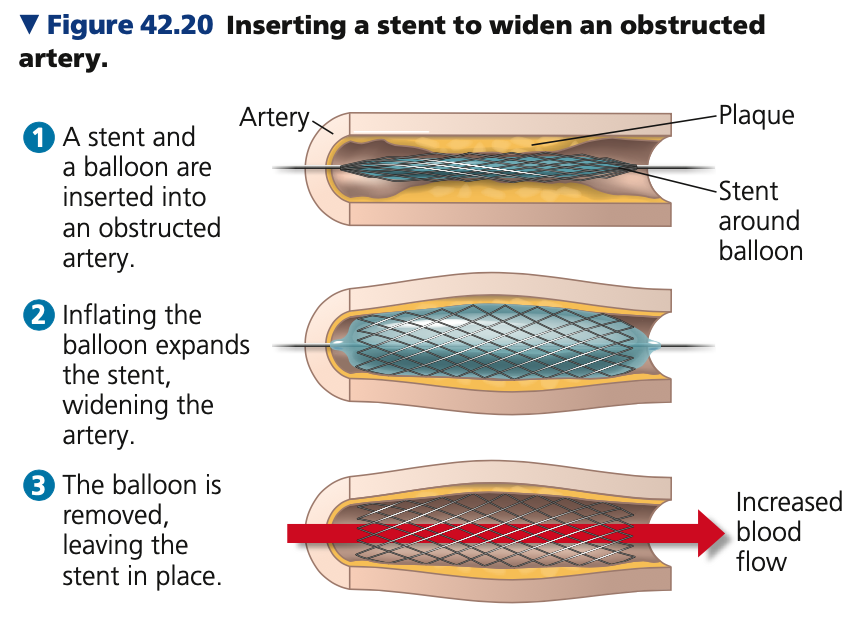
84
New cards
**Low-density lipoproteins (LDLs)**
* “**bad** cholesterol”
* Associated with plaque formation
* Associated with plaque formation
85
New cards
**High-density lipoproteins (HDLs)**
* “**good** cholesterol”
* Reduce the deposition of cholesterol.
* Reduce the deposition of cholesterol.
86
New cards
Hypertension
* high blood pressure
* Promotes atherosclerosis
* Increases the risk of heart attack and stroke.
* can be reduced by dietary changes, exercise, and/or medication
* Promotes atherosclerosis
* Increases the risk of heart attack and stroke.
* can be reduced by dietary changes, exercise, and/or medication
87
New cards
Gas Exchange
* Partial Pressure Gradients
* Respiratory Media
* Respiratory Surfaces
a. Gills (Aquatic Animals)
b. Tracheal Systems (Insects)
c. Lungs
* Respiratory Media
* Respiratory Surfaces
a. Gills (Aquatic Animals)
b. Tracheal Systems (Insects)
c. Lungs
88
New cards
Gas exchange
* **Uptake of molecular oxygen (O2)** from the environment and the **discharge of carbon dioxide (CO2)** to the environment.
* Different from the production of ATP in cellular respiration
* Different from the production of ATP in cellular respiration
89
New cards
gas, liquid, proportional, solution, air, higher
**Partial Pressure Gradients**
* Pressure exerted by a particular ___ in a mixture of gasses
* Can also be calculated for a gas dissolved in ____
* When water is exposed to air, the amount of a gas that dissolves in water is _____ to its partial pressure in air and its solubility in water
* At equilibrium, the partial pressure of the gas in the ______ = the partial pressure of the gas in the __
* Concentration of the gas in air and in water may differ, based on the solubility of the gas in the two media
* A gas always diffuses from a region of ____ partial pressure to a region of lower partial pressure
* Atmospheric pressure at sea level is thus 760 mm Hg
* Atmosphere is 21% O2 by volume
* Partial pressure of O2 is 0.21 x 760, or about 160 mm Hg.
* This value is called the *partial pressure* of O2 (abbreviated PO2)
* Pressure exerted by a particular ___ in a mixture of gasses
* Can also be calculated for a gas dissolved in ____
* When water is exposed to air, the amount of a gas that dissolves in water is _____ to its partial pressure in air and its solubility in water
* At equilibrium, the partial pressure of the gas in the ______ = the partial pressure of the gas in the __
* Concentration of the gas in air and in water may differ, based on the solubility of the gas in the two media
* A gas always diffuses from a region of ____ partial pressure to a region of lower partial pressure
* Atmospheric pressure at sea level is thus 760 mm Hg
* Atmosphere is 21% O2 by volume
* Partial pressure of O2 is 0.21 x 760, or about 160 mm Hg.
* This value is called the *partial pressure* of O2 (abbreviated PO2)
90
New cards
source, water, **lower,** saltier
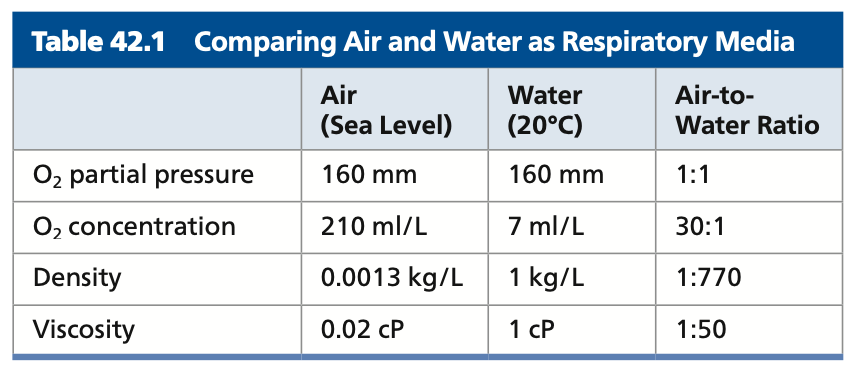
**Respiratory Media**
* The conditions vary depending on whether the ____ of oxygen (air or water)
* Air is less less dense and viscous than water; Breathing in air is relatively easy
* Gas exchange with ____ as the respiratory medium is much more demanding
* Dissolved oxygen levels in lakes, oceans, and other bodies of water are **always much ____** than the levels in an equivalent volume of air
* The warmer and ____ the water, the less dissolved O2 it can hold
* Water’s lower O2 content, greater density, and greater viscosity mean that aquatic animals must expend considerable energy to carry out gas exchange
* The conditions vary depending on whether the ____ of oxygen (air or water)
* Air is less less dense and viscous than water; Breathing in air is relatively easy
* Gas exchange with ____ as the respiratory medium is much more demanding
* Dissolved oxygen levels in lakes, oceans, and other bodies of water are **always much ____** than the levels in an equivalent volume of air
* The warmer and ____ the water, the less dissolved O2 it can hold
* Water’s lower O2 content, greater density, and greater viscosity mean that aquatic animals must expend considerable energy to carry out gas exchange
91
New cards
**moist,** diffusion, inversely, thin, large
**Respiratory Surfaces**
* **Part** of an animal where **gasses are exchanged** with the environment
* Always **____**
* Gasses must dissolve in water before
diffusing across respiratory surfaces
* Movements of CO2 and O2 occur entirely by _____
* The rate of diffusion is proportional to the surface area across which diffusion occurs, and _____ proportional to the square of the distance through which molecules must move
* To maximize gas exchange, respiratory surfaces tend to be ___and have ___ areas
* **Part** of an animal where **gasses are exchanged** with the environment
* Always **____**
* Gasses must dissolve in water before
diffusing across respiratory surfaces
* Movements of CO2 and O2 occur entirely by _____
* The rate of diffusion is proportional to the surface area across which diffusion occurs, and _____ proportional to the square of the distance through which molecules must move
* To maximize gas exchange, respiratory surfaces tend to be ___and have ___ areas
92
New cards
Size, Metabolic, outside, organ, skin, folded
**Respiratory Surfaces**
* Structure depends mainly on:
* ___ of the organism
* Whether it lives in water or on land
* _____ demands
* Ex: An endotherm requires a larger area of respiratory surface than a similar-sized ectotherm
* In some relatively simple animals, such as
sponges, cnidarians, and flatworms, the plasma membrane of every cell in the body is close enough to the _____ environment for gasses to diffuse in and out.
* In most animals, however, the bulk of the body lacks direct access to the respiratory medium.
* The respiratory surface in these animals is a thin, moist epithelium that constitutes a respiratory ____.
* Some animals, such as earthworms and some amphibians, use the ___ as a respiratory organ.
* Just below the moist skin is a dense net of capillaries.
* Because the respiratory surface must be moist, however, the possible habitats of these animals are limited to water or damp places.
* For most other animals, the general body surface is not sufficiently large to exchange gasses for the entire body.
* The solution is a respiratory organ that is extensively _____ or branched, thus enlarging the surface area for gas exchange
* Structure depends mainly on:
* ___ of the organism
* Whether it lives in water or on land
* _____ demands
* Ex: An endotherm requires a larger area of respiratory surface than a similar-sized ectotherm
* In some relatively simple animals, such as
sponges, cnidarians, and flatworms, the plasma membrane of every cell in the body is close enough to the _____ environment for gasses to diffuse in and out.
* In most animals, however, the bulk of the body lacks direct access to the respiratory medium.
* The respiratory surface in these animals is a thin, moist epithelium that constitutes a respiratory ____.
* Some animals, such as earthworms and some amphibians, use the ___ as a respiratory organ.
* Just below the moist skin is a dense net of capillaries.
* Because the respiratory surface must be moist, however, the possible habitats of these animals are limited to water or damp places.
* For most other animals, the general body surface is not sufficiently large to exchange gasses for the entire body.
* The solution is a respiratory organ that is extensively _____ or branched, thus enlarging the surface area for gas exchange
93
New cards
**Respiratory Surfaces**
a. Gills (Aquatic Animals)
b. Tracheal Systems (Insects)
c. Lungs
b. Tracheal Systems (Insects)
c. Lungs
94
New cards
outfoldings
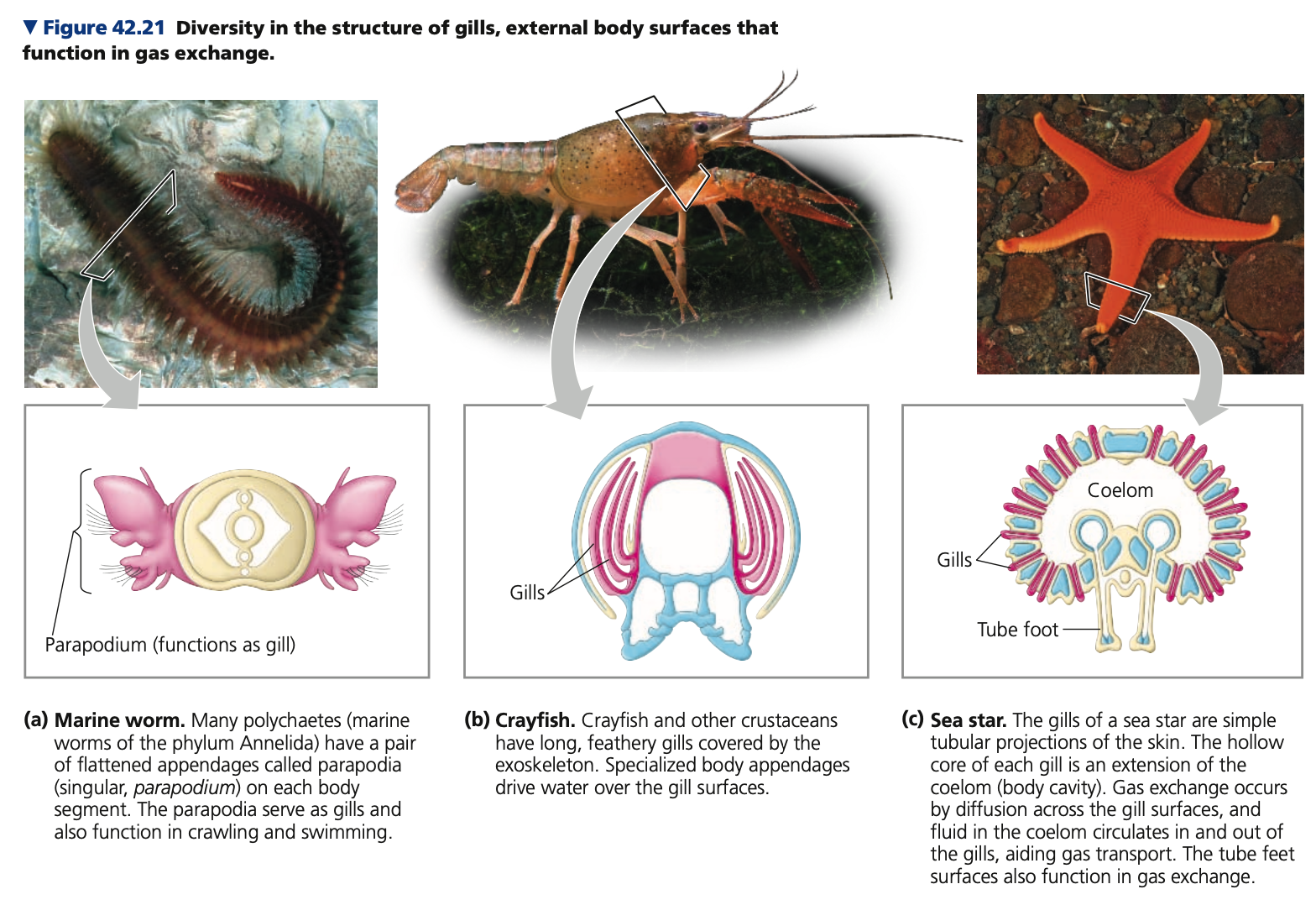
**Gills (Aquatic Animals)**
* Respiratory adaptations of most aquatic animals
* Gills are ______ of the body surface that are suspended in water
* The distribution of gills over the body can vary considerably
* The total surface area of gills is often much larger than that of the rest of the body
* Respiratory adaptations of most aquatic animals
* Gills are ______ of the body surface that are suspended in water
* The distribution of gills over the body can vary considerably
* The total surface area of gills is often much larger than that of the rest of the body
95
New cards
Ventilation
* Movement of the respiratory medium over the respiratory surface
* Maintains the partial pressure gradients of O2 and CO2 across the gill
* Maintains the partial pressure gradients of O2 and CO2 across the gill
96
New cards
Gill-bearing animals
* Move their gills through water or move water over their gills
97
New cards
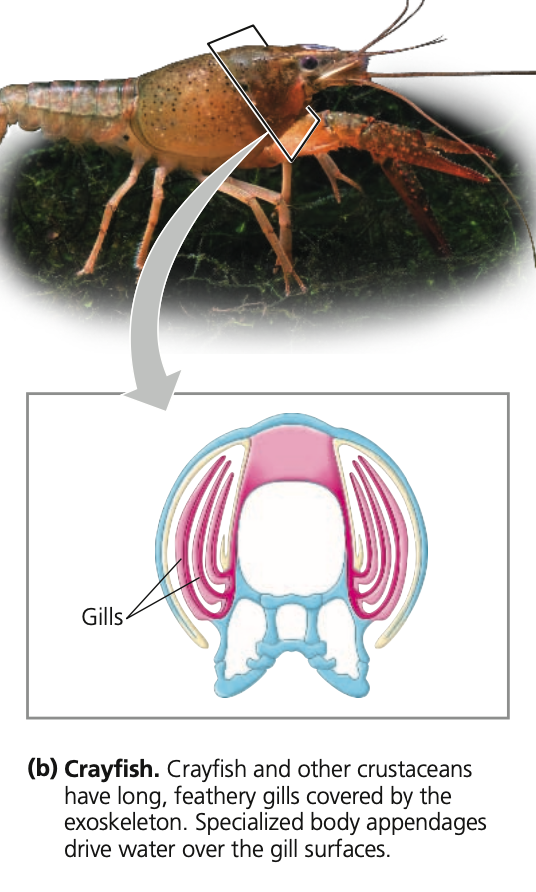
Crayfish and lobsters
* Paddle-like appendages that drive a current of water over their gills
98
New cards
Fish gills
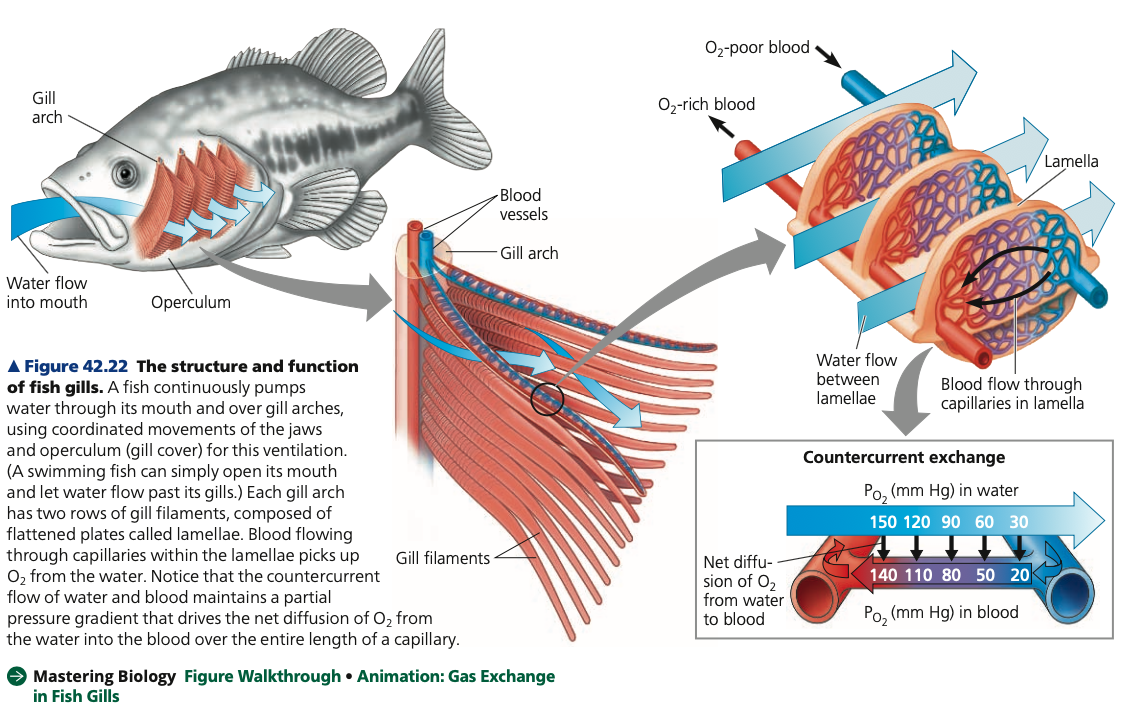
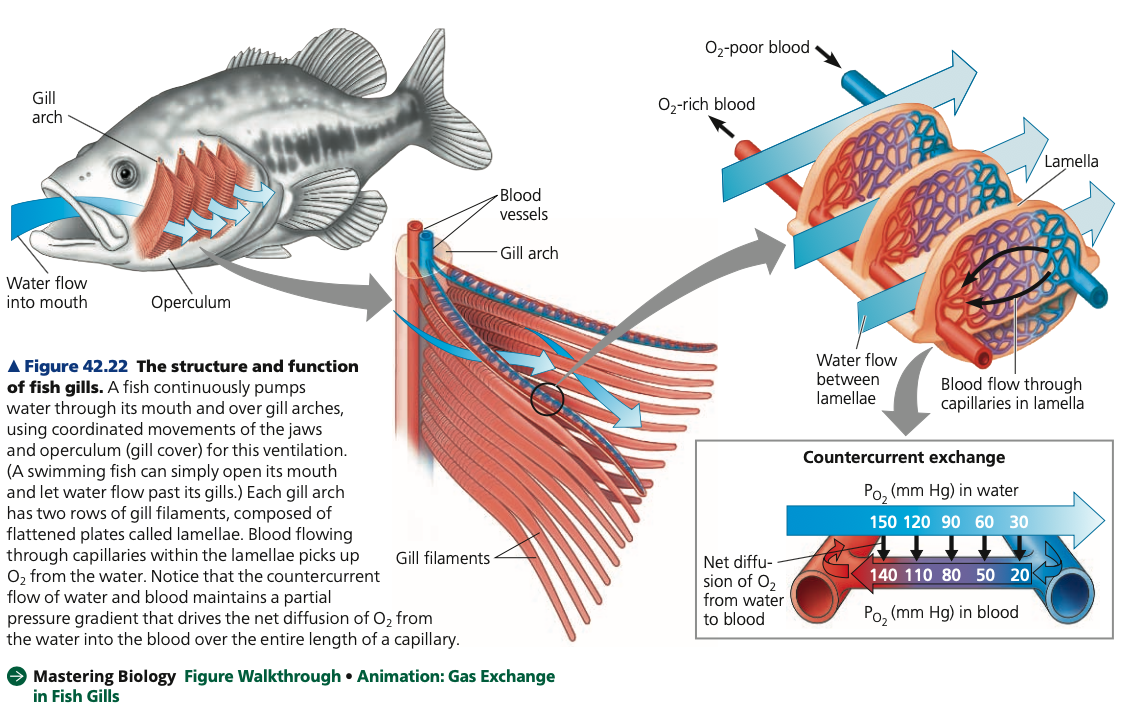
* Ventilated by a current of water that enters the mouth, passes through slits in the pharynx, flows over the gills, and exits the body
99
New cards
**countercurrent,** higher,
**Gills (Aquatic Animals)**
* To maximize gas exchange efficiency, the arrangement of blood capillaries in fish gills and the flow of water over the gills allow **_______ exchange**
* Blood flows in the opposite direction to the water flowing over the gills.
* As blood enters a gill capillary, it meets water that has already passed over the gill
* Although it has lost much of its dissolved oxygen, this water still has a ____ PO2 than incoming blood, and oxygen is exchanged from water to blood
* As blood moves over the gill, its PO2 increases, but so does the PO2 of the water it encounters
* A partial pressure gradient favors the diffusion of oxygen from water to blood along the length of the capillary
* To maximize gas exchange efficiency, the arrangement of blood capillaries in fish gills and the flow of water over the gills allow **_______ exchange**
* Blood flows in the opposite direction to the water flowing over the gills.
* As blood enters a gill capillary, it meets water that has already passed over the gill
* Although it has lost much of its dissolved oxygen, this water still has a ____ PO2 than incoming blood, and oxygen is exchanged from water to blood
* As blood moves over the gill, its PO2 increases, but so does the PO2 of the water it encounters
* A partial pressure gradient favors the diffusion of oxygen from water to blood along the length of the capillary
100
New cards
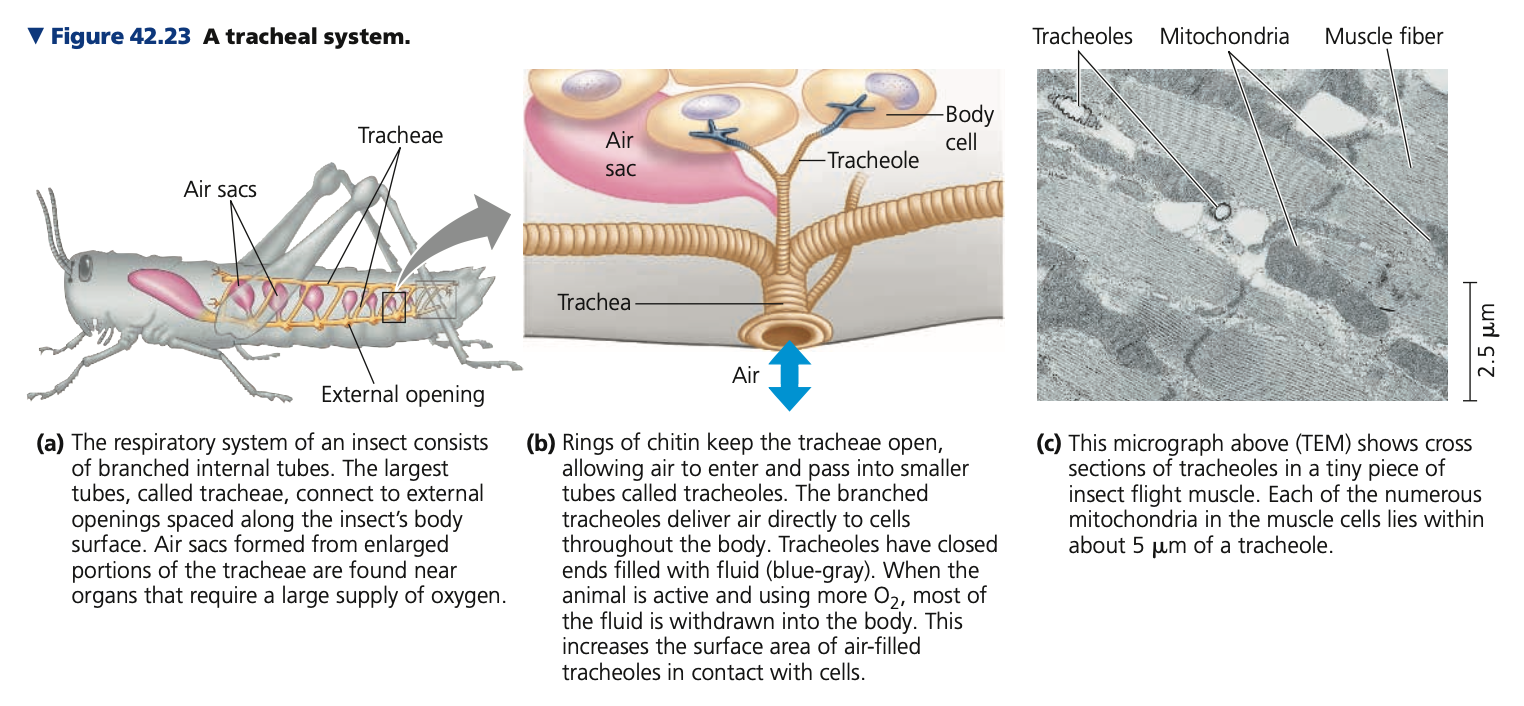
**tubes, o**pen, rhythmic, mitochondria
**Tracheal Systems (Insects)**
* Composed of **air ____** that branch throughout the body
* ____ circulatory system does not participate in the transportation of oxygen and carbon dioxide
* A small insect, diffusion through the trachea brings in enough O2 and removes enough CO2 to support cellular respiration.
* Larger insects with higher energy demands ventilate their tracheal systems with _____ body movements that compress and expand the air tubes like bellows
* Insect at flight
* Very High metabolic rate
* Alternating contraction and relaxation of flight muscles compress and expand the body, rapidly pumping air through the tracheal system
* The flight muscles are packed with _______, and the tracheal tubes supply each with ample oxygen
* Composed of **air ____** that branch throughout the body
* ____ circulatory system does not participate in the transportation of oxygen and carbon dioxide
* A small insect, diffusion through the trachea brings in enough O2 and removes enough CO2 to support cellular respiration.
* Larger insects with higher energy demands ventilate their tracheal systems with _____ body movements that compress and expand the air tubes like bellows
* Insect at flight
* Very High metabolic rate
* Alternating contraction and relaxation of flight muscles compress and expand the body, rapidly pumping air through the tracheal system
* The flight muscles are packed with _______, and the tracheal tubes supply each with ample oxygen